To quiz yourself select the cards option from the note card set and good luck with your class.
Here are other helpful study guides:
http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/70700
http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/13469
http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/3273
http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/4202
Which layer of the alimentary canal is responsible for segmentation and peristalsis?
mucosa
submucosa
serosa
muscularis externa
muscularis externa
Which of the following inhibits salivation?
sight or smell of food
sympathetic division of the
autonomic nervous system
spicy foods
parasympathetic
division of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
Which layer of the alimentary canal is constructed from either stratified squamous or simple columnar epithelium?
mucosa
serosa
muscularis externa
submucosa
mucosa
The nervous system does not regulate digestive activity.
True
False
False
Which histological layer of the digestive tract is composed primarily
of epithelial
tissue?
mucosa
adventitia
submucosa
lamina propria
mucosa
The lamina propria is composed of ________.
reticular connective
tissue
dense irregular connective tissue
loose connective
tissue
dense regular connective tissue
loose connective tissue
The capillaries that nourish the epithelium and absorb digested
nutrients lie in the
________.
submucosa
serosa
adventitia
lamina propria
lamina propria
Which of the following is NOT a function of saliva?
Saliva moistens food and helps compact it into a
bolus.
Saliva contains enzymes that begin the chemical breakdown
of proteins.
Saliva cleanses the mouth.
Saliva dissolves
food chemicals so they can be tasted.
Saliva contains enzymes that begin the chemical breakdown of proteins.
How many total deciduous teeth are there?
16
5
10
20
20
In the __________ phase of gastric secretion, chyme is moved into the
duodenum.
intestinal
cephalic
reflux
gastric phase
intestinal
Select the correct statement about the regulation of gastric
secretion.
Vagus stimulation of the stomach results in decreased
secretion of gastric juice.
The presence of food in the stomach
prevents hormonal control of gastric secretion.
Gastric secretion
can be stimulated before food has entered the mouth.
Gastric
secretion is enhanced by very low pH (below a pH of 2).
Gastric secretion can be stimulated before food has entered the mouth.
Pepsinogen is the precursor to the gastric enzyme for protein
digestion and is secreted by the parietal cells.
True
False
False
In order to prevent self-digestion of the pancreas, activation of
pancreatic proteases occurs in the __________.
gallbladder
duodenum
stomach
pancreas
liver
duodenum
During deglutition, the bolus passes into the stomach from the
esophagus through the __________.
esophageal
sphincter
gastroesophageal sphincter
pyloric
sphincter
urethral sphincter
ileocecal valve
gastroesophageal sphincter
During the intestinal phase of gastric regulation, __________.
the stomach is initially stimulated and later inhibited
the gastroenteric reflex reduces stomach activity
the
enterogastric reflex is turned off
hormones reduce chief cell
activity
secretin causes more HCl release
the stomach is initially stimulated and later inhibited
What intestinal structure(s) consist(s) of protective aggregated
nodules of lymphocytes and macrophages?
the muscularis
mucosae
the gastric pits
the intestinal crypts
Peyer’s patches
the muscularis externa
Peyer’s patches
What are the main organic molecules digested in the stomach?
nucleic acids
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
salts
proteins
The main propulsive force that occurs in the majority of the
alimentary canal is called __________.
defecation
segmentation
peristalsis
swallowing
ingestion
peristalsis
Which of the following is a characteristic of the large
intestine?
It is the site for acid neutralization.
It has villi.
It contains epiploic appendages.
It is
longer than the small intestine.
It provides no absorptive function.
It contains epiploic appendages.
Which regulatory chemical stimulates gastric gland activity and
motility?
gastrin
CCK
histamine
secretin
vasoactive peptide
gastrin
Which sequence below represents the correct order of the tunics of
the GI tract, starting from the layer adjacent to the lumen and moving
superficially?
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa,
serosa
muscularis externa, serosa, submucosa, mucosa
submucosa, mucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
mucosa, muscularis
externa, submucosa, serosa
serosa, mucosa, muscularis externa, submucosa
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
What substances from different organs would mix together at the
hepatopancreatic ampulla?
bile and pancreatic
enzymes
brush border enzymes and intrinsic factor
secretin
and CCK
HCl and pepsin
bile and pancreatic enzymes
What would be the effect of stripping the small intestines of their
villi?
Salivary amylase secretion would increase.
The large intestine would take over as the primary absorptive
site.
A duodenal ulcer would develop.
decreased surface
area for absorption
decreased surface area for absorption
Which of the following products does the stomach produce?
pepsinogen and secretin
HCl and intrinsic factor
bile and trypsin
mucus and amylase
HCl and intrinsic factor
The final product of carbohydrate digestion is __________.
glycogen
disaccharides
starch
monosaccharides
polysaccharides
monosaccharides
Which of the following cells produce HCl?
chief
cells
mucous cells
parietal cells
enteroendocrine
cells
G cells
parietal cells
Which of the following cells produce pepsinogen?
mucous
cells
chief cells
parietal cells
enteroendocrine
cells
G cells
chief cells
The digestive system in a cadaver is longer than in a living person
because, in a cadaver, there is NO __________.
digestion
taking place
food in the alimentary canal
muscle
tone
enzymatic activity
muscle tone
Emulsification of which organic molecules would be most affected if
the liver were severely damaged?
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
lipids
The short reflexes in the digestive system are stimulated by
__________.
the enteric nerve plexuses
the
sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
higher
brain centers
the parasympathetic division of the autonomic
nervous system
the enteric nerve plexuses
Which of the following statements about the mesentery is
INCORRECT?
It holds the organs of the abdomen in
place.
Omenta is the special name for part of the mesentery
extending from the curvatures of the stomach.
It is composed of
a layer of serous membrane fused with a layer of mucous
membrane.
It provides a route for blood vessels, lymphatics, and
nerves to reach the digestive viscera.
It is composed of a layer of serous membrane fused with a layer of mucous membrane.
Which of the following is the most common cause of peritonitis?
a ruptured pancreatic cyst
a perforating ulcer of the
stomach
a perforating abdominal wound
a burst appendix
a burst appendix
The myxovirus causes __________.
infectious
mononucleosis
measles
irritable bowel syndrome
mumps
mumps
Halitosis is caused by __________.
loss of teeth
lack of amylase in saliva
increased anaerobic bacterial activity
at the back of the tongue
increased salivation
increased anaerobic bacterial activity at the back of the tongue
Which of the following teeth are most commonly impacted?
incisors
wisdom teeth
deciduous teeth
premolars
wisdom teeth
Which of the following conditions is directly associated with an
increased risk for heart disease and stroke?
dental
caries
impacted wisdom teeth
gingivitis
periodontitis
periodontitis
The only stomach function that is essential to life is
__________.
the secretion of pepsinogen
the
presence of HCl
mechanical digestion
the secretion of
intrinsic factor
the secretion of intrinsic factor
Some aspects of the __________ phase of gastric secretion, which
occur before food enters the stomach, may be considered conditioned
reflexes.
intestinal
gastric
esophageal
cephalic
cephalic
The myenteric nerve plexus is located in which tunic of the
alimentary canal?
submucosa
serosa
mucosa
muscularis externa
muscularis externa
Which of the following is a function of the gallbladder?
secreting pancreatic juice
metabolizing carbohydrate
storing and concentrating bile
converting pepsinogen to pepsin
storing and concentrating bile
Many of the early food allergies seen in infants are caused by
__________.
excessive absorption of fat
absorption
of whole proteins
lactase deficiency
gallstones
absorption of whole proteins
Which of the following is a condition affecting the large intestine
that is NOT explained by anatomical or biochemical
abnormalities?
a hiatal hernia
irritable bowel
syndrome
pernicious anemia
celiac disease
irritable bowel syndrome
Which of the following is NOT an accessory organ of the digestive
system?
tongue
teeth
salivary glands
intestines
intestines
The major site for nutrient absorption is the __________.
small intestine
mouth
stomach
large intestine
small intestine
The enteric nervous system is the in-house nerve supply of the
alimentary canal.
True
False
True
The serous membrane that covers the external surfaces of most
digestive organs is called the __________.
visceral
peritoneum
parietal peritoneum
mesentery
omentum
visceral peritoneum
__________ circulation collects nutrient-rich blood from the GI tract
and delivers it to the liver.
Peritoneal
Aortic
Hepatic portal
Cardiac
Hepatic portal
serosa
protective outermost layer of the alimentary canal
mucosa
main site of nutrient absorption
submucosa
moderately dense connective tissue that has a rich supply of blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers
muscularis externa
responsible for segmentation and peristalsis
Saliva contains enzymes that break down proteins.
True
False
False
The permanent dentition consists of __________ teeth in a full
set.
10
16
20
32
32
A weak gastroesophageal (cardiac) sphincter can result in
heartburn.
True
False
True
Which of the following is NOT a function of the stomach?
chemical digestion of carbohydrates
temporary holding area for
food until it can be moved to the duodenum
absorption of a few
fat-soluble substances
mechanical breakdown of the bolus into chyme
chemical digestion of carbohydrates
The phases of gastric secretion, from first to last, are
__________.
cephalic phase, intestinal phase, gastric
phase
cephalic phase, gastric phase, intestinal phase
gastric phase, cephalic phase, intestinal phase
intestinal
phase, gastric phase, cephalic phase
cephalic phase, gastric phase, intestinal phase
The increased concentration of HCO3– in blood draining from the
stomach is called __________.
the enterogastric
reflex
the gastric phase
the chloride shift
the
alkaline tide
the alkaline tide
The __________ is the first segment of the small intestine.
ileum
colon
jejunum
duodenum
duodenum
Digestion of carbohydrates and proteins by brush border enzymes
occurs within the __________ of the small intestine.
circular folds
villi
microvilli
goblet cells
microvilli
Bile is stored and concentrated in the __________.
pancreas
gallbladder
liver
stomach
gallbladder
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the liver?
It is highly regenerative.
It stores glucose as
glycogen.
It has three lobes.
It has a role in detoxifying
the blood.
It has three lobes.
__________ is/are NOT found in pancreatic secretions.
Chymotrypsinogen
Procarboxypeptidase
Cholecystokinin
(CCK)
Bicarbonate ions
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Most digestion occurs in the small intestine.
True
False
True
Most water is absorbed in the __________.
small
intestine
large intestine
stomach
liver
small intestine
Bacterial flora in the large intestine does NOT produce
__________.
B vitamins
intrinsic factor
vitamin K
CO2
intrinsic factor
Diarrhea results when food passes too quickly through the large
intestine.
True
False
True
lipids
fatty acids and monoglycerides
proteins
amino acids
carbohydrates
monosaccharides
nucleic acids
nucleotides
Pepsin enzymatically digests __________.
carbohydrate
fat
protein
nucleic acids
protein
Someone on a fat-free diet would NOT efficiently absorb vitamin D
from the diet.
True
False
True
The serous membrane that covers the external surface of most digestive organs is called the __________.
parietal peritoneum
mesentery
omentum
visceral peritoneum
visceral peritoneum
__________ is the major means of propulsion in the digestive
system.
Peristalsis
Ingestion
Mechanical digestion
Defecation
Peristalsis
Which of the following statements about the mesentery is
incorrect?
It provides a route for blood vessels,
lymphatics, and nerves to reach the digestive viscera.
Omenta is
the special name for part of the mesentery.
It is composed of a
layer of serous membrane fused with a layer of mucus
membrane.
It holds the organs of the abdomen in place.
It is composed of a layer of serous membrane fused with a layer of mucus membrane.
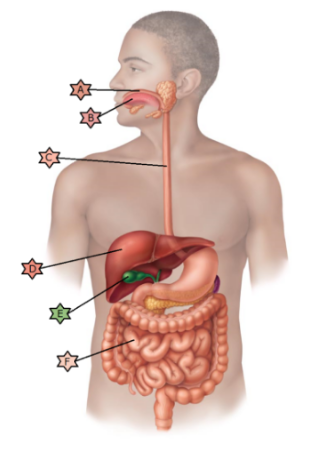
Identify the physiology associated with “E.”
Stores
nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
May be obstructed by
crystallized cholesterol.
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore
often damaged by chemotherapy leading to nausea and
vomiting.
May be affected by congenital condition called
ankyloglossia.
Lined with stratified squamous epithelia.
May
become ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
May be obstructed by crystallized cholesterol.
Match the following term to its correct description: Muscularis
externa.
Main site of nutrient absorption
Areolar
connective tissue that has a rich supply of blood, lymphatic vessels,
and nerve fibers
Protective outermost layer of the alimentary
canal
Responsible for segmentation and peristalsis
Responsible for segmentation and peristalsis
Match the following term to its correct description: Mucosa.
Protective outermost layer of the alimentary
canal
Responsible for segmentation and peristalsis
Main site
of nutrient absorption
Areolar connective tissue that has a rich
supply of blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers
Main site of nutrient absorption
Match the following digestive process with the correct description:
Chemical digestion.
Enzymatic degradation of foodstuffs
into simpler molecules
Elimination of indigestible
solids
Passage of digested materials from the lumen of the GI
tract into the blood or lymph
Chewing, mixing, churning, and
segmentation of food
Taking food into the digestive system
Enzymatic degradation of foodstuffs into simpler molecules
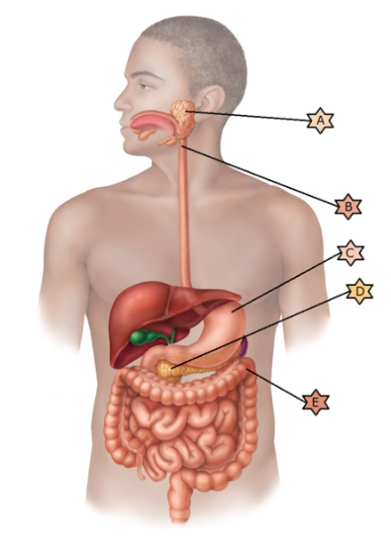
Identify the physiology associated with “E.”
Is one of
the first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the digestion of
starches
Composed of skeletal muscle and thus may be controlled
voluntarily
Is integral in preventing pernicious
anemia.
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be
necessary.
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all
categories of food stuffs.
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be necessary.
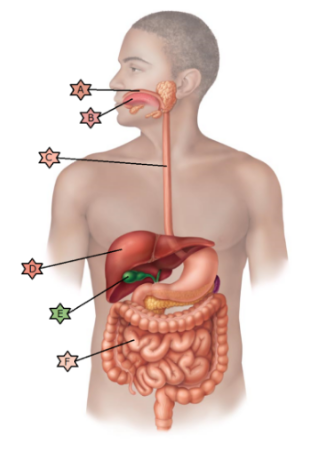
Identify the physiology associated with “D.”
Stores
nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
Lined with stratified
squamous epithelia.
May be affected by congenital condition
called ankyloglossia.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal
hernia.
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged by
chemotherapy leading to nausea and vomiting.
May be obstructed by
crystallized cholesterol.
Stores nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
Match the following term to its correct description: Mucosa.
Main site of nutrient absorption
Protective outermost layer
of the alimentary canal
Responsible for segmentation and
peristalsis
Areolar connective tissue that has a rich supply of
blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers
Main site of nutrient absorption
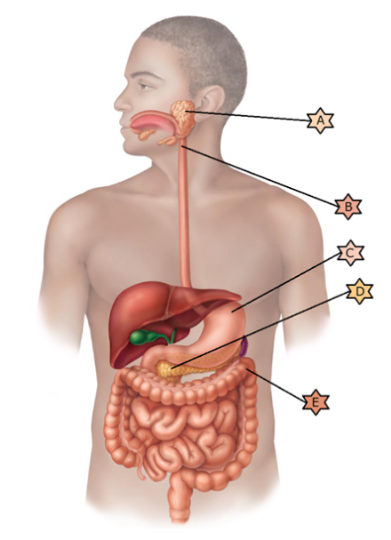
Identify the physiology associated with “B.”
Composed of
skeletal muscle and thus may be controlled voluntarily
Is one of
the first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the digestion of
starches
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be
necessary.
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all
categories of food stuffs.
Is integral in preventing pernicious anemia.
Composed of skeletal muscle and thus may be controlled voluntarily
Which of the following is not an accessory organ of the digestive system?
Tongue
Intestines
Salivary glands
Teeth
Intestines
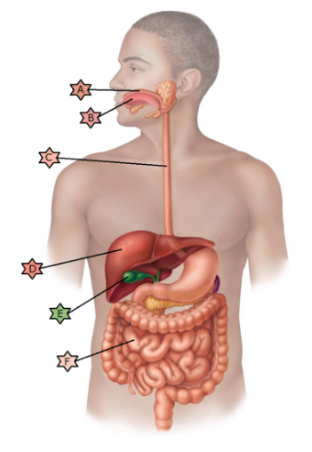
Identify the physiology associated with “F.”
Lined with
stratified squamous epithelia.
Stores nutrients, makes bile and
detoxifies.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
May be
affected by congenital condition called ankyloglossia.
Cells
divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy
leading to nausea and vomiting.
May be obstructed by
crystallized cholesterol.
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy leading to nausea and vomiting.
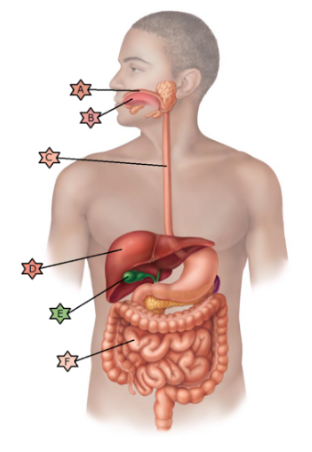
Identify the physiology associated with “C.”
Cells
divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy
leading to nausea and vomiting.
May be obstructed by
crystallized cholesterol.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal
hernia.
Stores nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
May be
affected by congenital condition called ankyloglossia.
Lined with
stratified squamous epithelia.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
Match the following digestive process with the correct description:
Chemical digestion.
Enzymatic degradation of foodstuffs
into simpler molecules
Chewing, mixing, churning, and
segmentation of food
Elimination of indigestible
solids
Passage of digested materials from the lumen of the GI
tract into the blood or lymph
Taking food into the digestive system
Enzymatic degradation of foodstuffs into simpler molecules
Hollow muscular organs, like the stomach, that act as reservoirs
exhibit __________.
receptive
relaxation
peristalsis
positive feedback
accommodation
accommodation
The short reflexes in the digestive system are mediated by
__________.
higher brain centers
the sympathetic
system
the enteric nerve plexuses
the parasympathetic system
the enteric nerve plexuses
Which of the following statements about the mesentery is incorrect?
Omenta is the special name for part of the mesentery.
It is
composed of a layer of serous membrane fused with a layer of mucus
membrane.
It holds the organs of the abdomen in place.
It
provides a route for blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to reach
the digestive viscera.
It is composed of a layer of serous membrane fused with a layer of mucus membrane.
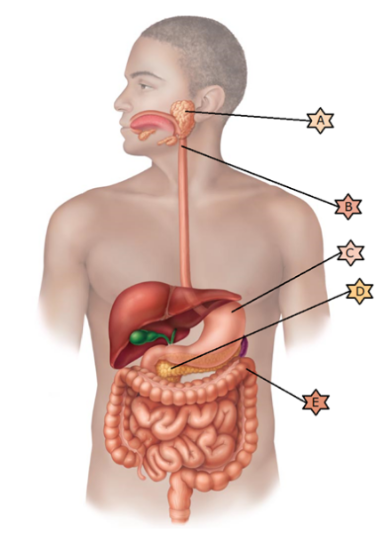
Identify the physiology associated with “C.”
Is integral in preventing pernicious anemia.
Is one of the
first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the digestion of
starches
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be
necessary.
Composed of skeletal muscle and thus may be controlled
voluntarily
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all
categories of food stuffs.
Is integral in preventing pernicious anemia.
The alimentary canal in a cadaver is longer than in a living person
because, in a cadaver, there is no __________.
digestion taking place
hormonal influence
muscle
tone
food in the tube
muscle tone
Which of the following is not an accessory organ of the digestive
system?
Teeth
Intestines
Tongue
Salivary glands
Intestines
Match the following digestive process with the correct description: Absorption.
Taking food into the digestive system
Elimination of
indigestible solids
Enzymatic degradation of foodstuffs into
simpler molecules
Passage of digested materials from the lumen of
the GI tract into the blood or lymph
Chewing, mixing, churning,
and segmentation of food
Passage of digested materials from the lumen of the GI tract into the blood or lymph
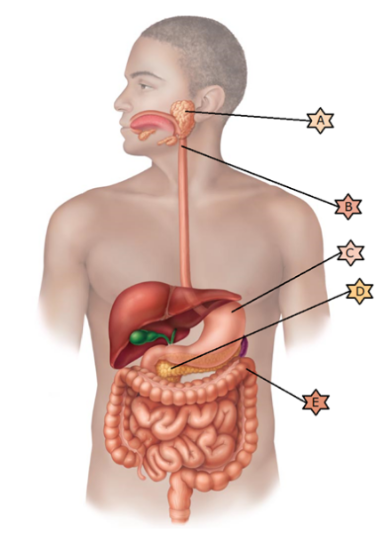
Identify the physiology associated with “E.”
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all categories
of food stuffs.
Is one of the first steps in chemical digestion
as it begins the digestion of starches
Composed of skeletal
muscle and thus may be controlled voluntarily
When infected by
C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be necessary.
Is integral in
preventing pernicious anemia.
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be necessary.
__________ is the major means of propulsion in the digestive system.
Defecation
Mechanical digestion
Peristalsis
Ingestion
Peristalsis
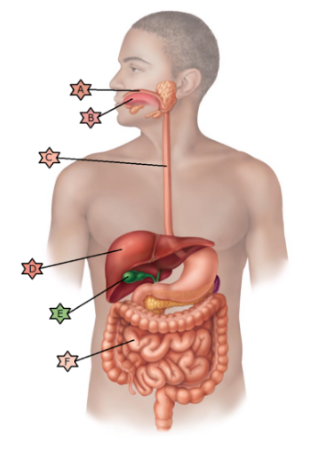
Identify the physiology associated with “F.”
May be obstructed by crystallized cholesterol.
May become
ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
Lined with stratified squamous
epithelia.
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged
by chemotherapy leading to nausea and vomiting.
Stores nutrients,
makes bile and detoxifies.
May be affected by congenital
condition called ankyloglossia.
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy leading to nausea and vomiting.
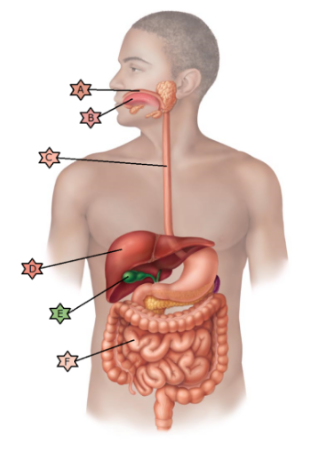
Identify the physiology associated with “D.”
Stores nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
Cells divide
rapidly and are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy leading to
nausea and vomiting.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal
hernia.
May be obstructed by crystallized cholesterol.
May
be affected by congenital condition called ankyloglossia.
Lined
with stratified squamous epithelia.
Stores nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
Match the following term to its correct description: Serosa.
Areolar connective tissue that has a rich supply of blood,
lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers
Responsible for segmentation
and peristalsis
Main site of nutrient absorption
Protective
outermost layer of the alimentary canal
Protective outermost layer of the alimentary canal
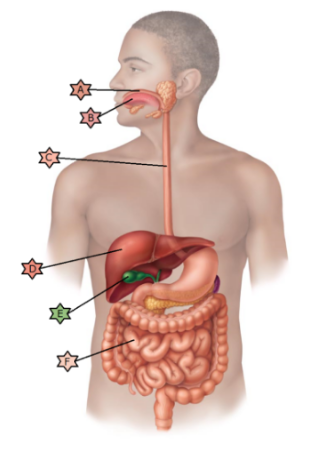
Identify the physiology associated with “C.”
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged by
chemotherapy leading to nausea and vomiting.
Lined with
stratified squamous epithelia.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal
hernia.
May be obstructed by crystallized
cholesterol.
Stores nutrients, makes bile and
detoxifies.
May be affected by congenital condition called ankyloglossia.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
Match the following digestive process with the correct description:
Absorption.
Enzymatic degradation of foodstuffs into
simpler molecules
Chewing, mixing, churning, and segmentation of
food
Taking food into the digestive system
Elimination of
indigestible solids
Passage of digested materials from the lumen
of the GI tract into the blood or lymph
Passage of digested materials from the lumen of the GI tract into the blood or lymph
Match the following term to its correct description: Muscularis externa.
Responsible for segmentation and peristalsis
Protective
outermost layer of the alimentary canal
Main site of nutrient
absorption
Areolar connective tissue that has a rich supply of
blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers
Responsible for segmentation and peristalsis
Match the following term with its correct description: Same structure
as the visceral peritoneum.
Submucosa
Muscularis
Mucosa
Serosa
Serosa
The serous membrane that covers the external surface of most
digestive organs is called the __________.
visceral peritoneum
mesentery
omentum
parietal peritoneum
visceral peritoneum
Match the following term with its correct description: Same structure
as the visceral peritoneum.
Muscularis
Serosa
Submucosa
Mucosa
Serosa
Which of the following statements about the mesentery is
incorrect?
It holds the organs of the abdomen in
place.
It provides a route for blood vessels, lymphatics, and
nerves to reach the digestive viscera.
Omenta is the special name
for part of the mesentery.
It is composed of a layer of serous
membrane fused with a layer of mucus membrane.
It is composed of a layer of serous membrane fused with a layer of mucus membrane.
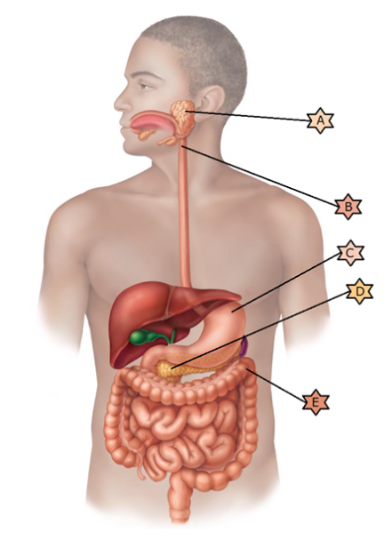
Identify the physiology associated with “D.”
Is one of the first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the
digestion of starches
Composed of skeletal muscle and thus may be
controlled voluntarily
Its name means “all meat” because it
breaks down all categories of food stuffs.
Is integral in
preventing pernicious anemia.
When infected by C.difficile, a
fecal transplant may be necessary.
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all categories of food stuffs.
The serous membrane that covers the external surface of most
digestive organs is called the __________.
mesentery
omentum
parietal peritoneum
visceral peritoneum
visceral peritoneum
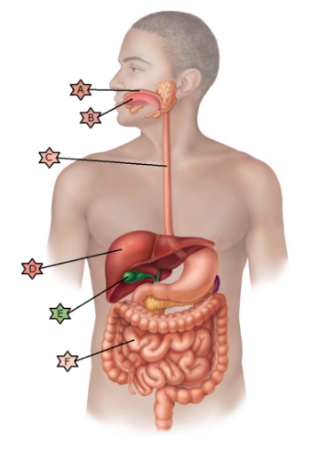
Identify the physiology associated with “B.”
Lined with stratified squamous epithelia.
May become
ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
Stores nutrients, makes bile, and
detoxifies.
May be affected by congenital condition called
ankyloglossia.
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore often
damaged by chemotherapy leading to nausea an vomiting.
May be
obstructed by crystallized cholesterol.
May be affected by congenital condition called ankyloglossia.
Match the following term to its correct description: Serosa.
Responsible for segmentation and peristalsis
Main site of
nutrient absorption
Protective outermost layer of the alimentary
canal
Areolar connective tissue that has a rich supply of blood,
lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers
Protective outermost layer of the alimentary canal
Which sequence below represents the correct layering of the wall of
the GI tract, starting from the layer next to the lumen?
Muscularis externa, serosa, submucosa, mucosa
Submucosa,
mucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
Mucosa, muscularis externa,
submucosa, serosa
Serosa, mucosa, muscularis externa,
submucosa
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
Match the following term to its correct description: Mucosa.
Main site of nutrient absorption
Areolar connective tissue
that has a rich supply of blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerve
fibers
Responsible for segmentation and
peristalsis
Protective outermost layer of the alimentary canal
Main site of nutrient absorption
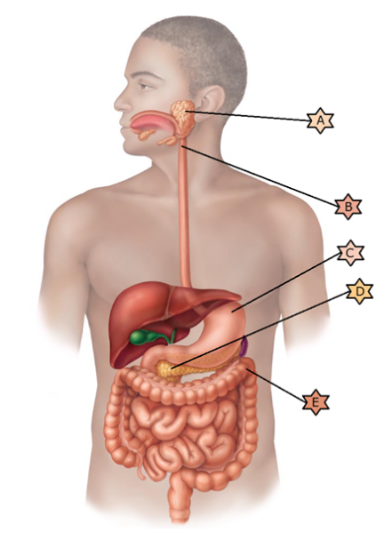
Identify the physiology associated with “A.”
Is one of
the first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the digestion of
starches
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all
categories of food stuffs.
Composed of skeletal muscle and thus
may be controlled voluntarily
Is integral in preventing
pernicious anemia.
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal
transplant may be necessary.
Is one of the first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the digestion of starches
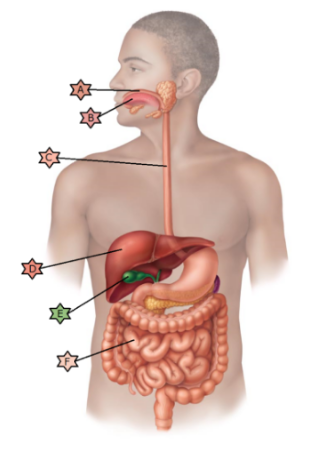
Identify the physiology associated with “E.”
Lined with
stratified squamous epithelia.
Cells divide rapidly and are
therefore often damaged by chemotherapy leading to nausea and
vomiting.
May be affected by congenital condition called
ankyloglossia.
May be obstructed by crystallized
cholesterol.
Stores nutrients, makes bile and
detoxifies.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
May be obstructed by crystallized cholesterol.
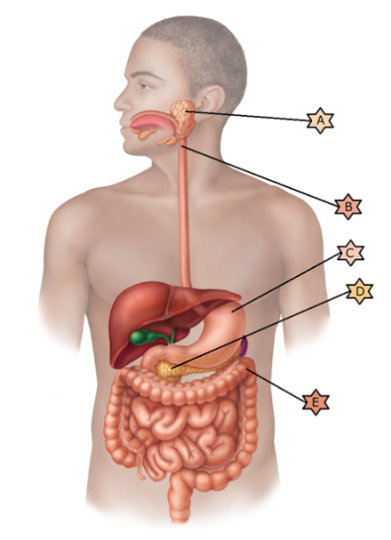
Identify the physiology associated with “D.”
Is one of
the first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the digestion of
starches
Composed of skeletal muscle and thus may be controlled
voluntarily
Is integral in preventing pernicious
anemia.
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be
necessary.
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all
categories of food stuffs.
Its name means “all meat” because it breaks down all categories of food stuffs.
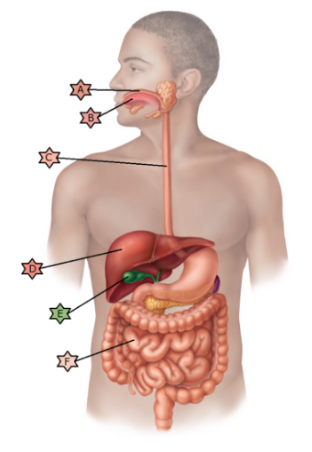
Identify the physiology associated with “F.”
Cells divide
rapidly and are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy leading to
nausea and vomiting.
May become ulcerated in a hiatal
hernia.
Lined with stratified squamous epithelia.
Stores
nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
May be obstructed by
crystallized cholesterol.
May be affected by congenital condition
called ankyloglossia.
Cells divide rapidly and are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy leading to nausea and vomiting.
Identify the physiology associated with “E.”
Is integral
in preventing pernicious anemia.
Its name means “all meat”
because it breaks down all categories of food stuffs.
Composed of
skeletal muscle and thus may be controlled voluntarily
When
infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be necessary.
Is
one of the first steps in chemical digestion as it begins the
digestion of starches
When infected by C.difficile, a fecal transplant may be necessary.
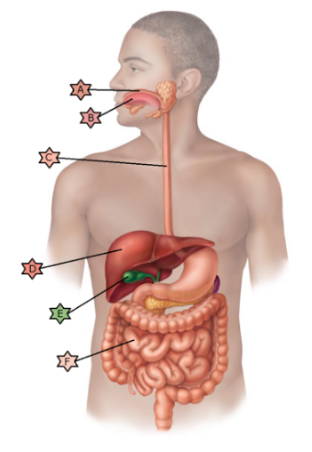
Identify the physiology associated with “D.”
Stores
nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
Cells divide rapidly and
are therefore often damaged by chemotherapy leading to nausea and
vomiting.
May be affected by congenital condition called
ankyloglossia.
Lined with stratified squamous epithelia.
May
become ulcerated in a hiatal hernia.
May be obstructed by
crystallized cholesterol.
Stores nutrients, makes bile and detoxifies.
Hollow muscular organs, like the stomach, that act as reservoirs
exhibit __________.
accommodation
receptive
relaxation
peristalsis
positive feedback
accommodation
Match the following term to its correct description: Muscularis
externa.
Responsible for segmentation and
peristalsis
Main site of nutrient absorption
Areolar
connective tissue that has a rich supply of blood, lymphatic vessels,
and nerve fibers
Protective outermost layer of the alimentary canal
Responsible for segmentation and peristalsis