The structure indicated in the diagram of male reproductive system is
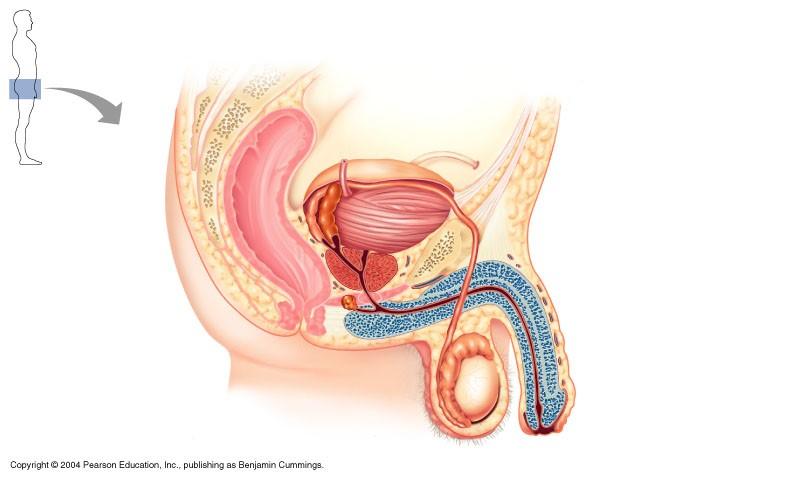
Vas deferens
The insertion of semen in a female genital tract to get her pregnant by unnatural means, if the male partner is impotent is the process of
artificial insemination
The uterine layer which gets shed with each menstrual cycle is
the functional layer of endometrium
These cells located in between seminiferous tubules produce testosterone
interstitial cells of leydig
the primary sex organ of the male is the
testis
a 28 years old female with regular menstrual cycles complaining of consecutive two missed period , the most probable cause of amenorrhea can be
pregnancy
The reason why the testes are suspended in the scrotum is
to provide for a cooler temperature
the sperm's acrosome
contains enzymes
the surge of LH that occurs during the middle of the ovarian cycle triggers
ovulation
the usual site of fertilization is the
ampulla of fallipian tube
Under which uterine phase does the functional layer of the endometrium start to rebuild
proliferative
Which form of birth control below is most effective
total abstinence
Which is the most correct sequence of sperm flow in the male duct system
seminiferous tubules, epididymis, vas deferens, ampulla, ejaculatory duct, urethra
Which male structure is homologous to the female's clitoris
penis
The indicated part of the female reproductive system is
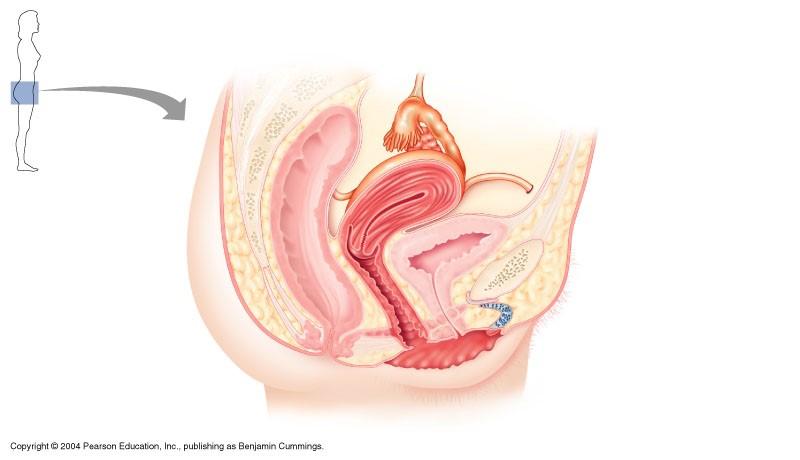
cervix
The structure indicated in the diagram below of the male reproductive system is
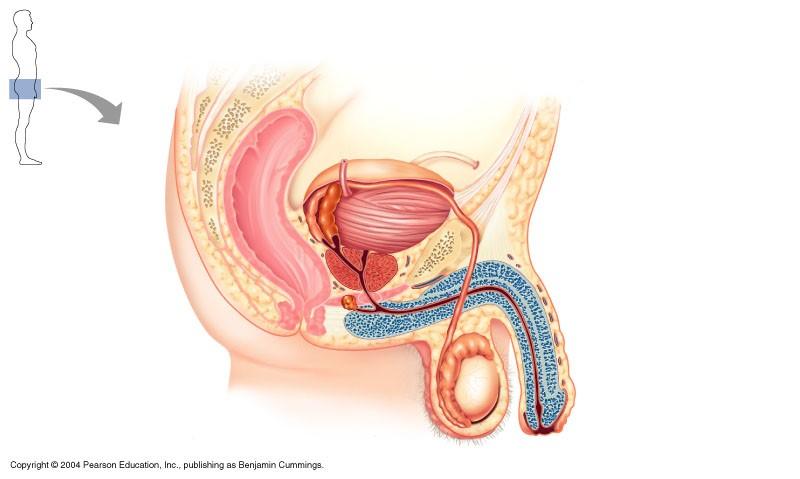
epididymis
The primary sex organ of the male is testes
true
the surge in LH that occurs during the middle of the ovarian cycle, in emales, triggers menstruation
false
The uterine layer which is shed with each monthly cycle is the stratum functionalis of endometrium
true
The cells located in between seminiferous tubules, which produces testosterone are the interstitial cells of leydig
true
A primary oocyte gets ovulated from the ovary upono ovulation
false
suspensory ligaments anchors the uterus laterally to the pelvic wall
false
Within the ovary after ovulation, progesterone is produced by the corpus albicon
false
Hormone responsible for secondary sex characteristics in women is released from placenta
false
The structure indicated in the diagram of the male reproductive system is the ejaculatory duct
false
a male structure homologous to the female's labia majora is prepuce
false
The structure indicated in the diagram of male reproductive system is epididymis
false
vasectomy is cutting the ductus deferens, which is 100% effective form of birth control
false
suspensory ligaments anchors the uterus laterally to the pelvic wall
true
broad ligament contains suspensory ligament, mesosalpinx, mesometrium, and the mesovarium
true
in a normal uterine cycle. days 1-5 are the menstrual phase. Days 6-14 is proliferative phase and days 15-28 are secretory phase
true
septa divide the testis into 250-300 lobules, each lobule containing 1-4 seminiferous tubules
false
corpora carvenosa is the structure that surrounds the urethra and expands to form the glans and bulb of the penis
false
Graafian follicle is a secondary follicle at its most mature stage that bulges from the surface of the ovary
false
the fallopian tube ends in the funnel-shaped, ciliated infundibulum containing fingerlike projections call fimbriae
true
rectouterine pouch lies between the rectum and the uterus
true
Follicular phase is the period of follicle growth in ovarian cycle from days 1-13 and luteal phase is the period of corpus luteum activity from days 15-28 in normal 28 days ovarian cycle
false
the most common STD in the US is syphilis
false
the indicated part of female reproductive system is fundus of uterus
false
identify the histology slide
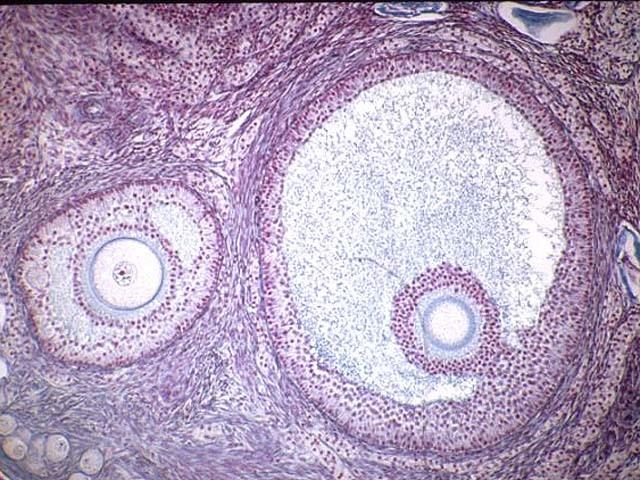
antrum
The hormone responsible for setting basal metabolic rate
thyroxine
posterior pituitary gland
Neurohypophysis
Leukotrienes and prostaglandins
eicosanoids
half life of hormone
it is the duration from the time of release of hormone to the time when its concentration is reduced by 50%
superior thyroid artery is a branch of internal carotid artery
false
a locally acting chemicals that affect cells other than those that secrete them are classified as paracrines
true
prostaglandin which inhibits the production of blood clots is called prostacyclin. Prostacyclin is a type of eicosanoids
true
a surge of leutinizing hormone in ovarian cycle triggers ovulation
true
one hormone cannot exert its effect without another hormone being present is the kind of hormone-hormone interaction called antagonism
false
mesometrium, mesosalpinx, and mesovarium are the parts of broad ligament of uterus
true
dartos muscle is the smooth muscle that gives a wrinkled appearance to endometrium in uterus
true
the theca folliculi and granulosa cells cooperate to produce estrogen
true
pain associated with menstruation is called mittelschmerz
false
tissue surrounding male urethra
corpus spongiosum
scar tissue in the ovary
corpus albican
testosterone
cells of lyedig
erectile tissue in male penis
corpus carvenosum
supraoptic nucleus
antidiuretic hormone
paraventricular nucleus
oxytocin
retouterine pouch
peritoneal extension between uterus and rectum
oral mucosa
adenohypophysis
ligamentum teres
remnant of umbilical vein
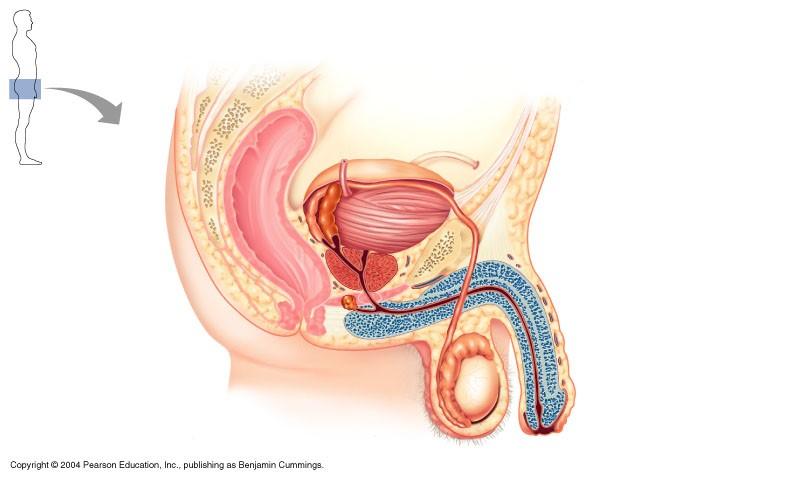
Male reproductive system
ampulla of ductus deferens
vas deferens
prostate
epididymis
testes
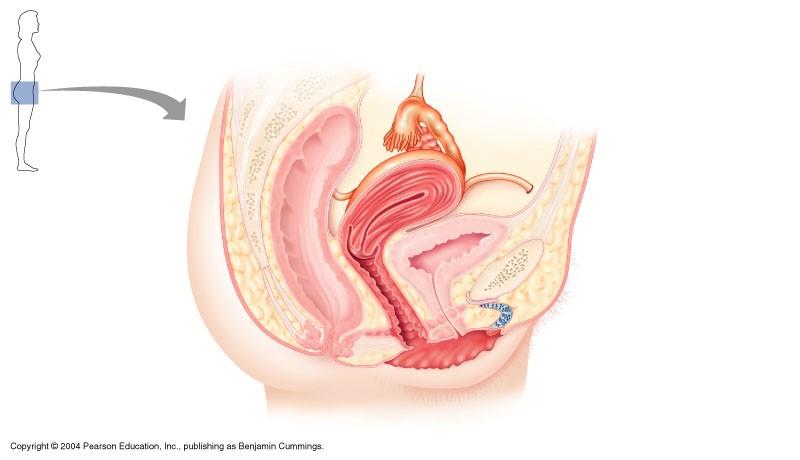
Female reproductive system
infundibulum
round ligament
cervix
vagina
uterosacral ligament
uterine tube
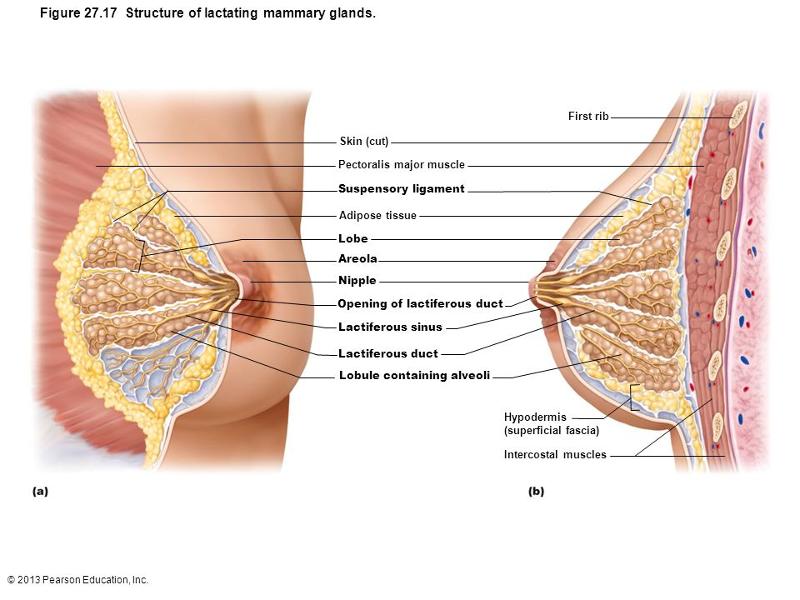
mammary gland
within the ovary after ovulation, progesterone is produced by the
corpus luteum
diploid stem cells of the ovaries
oogonium
The double layered membrane around the uterus is
perimetrium
Ovulation in a typical or "average" cycle usually occurs on
14
In the event of prolonged fasting, which of the following hormones stimulates follicle development int he ovaries
FSH
What is the stem cell of spermatozoa called
sperm
the thinnest part of the fallopian tube which is closest to the body of the uterus is called
isthmus
Name the male sex glands
prostate glands, seminal glands, bulbo-urethra gland
The process of formation of egg cells
oogenesis
the stage of the development of oogonium, when oogonium is surrounded by a single layer of flattened follicular cells is called the
primary oocyte
oocyte can stay alive for
6 to 7 days
the term for the absence of menstruation is
menopause
upon sexual excitement parasympathetic stimulation will increase which substance locally to increase the blood flow in the penile tissue
corpora cavernosa
the process of propulsion of semen from the male duct system is called
ejaculation
a minor surgical procedure to ligate and cut the vas deferens in males is called
vasectomy
another name for foreskin
prepuce
the testicular veins draining the testes arise from a network of capillaries called
pampiniform venous plexus
deep to the serous layer surrounding the testes is a layer of fibrous capsule called
tunica albuginea
name the dominant follicle which is selected for ovulation
secondary oocyte
interlobar connective tissue that attaches the breast tissue to the underlying muscle fascia and overlying dermis is called
suspensory ligament
coumpound alveolar glands of the breast produce milk which is carried through the duct to the nipple. the dilated portion of the duct just deep to areola is called
lactiferous sinus
progesterone level in a normal uterine cycle
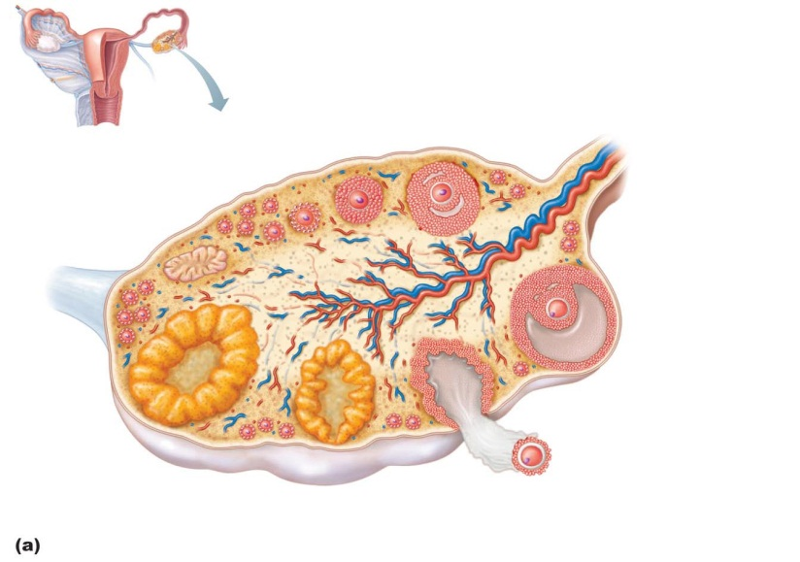
the ovary
primary follicle
theca folliculi
primary oocyte
zona pellucida
antrum
secondary oocyte
corpus luteum
embryo of 5 to 6 weeks old
gonadal ridge
mesonephros
cloaca
paramesonephros
metanephros
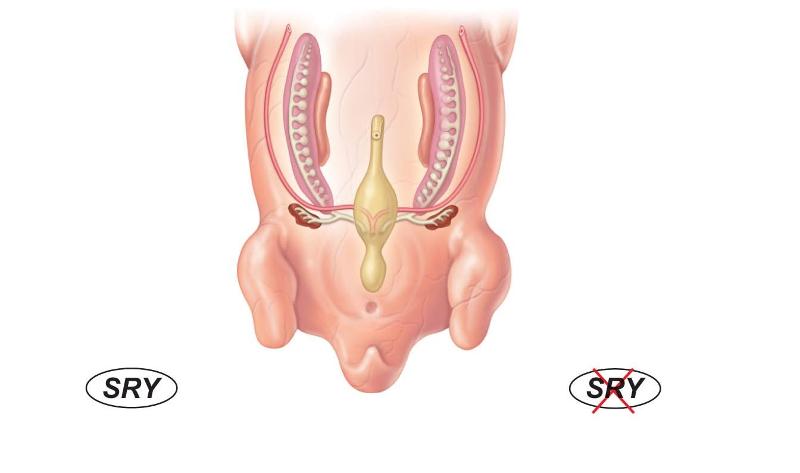
sexually indifferent stage
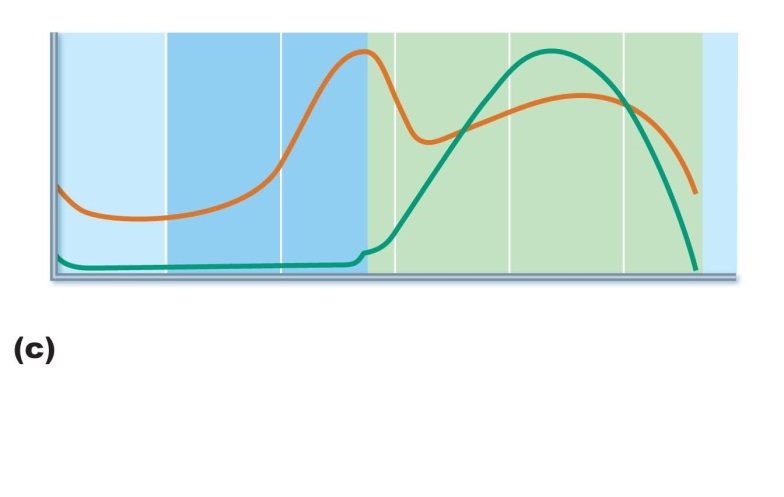
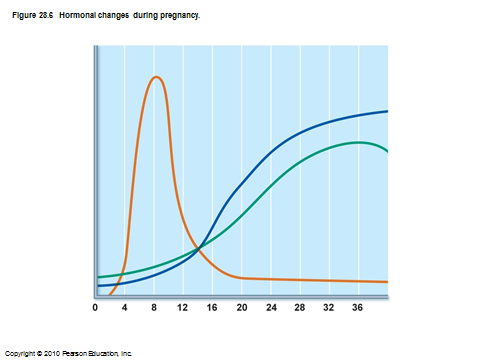
names of hormones during pregnancy
first long graph is beta hCG
second one is estrogen
third is progesterone
male reproductive structure