Purpose of Experiment 3?
Familiarize w/ the methods of separating substances from one another
...using (DES) techniques:
1. Decantation
2. Extraction
3. Sublimation
Purpose of Experiment 2?
Familiarize w/ procedures used in evaluating physical properties
and
use of these properties to identify substances.
Purpose of Experiment 1?
To learn the use of common, simple lab equipment.
Decantation:

(process of) separating a liquid from a solid (sediment) by gently pouring the liquid from the solid
- so as to not disturb the solid
Filtration:

(process of) separating a solid from a liquid by means of a porous substance (filter)
- allows the liquid to pass through but not the solid
common filters: paper, layers of charcoal, and sand
Silt and sand can be removed from our drinking water by this process
Extraction:
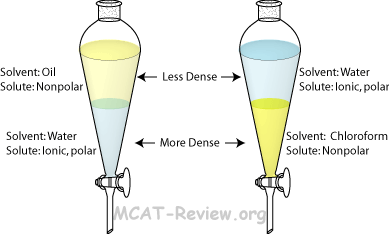
(separation of) a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent
By this process, a soluble compound is usually separated from an insoluble
Sublimation:

(process in which) a solid passes directly to the gaseous state and back to the solid state (w/o the appearance of the liquid state)
Can all substances be sublimed? Why or why not?
No, not all substances possess the ability to be sublimed.
Iodine, napthalene, and ammonium chloride= common substances easy to sublime
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances in which each substance retains its own chemical identity - and its own properties
Pure substances= fixed composition
Mixture= compositions vary
Two kinds of mixtures?
Homogenous- sugar water, air
- also called a solution
Heterogenous- cement, wood, rocks, soil (don't have the same composition, properties, appearance throughout
Fundamental properties of mixtures
1. Each of the substances in the mixture retains its chemical identity
2. separable into these components by physical means
Define preponderant.
Define impurities
1. substance whose amount far exceeds the amounts of the other substances in a mixture
2. the other substances in the mixture containing the preponderant