Business cycles are:
economic fluctuations, movements of GDP away from potential output, and periods in which real GDP grows too slow or too fast.
In macroeconomics short run:
prices do not fully adjust to changes in demand.
A period when economic growth is negative for at least six months is called a:
recession
The date at which a recession ends is:
a trough
The date at which a recession stars is:
a peak
Which of the following economic measures is/are procyclical?
investment spending, consumption, and price of stocks
Which of the following economic measures is countercyclical?
unemployment
Real business cycle theory emphasizes the role of:
technology shocks as a cause of economic fluctuations
Suppose consumer tastes and preferences shift from desire to ski to snowboarding. If skis and snowboards are produced by different firms, then firms that produce snowboards will:
experience a rise in prices, inducing them to increase production and the number of workers
Which of the following is a problem with the price system that can lead to a break down in the coordination of economic activity.
prices can be slow to adjust
Prices for industrial commodities such as steel rods or machine tools are
custom and sticky prices
If prices are sticky
economic activity will not be coordinated efficiently
Workers often have --- contracts and so their wages are ---
long-term, sticky
The short run in macroeconomics is the period in which
prices do not change (or at least do not change much) and demand determines output
Keynesian economics means that
demand determines output in the short run
Aggregate demand refers to the relationship between
the price level and the quantity of real GDP demanded
Which of the following does NOT shift the aggregate demand curve
decrease in price level
Which of the following cause an increase in aggregate demand?
an increase of GDP in a foreign country
Which of the following would cause a decrease in aggregate demand?
a fall in investor confidence
Assuming long-run classical aggregate supply curve, a decrease in the money supply results in --- in output and --- in prices
no change, a decrease
Assuming long-run aggregate supply curve, an increase in Japanese GDP results in --- in output and --- in prices
no change, an increase
Which of the following factors influence the position of the long-run classical aggregate demand curve?
the level of employment output
Assuming short-run Keynesian aggregate supply curve, an increase in government spending results in --- in output and --- in prices
an increase, a slight increase
Which of the following curves reflects the idea that in the short-run, prices are sticky and firms adjust production to meet demand?
the Keynesian aggregate supple curve
Assuming short-run Keynesian aggregate supply curve, an increase in the money supply results in --- in output and --- in prices
an increase, a slight increase
Assuming short-run Keynesian aggregate supply curve, a decrease in German GDP results in --- in output and --- in prices
a decrease, a slight decrease
The level of output determined by the intersection of the short-run Keynesian aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve:
may be above, below, or equal to full employment output.
Assuming short-run Keynesian aggregate supply curve, a massive crop failure results in --- in output and --- in prices
a decrease, and increase
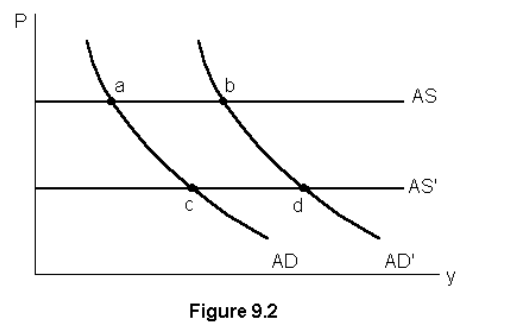
Using fig. 9.2 and economy-wide decrease in manufacturing costs is represented by a movement from points:
B to D
Expansionary policies are policies that
aim to increase level of GDP
Stabilization policies are
policies taken to move the economy closer to potential output
Automatic stabilizers
work without the need doe decisions from Congress or the White House
Increases in government spending and/or decreases in taxes will --- aggregate demand
increase
If the government wants to reduce unemployment, government spending should be __________ and/or taxes should be __________.
increased, decreased
he basic idea of the fiscal multiplier is that an initial increase in government spending will have a:
more than proportional impact on aggregate demand
Congress and the President typically use what kind of spending to conduct fiscal policies that affect the economy?
discretionary spending
Who sets the rules for "entitlements" when spending is authorized under this category?
the Congress when it appropriates spending
What is the largest single component of federal revenue?
individual income taxes
The largest category of discretionary federal spending is:
funding for the Defense Dept.
In a situation where the government is operating on a budget surplus, it can reduce its overall debt by _________.
buying back bonds it has sold to the public
If the budget were balanced and the economy entered a period of recession, what kind of budget would likely result?
deficit budget
Budget deficits tend to be procyclical for all the following reasons except:
the selling of government securities to pay for the deficit spurs private investment spending
Although running a budget deficit during a recession should not be a source of concern, running a budget deficit when there is no recession is a bad policy due to:
crowding out
According to Keynes, in the short-run the level of output is determined by
the demand for goods and services
In the Keynesian cross model, the 45 degree diagonal line represents the
set of points where output = demand
In a simple demand-side model with only consumers and firms, each of which demands a fixes amount of goods, equilibrium occurs where the C+I line
crosses the 45 degree line
If the demand for goods and services is less than output, then there will be
an increase in inventories (excess inventory)
If firms experience an unplanned increase in inventories, they are likely to
decrease production
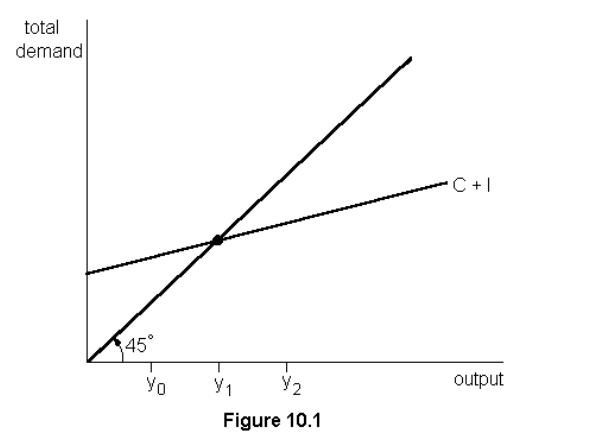
In fig. 10.1 if y0 is the level of output, unplanned inventories will
decrease, because demand exceeds output
If the consumption function is C=50+.75y then the marginal propensity to consume is:
.75
If the consumption function is C=50+.75y, then the level of autonomous consumption is
50
The slope of the consumption function is = to
the marginal propensity to consume
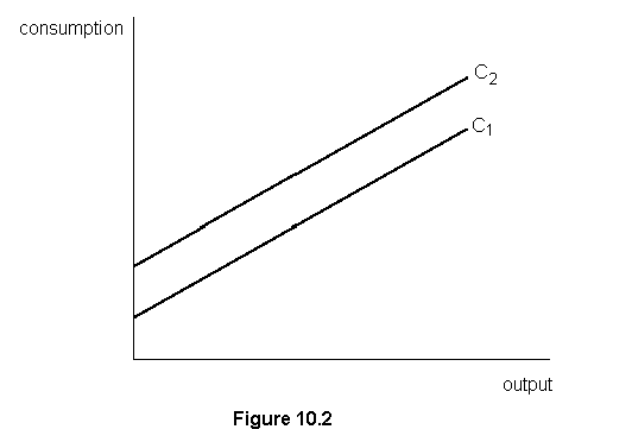
Decrease in consumer confidence shifts the consumption function in fig. 10.2 from
C2 to C1
A change in the MPC can occur as a result of
consumers' perceptions of change in their incomes and changes in tax rates
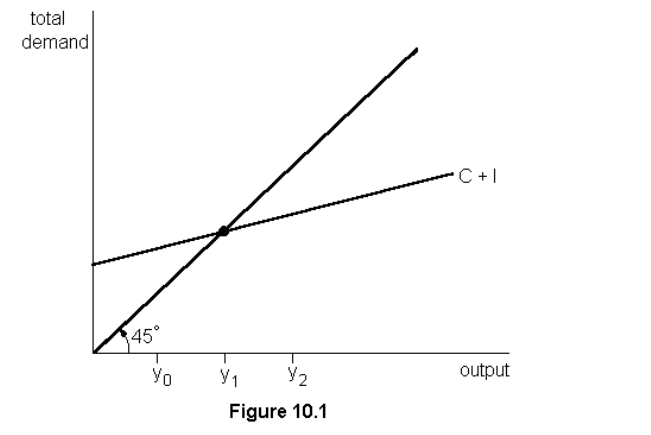
In figure 10.1, if y2 is the level of output, firms will --- production
decrese
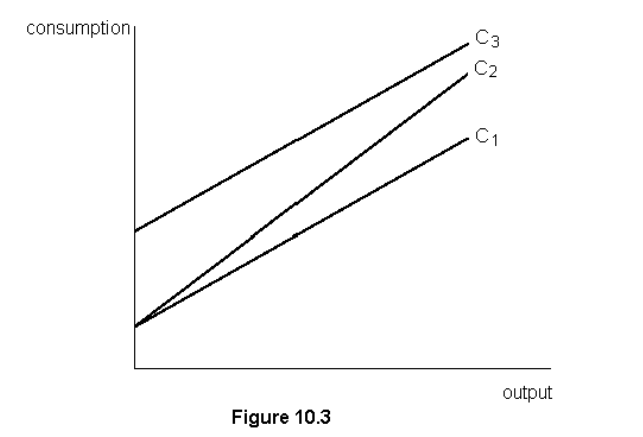
In fig. 10.3, a decrease in the marginal propensity to save is represented by a change in the consumption function from
C1 to C2
MPC= 1-MPS, so when MPS is smaller the slope is steeper
Let C =100 + 0.6y and I = 150. Then the equilibrium level of income y* is
625
y* = (Ca + I)/(1-b)
Let C =100 + 0.6y and I = 150. At the equilibrium level of income y*, the level of savings is
150, S=I
In the simple Keynesian cross model with no government or foreign sectors, the value of the multiplier is defined as
1/(1-MPC)
Let C =25 + 0.75y and I = 50. Assume no government or foreign sectors. If investment increases by 150, then the value of the multiplier is
4
The multiplier --- as the MPC increases
increases
The multiplier --- as autonomous consumption increases
is constant
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 50 + 0.8(y -T)
I = 200
G = 150
T = 100
What is the equilibrium level of output
1600, Demand is C +G + I and y* = 320/.2
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 50 + 0.8(y -T)
I = 200
G = 150
T = 100
What is the value of the government spending multiplier?
5, 1/(1-MPC) = 1/.2
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 50 + 0.8(y -T)
I = 200
G = 150
T = 100
If taxes decrease by 50, then the change in output is
200, y* = 360/.2
Suppose the MPC for the US is 0.7. If the policy makers wish to increase GDP by $50 billion, how much does government spending have to increase to meet this target?
$15 million
multiplier = 1/(1-.7) = 3.3
change in y* divided by ? is equal to 3.3 and solve
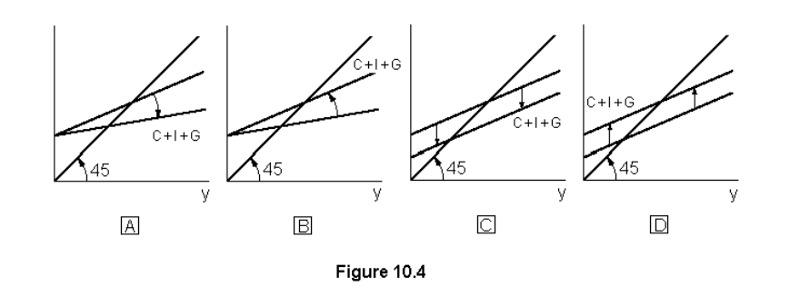
Refer to fig. 10.4. Which diagram illustrates the effect if an increase in the income tax rate?
A
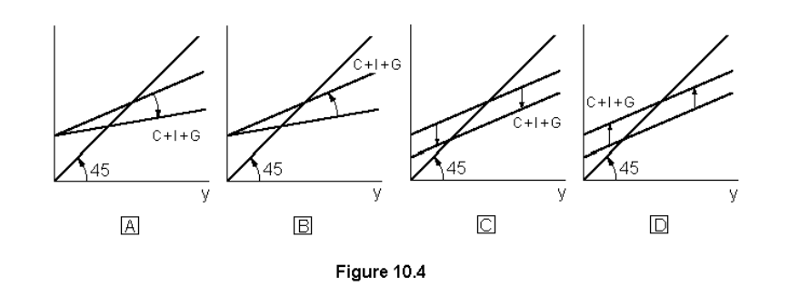
Refer to fig. 10.4. Which diagram illustrates the effect if an increase in government spending?
D
Which of the following is an example od an automatic stabilizer?
more unemployment benefits are paid during a recession
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 100 + 0.75(y -T)
I = 100
G = 150
T = 100
X = 75
M = 0.10y
What is the marginal propensity to consume?
0.25, 1-MPC = MPS
A decrease in the level of imports --- the demand for goods and services produced in the US
increases
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 100 + 0.75(y -T)
I = 100
G = 150
T = 100
X = 75
M = 0.10y
What is the value of the government spending multiplier?
2.86, 1/[1-(.75-1)], 1/[1-(b-m)]
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 100 + 0.75(y -T)
I = 100
G = 150
T = 100
X = 75
M = 0.10y
What is the equilibrium level of output?
1000
y* = (Ca - bT + I + G +X)/ 1(b-m)
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 100 + 0.75(y -T)
I = 100
G = 150
T = 100
X = 75
M = 0.10y
If the exports increase by 100 (X=175), what is the new equilibrium level of output?
1286
y* = (Ca - bT + I + G +X)/ 1(b-m)
The following questions are based upon the Keynesian model below.
C = 100 + 0.75(y -T)
I = 100
G = 150
T = 100
X = 75
M = 0.10y
If the marginal propensity to import increases to 0.2 (M = 0.20) what is the new level of equilibrium output?
777.78
y* = (Ca - bT + I + G +X)/ 1(b-m)
The interest rates quoted in the market are
nominal interest rates
Which of the following equations is correct?
real interest rate = nominal interest rate - inflation
Financial intermediaries are
firms that receive funds from savers and channel them to investors
Financial intermediaries
reduce the risks associated with investment
Firms are likely to --- investment spending when they believe that growth in real GDP will ---
increase, increase
accelerator theory
The model in which downturn in real GDP leads to a sharp fall in investment, which further reduces GDP through the multiplier, is known as the --- model
multiplier-accelerator
the interest rate on a loan will be --- as its risk --- and its maturity ---
higher, increases, lengthens
Compared to a 30 yr. US Treasury, the interest rate on a 30 year fixed mortgage will be --- because it is a loan with ---
higher, more risk
If the nominal interest rate is 8% and the inflation rate is 5% then the real rate of interest is
3%
If you have $200 to invest at a nominal interest rate of 8% and the inflation rate is 3%, then the real return on your investment is
$10. .05 x 200
If you have $300 and the inflation rate is 6%, in order to earn a real return of $18 on your investment, the nominal interest rate must be
12%, 18/300 = 6 +6 = 12
Expected real interest rates are the
interest rates quoted in the market minus the expected inflation rate
If the nominal interest rate is 7%, the expected real interest rate is 3%, and the inflation rate for the past year was 3%, then the expected inflation rate is --- the past inflation rate
greater than, nom. - expected is greater than 3 (past year's rate)
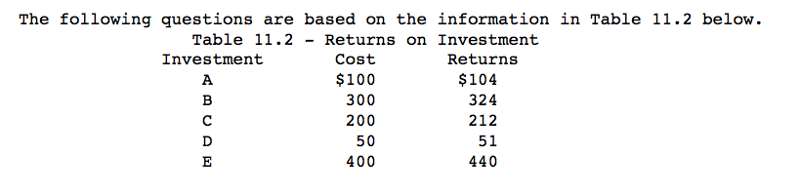
Referring to table 11.2 , if the nominal interest rate is 9% and there is no inflation, which investment should be undertaken?
investment E
Referring to table 11.2 , if the nominal interest rate is 3% and there is no inflation, which investment should be undertaken?
investments E, B, C, and A
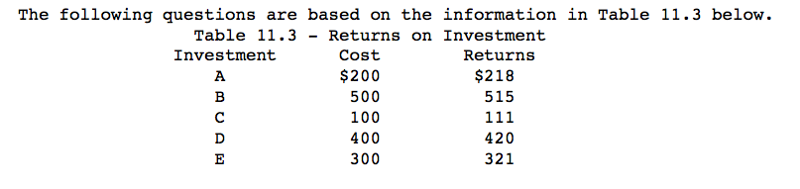
Table 11.3 represents all the investments available to the economy, the nominal interest rate is 10 % and there is no inflation, what will(should) be the level of investment in the economy?
$100
As the real interest rate ---, the real investment spending ---
increases, decreases and decrease, increases
inverse relationship
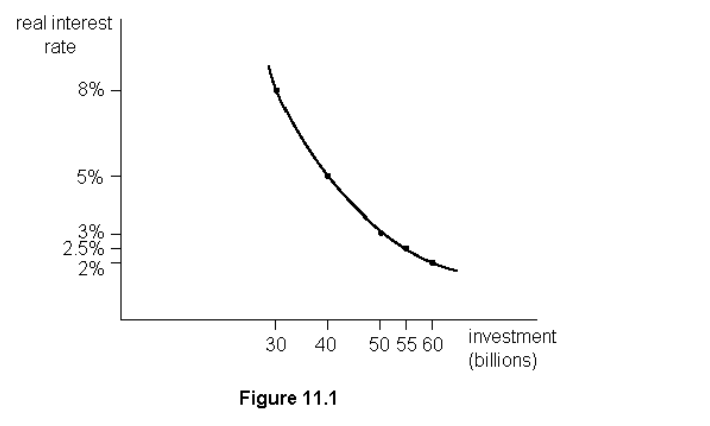
Referring to fig. 11.1, if the real interest rate is 5% then the level of investment is
$40 billion
The neoclassical theory of investment
emphasizes the role of real interest rates and taxes
The Q-theory of investment
links investment spending to stock prices
Financial intermediaries are institutions that facilitate the movement of funds from savers to investors because they
reduce costs of negotiating transactions, monitor investments, reduce risks, and provide liquidity
Financial intermediaries reduce risk by
investing in a large number of projects with independent return, and expertise
Insurance companies can reduce risk by accepting premiums from:
many people to insure against independent events
In the US, runs on banks are prevented by
the government guarantees banks' accounts up t0 $100,000
The supply of money in the economy is determined primarily by
the banking system and the actions of the Federal Reserve
In the --- increases in the supply of money will ---
short run, raise total demand and output and long run, lead to higher prices
Money is
anything that is regularly used in economic transactions or exchanges
Barter transactions will occur only when
there exists a double coincidence of wants
Money solves the dilemma of a double coincidence of wants by serving as a
medium of exchange
When money is used to express the value of goods and services it is functioning as a
unit of account
As inflation rates increase, money becomes less useful as a
store of value
Suppose after a semester ends, you take a trip to an island. Upon arriving you make a stop at a market and notice everyone is carrying around jars of small turtles. You also notice the person in line in front of you just paid for a bottle of rum with 6 turtles, and someone else a straw hat with 2 turtles. You can conclude that
the little turtles are serving the function of money
Checking account balances are included in
both M1 and M2
Which of the following is not included in M1?
savings accounts
Checking accounts that pay interest are included in the
"other checkable deposits" part of M1
Which of the following is included in M2?
savings accounts
Which of the following appears in M2 and not M1?
money market mutual funds
Economists keep an eye on both M2 and M1 because
it is not clear how citizens use money market accounts
From the point of view of a commercial bank, a --- is a(n) ---
loan, asset and deposit, liability
Given the following information:
Assets $2,500
Liabilities $2,100
A bank's net worth is
$400
Which of the following is a bank liability?
demand deposit balances
The fraction of deposits that banks are required by law to hold and not lend out are called
required reserves
Suppose that while vacationing in Monaco, you won 25,000 French fans which is = to $5,000. When you return to the US you deposit $5,000 into your checking account. The effect (assuming the required reserve ratio is 20%) is
to increase your bank's liabilities by $5,000, increase your bank's excess reserves by $4,000, lead to a multiple expansion in the money supply(checking account balances) by $25,000, and increase your bank's required reserves by $1,000.
Meg digs out $100 from under her bed and deposits it into a bank. As a result of this single transaction, M1 has
not changed, because the money was already in circulation even if she didn't know it
Given the information about Acme Bank
Bank Deposits $30,000
Loans $20,000
Reserves $5,000
Reserve Requirement 10%
Acme bank is holding --- in excess reserves
$2,000
Suppose a bank has $200,000 in deposits, a required reserve ratio of 5%, and a bank reserve of $12,000. The bank can make new loans in the amount of
$2,000
Suppose a bank has $2 million in deposits, a required reserve ration of 15%, and bank reserves of $320,000. The bank can make new loans in the amount of
none of the listed answers, $20,000 is the correct amount
Suppose Barry deposits $10, 000 in his bank. If the reserve ratio is 20%, this will lead to an increase of --- in his checking account balances
$50,000 because $10,000/ 0.2
Suppose Kirk deposits $5,000 in his bank. If the reserve requirement is 25%, this will lead to an increase of --- in M1
$15,000, because $5,000/0.25 = $20,000 - $5,000
If the banking system has a required reserve ratio of 5%, then the money multiplier will be
20
A bank may make loans until its
excess reserves are exhausted
The money multiplier tends to be greater when
banks hold few excess reserves
The money multiplier is smaller when
bank customers prefer to hold a bigger amount of their money as cash and banks prefer to lend out 95% of their excess reserves instead of 100%
Which of the following is responsible for buying government securities in order to influence monetary policies?
The Federal Reserve
An open market purchase occurs when
the Federal Reserve purchases Treasury Bonds
An open market sale by the Fed
decreases the total amount of reserves in the banking system
If the Fed sells $7.5 million of US bonds and the reserve requirement is 25%, M1 will eventually
none of the listed answers, it will decrease by $30 million
If the Fed by $60,000 of US bonds and the reserve requirement is 10%, M1 will eventually
increase by $600,000
Changing the reserve requirement will
disrupt the banking system
In the federal funds market --- will barrow or lend reserves to ---
a bank, another bank
An increase in the discount rate
increases the cost of reserves borrowed fro the Fed
A decrease in the discount rate will
increase the money supply
In practice, the Federal Reserve keeps the discount rate close to the --- rate in order to avoid large swings in borrowed reserves by banks
federal funds
members of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors are
appointed to 14 yr. terms, confirmed by the Senate, members of the Federal Open Market Committee, and serve in Washington DC
Which of the following is responsible for decisions on monetary policy?
The Federal Open Market Committee
The Federal Open Market Committee is composes of
the members of the Board of Governors and all the Presidents of the 12 Federal Reserve banks
The president of the --- Federal reserve Bank is always a member of the FOMC
New York
In the short run when prices don't have enough time to change, the Federal reserve
can influence the level of interest rates in the economy
Generally when the Federal Reserve lowers interest rate, investment spending --- and GDP ---
increases, increases (Law of Demand)
Decreased investment spending in the economy would be a possible result of
an open market sale of bonds
The transactions demand for money comes mostly from the fact that
money makes it easier to make purchases
The opportunity cost of holding money is
the return that could have been earned from holding wealth in other assets
An increase in interest rates leads to
a leftward movement up along the demand for money curve
The demand for money curve has shifted left. This may be the result of
a decrease ub the level of prices and a decrease in real GDP
Speculative demand for money is the demand for money that arises
because money is less risky than other assets
The demand for money in practice is the sum of
transactions, liquidity, and speculative demands
The --- determines the supply of money
Federal reserve
If the quantity of money demanded = the quantity of money supplied then the
interest rate will be in equilibrium
If the Federal Reserve conducts an open market sale then the
interest rate will increase
Based on the model of the money market, when prices in the economy increase, the equilibrium interest rate should
increase
Based on the model of the money market, when real income decreases, the equilibrium interest rate should
decrease
Based on the model of the money market, when the risk associated with holding other assets increases, the equilibrium interest rate should
increase
If a bond were to pay off one yr. from now for $200 and the interest rate is 10%, that is the price of the bond (rounded)?
$182, 200/ (1+0.1)
Ifa bond were to pay off one yr. later for $200 and was purchases for 4182, what is the interest rate
10%
An open market purchase by the Fed
increases investment and output
Actions by the Federal reserve to influence the level of GDP are known as
monetary policy
An increase in the reserve requirement
increases interest rates and decreases output
A decrease in the money supply and increase in GDP are consistent with
none of the listed answers,
An increase in the money supply should increase output
An increase in the money supply and a decrease in GDP are consistent with
none of the listed answers
If the Fed wished to decrease inflation, it could
increase in the reserve requirement or conduct an open market sale
The exchange rate is
the rate at which one currency trades for another currency
Higher US interest rates cause the value of the dollar to
rise, making US goods relatively more expensive on world markets
An open market purchase by the Fed causes the value of the dollar to
fall, increasing net exports
The depreciation of the dollar will make US goods --- to foreigners and make exports --- for US residents
cheaper, more expensive
Policies taken to move the economy closer to potential output are called
stabilization policies
An outside lag is
the period of time it takes for policies to work
Outside lags are usually
longer for monetary policy than fiscal policy