
The structure shown above is a(n)
- nucleic acid
- fatty acid molecule
- phospholipid molecule
- sterol molecule
- carbohydrate molecule
D
Sulfur is in the same column of the periodic table as oxygen, but has electronegativity similar to carbon. Compared to water molecules, molecules of H2S
- will ionize readily
- will be more likely to form hydrogen bonds with each other
- will be less likely to form hydrogen bonds with each other
- can absorb more heat from the environment
- both A and B are correct
C
Amino acids can be characterized as charged, polar, or non-polar because of the characteristics of the amino acid's
- amino group
- central carbon
- R-group
- carboxy group
C
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxyl ion [OH-] concentration of 10-4 M?
- pH 10
- pH 12
- pH 4
- pH 2
A
Which of the following is NOT a polymer?
- DNA
- starch
- glucose
- cellulose
C
Molecules within a crystal can be held together by ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds. Crystals held together by which bonds are likely to dissolve in water?
- ionic, covalent and hydrogen bonds
- ionic bonds only
- covalent bonds only
- ionic and covalent bonds
- ionic and hydrogen bonds
E
I. The size of the drug molecule.
II. The shape of the drug molecule
III. The physical properties of the drug molecule.
IV. The chemical formula of the drug molecule.
You wish to develop a new drug that will bind to the active site of an enzyme. Which of the traits listed above are important to consider as you design this drug?
- I, II, III
- II and III
- I and II
- all four of these are important
- Just III
A
Phospholipids form which kinds of structures when added to water?
- bilayers only
- micelles only
- bilayers and micelles
- none of the above, phospholipids are not water soluble
C
Which of these molecules is/are water soluble?
- neither C2H5OH nor C2H5COOH.
- just C2H5COOH
- just C2H5OH
- both C2H5OH and C2H5COOH are polar molecules
D
The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the formula of a molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration?
- C18H32O16
- C18 H30O15
- C18H36O18
- C6H10O5
B
Humans can obtain energy from starch but not cellulose because _____.
- the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is galactose.
- humans have enzymes that can break down starch but not cellulose
- the monomer of starch is fructose, while the monomer of cellulose is glucose
- starch monomers are joined by covalent bonds and cellulose monomers are joined by ionic bonds
B
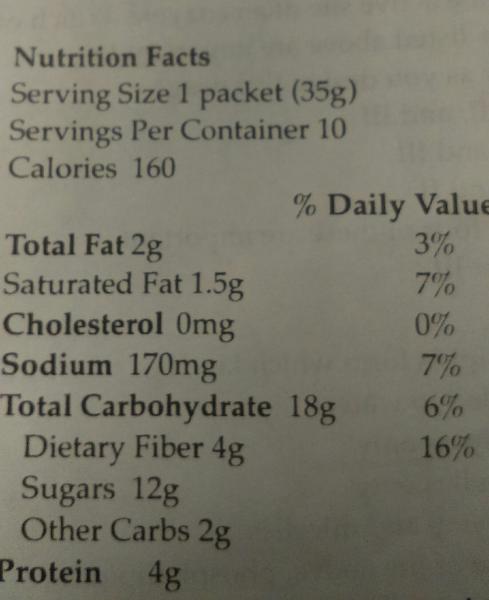
How many calories in this food were contributed by carbohydrate?
- 18
- 96
- 9
- 72
- 56
E
Which of the following are found in both RNA and DNA?
- cytosine and uracil
- cytosine, uracil, and guanine
- cytosine, thymine, and guanine
- cytosine and thymine
- cytosine, uracil, and thymine
- all
F
Which of these contains significant amounts of carbohydrate?
- cellery
- chicken
- butter
- fish
- vegetable oil
A
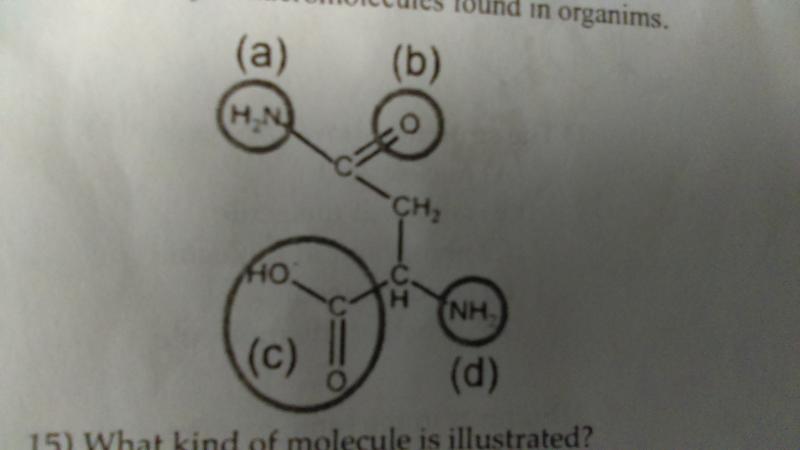
What kind of molecule is illustrated?
- amino acid
- lipid
- carbohydrate
- nucleic acid
A
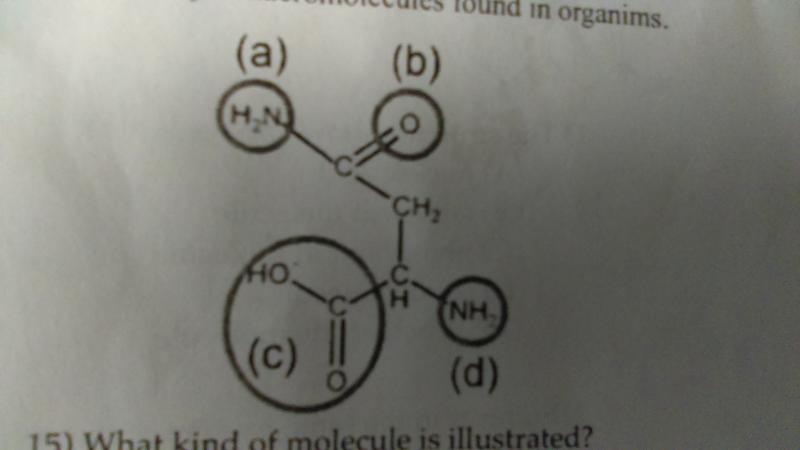
In a polymer of this molecule, which of the functional groups indicated would be joined to other monomers in covalent bonds?
- c and d
- b and d
- a and b
- a and c
- all of these functional groups could be joined to other monomers in covalent bonds
A
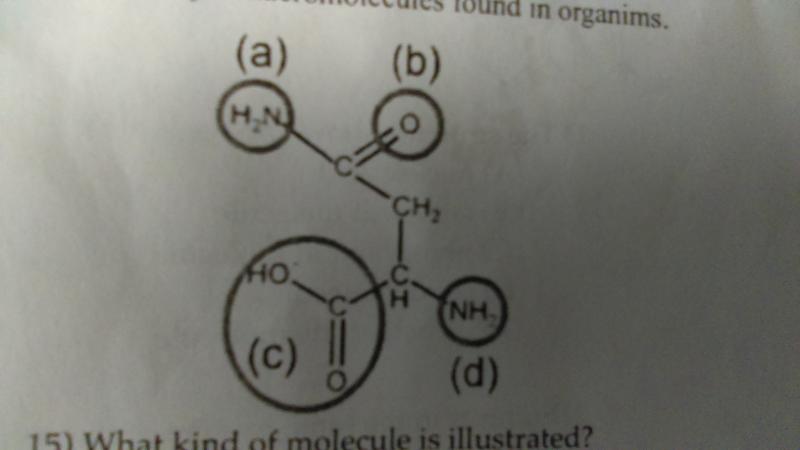
When joined with other monomers into a polymer, which of the functional groups are most likely to interact with other molecules?
- a and b
- c and d
- b and d
- a and c
- all of these functional groups are likely to interact with other molecules
A
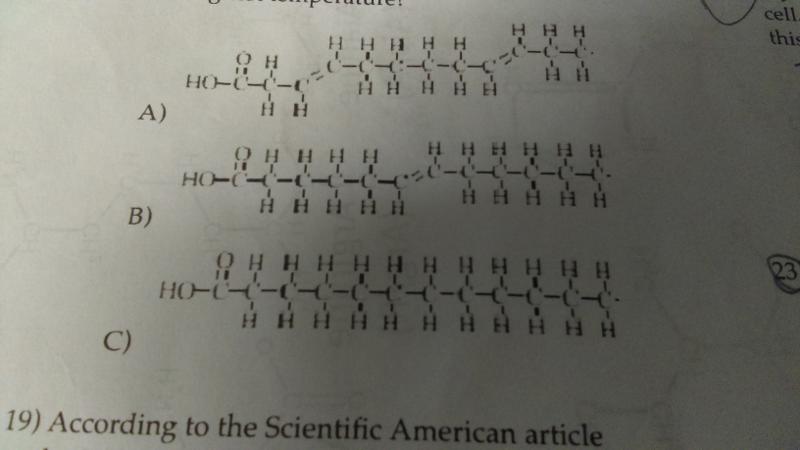
Which of the following would remain a solid at the highest temperature?
- a
- b
- c
C
According to the Scientific American article by Willett and Stampfer, for a healthy diet you should
- avoid meat
- eat fewer total carbs and total lipid
- eat more unsaturated fats
- eat more protein
- none of the above
C
The tertiary structure of a protein is the ______.
- order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain
- unique three-dimensional shape of the fully-folded polypeptide
- overall protein structure resulting from the aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits
- organization of a polypeptide chain into an a-helix or B-pleated sheet
B
If a DNA sample were composed of 10% thymine, what would be the percentage of guanine?
- 80
- 40
- 10
- It is impossible to tell from the information given.
B
If you give radioactive nitrogen to a growing cell, in which macromolecules would most of this nitrogen be found?
- nucleic acids and carbs
- both nucleic acids and proteins
- all four macromolecules would contain the radioactive nitrogen
- both proteins and lipids
- proteins only
B
Which of the following is NOT found in nucleic acids?
- amino group
- pentose sugar
- nitrogenous base
- phosphate group
A
The myoglobin protein, which carries oxygen in muscle cells, has only the first three levels of protein structure. In other words, it lacks a quaternary level. From this you can conclude that myoglobin ____.
- is made of nucleic cells
- is made of only one polypeptide chain
- lacks hydrogen bonds
- is a fiber
- is not helical or pleated
B
Cooking oil and gasoline ( a hydrocarbon) are not amphipathic molecules. Why?
- They do not have a hydrophobic region.
- They are highly reduced molecules.
- They spontaneously form micelles or liposomes in solution.
- They do not have a polar or charged region.
D
Asbestos is a material that was once used extensively in construction. One risk from working in a building that contains asbestos is the development of abestosis caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers. Cells will phagocytize asbestos, but are not able to degrade it. As a result, asbestos fibers accumulate in _____.
- the cytoplasm
- lysosomes
- Golgi
- ER
B
I) protein synthesis would stop
II) the cell would change shape
III) small hydrophilic molecules would no longer be able to cross the membrane
IV) transport of vesicles and organelles inside the cell would stop
A cell is exposed to a chemical that disrupts the cytoskeleton. Which of the following is a likely effect on the cell?
- III and IV
- Just I
- II and IV
- I and II
- all of these would happen
C
Which best describes production of eukaryotic cytoskeletal proteins?
- They are sorted from other proteins in the Golgi apparatus.
- They are exported from the cell in transport vesicles.
- They are manufactured on free ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
- All of the above.
C
A mutation disrupts the ability of an animal cell to add carbohydrate chains to proteins. The function of which organelles are most likely affected?
- ER or Golgi apparatus
- ER and vesicles
- Golgi apparatus or ribosomes
- ribosomes or nucleus
A
You have a cube of modeling clay in your hands. Which of the following changes to the shape this cube of clay will decrease its surface area relative to its volume?
- Flatten the cube into a pancake shape.
- Pinch the edges of the cube to make small folds
- Round the clay up into a sphere
- Stretch the cube into a long, shoebox shape
C
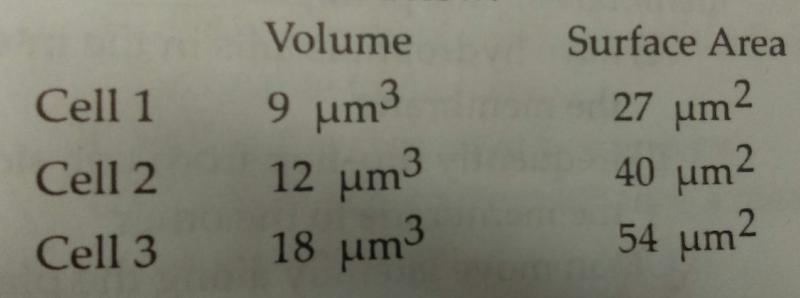
Both the volume and the surface area for three different cells were measured. These values are listed above:
- Cell 3 since it has the largest surface area which will enable it to eliminate all of its wastes quickly.
- Cell 3 because it is big enough to allow wastes to easily diffuse through the plasma membrane.
- Cell 1 since it has the smallest volume and will not produce as much waste as the other cells.
- Cell 2 since it has the highest surface area-to-volume ratio which facilitates the exchange of materials between a cell and its environment.
D
Researchers tried to explain how vesicular transport occurs in cells by attempting to assemble the transport components. They set up microtubular tracks along which vesicles could be transported, and they added vesicles and ATP (because they knew the transport process requires energy). Yet, when they put everything together, there was no movement or transport of vesicles. What were they missing?
- ribosomes
- endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- motor proteins
D
Which of the following is present in a prokaryotic cell?
- ribosome
- mitochondrion
- chloroplast
- ER
- all of the above
A
White blood cells engulf bacteria using _____.
- phagocytosis
- osmosis
- receptor-mediated exocytosis
- pinocytosis
A
According to the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, phospholipids ______.
- have hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane
- frequently flip-flop from one side of the membrane to the other
- can move laterally along the plane of the membrane
- occur in an uninterrupted bilayer, with membrane proteins restricted to the surface of the membrane
C
Which of the following is a reasonable explanation for why unsaturated fatty acids help keep a membrane more fluid at lower temperatures?
- The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails, preventing adjacent lipids from packing tightly.
- Unsaturated fatty acids are more polar than saturated fatty acids
- Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content and, therefore, more cholesterol in membranes
- The double bonds block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
A
Which of the following would likely move through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane most rapidly?
- CO2
- K+
- an amino acid
- glucose
A
Which are NOT embedded in the hydrophobic portion of the bilayer at all?
- transmembrane proteins
- peripheral proteins
- integral proteins
- all of these are embedded in the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer
B
I) is a passive process
II) it requires an expenditure of energy by the cell
III) requires integral proteins in the cell membrane
IV) is very rapid over long distances
Which of the above is true of Diffusion?
- III and IV
- I only
- II and III
- I and IV
- all of these are true
B
Which of the following is true of osmosis?
- In osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration
- Osmosis only takes place in red blood cells.
- Osmosis is an energy-demanding or "active" process
- In osmosis, solutes moves across a membrane from areas of higher solute concentration to areas of lower solute concentration.
A
The sodium-potassium pump is called an electrogenic pump because its _____.
- pumps equal quantities of Na+ and K+ across the membrane
- helps create an electric charge difference across the membrane
- is used to drive the transport of other molecules against a concentration gradient
- ionizes sodium and potassium atoms
B
Which of the following would increase the electrochemical gradient across a membrane?
- a sucrose-proton cotransporter
- a proton pump
- a potassium channel
- both a proton pump and potassium channel
B
A patient involved in a serious accident has lost a large quantity of blood. To replenish body fluids, distilled water---equal to the volume of blood lost---is added to the blood directly via one of his veins. As a result of this transfusion, the patient's red blood cells will
- swell and may burst because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells
- shrivel up because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells
- shrivel up because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells
- swell and may burst because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells
D
Proton pumps are used in various ways by members of every domain of organisms: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. What does this most probably mean?
- The high concentration of protons in the ancient atmosphere must have necessitated a pump mechanism
- Proton gradients across a membrane were used by cells that were the common ancestor of all three domains of life
- Proton pumps are necessary to all cell membranes
- Cells of each domain evolved proton pumps independently when oceans became more acidic.
B
During a laboratory experiment, you discover that an enzyme-catalyzed reaction has delta-G of -20 kcal/mol. If you double the amount of enzyme in the reaction, what will be the delta G for the new reaction?
- 0 kcal/mol
- +20 kcal/mol
- -20 kcal/mol
- -40 kcal/mol
C
Anabolic pathways ______.
- consume energy to decrease the entropy of the organism and its environment
- consume energy to build up polymers from monomers
- release energy as they degrade polymers to monomers
- are usually highly spontaneous chemical reactions
B
The mathematical expression for the change in free energy of a system is delta G = delta H - T(delta S). Which of the following is (are) correct?
- T is the temperature in Celsius
- delta H is the change in entropy, the energy available to do work.
- delta G is the change in free energy
- delta S is the change in enthalpy, a measure of randomness
C
Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism?
- Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
- Its terminal phosphate bond has higher energy than the other two phosphate bonds
- Its terminal phosphate group contains a strong covalent bond that, when hydrolyzed, releases free energy.
- It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
D
Which of the following is true of enzymes?
- Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by lowering activation energy.
- Enzymes increase the rate of chemical by providing activation energy to the substrate
- If the 3-D structure or conformation of an enzyme is altered, enzyme function will probably increase.
- Enzyme function is independent of chemical and physical environmental factors such as pH and temperature.
A
Increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic could overcome which of the following?
- the need for a coenzyme
- allosteric inhibition
- insufficient cofactors
- competitive inhibition
D
A noncompetitive inhibitor decreases the rate of an enzyme reaction by ____.
- changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
- acting as a coenzyme for the reaction
- binding at the active site of the enzyme
- changing the free energy change of the reaction
A
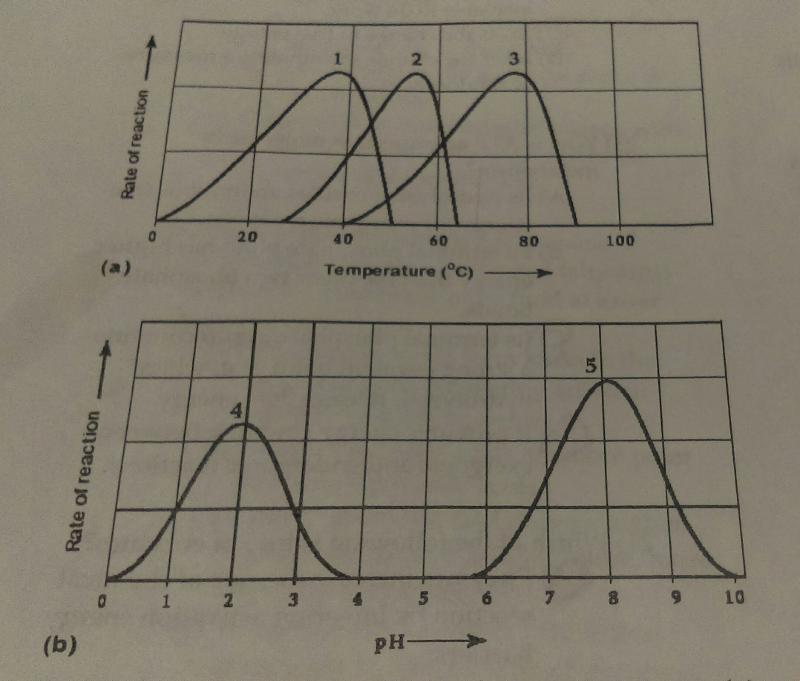
Which curves on the graphs may represent the temperature an pH profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly alkaline hot springs at temperatures 70 degrees C or higher?
- curves 2 and 5
- curves 3 and 4
- curves 3 and 5
- curves 1 and 5
C
Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs
- in the citric acid cycle only
- during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
- during glycolysis only
- during oxidative phosphorylation only
- during glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
B
After glycolysis, pyruvate is modified by a series of reactions before entering the Citric Acid cycle. These reactions produce ______.
- acetyl CoA, NADH, and CO2
- acetyl CoA, FADH2, and CO2
- acetyl CoA, O2, and ATP
- acetyl CoA, NAD+, ATP, and CO2
A
The glucose molecule has a large quantity of energy in its _____.
- C-H bonds
- C-O bonds
- C-N bonds
- polar structure
- number of oxygen atoms
A
Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle?
- 3 ATP, 6 CO2, 9 NADH, and 3 FADH2
- 38 ATP, 6 CO2, 3 NADH, and 12 FADH2
- 1 ATP, 2 CO2, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2
- 2 ATP, 2 CO2, 3 NADH, and 3 FADH2
- 3 ATP, 3 CO2, 3 NADH, and 3 FADH2
A
In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate _____.
- two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced
- four molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced
- two molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced
- two molecules of ATP are used and six molecules of ATP are produced
A
What percentage of the ATP formed during anerobic respiration is made by chemiosmosis?
- 38%
- 0%
- 2%
- 100%
B
Which best describes the movement of electrons during aerobic respiration?
- glucose -->pyruvate-->ATP-->oxygen
- glucose-->glycolysis-->citric acid cycle-->NADH--> ATP
- glucose-->NADH-->electron transport chain-->oxygen
- glucose-->ATP-->electron transport chain-->NADH
C
Oxidative phosphorylation uses energy released by movement of protons down their electrochemical gradient to ATP. This is an example of _____.
- simple diffusion
- an endergonic reaction coupled to an exergonic reaction
- the release of energy by active transport
- a reaction with a positive delta G
B
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is released during which stages of cellular respiration?
- oxidative phosphorylation and lactic acid fermentation
- lactic acid fermentation and glycolysis
- the citric acid cycle only
- oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
- glycolysis and the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D
Which of the following can yeast cells metabolize under anerobic conditions to make ATP?
- ethanol
- pyruvate
- glucose
- lactic acid
- either ethanol or lactic acid
C
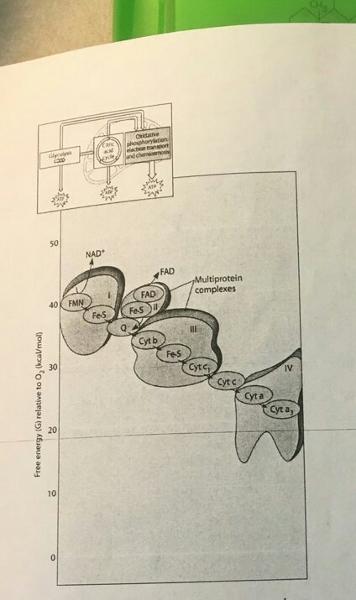
Which of the following most accurately describes what is happening along the electron transport chain in the accompanying figure?
- Each electron carrier alternates between being reduced and being oxidized
- Electrons are transferred to ADP to generate ATP at each step in the process
- Molecules in the chain give up some of their potential energy
- Energy of the electrons increases at each step of the process
- ATP is generated at each step of the process
A
Which occurs in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell?
- oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
- fermentation and chemiosmosis
- glycolysis and fermentation
- citric acid cycle
C
One function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation reactions is to
- produce ATP
- break down pyruvate to collect energy
- oxidize NADH to NADH+
- produce CO2
- reduce NADH and NADH+
C
Even though plant cells photosynthesize. they still use their mitochondria for oxidation of pyruvate. This will occur in _____.
- all cells all the time
- cells that are storing glucose only
- photosynthesizing cells in the light and and in other tissues int he dark
- photosynthetic cells in the light, while photosynthesis occurs concurrently
A
The ATP made during anerobic respiration is generated by _____.
- oxidative phosphorylation
- substrate -level phosphorylation
- the electron transport chain
- both A and B
- all of the above
B
A mutation in yeast makes it unable to convert pyruvate to ethanol. How will this mutation affect these yeast cells? The mutant yeast cells will _____.
- grow anerobically only when given glucose
- die because they cannot regenerate NAD+ from NADH
- be unable to metabolize glucose
- be unable to grow aerobically
- be unable to grow anerobically
E
In plant cells, synthesis of ATP by chemiosmosis occurs during
- respiration only
- photosynthesis and respiration
- photosynthesis only
- neither photosynthesis nor respiration
B
Which of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin cycle?
- ATP and NADPH
- ADP, Pi, and NADP+
- H2O and O2
- CO2 and glucose
- electrons and H+
A
Which sequence correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
- H2O-->chlorophyll-->NADPH-->sugar
- NADPH-->O2-->CO2
- light-->H2O-->chlorophyll-->ATP-->sugar
- H2O-->NADPH-->chlorophyll-->O2
- light-->NADPH-->O2-->sugar
A
Plants photosynthesize _____.
- and respire only in the light
- only in the light but respire only in the dark
- only in the light but respire in light and dark
- and respire only in dark
- only in the dark but respire only in the light
C
What molecule provides electrons to the light-independent reactions of plants?
- CO2
- NADPH
- ATP
- oxygen
B
How does the Calvin cycle help plants?
- it transports ATP out of the chloroplast
- it makes ATP and NADPH
- it uses ATP and NADPH to make CO2
- it makes simple sugars from CO2
- it splits water to release oxygen
D
When is CO2 split to form oxygen gas and carbon compounds?
- during photosynthesis only
- in neither photosynthesis nor respiration
- during photosynthesis and respiration
- during respiration only
B
If a chloroplast has enough NADPH but not enough ATP for carbon fixation it
- will have to stop producing O2 in order to make more ATP
- can make more ATP via cyclic electron flow
- can use NADPH to make ATP
- can make more ATP via cell respiration
B
A spaceship is designed to support animal life for a multiyear voyage to the outer planets of the solar system. Plants will be grown to provide oxygen and to recycle carbon dioxide. Since the spaceship will be too far from the sun for photosynthesis, an artificial light source will be needed.
If the power fails and the lights go dark, CO2 levels will ______.
- rise as a result of animal but not plant respiration
- fall because plants will cease to respire in the dark
- rise as a result of both animal and plant respiration
- fall because plants will increase CO2 fixation
- remain balanced because plants will continue to fix CO2 in the dark
C
Codons are part of the molecular structure of _____.
- mRNA
- rRNA
- tRNA
- a protein
A
Altering patterns of gene expression in prokaryotes would most likely serve the organism's survival in which of the following ways?
- allowing each gene to be expressed an equal amount of times
- organizing gene expression so that genes are expressed in a given order
- allowing environmental changes to alter the prokaryote's genome
- allowing the organism to adjust to changes in environmental conditions
D
The trp repressor blocks transcription of the trp operon when the repressor ____.
- binds to the tryptophan
- is not bound to tryptophan
- binds to the inducer
- is not bound to the operator
A
Alternative RNA splicing ______.
- can allow the production of similar proteins from different RNAs.
- increases the rate of transcription
- is a mechanism for increasing the rate of translation
- can allow the production of proteins of different sizes and functions from a single mRNA
D
In the process of transcription, ______.
- proteins are synthesized
- RNA is synthesized
- DNA is replicated
- mRNA attaches to ribosomes
B
In positive control of several sugar-metabolism-related operons, the catabolite activator protein (CAP) binds to DNA to stimulate transcription. What causes an increase in CAP activity in stimulating transcription?
- an increase in glucose and increase in cAMP
- a decrease in glucose and an increase in cAMP
- an increase in glucose and a decrease in cAMP
- a decrease in glucose and a decrease in the repressor
B
3' CUGCCG 5'
5' GTCAGTTGACGGCTGATAGC 3'
In the above molecule, the top strand is an RNA primer added by primase to the template strand of DNA. If DNA polymerase extended this strand, what would be the sequence of the newly synthesized DNA be?
- 5' CAGTCAA 3'
- 5' TGATAGC 3'
- 3' CAGTCAA 5'
- 3' ACTATCG 5'
C

What type of bonding is responsible for maintaining the shape of the tRNA molecule shown in the figure above?
- ionic bonding between phosphates
- hydrogen bonding between base pairs
- peptide bonding between amino acids
- van der Waals interactions between hydrogen atoms
B
What is the function of topoisomerase?
- stabilizing single-stranded DNA at the replication fork
- elongating new DNA at a replication fork by adding nucleotides to the existing chain
- relieving strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork
- unwinding of the double helix
C
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA replication?
- It joins Okazaki fragments together
- It unwinds the parental double helix
- It synthesizes RNA molecules to make a primer
- It stabilizes the unwound parental DNA
A
5' TAATTAGTTAA 3'
3' ATTAATCAATT 5'
Using the sequence above, if the top strand is the template strand, the RNA sequence transcribed would be:
- 5' TTAACTAATTA 3'
- 5' TAATTAGTTAA 3'
- 5' UUAACUAAUUA 3'
- 3' UUAACUAAUUA 5'
C
Cytosine makes up 42% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism. Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this sample will be thymine?
- 58%
- 8%
- 16%
- 42%
B
In E. coli, what is the function of DNA polymerase?
- to add nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing DNA strand
- to degrade damaged DNA molecules
- to seal together the broken ends of DNA strands
- to unwind the DNA helix during replication
A
A new DNA strand elongates only in the 5' to 3' direction because _____.
- the polarity of the DNA molecule prevents addition of nucleotides at the 3' end
- DNA polymerase can add nucleotides only to the free 3' end
- DNA polymerase begins adding nucleotides at the 5' end of the template
- replication must progress toward the replication fork
B
Using RNA as a template for translation instead of making proteins directly from DNA is advantageous for the cell because
- RNA acts as an expendable copy of the genetic material
- tRNA, rRNA and others are not transcribed
- RNA is much more stable than DNA
- only one mRNA molecule can be transcribed from a single gene, lowering the potential rate of gene expression
- mRNA molecules are subject to mutation but DNA is not
A
What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding the strands that make up DNA?
- Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands
- One strand contains only purines and the other contains only pyrimidines
- The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand
- The twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands
C
Which of the following mechanisms is (are) used to coordinate the expression of multiple, related genes in eukaryotic cells?
- The genes are organized into a a large operon, allowing them to be coordinately controlled as a single unit
- Environmental signals enter the cell and bind directly to promoters
- A single repressor is able to turn off several related genes
- The genes share a single common enhancer, which allows appropriate activators to turn on their transcription at the same time
D
The lactose operon is likely to be transcribed when _____.
- there is more glucose in the cell than lactose
- there is glucose but no lactose in the cell
- the cAMP level is high and the lactose level is low
- the cyclic AMP and lactose levels are both high within the cell
D
Which of the following, when taken up by a cell, binds to a repressor so that the repressor no longer binds to the operator?
- corepressor
- repressor
- promoter
- inducer
D
Which of the following does not occur in prokaryotic gene expression, but does occur in eukaryotic gene expression?
- RNA polymerase requires a primer to elongate the molecule
- mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are transcribed
- A cap is added to the 5' end of mRNA
- RNA polymerase binds to the promoter
C
3'-GCAACTGAAATAGCTTTGACCCC-5'
Which would serve as a primer in PCR for the DNA molecule shown above?
- 5'-CTGGGG-3'
- 5'-CGTTGA-3'
- 5'-GACCCC-3'
- 3'-GCAACT-5'
B
How does termination of translation take place?
- The poly-A tail is reached
- The end of the mRNA molecule is reached
- The 5' cap is reached
- A stop codon is reached
D
The leading and the lagging strands differ in that
- the leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end
- the leading strand is synthesized at twice the rate of the lagging strand
- the leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction
- the lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together
C
A particular triplet of bases in the template strand of DNA is 5' AGT 3'. THe corresponding codon for the mRNA transcribed is ____.
- 3' UGA 5'
- 3' ACU 5'
- 3' UCA 5'
- 5' TCA 3'
C
A mutant bacterial cell has a defective aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that attaches a lysine to tRNAs with the anitcodon AAA instead of the normal phenylalanine. The consequence of this for the cell will be that _____.
- none of the proteins in the cell will phenylalanine
- the ribosome will skip a codon every time a UUU is encountered
- the cell will compensate for the defect by attaching phenylalanine to tRNAs with lysine-specifying anticodons
- proteins in the cell will include lysine instead of phenylalanine at amino acid positions specified by the codon UUU
D
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple offspring. The part of the radish we eat may be oval or long, with long being the dominant trait. If true-breeding red long radishes are crossed with true-breeding white oval radishes, the F1 will be expected to be which of the following?
- white and long
- purple and oval
- purple and long
- red and long
C
Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son. What are the genotypes of the parents?
- XNXn and XNY
- XNXN and XnY
- XNXN and XNY
- XnXn and XnY
A
In the cross AaBbCc x AaBbCc, what is the probability of producing the genotype AABBCC?
- 1/4
- 1/16
- 1/8
- 1/64
D
A woman who has blood type A positive has a daughter who is type O positive and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a trait that shows dominance over Rh negative. Which of the following is a possible phenotype for the father?
- B positive
- AB negative
- A negative
- O negative
A
Four genes are located close together on a single chromosome. The distance between the different genes are as follows: A-B = 8 mu, A-C = 15 mu, B-C = 23 mu, B-D = 13 mu and D-C = 10 mu. What is the correct order of these genes?
- CADB
- ADCB
- BADC
- DACB
C

Which diagram represents anaphase II of meiosis?
- I
- III
- IV
- V
D
When Mendel crossed yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants, all the offspring were yellow-seeded. When he took these F1 yellow seeded plants and crossed them to green-seeded plants, what genotypic ratio was expected?
- 3:1
- 1:1
- 1:1:1:1
- 1:2:1
B
Which of the following statements about independent assortment and segregation is correct?
- The law of segregation requires describing two or more genes relative to one another.
- The law of assortment is accounted for by observations of prophase I.
- The law of segregation is accounted for by anaphase of mitosis.
- The law of independent assortment requires describing two or more genes relative to each other.
D

Pedigree chart for family in which some members exhibit the dominant trait, W, represented by dark square or circle.
What is the likelihood that the progeny of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait?
- 50%
- 75%
- 0%
- 100%
A

Pedigree chart for family in which some members exhibit the dominant trait, W, represented by dark square or circle.
What is the genotype of individual II-5?
- ww or Ww
- ww
- Ww
- WW
B
Phenylketonuria is an inherited disease caused by a recessive autosomal allele. If a woman and her husband are both carriers, what is the probability that their child will be a phenotypically normal girl?
- 1/4
- 1/16
- 3/16
- 3/8
D
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a serious condition by a recessive allele of a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients have muscles that weaken over time because they have absent or decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein. They rarely live past their twenties. How likely is it for a woman to have this condition?
- Women can never have this condition.
- One-fourth of the daughters of an affected mean would have this condition.
- Only if a woman is XXX could she have this condition.
- One-half of the daughters of an affected father and a carrier mother could have this condition.
D
Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails (T) are dominant to long tails (t). What fraction of the progeny of crosses BbTt x BBtt will be expected to have black fur and long tails?
- 1/16
- 1/2
- 9/16
- 3/8
B
A red guinea pig crossed with a brown guinea pig produced twelve red offspring. When the brown was crossed with a second red animal, six red and six brown were obtained. What is the best explanation for this genetic situation?
- Brown is recessive; red is dominant
- Brown is recessive; red is codominant
- Brown is dominant; red is incompletely dominant
- Brown and red are codominant
A
Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16?
- Each diploid cell has eight homologous pairs.
- The species has 16 sets of chromosomes per cell.
- The species is diploid with 32 chromosomes per cell.
- A gamete from this species has four chromosomes.
A
Which of the following statements is true of linkage?
- The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
- The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a maximum value of 100%.
- Linked genes are found on different chromsomes.
- All of the traits that Mendel studied - seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others - are due to genes linked on the same chromosome.
A
Which of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance?
- white and purple flower color in peas
- the ABO blood group
- skin pigmentation in humans
- pink flowers in snapdragons
C
After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is _____.
- diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids
- haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids
- haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid
- diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid
B
In humans, ABO blood types refer to glycoproteins in the membranes of red blood cells. If a woman with type AB blood marries a man with type O blood, which of the following blood types could their children possibly have?
- A, B, and O
- AB and O
- A and B
- A, B, AB, and O
C
Homologous chromosomes _____.
- align on the metaphase plate in meiosis II.
- carry information for the same traits.
- carry the same alleles
- are identical
B

A female with a paternal set of one orange and one long gene chromosome and a maternal set comprised of one blue and one short gene chromosome is expected to produce which of the following types of eggs after meiosis?
- all eggs will have maternal types of gene combinations
- all eggs will have paternal types of gene combinations
- each egg has one-fourth chance of having either blue long, blue short, orange long, or orange short combinations
- Half the eggs will have maternal and half will have paternal combinations
C
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses with dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all. If doubly heterozygous SsNn cactuses were allowed to self-pollinate, the F2 would segregate in which of the following ratios?
- 1 sharp-spined: 1 dull-spined: 1 spineless
- 3 sharp-spined: 1 spineless
- 1 sharp-spined: 2 dull-spined: 1 spineless
- 9 sharp-spined: 3 dull-spined: 4 spineless
D
Which of the following occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
- alignment of chromosomes at the equator
- chromosome replication
- condensation of chromosomes
- synapsis of chromosomes
D
Albinism is an autosomal trait (not sex-linked) recessive trait. A man and woman are both of normal pigmentation, but both have one parent who is albino (without melanin pigmentation). What is the probability that their first child will be an albino?
- 1/4
- 1/2
- 1
- 0
A
In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous (Rr) offspring of red (RR) and white (rr) homzygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of 1 red: 2 roan: 1 white?
- red x roan
- roan x roan
- white x roan
- red x white
B