Which of these joints would be functionally classified as diarthrotic?
None of the listed responses is correct.
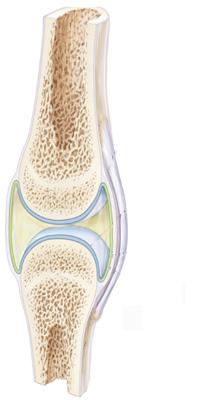
The generalized model for the structural type of joint illustrated shares the LEAST number of features with which of the following?
intervertebral joint
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
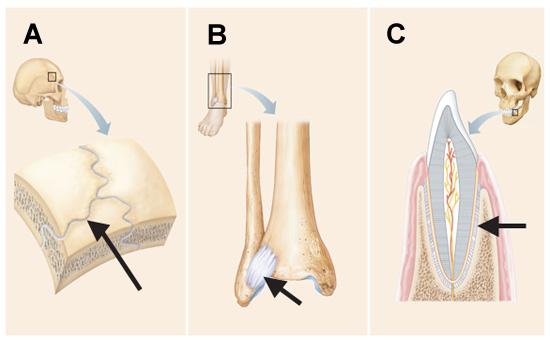
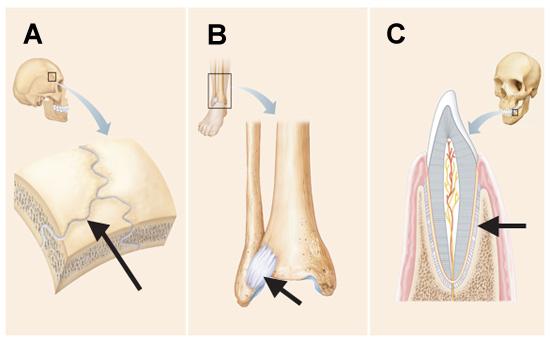
Which of the following is true regarding the structure indicated by the arrow in the joint depicted in A?
It becomes ossified late in adult development.
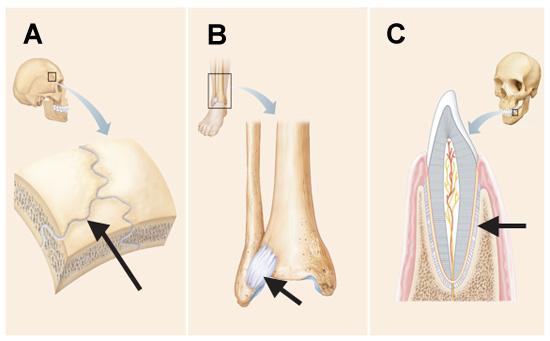
The arrows in B and C point to structures that can both be described as a ______.
ligament
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
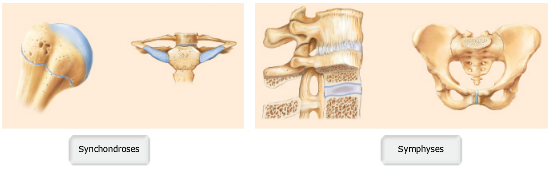
Which of the joints will eventually develop into a synostosis?
A
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
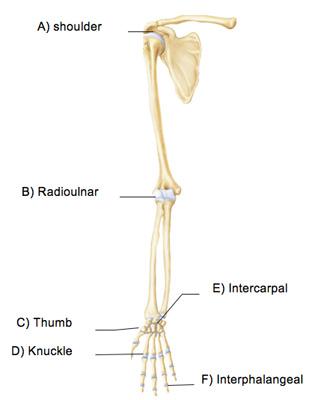
Which of the following is a hinge joint?
F
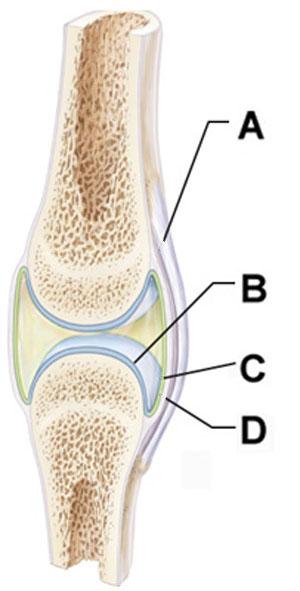
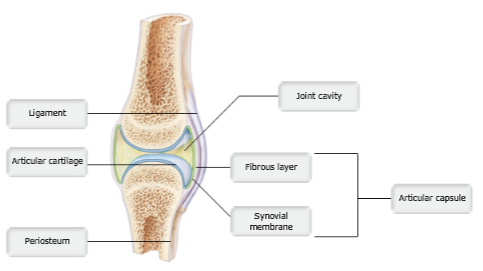
Which structure is composed primarily of dense irregular connective tissue?
D
Functional classification of joints is based on ________.
the amount of movement allowed by the joint
Which of the following does NOT represent a structural classification of joints?
diarthrosis
Articulations permitting only slight degrees of movement are ________.
amphiarthroses
Synarthrotic joints ________.
permit essentially no movement
The amount of movement permitted by a particular joint is the basis for the functional classification of joints.
True
All joints permit some degree of movement, even if very slight.
False
The structural classification of joints is based on the composition of the binding material and the presence or absence of a joint cavity.
True
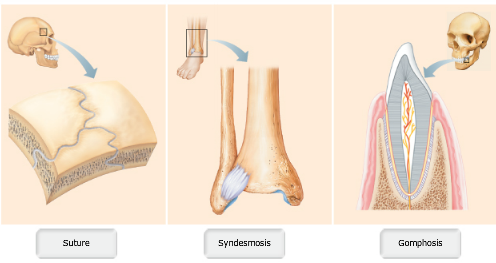
Fibrous joints are classified as ________.
sutures, syndesmoses, and gomphoses
Which of the following statements defines synchondroses?
cartilaginous joints where hyaline cartilage unites the ends of bones
Which of the following is one difference between bursae and tendon sheaths?
Bursae are flattened fibrous sacs wedged between adjacent structures, while tendon sheaths are elongated fibrous sacs that wrap around tendons.
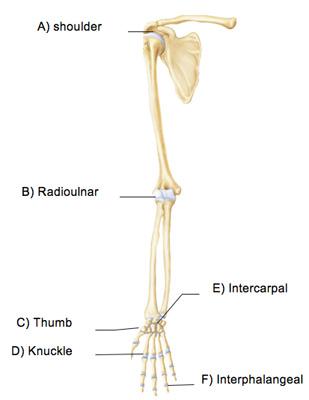
The thumb joint indicated by C mediates which of the following special movements?
opposition
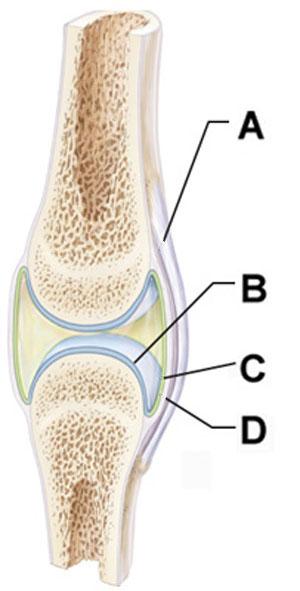
Which structure is composed primarily of dense irregular connective tissue?
D
Connective tissue sacs lined with synovial membranes that act as cushions in places where friction develops are called ________.
bursae
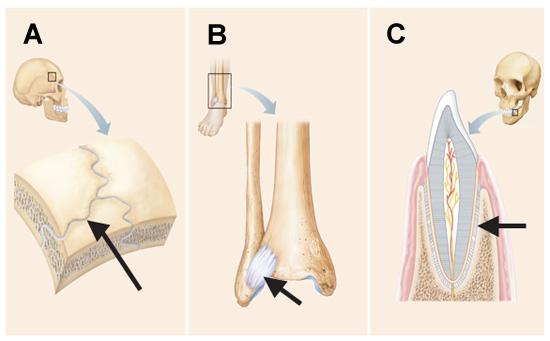
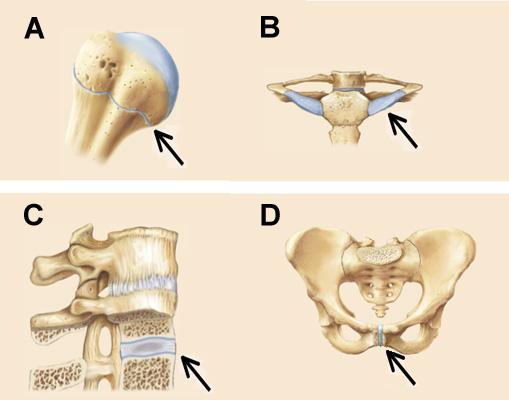
All three joints in the below figure are classified as ______.
fibrous joints
Which of the joints will eventually develop into a synostosis?
A
A fibrous joint that is a peg-in-socket is called a ________ joint.
gomphosis
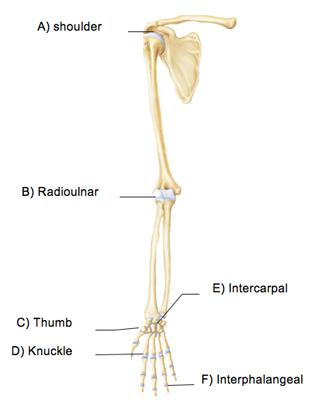
Which joint in the above figure is limited to nonaxial gliding movements?
E
Pointing the toes is an example of ________.
plantar flexion
Saddle joints have concave and convex surfaces. Identify the saddle joint of the skeleton.
Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb.
Which of the following is NOT a structural feature of synovial joints?
bone ends united by fibrocartilage
Which of the following does NOT represent a structural classification of joints?
diarthrosis
Which of the following is a true statement regarding gliding movements?
Gliding movements occur at the intercarpal and intertarsal joints.
The structural classification of joints is based on the composition of the binding material and the presence or absence of a joint cavity.
True
Bending your head back until it hurts is an example of ________.
hyperextension
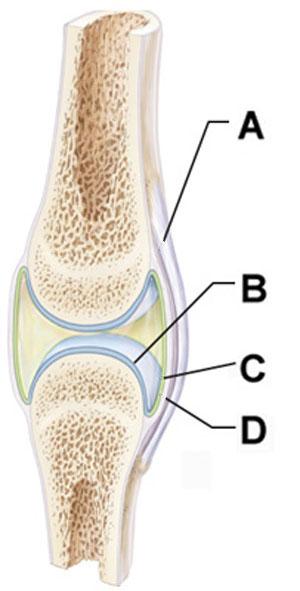
Structure C and D collectively form which of the following?
articular capsule
The shoulder and hip are examples of ________.
ball-and-socket joints
The terms inversion and eversion pertain only to the ________.
feet
Articulations permitting only slight degrees of movement are ________.
amphiarthroses
In a sprain, the ________ of a joint are stretched or torn.
ligaments
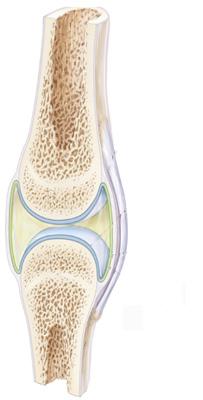
Which of the following terms describes the functional classification of the illustrated joint with regard to its range of movement?
diarthrotic
Which of the following is NOT a factor that contributes to joint stability?
amount of synovial fluid in the joint cavity
Synovial fluid does NOT ________.
prevent the articulating bones from dislocating
The hip joint is a good example of a(n) ________ synovial joint.
multiaxial
Functional classification of joints is based on ________.
the amount of movement allowed by the joint
Which joint has sacrificed stability to provide great freedom of movement?
shoulder
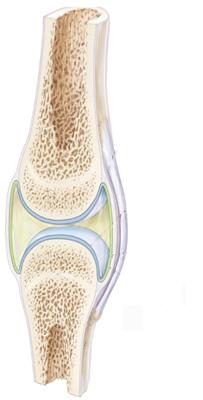
Which of the following terms describes the functional classification of the illustrated joint with regard to its range of movement?
diarthrotic
Functional classification of joints is based on ________.
the amount of movement allowed by the joint
All joints permit some degree of movement, even if very slight.
False
Which movement increases the angle between articulating bones?
extension
In the classification of joints, which of the following is true?
All synovial joints are freely movable.
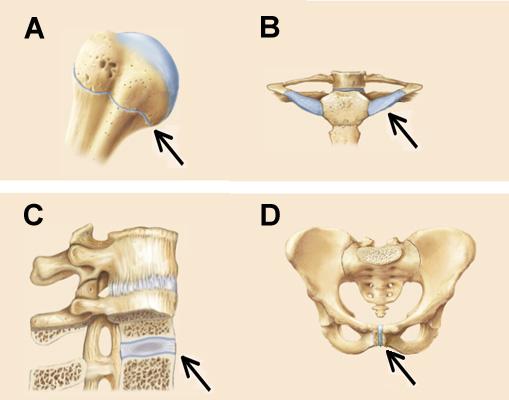
Which of the joints will eventually develop into a synostosis?
A
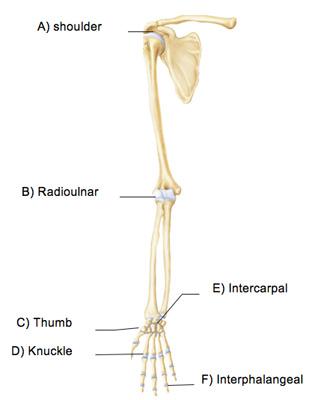
The thumb joint indicated by C mediates which of the following special movements?
opposition
Which ligament would one tap to generate the knee-jerk reflex?
patellar ligament
Which of the following is CORRECTLY paired?
multiaxial movement: movement in all three planes and around all three axes
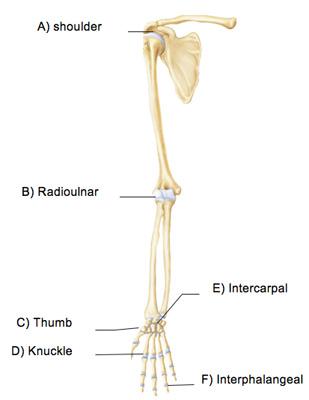
Which joint in the above figure is limited to nonaxial gliding movements?
E
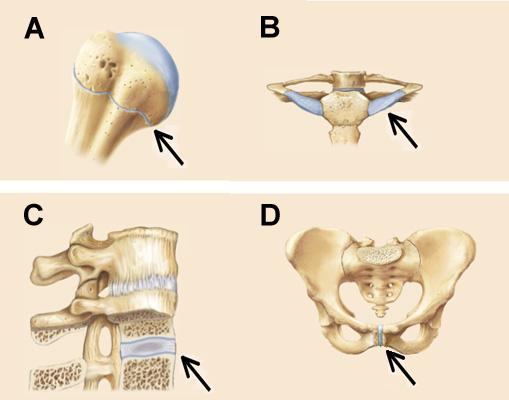
The joints indicated by the arrows in C and D are distinguished from those indicated in A and B by the presence of which of the following tissues?
fibro-cartilage
Saddle joints have concave and convex surfaces. Identify the saddle joint of the skeleton.
Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb.
Pointing the toes is an example of ________.
plantar flexion
In a sprain, the ________ of a joint are stretched or torn.
ligaments
Which joint has sacrificed stability to provide great freedom of movement?
shoulder
The hip joint is a good example of a(n) ________ synovial joint.
multiaxial
The shoulder and hip are examples of ________.
ball-and-socket joints
Which of the following refers to a joint that is immovable?
synarthrosis
Which of the following is NOT a structural feature of synovial joints?
bone ends united by fibrocartilage
The amount of movement permitted by a particular joint is the basis for the functional classification of joints.
True
Using the structural classification, what type of joint is the epiphyseal plate?
cartilaginous joint
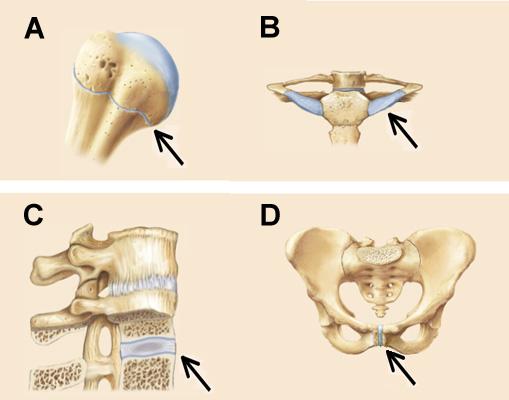
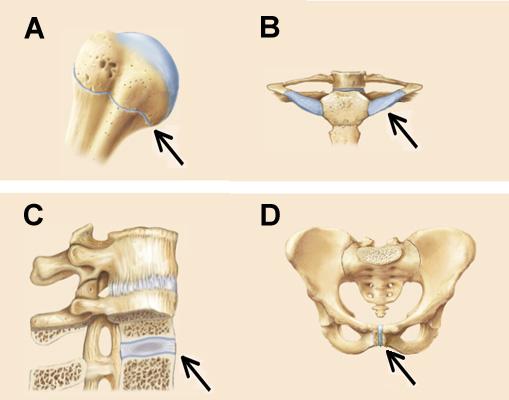
Joints A, B, C, and D in the figures below are all classified as ______.
cartilaginous joints
A fibrous joint that is a peg-in-socket is called a ________ joint.
gomphosis
When a person makes a pinching motion with their thumb and forefinger they are performing a movement called ________.
opposition
Which type of movement occurs at the intercarpal and intertarsal joints?
gliding movement