1. gluteus maximus
2. adductor magnus
3. biceps femoris
4. transversus abdominus
1. relative size of the muscle
2. action of the muscle
3. number of origins
4. direction in which the muscle fibers run relative to some imaginary line
5. extensor carpi ulnaris
6. trapezius
7. rectus femoris
8. extenal oblique
5. action of the muscle
6. shape of the muscle
7. direction in which the muscle fibers run relative to some imaginary line
8. location of the origin and/or insertion of the muscle
primer mover (agonist)
--term for the biceps brachii during elbow flexion
--term for the iliopsoas during hip extension
antagonist
--term for the triceps brachii during elbow flexion
--term for the gluteus maximus during hip extension when walking up stairs
synergist
--term that describes the relation of the brachialis to the biceps brachii during elbow flexion
fixator
--term for the rotator cuff muscle and deltoid when the elbow is flexed and the hand grabs a tabletop to lift the table
Muscles of the Head and Neck
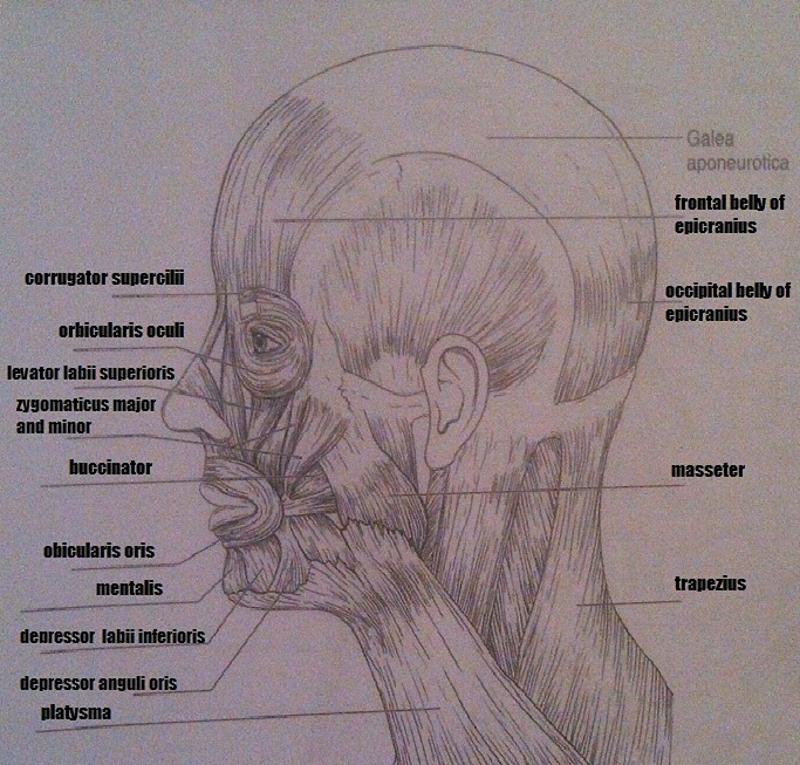
Muscles of the Head and Neck
1. used in smiling
2. used to suck in your cheeks
3. used in blinking and squinting
4. used to pout (pulls the corners of the mouth downward)
5. raises your eyebrows for a questioning expression
1. zygomaticus major and minor
2. buccinator
3. orbicularis oculi
4. depressor anguli oris
5. frontal belly of epicranius
6. used to form the vertical frown crease on the forehead
7. your "kisser"
8. prime mover to raise the mandible
9. tenses skin of the neck during shaving
6. corrugator supercilii
7. orbicularis oris
8. masseter
9. platysma
Muscles of the Trunk
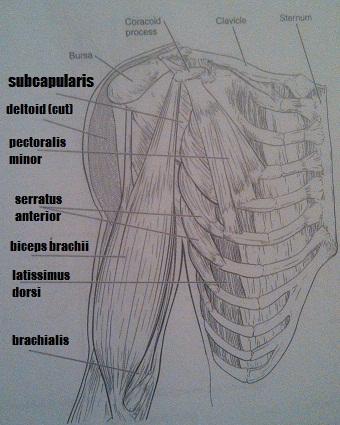
Muscles of the Trunk
1. a major spine flexor
2. prime mover for pulling the arm posteriorly
3. prime mover for shoulder flexion
4. assume major responsibility for forming the abdominal girdle (three pairs of muscles)
1. rectus abdominus
2. latissimus dorsi
3. pectoralis major (cut)
4. external oblique, internal oblique, rectus abdominis
5. pulls the shoulder backward and downward
6. prime mover of shoulder abduction
7. important in shoulder adduction; antagonists of the shoulder abductor (two muscles)
5. pectoralis minor
6. deltoid (cut)
7. latissimus dorsi, h. pectoralis major (cut)
8. moves the scapula forward and downward
9. small, inspiratory muscles between the ribs, elevate the ribs
10. extends the head
11. pull the scapulae
8. serratus anterior
9. external intercostals
10. trapezius
11. rhomboids
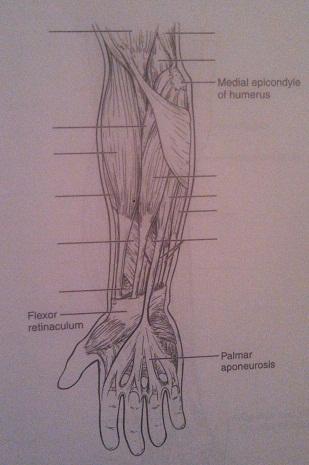
Muscles of the Upper Limb
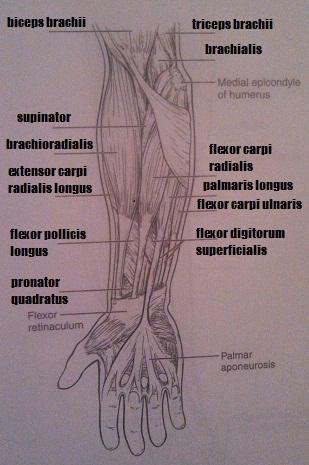
1. flexes the forearm and supinates the hand
2. synergist for supinating the hand
3. forearm flexors; no role in supination (two muscles)
4. elbow extensor
1. biceps brachii
2. supinator
3. brachialis, brachioradialis
4. elbow extensor
5. power wrist flexor and abductor
6. flexes wrist and middle phalanges
7. pronate the hand (two muscles)
8. flexes the thumb
5. flexor carpi radialis
6. flexor digitorum superficialis
7. pronator quadratus, pronator teres
8. flexor pollicis longus
9. extends and abducts the wrists
10. extends the wrists and digits
11. flat muscle that is a weak wrist flexor; tenses skin of palm
9. extensor carpi radialis longus
10. extensor digitorum
11. palmarus longus
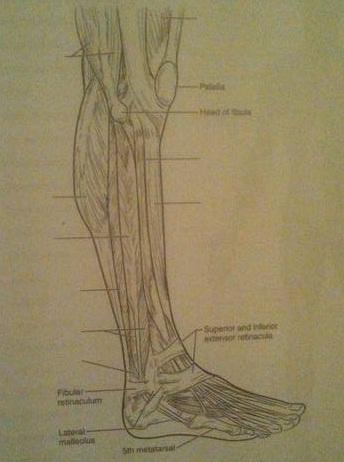
Muscles of the Lower Limb
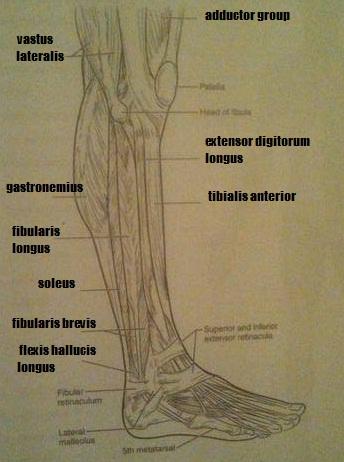
Muscles of the Lower Limb
1. flexes the great toe and inverts the ankle
2. lateral compartment muscles that plantar flex and evert the ankle (two muscles)
3. abduct the thigh to take the "at ease" stance (two muscles)
4. used to extend the hip when climbing stairs
1. flexor hallicus longus
2. fibularis brevis, fibularis longus
3. tensor fasciae latae, gluteus medius
4. gluteus maximus
5. prime movers of ankle plantar flexion (two muscles)
6. major foot inverter
7. prime mover of dorsiflexion of the foot
8. adduct the thigh, as when standing at attention
5. g. gastrocnemius, soleus
6. p. tibialis posterior
7. o. tibialis anterior
8. a. adductor group
9. extends the toes
10. extends thigh and flexes knee (three muscles)
11. extends knee and flexes thigh
9. c. extensor digitorum longus
10. b. biceps femoris, k. semimembranosus, l. semitendonosus
11. j. rectus femoris

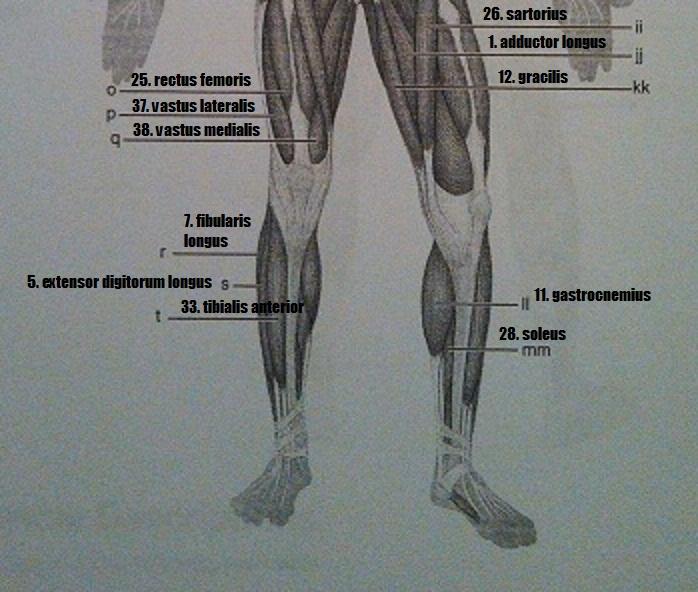
Muscle Recognition: Anterior Superficial Musculature
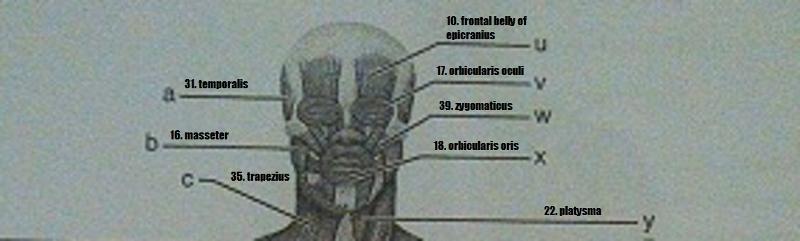

Muscle Recognition: Anterior Superficial Musculature
Muscle Recognition: Anterior Superficial Musculature
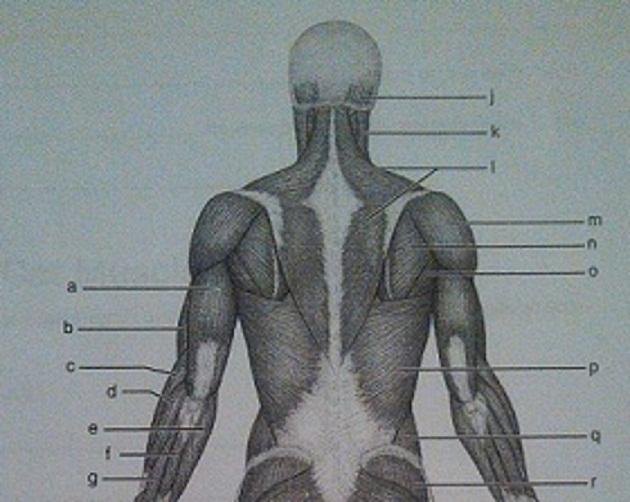
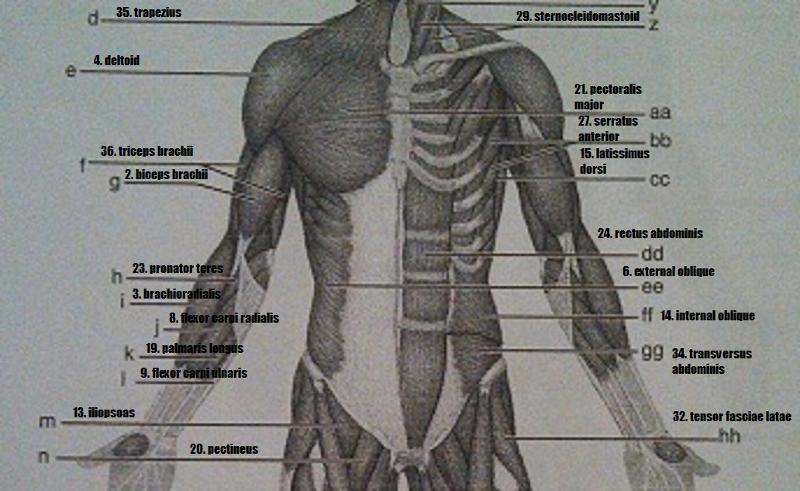
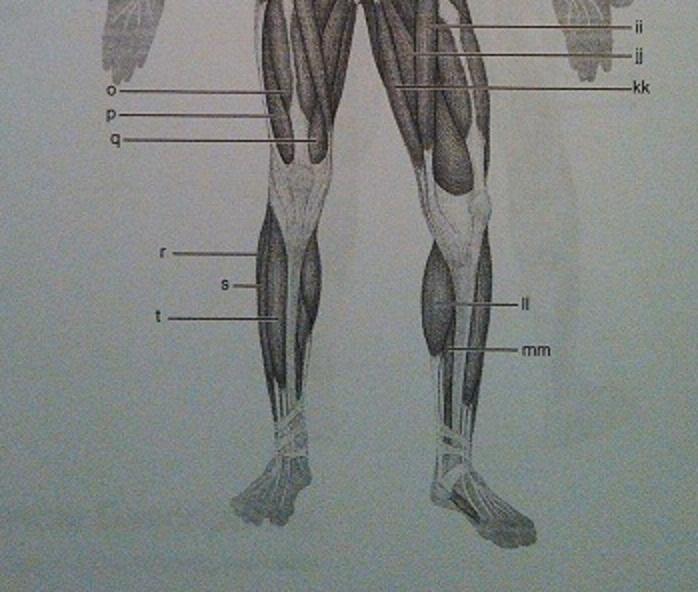
Muscle Recognition: Posterior Superficial Musculature
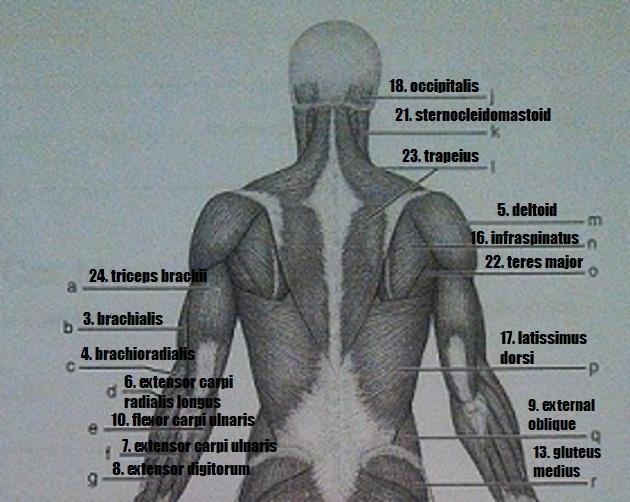
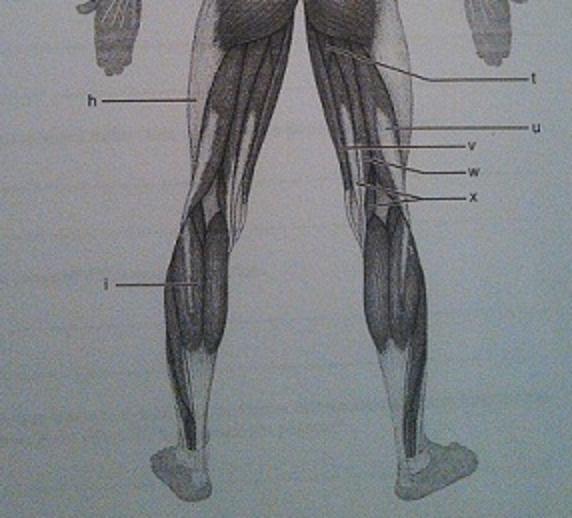
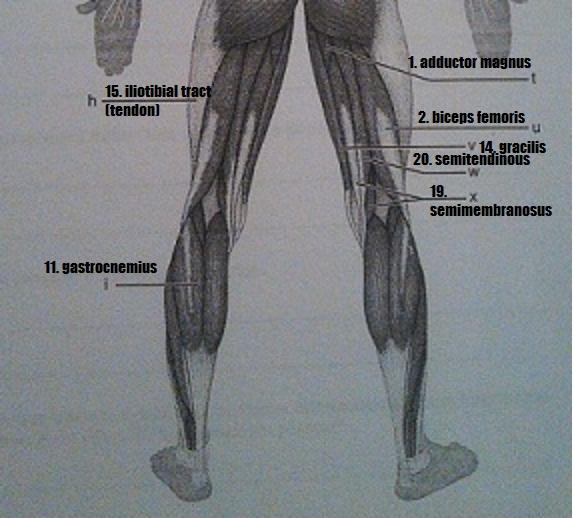
Muscle Recognition: Posterior Superficial Musculature
The __________, __________, __________ and __________ are commonly used for intramuscular injections (four muscles).
deltoid, vastus lateralis, gluteus medius, gluteus maximus
The insertion tendon of the __________ group contains a large sesamoid bone, the patella.
quadriceps
The triceps surae insert in common into the ___________ tendon.
Achilles
The bulk of the tissue of a muscle tends to lie __________ to the part of the body it causes to move.
proximal
The extrisinc muscle of the hand originates on the __________.
forearm
Most flexor muscles are located on the __________ aspect of the body, most extensors are located __________. An exception to this generalization is the extensor-flexor musculature of the __________.
anterior, posterior, knee,
How does the human trapezius muscle differ from the cat's?
Humans have a single large trapezius muscle, but the cat has three sperate muscles- the clavotrapezius, acroliotrapezius, and spinotrapezius- that together perdorm a similar function.
How does the deltoid differ?
The deltoid muscle in a cat does not connect directly to its skeletal frame, whereas, in a human, it does.
How do the extent and orientation of the human gluteus muscles differ from their relative positions in the cat?
In humans, it is a large fleshy muscle. In the cat, it is only 1.3 cm wide by 5 cm long.
Explain these differences in cat and human muscles in terms of differences in function.
*Have not found the answer*
The human rectus abdominis is definitely divided by four transverse tendons (tendinous intersections). These tendons are absent or difficult to identify in the cat. How do these tendons affect the human upright posture?
*Have not found the answer*
1. to separate muscles
2. to fold back a muscle
3. to cut through a muscle
4. to preserve tissue
1. dissect
2. reflect
3. transect
4. embalm