Innate immunity
A) is activated immediately upon infection.
B) depends on a newly infected animal's previous exposure to the
same pathogen.
C) is based on recognition of antigens that are
specific to different pathogens.
D) is found only in vertebrate animals.
Answer: A
Engulfing-phagocytic cells of innate immunity include
________.
I) neutrophils
II) macrophages
III)
dendritic cells.
IV) natural killer cells
A) I and IV
B) II and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) I
and III
Answer: C
Inflammatory responses typically include
A) clotting proteins
migrating away from the site of infection.
B) increased activity
of phagocytes in an inflamed area.
C) reduced permeability of
blood vessels to conserve plasma.
D) release of substances to
decrease the blood supply to an inflamed area.
Answer: B
A newborn who is accidentally given a drug that destroys the thymus
would most likely
A) lack class I MHC molecules on cell
surfaces.
B) lack humoral immunity.
C) be unable to
genetically rearrange antigen receptors.
D) be unable to
differentiate and mature T cells.
Answer: D
What type of immunity is associated with breast feeding?
A)
active immunity
B) cell-mediated immunity
C) innate
immunity
D) passive immunity
Answer: D
To maintain homeostasis freshwater fish must ________.
A)
excrete large quantities of electrolytes
B) take in electrolytes
through simple diffusion
C) excrete large quantities of
water
D) consume large quantities of water
Answer: C
The force driving simple diffusion ____, while the energy source for
active transport is ____.
A) the concentration gradient;
ATP
B) phosphorylated protein carriers; ATP
C) transmembrane
pumps; electron transport
D)the concentration gradient; ADP
Answer: A
In animals, nitrogenous wastes are produced mostly from the
catabolism of
A) starch and cellulose.
B) triglycerides
and steroids.
C) proteins and nucleic acids.
D)
phospholipids and glycolipids.
Answer: C
Birds secrete uric acid as their nitrogenous waste because uric acid
A) is readily soluble in water.
B) is metabolically less
expensive to synthesize than other excretory products.
C)
requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal, thus reducing
body mass.
D) excretion allows birds to live in desert environments
Answer: C
(DIAGRAM) The figure above shows a nephron. Filtration takes place
int he structure labeled ________.
A) a
B) b
C)
c
D) d
Answer: A
A fruit fly, internally infected by a potentially pathogenic fungus,
is protected by
A) its plasma cells.
B) its
immunoglobulins.
C) its antibodies.
D) its antimicrobial peptides.
Answer: D
The cells and signaling molecules that initiate inflammatory
responses are
A) the phagocytes and the lysozymes.
B) the
phagocytes and the chemokines.
C) the dendritic cells and the
interferons.
D) the mast cells and the histamines.
Answer: D
The eyes and the respiratory tract are both protected against
infections by
A) the mucous membranes that cover their surface.
B) the secretion of complement proteins.
C) the release of
slightly alkaline secretions.
D) the secretion of lysozyme onto
their surfaces.
Answer: D
Mammals have Toll-like receptors (TLRs) that can recognize a kind of
macromolecule that is absent from vertebrates but present in/on
certain groups of pathogens, including viral
A)
lipopolysaccharides.
B) double-stranded DNA.
C)
double-stranded RNA.
D) glycoproteins.
Answer: C
The cells involved in innate immunity, whose absence increases the
chances of developing malignant tumors, are
A) cytotoxic T cells.
B) natural killer cells.
C) helper T cells.
D) macrophages.
Answer: B
You and a friend were in line for a movie when you noticed the woman
in front of you sneezing and coughing. Both of you were equally
exposed to the woman's virus, but over the next few days, only your
friend acquired flu-like symptoms and was ill for almost a week before
recovering. Which one of the following is a logical explanation for
this?
A) You had an adaptive immunity to that virus.
B) Your
friend had allergies.
C) Your friend had an autoimmune disorder.
D) Your friend had antibodies to that virus.
Answer: A
Clonal selection and differentiation of B cells activated by antigen
exposure leads to the production of
A) short-lived plasma cells
that secrete antibodies for the antigen.
B) large quantities of
the antigen initially recognized.
C) vast numbers of B cells
with random antigen-recognition receptors.
D) long-lived
erythrocytes that can later secrete antibodies for the antigen.
Answer: A
An immunoglobulin (Ig) molecule, of whatever class, with regions
symbolized as C or V, H or L, has a light chain made up of
A)
one C region and one V region.
B) three C regions and one V
region.
C) one H region and one L region.
D) three H
regions and one L region.
Answer: A
Lymphocytes mature in the ________.
I) spleen
II)
tthymus
III) bone marrow
A) I, II, and III
B) only I and II
C) only II and
III
D) only I and III
Answer: C
Which of the following is a difference between B cells and T
cells?
A) B-cells are activated by free-floating antigens in the
blood or lymph. T cells are activated by membrane-bound
antigens.
B) One has a major role in antibody production, while
the other has a major role in cytotoxicity.
C) One binds a
receptor called BCR (B-cell receptor), while the other recognizes a
receptor called TCR (T-cell receptor).
D) T cells are produced in
the thymus and B cells are produced in the bone marrow.
Answer: B
Phagocytosis of microbes by macrophages is enhanced by
I) the
binding of antibodies to the surface of microbes
II)
antibody-mediated agglutination of microbes.
III) the release of
cytokines by activated B cells.
A) only I and III
B) only I and II
C) I, II, and
III
D) only II and III
Answer: B
Naturally acquired passive immunity results from the
A)
injection of vaccine.
B) ingestion of interferon.
C)
placental transfer of antibodies.
D) absorption of pathogens
through mucous membranes.
Answer: C
Which of the following components of the immune system destroys
bacteria in a way similar to an antitank weapon destroying armored
tanks by punching holes in the wall of the bacteria?
A) plasma
cells
B) complement protein
C) major histocompatibility
complex proteins
D) macrophages
Answer: B
A bone marrow transplant may not be appropriate from a given donor
(Jane) to a given recipient (Jane's cousin Bob), even though Jane has
previously given blood for one of Bob's needed transfusions, because
A) even though Jane's blood type is a match to Bob's, her MHC
proteins may not be a match.
B) a blood type match is less
stringent than a match required for transplant because blood is more
tolerant of change.
C) for each gene, there is only one blood
allele but many tissue alleles.
D) Jane's class II genes are not
expressed in bone marrow.
Answer: A
Which of the following should be the same in identical twins?
A) the set of antibodies produced
B) the set of major
histocompatability (MHC) molecules produced
C) the set of T cell
antigen receptors produced
D) the susceptibility to a particular virus
Answer: B
Which of the following is the best definition of autoimmune
disease?
A) a condition in which B cells and T cells respond
independently to antigens and do not interact correctly
B) a
condition in which self molecules are treated as non-self
C) a
condition in which the adaptive immune system fails to recognize the
second infection by the same antigen
D) a condition in which the
immune system creates random antibodies without being triggered by an antigen
Answer: B
Single-celled Paramecium live in pond water (a hypotonic
environment). They have a structural feature, a contractile vacuole,
which enables them to osmoregulate. If you observed them in the
following solutions, at which sucrose concentration (in millimolars,
mM) would you expect the contractile vacuole to be most
active?
A) 0.05 mM saline
B) 1.0 mM saline
C) 0.08 mM
sucrose
D) 0.001 mM sucrose
Answer: D
The body fluids of an osmoconformer would be ________ with its
________ environment.
A) hyperosmotic; freshwater
B)
isotonic; freshwater
C) hyperosmotic; saltwater
D)
isoosmotic; saltwater
Answer: D
Ammonia is likely to be the primary nitrogenous waste in living
conditions that include
A) lots of fresh water flowing across
the gills of a fish.
B) lots of seawater, such as a bird living
in a marine environment.
C) lots of seawater, such as a marine
mammal (e.g., a polar bear).
D) a terrestrial environment, such
as that supporting crickets.
Answer: A
Which nitrogenous waste has the greatest number of nitrogen atoms?
A) ammonia
B) ammonium ions
C) urea
D) uric acid
Answer: D
Which of the following animals generally has the lowest volume of
urine production?
A) a vampire bat
B) a salmon in fresh
water
C) a marine bony fish
D) a freshwater bony fish
Answer: C
Which of the following most accurately describes selective
permeability?
A) An input of energy is required for
transport.
B) There must be a concentration gradient for
molecules to pass through a membrane.
C) Lipid-soluble molecules
pass through a membrane.
D) Only certain molecules can cross a
cell membrane.
Answer: D
Why are the renal artery and vein critical to the process of
osmoregulation in vertebrates?
A) The renal artery and vein are
the main pathways regulating how much is produced by the kidneys.
B) The kidneys require constant and abnormally high oxygen
supply to function.
C) The kidneys require higher than normal
levels of hormones.
D) The renal artery delivers blood with
nitrogenous waste to the kidney and the renal vein brings blood with
less nitrogenous wastes away from the kidneys.
Answer: D
Materials are returned to the blood from the filtrate by which of the
following processes?
A) filtration
B) ultrafiltration
C) selective reabsorption
D) secretion
Answer: C
The osmoregulatory/excretory system of a freshwater flatworm is based
on the operation of
A) protonephridia.
B) metanephridia.
C) Malpighian tubules.
D) nephrons.
Answer: A
A primary reason that the kidneys have one of the highest metabolic
rates of all body organs is that
A) it stores the body's excess
fats.
B) it has membranes of varying permeability to water.
C) it operates an extensive set of active-transport ion pumps.
D) it is the body's only means of shedding excess nutrients.
Answer: C
The loop of Henle dips into the renal cortex. This is an important
feature of osmoregulation in terrestrial vertebrates because
A)
differential permeabilities of ascending and descending limbs of the
loop of Henle are important in establishing an osmotic
gradient
B) additional filtration takes place along the loop of
Henle
C) the loop of Henle plays an important role in
detoxification
D) absorptive processes taking place in the loop
of Henle are hormonally regulated
Answer: A
Natural selection should favor the highest proportion of
juxtamedullary nephrons in which of the following species?
A) a
river otter
B) a mouse species living in a tropical rain forest
C) a mouse species living in a temperate broadleaf forest
D) a mouse species living in a desert
Answer: D
Increased antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion is likely after
A) drinking lots of pure water.
B) sweating-induced
dehydration increases plasma osmolarity.
C) ingestion of ethanol
(drinking alcoholic drinks).
D) eating a small sugary snack.
Answer: B
After drinking alcoholic beverages, increased urine excretion is the
result of
A) increased aldosterone production.
B)
increased blood pressure.
C) inhibited secretion of antidiuretic
hormone (ADH).
D) increased reabsorption of water in the
proximal tubule.
Answer: C
Testosterone is an example of a chemical signal that affects the very
cells that synthesize it, the neighboring cells in the testis, along
with distant cells outside the gonads. Thus, testosterone is an
example of
I) an autocrine signal.
II) a paracrine signal.
III) an endocrine signal.
A) only I and III
B) I, II, and III
C) only II and
III
D) only I and II
Answer: B
Prostaglandins are local regulators whose chemical structure is
derived from
A) fatty acids
B) amino acids
C)
steroids
D) oligosaccharides
Answer: A
A cell with membrane-bound proteins that selectively bind a specific
hormone is called that hormone's
A) secretory cell.
B)
plasma cell.
C) endocrine cell.
D) target cell.
Answer: D
The reason that the steroid hormone aldosterone affects only a small
number of cells in the body is that
A) only its target cells get
exposed to aldosterone.
B) only its target cells contain
aldosterone receptors.
C) it is unable to enter nontarget cells.
D) nontarget cells destroy aldosterone before it can produce any effect.
Answer: B
Different body cells can respond differently to the same peptide
hormones because
A) different target cells have different sets
of genes.
B) each cell converts that hormone to a different
metabolite.
C) a target cell's response is determined by the
components of its signal transduction pathways.
D) the
circulatory system regulates responses to hormones by routing the
hormones to specific targets.
Answer: C
The steroid hormone that coordinates molting in arthropods is
A) ecdysone.
B) glucagon.
C) thyroxine.
D) oxytocin.
Answer: A
Insect hormones and their receptors
A) act independently of
each other.
B) are a focus in pest-control research.
C)
utilize cell-surface receptors only.
D) are active independently
of environmental cues.
Answer: B
What property of steroid hormones allows them to cross the
phospholipid bilayer?
A) Steroid hormones can act in very small
concentrations and very few molecules of steroids need to cross the
lipid bilayer.
B) Steroid hormones are lipid soluble and easily
cross the phospholipid bilayer.
C) Steroid hormones act on cells
close to where they were produced and very few molecules are required
to travel such a short distance to cross the lipid bilayer.
D)
Steroid hormones act on the same cells in which they are produced and,
therefore, are within the cell they are acting upon.
Answer: B
If a biochemist discovers a new molecule, which of the following
pieces of data would allow her to draw the conclusion that the
molecule is a steroid hormone?
I) The molecule is lipid
soluble.
II) The molecule is derived form a series of steps
beginning with cholesterol.
III) The molecule acts at a target
tissue some distance from where it is produced.
IV) The molecule
uses a carrier protein when in an aqueous solution such as blood.
A) only II and IV
B) only only I and III
C) only I, III,
and IV
D) I, II, IIII, and IV
Answer: D
During mammalian labor and delivery, the contraction of uterine
muscles is enhanced by oxytocin. This is an example of
A) a
negative feedback system.
B) a hormone that acts in an
antagonistic way with another hormone.
C) a hormone that is
involved in a positive feedback loop.
D) signal transduction
immediately changing gene expression in its target cells.
Answer: C
Which of the following has both endocrine and exocrine activity?
A) the pituitary gland
B) parathyroid glands
C)
salivary glands
D) the pancreas
Answer: D
An example of antagonistic hormones controlling homeostasis is
A) thyroxine and parathyroid hormone in calcium balance.
B) insulin and glucagon in glucose metabolism.
C)
progestins and estrogens in sexual differentiation.
D)
epinephrine and norepinephrine in fight-or-flight responses.
Answer: B
Hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary gland are made in the
________.
A) thalamus
B) medulla oblongata
C)
cerebellum
D) hypothalamus
Answer: D
In a lactating mammal, the two hormones that promote milk synthesis
and milk release, respectively, are
A) prolactin and calcitonin.
B) prolactin and oxytocin.
C) follicle-stimulating hormone
and luteinizing hormone.
D) luteinizing hormone and oxytocin.
Answer: B
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for
hypothyroidism in a patient whose iodine level is normal?
A)
greater production of T₃ than of T₄
B) hyposecretion of TSH
C) hypersecretion of TSH
D) hypersecretion of MSH
Answer: B
Fight-or-flight reactions include activation of
A) the
parathyroid glands, leading to increased metabolic rate.
B) the
thyroid gland, leading to an increase in the blood calcium
concentration.
C) the anterior pituitary gland, leading to
cessation of gonadal function.
D) the adrenal medulla, leading
to increased secretion of epinephrine.
Answer: D
People with type II diabetes mellitus have defective insulin
receptors that cannot respond to insulin properly. Relative to normal
individuals, what would be the effect on blood glucose levels under
conditions of chronic stress that kept blood cortisol levels high?
There would be ________.
A) less increase in blood glucose levels
in individuals with type II diabetes mellitus than in normal
individuals.
B) less decrease in blood glucose levels in
individuals with type II diabetes mellitus than in normal
individuals.
C) a greater increase in blood glucose levels in
individuals with type II diabetes mellitus than in normal
individuals.
D) a greater decrease in blood glucose levels in
individuals with type II diabetes mellitus than in normal individuals.
Answer: C
Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically
identical to their parent. What type of cell process occurs to
generate this type of offspring?
A) meiosis
B)
mitosis
C) cell fusion
Answer: B
What makes sexually reproduced offspring genetically different from
their parents?
A) genetic recombination during mitosis
B)
crossing over during mitosis
C) genetic recombination during
mitosis
D) sexual reproduction does not produce genetically
different offspring
Answer: A
Which of the following is most true of sexual reproduction?
A)
Only half of the offspring from sexually reproducing females are also
females.
B) Sexual reproduction is completed more rapidly than
asexual reproduction.
C) Asexual reproduction is better suited to
environments with extremely varying conditions.
D) Asexual
reproduction produces offspring of greater genetic variety.
Answer: A
In an animal that switches between sexual and asexual reproduction,
when is sexual reproduction more likely to occur?
A) when males
and females find each other
B) when conditions for survival are
favorable
C) when conditions for survival are unfavorable
D)
what conditions favor sexual over asexual remains a complete mystery.
Answer: C
Animals that have external fertilization are most likely to reproduce
in which of the following areas?
A) sand dune
B) tallgrass
prairie
C) polar ice sheet
D) shallow lake
Answer: D
In humans, the follicular cells that remain behind in the ovary
following ovulation become
A) the ovarian endometrium that is
shed at the time of the menses.
B) a steroid-hormone
synthesizing structure called the corpus luteum.
C) the
thickened portion of the uterine wall.
D) swept into the
fallopian tube.
E) the placenta, which secretes cervical mucus.
Answer: B
At the time of fertilization, the complete maturation of each
oogonium has resulted in
A) one secondary oocyte.
B) two
primary oocytes.
C) four secondary oocytes.
D) four
primary oocytes.
Answer: A
Which of the following correctly describes a difference between
spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
A) In spermatogenesis, mitosis
occurs twice and meiosis once, while in oogenesis, mitosis occurs once
and meiosis twice.
B) Spermatogenesis result sin four mature
sperm cells, while oogenesis results in one mature egg cell. In
spermatogenesis, mitosis occurs twice and meiosis once, while in
oogenesis, mitosis occurs once and meiosis twice.
C)
Spermatogenesis results in one mature sperm cell, while oogenesis
results in four mature egg cells.
D) Spermatogenesis results in
four mature sperm cells, while oogenesis results in one mature egg cell.
Answer: D
Mature human sperm and ova are similar in that
A) they both
have the same number of chromosomes.
B) they are approximately
the same size.
C) they each have a flagellum that provides
motility.
D) they are produced from puberty until death.
Answer: A
Among mammals, the male and female genital structures that consist
mostly of erectile tissue include the
A) penis and clitoris.
B) vas deferens and oviduct.
C) testes and ovaries.
D) seminiferous tubules and hymen.
Answer: A
Among human males, both semen and urine normally travel along the
A) vas deferens.
B) urinary bladder.
C) seminal
vesicle.
D) urethra.
Answer: D
Human sperm cells first arise in the
A) prostate gland.
B) vas deferens.
C) seminiferous tubules.
D) epididymis.
Answer: C
A primary response by the Leydig cells in the testes to the presence
of luteinizing hormone is an increase in the synthesis and secretion
of
A) inhibin.
B) testosterone.
C) oxytocin.
D) prolactin.
Answer: B
In correct chronological order, the three phases of the human ovarian
cycle are
A) menstrual → ovulation → luteal.
B) follicular
→ luteal → secretory.
C) menstrual → proliferative → secretory.
D) follicular → ovulation → luteal.
Answer: D
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants somewhere
other than in the lining of the uterus. Usually it implants in the
oviduct. Which of the following would be the most likely explanation
for such a pregnancy being unsuccessful?
A) The necessary
hormones cannot reach the developing fetus in the oviduct.
B) The
lining of the oviduct is unable to support the developing
fetus.
C) Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) cannot be produced
in the oviduct.
D) The orientation of the baby would be sideways.
Answer: B
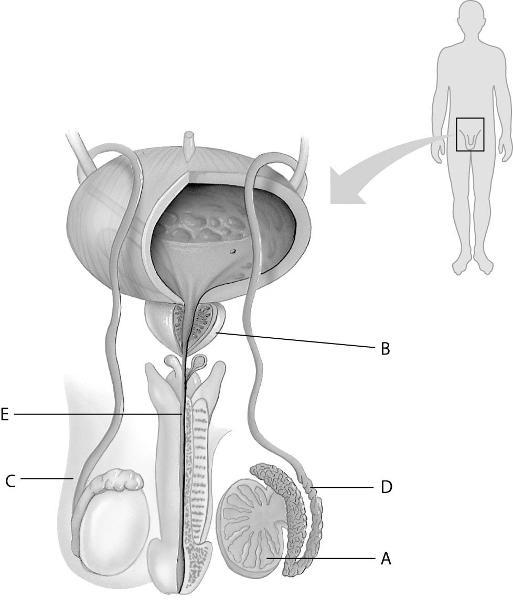
In the above figure, which letter points to the prostate gland?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: B
In the above figure, which letter points to the vas deferens?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: D
(PARAGRAPH) Refer to the paragraph on the effects of estrogens in the
environment. What is the significance of using the concentrations of
5, 25, and 100 ng/l of 17B-estradiol for the dose in this
experiment?
A) These concentrations are effective, yet not lethal
to the fish.
B) These concentrations are standard in toxicology
assays.
C) These concentrations are similar to those found in
many animals.
D) These concentrations are found in the environment.
Answer: D
(PARAGRAPH) Refer to the paragraph on the effects of estrogens in the
environment. You are assigned to write the report to the Environmental
Protection Agency, which needs to decide what level of 17B-estradiol
to permit in sewage output. You do not want to make the level any
lower than necessary, because it requires substantial additional money
for the extra treatment of sewage. Given the data presented above,
what level of 17B-estradiol would you suggest is safe to prevent
feminization of fish?
A) 25 ng/l
B) 12.5 ng/l
C) 100
ng/l
D) 2.5 ng/l
Answer: A
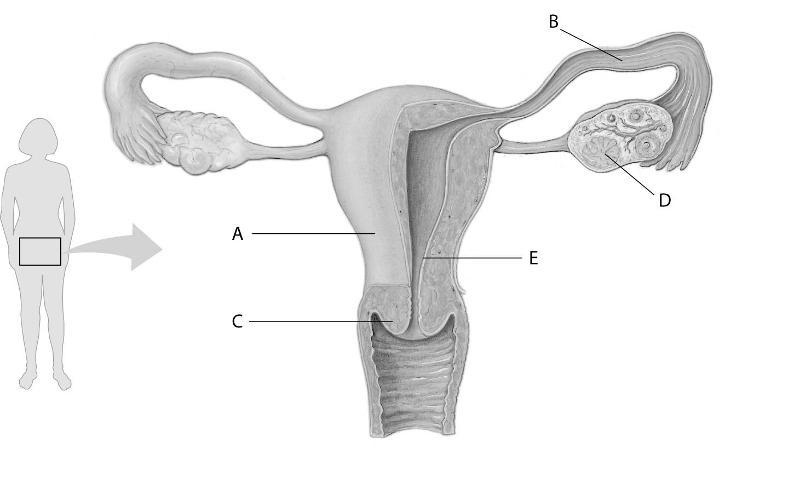
In the above figure, which letter points to the corpus luteum?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: D
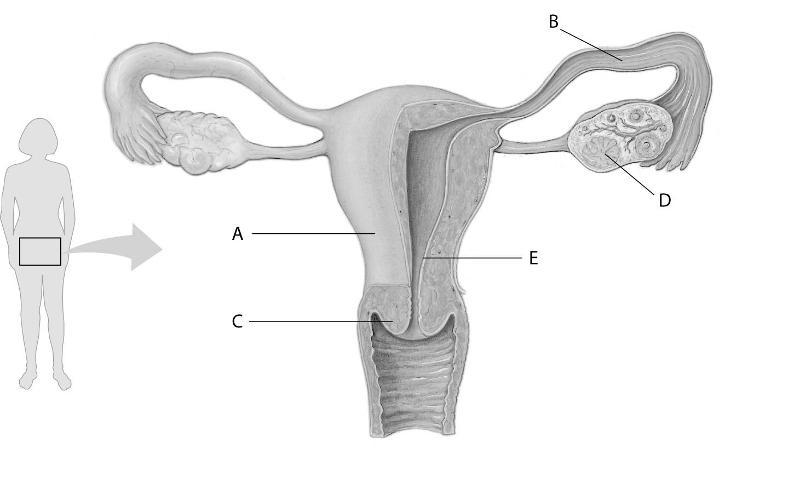
In the above figure, which letter points to the cervix?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: C