Government policies designed to promote efficiency:
usually do so at the expense of equity.
All of the following can be considered a student's costs of going to college, EXCEPT:
textbooks, tuition and fees, the student's time, which can no longer be devoted to earning a salary.
A: room and board (that costs her about the same as she was paying before entering college)
An airline's plane from Los Angeles to New York is about to take off, but it still has a few seats empty. If the average cost per seat is $500, what price should the airline charge passengers in standby to fill in those remaining seats? (Consider that quantitative decisions are made at the margin)
Any price above zero that will entice standby passengers to take the flight.
The Federal government enacted regulation in the 1960s requiring people to wear seatbelts in their cars. All of the following resulted from this regulation, EXCEPT:
overall deaths due to car accidents changed very little in the United States, fewer deaths occurred per accident, the frequency of accidents increased.
A: fewer pedestrians were killed in car accidents
When two persons trade goods:
both persons usually gain from the exchange.
In a market economy, the decisions of what and how much to produce are made by:
all producers and consumers.
Even though markets do a great job in organizing economic activity, governments are needed to do all of the following EXCEPT:
establish and enforce property rights, intervene when markets fail due to externalities, intervene when markets fail due to market power
A: decide what and how much should be produced.
Living standards in the United States have risen tremendously over the years, mainly due to:
relentless increases in the productivity of labor over the years.
Rapid and persistent inflation occurs mainly due to:
rapid increases in the quantity of money in the economy.
A government that implements a policy designed to reduce inflation can expect unemployment to:
increase in the short-run.
Which of the following is FALSE, regarding economics as a science?
Economic theories represent irrefutable facts.
Economists use assumptions in order to:
simplify economic theories, so as to make it possible to answer economic questions.
Economic models are:
simplified versions of economic theories.
created by making assumptions.
usually composed of diagrams and equations.
All of the following are characteristics of the Circular Flow Model of the economy, EXCEPT:
the model describes two circular flows: one for inputs and one for resources.
The circular flow model of the economy demonstrates that:
dollars in the economy are used over and over in an endless cycle.
Which of the following is true regarding the Production Possibilities Frontier Model of the economy?
Any point along the PPF represents an efficient level of production.
Economic growth in the economy can be portrayed in the Production Possibilities Frontier model as a:
shift of the PPF away from the origin.
Microeconomics is the study of:
how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets.
Which of the following is an example of a normative statement?
The government should increase spending during recessions, so that the economy recovers quickly.
Economists tend to disagree with each because:
different economists espouse different theories, so they believe different things are going on in the economy.
different economists make different assumptions, leading them to different conclusions in economic matters.
different economists have different values and priorities in economic matters.
The production possibilities frontiers used to explain trade in the text are straight lines because:
the author assumes the farmers can switch at a constant rate from producing meat to producing potatoes.
The principle of Absolute Advantage refers to the situation in which one producer:
can produce a good using fewer resources than other producers.
The principle of Comparative Advantage refers to the situation in which one producer:
has a lower opportunity cost than other producers in the production of a good.
Which of the following is true regarding the principle of Absolute Advantage?
Nations should specialize in producing those goods for which they have an Absolute Advantage.
Which of the following is true regarding the principle of Comparative Advantage?
Nations should specialize in producing those goods for which they have the lowest opportunity cost.
The boy next door has offered to mow Tiger Woods' lawn. It will take this boy twice as long as Tiger Woods to mow the lawn. Would Tiger Woods let the boy mow his lawn, instead of doing it himself?
Yes, as long as the boy's opportunity cost is less than half of Tiger Woods' opportunity cost.
Suppose that engaging in free trade means we have to stop making cars, which will cause bankruptcies and will make people lose their jobs. Is it still worth having free trade?
Yes, because the gains outweigh the losses: new businesses and new jobs will flourish in other industries.
Suppose that Jill can type 10 pages per hour in the computer, while Jim can only type 8. Further suppose that Jill can review 5 articles per hour while Jim can only review 2. If they are working on a final project together, who should specialize in what task in order to be as productive as possible?
Jill should specialize in reviewing articles and Jim in typing.
Suppose that Jill can type 10 pages per hour in the computer, while Jim can only type 8. Further suppose that Jill can review 5 articles per hour while Jim can only review 2. Based on this, we can say that:
Jill has an absolute advantage over Jim in reviewing articles.
The principle of Comparative Advantage argues all of the following, EXCEPT:
free trade tends to cause bankruptcies and high unemployment in the long run.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
It is difficult for new firms to enter the market.
A market with only one firm is known as a:
monopoly.
An increase in demand means that:
consumers are willing to purchase greater quantities of the good at any given price.
If good B is a substitute for good A, and the price of good B increases:
the demand for good A will increase.
When the price of a good increases:
the quantity supplied of the good will increase.
A new technology that helps firms reduce production costs will cause a:
shift to the right of the supply curve.
If the price in a market happens to be below equilibrium, there will be a ________ in the market, and the price will tend to ________.
shortage, rise
If the price in a market happens to be above equilibrium, there will be a ________ in the market, and the price will tend to ________.
surplus, drop
Suppose that a scientific study just published demonstrates that eating apples makes people much healthier. How will this affect the equilibrium price and quantity in the market?
Both the equilibrium quantity and price will increase.
Suppose the price of corn syrup increases. Given that corn syrup is a major ingredient in the production of soft drinks, how will this affect the equilibrium price and quantity in the soda market?
The equilibrium price will increase and the equilibrium quantity will decrease.
A good will tend to have an inelastic demand if:
the market is defined very broadly.
A perfectly elastic demand is represented graphically by a:
horizontal demand curve.
What effect will an increase in the price have on Total Revenue, if demand is elastic?
Total Revenue will decrease.
The price elasticity of demand tends to be more elastic:
at points further up and to the left along the demand curve.
Suppose that General Cars increases the price of its Cadiclap model from $13,500 to $16,500. As a result of this, the quantity demanded of the Cadiclap model decreases from 600,000 to 400,000 per year. Find the price elasticity of demand of the Cadiclap using the Mid-Point method.
-2.0
If a firm needs to increase its Total Revenue, the firm should ________ the price, if the demand for its product is ________.
drop, elastic
Suppose that consumers' incomes rise by 3%, and that this causes the quantity demanded for a good to increase by 4.5%. What is the income elasticity of demand?
1.50
Suppose that a good has an income elasticity of demand of -2.0. This means that the good is:
inferior.
If two goods have a cross-price elasticity of demand of -0.8. This means that these goods are:
complements.
The price of good A increases from $4.50 to $5.50. This causes the quantity demanded of good B to increase from 900 to 1100 units per month. Find the cross price elasticity of demand using the Mid-Point method.
+1.0
Suppose that a regulation is in place that does not allow the price of a good to exceed $5. If this price is above the equilibrium price in the market, this would be an example of a:
not binding price ceiling.
Suppose that a regulation is in place that does not allow the price of a good to fall below $10. If this price is above the equilibrium price in the market, this would be an example of a:
binding price floor.
Suppose that a regulation is in place that does not allow the price of a good to exceed $5. If this price is below the equilibrium price in the market, this would be an example of a:
binding price ceiling.
If a price floor is in place and it is binding, the market will:
experience a surplus.
If a price ceiling is in place and it is binding, the market will:
experience a shortage.
If a price floor is in place and it is not binding, the market will:
remain in equilibrium, unaffected by the price floor.
If a tax is imposed on buyers of a good, the ________ curve of the good will shift ________ by the amount of the tax.
demand, downward
If a tax is imposed on sellers of a good, the ________ curve of the good will shift ________ by the amount of the tax.
supply, upward
If a tax is imposed on a good and the incidence of the tax ends up falling more heavily on the sellers than on the buyers, this will be because:
demand is more elastic than supply for that good.
If a tax is imposed on a good and the incidence of the tax ends up falling more heavily on the buyers than on the sellers, this will be because:
demand is less elastic than supply for that good.
Consumer surplus is the:
difference between what the consumer is willing to pay and what the consumer has to pay.
The consumer surplus can be expressed graphically as the area:
below the demand curve and above the price of the good.
The producer surplus can be expressed graphically as the area:
above the supply curve and below the price.
The producer surplus represents the:
difference between the price of the good and the cost to the seller.
A price increase will cause consumer surplus to ________.
decrease
A price increase will cause producer surplus to ________.
increase
Total Surplus can be calculated as follows:
Value to buyers minus cost to sellers.
Total surplus in a market is usually maximized when:
the market is in equilibrium.
If the quantity traded in a market is less than the equilibrium quantity:
the value to consumers for additional units is greater than the cost to sellers of producing those units.
If a market is not very competitive and/or if there are externalities, we can expect the market outcome:
not to be efficient, and total surplus will not be maximized.
All of the following occur when a tax is levied on a good, EXCEPT:
total surplus increases.
When a tax is imposed, the quantity traded in a market will ________ and total surplus will ________.
decrease, decrease
The loss of total surplus in a market resulting from a tax is called:
deadweight loss.
Deadweight loss in a taxed market occurs because:
the tax causes the market to trade less than the optimal units, so all the surplus of the units not traded is lost.
A given tax will cause a bigger deadweight loss if demand and supply are:
elastic.
Which of the following will cause the deadweight loss of taxation to be bigger?
A bigger tax.
According to the Laffer curve, if the government wants to increase its revenue from taxes:
sometimes the way to do so will be by lowering the size of the tax.
When the size of the tax is too big, a further increase in the size of the tax will cause:
the revenue generated by the tax to decrease.
A bigger tax will cause the deadweight loss in the market to:
increase, and it might cause the tax revenue to decrease.
When a tax is imposed, which of the following will occur?
A deadweight loss will occur in the market.
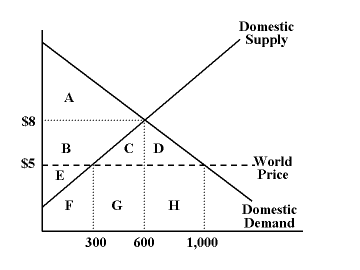
In the diagram, what area represents the total surplus when there is no international trade?
A + B + E
In the diagram, what area represents the gains from free international trade?
C + D

In the diagram, what area represents the total surplus when there is free international trade?
A + B + C + D + E
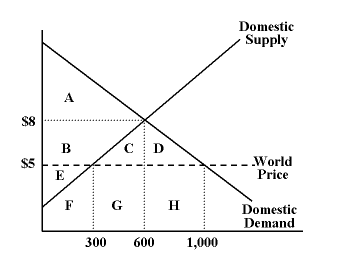
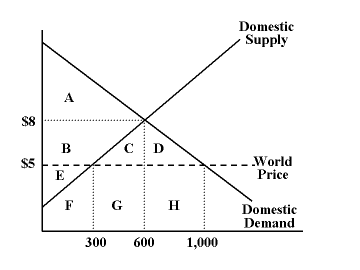
Which of the following statements is true regarding the diagram?
The diagram represents the situation of an importing country.
Which of the following statements is true regarding international trade?
For the importing country, the gains from international trade outweigh the losses.
Which of the following statements is true about tariffs?
Tariffs reduce the welfare of importing countries.
Which of the following statements is true regarding externalities?
Both negative and positive externalities lead to inefficient outcomes in markets.
Positive externalities cause the market to trade a quantity:
smaller than the optimal quantity.
Negative externalities cause the market to trade a quantity:
greater than the optimal quantity.
Markets with positive externalities do not trade the optimal quantity because:
consumers fail to consider the external benefit in their decision making process.
Markets with negative externalities do not trade the optimal quantity because:
producers fail to consider the external cost in their decision making process.
The Coase Theorem states that:
efficient outcomes can be accomplished by private parties, even when externalities are present, as long as there are no bargaining costs.
Private solutions to externalities are not always possible because:
sometimes there are simply too many people involved for them to be able to reach a negotiated solution.
Which of the following statements is true about regulating externalities?
Regulation is a command and control policy that can be used to deal with externalities.
Which of the following is false regarding Pigovian subsidies?
Pigovian subsidies can only be applied effectively in situations with negative externalities.
Which of the following is false regarding a Pigovian tax?
A Pigovian tax can only be applied effectively in situations with positive externalities.
Private goods are:
both excludable and rival.
Public goods are:
neither excludable nor rival.
Common resources are:
rival, but not excludable.
The free-rider problem refers to the:
fact that when public goods are provided by someone, there is no way of preventing others from using them, even if they do not pay for them.
All of the following are examples of public goods, EXCEPT:
clean air and water.
The tragedy of the commons refers to:
the grounds surrounding medieval towns, which became barren through overuse.
All of the following are solutions to the problem of common resources being overused, EXCEPT:
having the government provide more of the common resource.
Which of the following is a good example of a common resource?
Congested freeways.
Which of the following is the most effective solution to congested freeways?
Make freeways into toll ways, with the toll being steep enough to discourage some drivers from using them.
Which of the following will help solve the free-rider problem of public goods?
Have the government itself provide the good.
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding government tax revenue in the United States?
During the 20th century, state and local governments increased their tax revenue much faster than the Federal government.
The main source of revenue for the U.S. Federal government is:
individual income taxes.
The biggest spending item for the U.S. Federal government is:
Social Security.
The main source of revenue for state and local governments in the U.S. is:
sales taxes.
The biggest spending item for state and local governments in the U.S. is:
education.
Which of the following is a cost of taxation to taxpayers?
The tax payment itself.
The deadweight cost of taxation.
The administrative burden of taxation.
Which of the following tax reforms will encourage people to save more?
Replace the current income tax with a consumption tax.
Which of the following is an example of the administrative burden of taxation?
The fee paid to an accountant for preparing our tax statements.
Progressive taxation leads to ________ marginal tax rates as income rises, which ________ people from earning more money.
high, discourages
The idea that those who use the public goods provided by the government should be the ones to pay the taxes needed to provide such goods is called the ________ principle.
benefits
Which of the following would be a good example of an implicit cost incurred by Superior Airways?
The rent that could be earned on an aircraft that is owned and used by Superior.
Everything that needs to be given up whenever a choice is made is called:
an opportunity cost.
Accounting profit is ________ compared to economic profit, because accountants ________ implicit costs in their calculations.
bigger, do not consider
The property of diminishing marginal product of labor states that:
every additional worker hired contributes a smaller increase in production than previously hired workers.
The cost of raw materials will fall under the category of:
variable costs.
The lease payments made by a firm fall under the category of:
fixed costs.
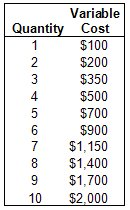
Based on the table, if the Fixed Cost is $500, what is the Marginal Cost of the 10th unit?
$300
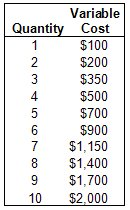
Based on the table, if the Fixed Cost is $500, what is the Average Total Cost of the 5th unit?
$240

Based on the table, if the Fixed Cost is $500, what is the Average Variable Cost of the 4th unit?
$125
Economies of scale occur when the ________ as the quantity of output increases.
long-run Average Total Cost falls
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a competitive market?
Firms set the price.
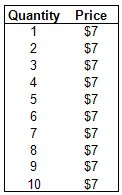
Use the table to find the Total Revenue when the quantity is 8 units.
$56
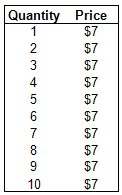
Use the table to find the Marginal Revenue when the quantity is 5.
$7
Which of the following statements is true, regarding the revenues of a firm?
The Marginal Revenue and the Average Revenue are equal to the price.
A firm will maximize profits when its:
Marginal Revenue is equal to its Marginal Cost.
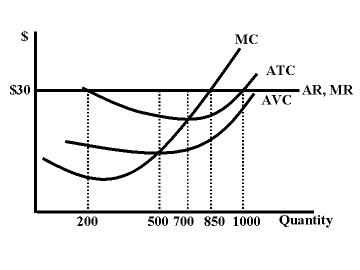
Which is the profit maximizing quantity according to the graph?
850
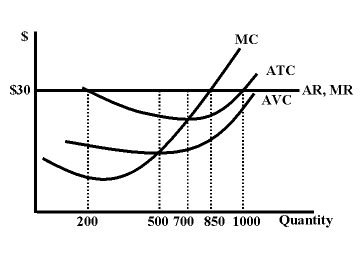
Based on the graph, which of the following statements is FALSE?
The firm maximizes its profits by producing 700 units.
The short-run supply curve of a firm in perfect competition is the segment of its:
marginal cost curve that lies above the minimum average variable cost.
Which of the following is an example of a barrier to entry into a monopoly market?
A restaurant at the top of the cliff possesses the only location in town with a spectacular view.
The demand curve faced by a monopoly is:
downward sloping.
A monopoly is a ________, therefore the demand curve it faces is ________.
price setter, downward-sloping
As output increases in a monopoly, the firm's total revenue:
first increases and then decreases.
Marginal revenue in a monopoly is:
always smaller than the price

Which of the following statements is true, regarding the monopoly described by the graph?
The firm will charge a price of $11.
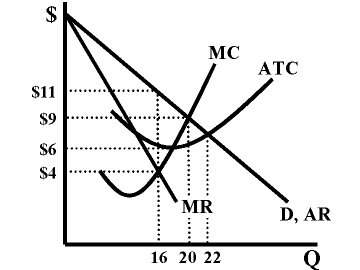
Use the diagram to calculate the profit of the monopoly.
$80
A monopoly tends to sell a ________ quantity at a ________ price than perfect competition.
smaller, higher
Which of the following statements is true regarding a profit maximizing monopoly?
It will cause a deadweight loss.
It will produce less than perfect competition.
It will sell at a higher price than perfect competition.
Which of the following are government policies designed to deal with
monopolies?
i. Try to make monopolized industries more competitive.
ii. Regulate the behavior of monopolies.
iii. Turn some
private monopolies into public enterprises.
iv. Do nothing at all.
all four policies
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
Monopolistic competition is an industry with only a few sellers.
Which of the following statements is true?
Oligopolies sell more output than monopolies.
When an oligopoly without collusion is in a Nash equilibrium, which of the following will be true?
Firms will choose not to change their price or output.
The larger the number of firms in an oligopoly, the ________ the price and the ________ the output of the industry.
lower, greater
A strategy that is best for a player in a game regardless of the strategies chosen by the other players is called the:
dominant strategy.
In the case of the prisoners' dilemma, the dominant strategy for both prisoners is to:
confess.
The prisoners' dilemma game theory shows us that:
following a logical self-interested strategy may not result in the best outcome for decision makers.
The prisoner's dilemma game theory helps us understand:
why collusive agreements so often fall apart through cheating.
Cartels are sometimes able to continue working in the long run. This tends to occur when the firms involved consider playing the game ________, and there ________ a credible threat involved with cheating.
repeatedly, is
Which of the following is NOT one of the controversies listed in the text regarding antitrust policy?
import tariffs
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
The goods are identical.
The diagram depicting monopolistic competition in the short run:
is very similar to the short run monopoly diagram.
If the Average Total Cost curve of a firm in monopolistic competition happens to be above the demand curve, it means:
that firms in that industry will be incurring losses in the short run.
In the long run, firms in monopolistic competition will see their price:
become equal to their Average Total Cost.
If firms in monopolistic competition are enjoying positive economic profits, in the long run:
this will attract new firms into the industry, causing prices to drop and profits to disappear.
Firms in monopolistic competition in long run equilibrium ________ than firms in perfect competition.
produce less
In monopolistic competition in long run equilibrium, the price will be equal to:
average total cost.
A major critique of advertising is that:
it manipulates people's tastes, leading people to make bad choices.
A major argument in favor of advertising is that:
it provides information to consumers that allows them to make better choices.
Branding can be good for society because:
it provides useful information to consumers about the quality of branded goods.