Phase of metabolism that provides energy by BREAKING DOWN COMPLEX MOLECULES into SIMPLE MOLECULES. (e.g.) PROTEINS → AMINO ACIDS
CATABOLISM
ISOTOPES
- Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but differing numbers of neutrons. Isotopes are different forms of a single element.
- EXAMPLES... Carbon 12 and Carbon 14 are both isotopes of carbon, one with 6 neutrons and one with 8 neutrons (both with 6 protons).
Heterogeneous, will settle
Suspensions
What type of homeostatic feedback reflex is the withdrawal reflex?
negative
An atom with ________ electrons could be an anion when ionically bonded.
ANSWER: 9
in certain kinds of muscle cells, calcium ions are stored
in the smooth ER
An example of a coenzyme is
riboflavin (vitamin B2)
What is a DIPOLE?
POLAR MOLECULE
Two good examples of a colloid would be Jell-O® or
cytosol
Phase of metabolism that uses the energy from CATABOLISM to build up the BODY'S STRUCTURAL and FUNCTIONAL COMPONENTS. It is also called BIOSYNTHESIS. (e.g.) AMINO ACIDS → PROTEINS.
ANABOLISM
The coiling of the protein chain backbone into an alpha helix is referred to as the ________.
secondary structure
Which of the following are subdivisions of anatomy?

regional, systemic, and surface
A solution that has a pH of 2 could best be described as being ________.
acidic
In a DNA molecule, the phosphate serves
to hold the molecular backbone together
The numbers listed represent the first, second, and third energy levels, respectively. On this basis, which of the following is an unstable or reactive atom?
2, 8, 1
The ATP molecule is not used in?
chemical work
mechanical work
ANSWER:
transport
pigments
Which of the following is a neutralization reaction?
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
What is the pathway between the receptor and the control center in the reflex pathway called?
afferent pathway

In certain kinds of muscle cells, calcium ions are stored in

the smooth ER
- Abundant in tissues subjected to great mechanical stress.
- type of anchoring junction.
- Communicating junction.
- Present in electrically excitable tissues.
- Desmosomes
- Desmosomes
- Gap junctions
- Gap junctions
If an atom were to have two protons, then it would
be very stable
Which body system would be most affected by a lower than normal atmospheric pressure?
respiratory system
Most fibrous proteins in the body contain all of these except:
keratin
elastin
eledin
collagen

Can lungs carry out excretory functions? Explain your answer.

Yes, carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste the lungs excrete.
- Heat shock proteins (hsp) are a type of protein called
- Stress proteins are a type of protein called
- chaperonins
HYDROGEN
Which bonds often bind different parts of a molecule into a specific three-dimensional shape?
In liquid XYZ, you notice that light is scattered as it
passes through. There is no precipitant in
the bottom of the beaker, though it has been sitting
for several days. This liquid must be a
Heterogeneous, will not settle
colloid

- Plays a role in the synthesis of steroid-based hormones and proteins.
- The actual site of protein synthesis
- Hollow cytoskeletal elements that act as organizers for the cytoskeleton.
- Houses DNA and RNA.
- Dense spherical bodies in the nucleus that are the synthesis site for ribosomal RNA.

- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Ribosomes
- Microtubules
- Nucleus
- Nucleoli

Which of the following is not considered a factor in influencing a reaction rate?

TIME
In redox reactions ________.
both decomposition and electron exchange occur
What is a vertical section through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior regions called?
FRONTAL
Select which reactions will usually be irreversible
regarding chemical equilibrium in living
systems.
glucose to CO2 & H2O
Select the statement about mixtures that is correct.
A) A
solution contains solvent in large amounts and solute in
smaller quantities.
B) Solutions contain particles that settle out in time.
C) Suspensions can change
reversibly from liquid to solid.
D) Suspensions are homogeneous mixtures of two or
more components.
Answer: A

What broad term covers all chemical reactions that occur within the body cells?

metabolism
Fibrous proteins
are very stable and insoluble in water
Which of the following is true regarding the concentration of solutions?
A) Percent solutions are parts per 1000 parts.
B)
Molarity is one mole of solute per 1000 ml of solution.
C) To calculate molarity, one must know the atomic
number of the solute.
D) To calculate molarity, one
must know the atomic weight of the solvent.
Answer: B

- What does gross anatomy study?
- In which body cavities are the lungs located?
- The pH of body fluids must remain fairly constant for the body to maintain homeostasis

- Larger structures of the body that can be seen with the naked eye.
- pleural, ventral, and thoracic
- TRUE
- What is the goal of all of the negative feedback mechanisms of the body?
- Which of the following describes a parasagittal plane?
- What is a vertical section through the body, dividing it into left and right, called?

- The goal is to prevent sudden severe changes within the body.
- sagittal
- any sagittal plane except in the midline
- What is a dynamic equilibrium of your internal environment termed?
- The body cavities that protect the nervous system are located in the ____ cavity.

- homeostasis
- dorsal

- Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate.
- Chromosomes align on the spindle equator.
- Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell
- Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin.
- Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends of the cell.

- Late prophase
- Metaphase
- Early prophase
- Telophase
- Anaphase
The single most abundant protein in the body is ________.
COLLAGEN
- Similar cells that have a common function are called ________. Answer:
- Which of the following organs or structures would be found in the left iliac region?

- tissues
- Intestines
.gif)
THE FOLLOWING DESCRIBE ENZYMES?
.gif)
- some enzymes are protein plus a cofactor. Each enzyme is chemically specific.Some enzymes are purely protein
- They are proteins.
- They have specific binding sites for specific substrates.
- They lower the activation barrier for a specific reaction.
- The names end in "ase."
- They can be denatured.
- They can be used again and again.
The parietal pleura would represent a serous membrane
LINING THE THORACIC CAVITY
Smallest particle of an element that retains its properties.
ATOM
If cells are placed in a hypertonic solution containing a solute to which the membrane is impermeable, what could happen?
The cells will lose water and shrink.
What moves cell organelles from one location to another inside a cell?
Motor proteins
The basic structural material of the body consists of
PROTEINS

Help prevent molecules from passing through the extracellular space between adjacent cells.

Tight junctions
An amino acid may act as a proton acceptor or donor.
Amino acids have two components--a base group (proton acceptor) and an organic acid part (a proton donor). Some have additional base or acid groups on the ends of their R groups as well.
A dipeptide can be broken into two amino acids by dehydration synthesis.
TRUE
In general, the lipids that we refer to as oils have ________.
a high degree of unsaturated bonds
Many plasma proteins may function as _________.
BUFFERS
Hydrogen bonds are too weak to bind atoms together to form molecules but are important intramolecular bonds
TRUE
Which one of the following systems responds fastest to environmental stimuli?
NERVOUS
- Act as "interpreter" molecules that recognize specific amino acids and nucleotide base sequences.
- Produced in the nucleus, this molecule specifies the exact sequence of amino acids of the protein to be made.
Transfer RNA
Messenger RNA

- Ribosomal RNA

- Attaches the correct amino acid to its transfer RNA
- Forms part of the protein synthesis site in the cytoplasm.
Which structures are fingerlike projections that greatly increase the absorbing surface of cells?
MICROVILLI
May be attached to the ER or scattered in the cytoplasm
Synthetase enzymes
- In a DNA molecule, the phosphate serves
- The genetic information is coded in DNA by the ________.
- The RNA responsible for bringing the amino acids to the ribosome for protein formation is
- The RNA that has an anticodon and attaches to a specific amino acid is ________ RNA
- to hold the molecular backbone together
- sequence of the nucleotides
- tRNA
- transfer

- ATP

- Provides the energy needed for synthesis reactions.
- The ________ molecule directly provides energy for cellular work. Answer:
Anything that occupies space and has mass.
MATTER
Although a man who weighs 175 pounds on Earth would be lighter on the moon and heavier on Jupiter, his ________ would not be different.
MASS
Which of the following is not true of proteins?
They appear to be the molecular carriers of coded hereditary information.
Coenzymes are ________.
organic molecules derived from vitamins
- BLOOD
- A red blood cell placed in pure water would
- MIXTURE
- swell and burst
What type of chemical bond can form between an element with 11 protons and an element with 17 protons?
IONIC
Carbohydrates and proteins are built up from their basic building blocks by the ________.
removal of a water molecule between each two units
- Neutral subatomic particle
- What happens when globular proteins are denatured?
- Neutron
- The active sites are destroyed.
Is a function of, and varies with, gravity.
WEIGHT
Dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide).
COMPOUND
Which of the following describes the plasma membrane?
a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell
Legs moving the pedals of a bicycle.
MECHANICAL
When the bonds of ATP are broken, energy is released to do cellular work.
Chemical energy

Can be measured only by its effects on matter

ENERGY
The lower the pH, the higher the hydrogen ion concentration.
TRUE
Are able to detoxify substances by enzymatic action.
Peroxisomes
Are hollow tubes made of spherical protein subunits called tubulins. Answer:
Microtubules
Carbon
element
Which of the following is not a role of molecular chaperonins?
act as a platform for assembling primary protein structure
Represented by the flow of charged particles along a conductor, or the flow of ions across a membrane.
Electrical energy
Which of the following does NOT describe enzymes?
Enzymes work by raising the energy of activation.

What does the polar end of a phospholipid contain?

phosphorus-containing group
Which metals have a toxic effect on the body?
heavy metals such as bismuth, Most often the definition of toxic metals includes at least cadmium, manganese, lead, mercury and the radioactive metals.
Removes and filters excess fluid from tissues.
Lymphatic
- If you consider your home air conditioner in terms of homeostasis, then the wall thermostat would be the
- How many phosphates would AMP have attached to it?
- A chemical reaction in which bonds are broken is usually associated with ________.
- CONTROL CENTER
- ONE
- the release of energy

- A structure that is composed of two or more tissue types that work together to perform specific functions for the body is a(n
- Glucose is an example of a monosaccharide.

- ORGAN
- TRUE
- Which of the following is NOT a function of lysosomes?
- Mixtures are combinations of elements or compounds that are physically blended together but are not bound by chemical bonds
- forming acid hydrolases which are necessary to help form cell membranes
- TRUE
Which feedback mechanism causes the variable to deviate further and further from its original value or range? Answer:
POSTIVE FEEDBACK
- a polymer of glucose found in animals; stored form of glucose
- Starch is the stored carbohydrate in plants, while ______ is the stored carbohydrate in animals.
- Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscles in the form of ________.
- GLYCOGEN
- glycogen
- GLYCOGEN
- Ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus functionally act in sequence to synthesize and modify proteins for secretory use (export) only, never for use by the cell. This statement is ________.
- What is the main, general purpose of negative feedback?
- false; integral cell membrane proteins are also synthesized this way
- to maintain homeostasis

- contain some of the DNA and RNA code necessary for their own function
- Other than the nucleus, which organelle has its own DNA?
- Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the ________. Answer:
- Mitochondria
- Buffers resist abrupt and large changes in the pH of the body by releasing or binding ions
- Weak acids and bases make good _______.
- TRUE
- BUFFERS

- Passive membrane transport processes include
- Which of the following statements is correct regarding net diffusion?

- movement of a substance down its concentration gradient
- The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate.
The higher we go in the mountains, the greater the atmospheric pressure, resulting in an increase in available oxygen. Comment on this statement.
At high altitudes, the atmospheric pressure is less than at lower levels resulting in a decrease in oxygen levels. The lower oxygen levels may be inadequate to support cellular metabolism.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
protein synthesis in conjunction with ribosomes
A holoenzyme is composed of an apoenzyme and a(n) ________. Answer:
cofactor
- is division of the nucleus
- The metabolic or growth phase of a cell life cycle is called ________.
- Mitosis
- interphase

Why are the abdominopelvic cavity organs the most vulnerable to blunt deceleration in an automobile accident with seat belts?

The walls of the abdominal cavity are formed only by trunk muscles and are not reinforced by bone. The pelvic organs receive a somewhat greater degree of protection from the bony pelvis.
What can happen when the usual negative feedback mechanisms are overwhelmed and destructive positive feedback mechanisms take over?
Homeostatic imbalances increase our risk for illness and produce the changes we associate with aging
Which of the following is not a factor that binds cells together?
glycolipids in the glycocalyx
Hydrogen bonds are more like a type of weak ________ than true bonds.
attraction
- Will not scatter light.
- _______ have a bitter taste, feel slippery, and are proton acceptors. Answer:
- Number of protons in an atom
- Solutions
- Bases
- ATOMIC NUMBER
Current information suggests that omega-3 fatty acids decrease the risk of heart disease.
TRUE
Which of these is an inclusion, not an organelle?
cilia
lysosome
ANSEWER:
melanin
microtubule
Combined number of protons and neutrons in an atom
Mass number of an element
- An atom with three electrons would have a valence of ________. Answer: one
- Smallest particle of a compound that still retains its properties.
- First one or two letters of an element's name
- ONE
- Molecule
- ATOMIC SYMBOL
Electrically charged particle due to loss of an electron.
CATION
- Which transport process is the main mechanism for the movement of most macromolecules by body cells?
- receptor-mediated endocytosis
- If the nucleotide or base sequence of the DNA strand used as a template for messenger RNA synthesis is
- If a tRNA had an AGC anticodon, it could attach to a(n) ________ mRNA codon.
- Which of the following statements is correct regarding RNA
- UGCAA
- UCG
- Messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA play a role in protein synthesis.
- The atomic number is equal to the number of ________. Answer:
- Which cavity contains the bladder, some reproductive organs, and the rectum? Answer:
- protons (and electrons)
- pelvic
- In which stage of mitosis do the identical sets of chromosomes uncoil and resume their chromatin form?
- hoose the following statement that is not completely correct regarding serous membranes.
- telophase
- Visceral pericardium covers the outer surface of the heart, and parietal pericardium lines the internal walls of the heart.
- Which of the following does not serve as a signal for cell division?
- The numbers listed represent the number of electrons in the first, second, and third energy levels, respectively. On this basis, which of the following is an unstable or reactive atom?
- repressor genes
- 2, 8, 1
- Riboswitches are folded RNAs that act as switches to turn protein synthesis on or off in response to
- changes in the environment
- SPECIALIZATION of the CELLS.
- Once solid material is phagocytized and taken into a vacuole, which of the following statements best describes what happens?
- DIFFERENTIATION
- A lysosome combines with the vacuole and digests the enclosed solid material.
- Which statement is the most correct regarding transcription/translation?
- FORMATION of new CELLS; or FORMATION of new INDIVIDUAL.
- The nucleotide sequence in a tRNA anticodon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it except that uracil is substituted for thymine.
- REPRODUCTION

Which of the following statements is most correct regarding the intracellular chemical signals known as "second messengers"?

Cyclic AMP and calcium may be second messengers.

- The main component of the cytosol is
- Which of the following is a principle of the fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure?

- water
- Phospholipids form a bilayer that is largely impermeable to water-soluble molecules.
- The functions of centrioles include ________.
- Which of the following is the major positive ion outside cells?
- organizing the mitotic spindle in cell division
- sodium
- A gene can best be defined as
- In order for the DNA molecule to get "short and fat" to become a chromosome, it must first wrap around small molecules called ________. Answer:
- a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for one polypeptide chain
- histones

Crenation (shrinking) is likely to occur in blood cells immersed in ______.
Caveolae are closely associated with all of the following?

- a hypertonic solution
- lipid rafts, receptors for hormones, enzymes involved in cell regulation.
- Some hormones enter cells via
- A chemical reaction in which bonds are broken is usually associated with
- Which of the following elements is necessary for proper conduction of nervous impulses?
- receptor-mediated endocytosis
- the release of energy
- Na
- Hollow cylinders that connect plasma membranes composed of transmembrane protein are called
- The electron microscope has revealed that one of the components within the cell consists of pinwheel array of 9 triplets of microtubules arranged to form a hollow tube. This structure is a
- connexon
- centriole
Describe two important functions of the Golgi apparatus.
To modify, sort, and package proteins.
- Which type of cell junction acts as anchors and distributes tension through a cellular sheet and reduces the chance of tearing when it is subjected to great mechanical stress?
- desmosomes
- The process of discharging particles from inside a cell to the outside is called
- Salts are always
- Why is anatomical terminology necessary?
- exocytosis
- ionic compounds
- Anatomical terms are precise words that have limited usage, which prevents confusion when describing the location of body parts.
- A bond in which electrons are completely lost or gained by the atoms involved.
- Briefly describe the glycocalyx and its functions.
- Ionic bond
- The glycocalyx is the sticky, carbohydrate-rich area on the cell surface. It helps bind cells together and provides a highly specific biological marker by which cells can recognize each other.
Explain the term genetic code. What does it code for? What are the letters of the code?
The genetic code is the information encoded in the nucleotide base sequence of DNA. A sequence of three bases, called a triplet, specifies an amino acid in a protein. The letters of the code are the four nucleotide bases of DNA designated as A, T, C, and G.

- Why are free radicals so dangerous to cells, and how are they dealt with by the body?
- A charged particle is generally called an ion or electrolyte

- Free radicals are highly reactive chemicals that cause havoc in any cellular environment by reacting with things they should not. Cells with peroxisomes have enzymes specific to reducing free radicals into less reactive chemicals.
- TRUE
- A bond in which electrons are shared equally.
- What processes maintain a steady state "resting" membrane potential?
- Nonpolar covalent bond
- Both diffusion and active transport mechanisms operate within the cell membrane to maintain a resting membrane potential
- Which of the following is NOT a role of cell adhesion molecules
- Why can we say that a cell without a nucleus will ultimately die?
- initiators of cell-to-cell signaling for muscle contraction
- Without a nucleus, a cell cannot make proteins, nor can it replace any enzymes or other cell structures (which are continuously recycled). Additionally, such a cell could not replicate.
- How are the products of free ribosomes different from membrane-bound ribosomes?
- The acidity of a solution reflects the free hydrogen ions in the solution
- Free ribosomes make soluble proteins that function in the cytosol. Membrane-bound ribosomes produce proteins that are to be used on the cell membrane or exported from the cell.
- TRUE
What is the common route of entry for flu viruses into a cell?
Flu viruses and diphtheria toxins use receptor-mediated endocytosis. The virus can attach to the receptors or to the substances the receptors accept to "hitch a ride" into the cell.
How are peroxisomes different from lysosomes?
Peroxisomes contain oxidases that use oxygen to detoxify harmful substances. They are very good at neutralizing free radicals. Peroxisomes directly bud from the ER. Lysosomes contain powerful hydrolytic enzymes that will pretty much destroy anything they come in contact with. They are manufactured by the Golgi apparatus.
Briefly name the subphases of interphase and tell what they do.
G1 - growth phase. The cell is metabolically active and the centriole begins to divide at the end of this phase. S - DNA replicates itself. New histones are made and assembled into chromatin. G2 - Enzymes and proteins are synthesized and centriole replication is completed. This is the final phase of interphase.
- Which of the following is a role of cell adhesion molecules
- The fact that no chemical bonding occurs between the components of a mixture is the chief difference between mixtures and compounds
- anchor cells to molecules in the extracellular space and to each other transmitters of intracellular signals that direct cell migration, proliferation, and specialization mechanical sensors
- TRUE
- Caveolae are closely associated with all of the following except
- What happens in redox reactions?
- A type of bond important in tying different parts of the same molecule together into a three-dimensional structure.
- enzymes involved in cell metabolism
- both decomposition and electron exchange occur
- Hydrogen bond
- Each daughter cell resulting from mitotic cell division has exactly as many chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Introns represent a genome scrap yard that provides DNA segments for genome evolution and a variety of
- Final preparation for cell division is made during the cell life cycle subphase called G2. Lipid rafts, found in the cell
- Lipid rafts, found in the cell outer membrane surface, are concentrating platforms for certain receptor molecules or for protein molecules needed for cell signaling..
- TRUE
- TRUE
- TRUE
- TRUE
- Concentration differences cause ionic imbalances that polarize the cell membrane, and active transport processes.
- The speed of individual particle diffusion is influenced by temperature and particle size, not by concentration.
- Nitric oxide is known to be the first gas to act as a biological messenger.
- There is only one cell type in the human body that has a flagellum.
- TRUE
- TRUE
- TRUE
- TRUE
- Cholesterol helps to stabilize the cell membrane while decreasing the mobility of the phospholipids.
- Interstitial fluid represents one type of extracellular material.
- The orderly sequence of the phases of mitosis is prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- TRUE
- TRUE
- TRUE
- Which of the following would be regarded as an organic molecule?
- What is a chain of more than 50 amino acids called?
- Choose the answer that best describes fibrous proteins.
- CH4
- protein
- are very stable and insoluble in water

- What level of protein synthesis is represented by the coiling of the protein chain backbone into an alpha helix?
- A bond in which electrons are shared unequally

- secondary structure
- Polar covalent bond
- Carbohydrates and proteins are built up from their basic building blocks by the
- Which of the following does not describe uses for the ATP molecule?
- removal of a water molecule between each two units
- pigment structure
- Choose the answer that best describes HCO3-.
- It is the difference in the R group that makes each amino acid chemically unique
- a bicarbonate ion
- TRUE

The ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them is called?.

responsiveness or excitability
.gif)
What is the ratio of fatty acids to glycerol in neutral fats?
Neutral fats have a________ ratio of fatty acids to glycerol.
.gif)
3:1
is fat soluble, produced in the skin on exposure to UV radiation, and necessary for normal bone growth and function
VITAMIN D
The four elements that make up about 96% of body matter are
carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
Molecules such as methane that are made of atoms that share electrons have ________ bonds. Answer:
covalent

Atom X has 17 protons. How many electrons are in its valence shell?

7
Which property of water is demonstrated when we sweat?
high heat of vaporization
Which protein types are vitally important to cell function in all types of stressful circumstances?
molecular chaperones
If atom X has an atomic number of 74 it would have which of the following?
74 protons
The atomic weight is only an average of relative weights of an atom and its isotopes, and it may vary from the weight of a specific isotope
TRUE
What does the formula C6H12O6 mean
There are, 6 carbon, 12 hydrogen, and 6 oxygen atoms.
Explain the difference between potential and kinetic energy.
Potential energy is inactive stored energy that has potential to do work. Kinetic energy is energy in action.
How can phospholipids form a film when mixed in water?
Phospholipids have both polar and nonpolar ends. The polar end interacts with water, leaving the nonpolar end oriented in the opposite direction.
Select the most correct statement regarding nucleic acids.
DNA is a long, double-stranded molecule made up of A, T, G, and C bases.
Which of the following statements is false?
A)The more hydrogen ions in a solution, the more acidic the solution.
B)The pH of blood is slightly basic.
C)When the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, the hydroxyl ion concentration also decreases.
D)When acids and bases are mixed, they react with each other to form water and a salt
Which of the following statements is false?
A)Catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions, sometimes while undergoing reversible changes in shape.
B)Larger particles move faster than smaller ones and thus collide more frequently and more forcefully.
C)Chemical reactions progress at a faster rate when the reacting particles are present in higher numbers.
D)Chemical reactions proceed more quickly at higher temperatures.
Select the most correct statement.
A)The endocrine system is not a true structural organ system.
B)Organ systems operate independently of each other to maintain life.
C)The immune system is closely associated with the lymphatic system.
D)Organ systems can be composed of cells or tissues, but not both.
Which of the following are survival needs of the body?
nutrients, water, atmospheric pressure, and oxygen
One of the functional characteristics of life is excitability or responsiveness. This refers to
Sensing changes in the environment and then reacting or responding to them
What does the "principle of complementarity of structures and function" mean? Answer:
What a structure can do depends on its specific form, or "structure determines function."
______ is explained by chemical and physical principles and is concerned with the function of specific organs or organic systems. Answer:
Physiology
Which of the following imaging devices would best localize a tumor in a person's brain?
MRI
_ _ physiology concerns urine production and kidney function. Answer:
Renal
What is the function of the serous membranes? Answer:
They act to reduce friction and allow the organs to slide across cavity walls.
Fully describe the anatomical position for the human body. Answer:
The body is erect, arms hanging at the sides, palms forward, and thumbs pointed away from the midline.
Which of the following statements is the most correct regarding homeostatic imbalance?
It is considered the cause of most diseases.
- Provides support and levers for muscles to pull
- Homeostasis is the condition in which the body maintains
- The study of large body structures, visible to the naked eye, such as the heart is called ________ anatomy.
- Histology would be best defined as a study of
- Skeletal
- a relatively stable internal environment, within limits.
- gross
- tissues
- HEAD, NECK, THORAX, ABDOMEN, PELVIS.
- UPPER LIMBS, LOWER LIMBS.
- AXIAL PART:
- APPENDICULAR PART

- The anatomical position is characterized by all of the following except ________.
- Protects underlying organs from environmental damage and synthesizes vitamin D

- palms turned posteriorly
- Integumentary
- Which of the following statements is true concerning feedback mechanisms?
- Negative feedback mechanisms work to prevent sudden severe changes within the body.
- Delivers oxygen and nutrients to the tissues
- Controls the body with chemical molecules called hormones.
- Produces antibodies that attach to foreign substances
- esponds to environmental changes by transmitting electrical impulses
- Cardiovascular
- Endocrine
- Immune
- Nervous

-
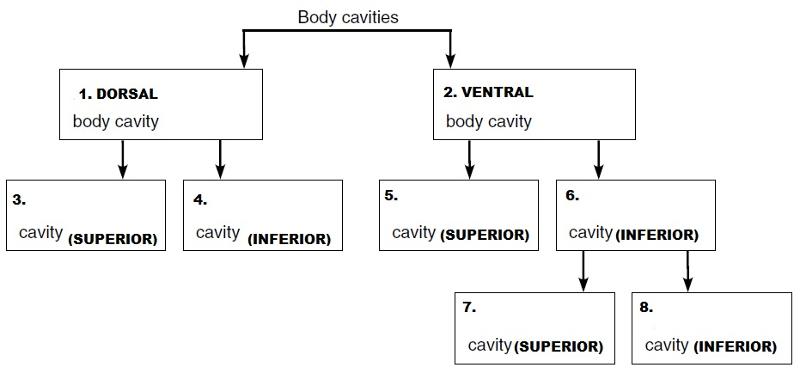
is located near the back of the body. It is divided
into TWO CAVITIES:
- Formed by the CRANIAL BONES; it houses the BRAIN.
- Formed by VERTEBRAE of the backbone, it contains SPINAL CORD, and ROOTS of SPINAL NERVES.

- THE DORSAL (POSTERIOR) BODY CAVITY:
- CRANIAL CAVITY:
- VERTEBRAL (SPINAL) CAVITY:
a type of bond important in tying different parts of the same molecule together into a three-dimensional structure
hydrogen bond
- a bond in which electrons are NOT shared equally
- a bond in which electrons are completely lost or gained by the atoms involved
- a bond in which electrons are equally shared
- polar covalent bond
- ionic bond
- nonpolar covalent bond
electrically charged particle from gain of an electron
anion

- subatomic particle with no charge
- smallest particle of an element that retains is properties
- smallest particle of a compound that still retains its properties

- neutron
- atom
- molecule
electrically charged particle from loss of an electron
CATION
- phospholipids
- triglycerides
- major component of cell membranes
- used for energy storage and for insulation
- fatty acids with all single bonds between carbon atoms
- fatty acids with one double bond between carbon atoms
- fatty acids with more than one double bond between carbon atoms
- trans fats
- omega-3 fats
- saturated
- monounsaturated
- polyunsaturated
- ”bad” fats
- ”good” fats
- A + B → AB
- AB → A + B
- AB + C → AC + B
- A + B ←→ AB
- synthesis reaction
- decomposition
- exchange reaction
- reversible reaction
- the linear sequence of amino acids comprising a protein chain
- composed of alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets
- alpha-helical or beta-pleated regions folded upon each other
- two or more proteins aggregated together
- primary structure
- secondary structure
- tertiary structure
- quaternary structure
- legs moving the pedals of a bicycle
- energy released to do cellular work when the bonds of ATP are broken
- energy that travels in waves; part of the electromagnetic spectrum
- represented by the flow of charged particles along a conductor or the flow of ions across a membrane
- mechanical energy
- chemical energy
- radiant energy
- electrical energy
-
The genetic code consists of the sequence of
bases in ________ molecules -
The genetic code is transcribed to the sequence
of bases in _____ molecules.
Protein Synthesis
- DNA
- mRNA
Protein Synthesis
-
Molecule that carries instructions for protein
synthesis to ribosomes. -
Molecule that carries amino acids to ribosome
for addition to amino acid chain. -
Small molecules that join to form a protein
during translation.
- mRMA
- tRNA
- Amino acids
Protein Synthesis

1 ) Division of the cytoplasm.
2) Replication of chromosomes.
3) Chromosomes appear as threadlike bodies.
4) Chromatids move toward ends of spindle.

- Telophase
- Interphase
- Prophase
- Anaphase
- New nuclei start to form.
- Occupies most of cell cycle
- Chromosomes line up at equator of spindle.
- Cell performs its normal functions.
- Telophase
- Interphase
- Metaphase
- Interphase
- Diffusion of water.
- Engulfment of liquid droplets.
- Osmosis
- Pinocytosis
- Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
- Results from random molecular movement.
- Diffusion
- Diffusion; Osmosis
The source of energy captured in ATP. ______.
Glucose
The building blocks of nucleic acids are
Nucleotides

- The heart lies specifically in the _____ space.
- ORGANS FOUND IN THE THORACIC CAVITY
- Which of these is not part of the dorsal cavity?

- Thoracic cavity
- HEART, LUNGS
- THORACIC CAITY
- The _____ system plays a role in moving fluids, wastes, and bones?
- Directly causes mechanical motion
- Muscular
The _____ system plays a role in moving fluids, wastes, and bones?
Excretory
The lower ribs are below the _____ region
Hypochondriac
Sum of all CHEMICAL PROCESSES that keep our bodies alive and healthy. It is divided into 2 phases (parts): CATABOLISM & ANABOLISM:
METABOLISM

The central abdominal area is the _____ region.

Hypogastric

A _____ fracture occurred in the elbow area.

dorsum

The process of turning molecules that are ingested into forms that are compatible with the organism is _____.

Assimilation

The force that water exerts on a system is referred to as the ________.

Hydrostatic pressure
a vertical line which divides the body into a left section and a right section.
Sagittal plane
a vertical line which divides the body into a front (anterior) section and back (posterior) section.
Coronal plane

a horizontal line which divides the body into an upper (superior) section and a bottom (inferior) section. The plane divides the body into top and bottom.

Transverse plane
subunits that make up nucleic acids
Nucleotides
the chemical bond that links two amino acids by connecting the amino group of one amino acid to the acid group of another
Peptide bond
a lipid containing phosphate group
phospholipids
a molecule made of many similar subunits
Polymer
a long chain of amino acids
polypeptide
one of two kinds of information-carrying nucleic acids found in cells; ribonucleic acid
RNA
- a class of lipids with a structure that is different from other lipids; cholesterol, testosterone, and estrogen are three well-known steroids
- SEX HORMONES
- Steroids
compounds composed of a glycerol molecule with three fatty acids attached
Triglycerides
adenosine triphosphate; a nucleotide composed of an adenine base, a sugar, and three phosphate groups
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
pairs of complementary nucleic acid bases; that is, A and T or C and G
base pair
a polymer of nucleotides with the bases adenosine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine; deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA
- proteins that speed up specific biological reactions
- Enzymes may be damaged by high temperature. Enzymes have the ability to accelerate reactions as much as a billion-fold. Enzymes may use coenzymes derived from vitamins or cofactors from metallic elements.
- ENZYMES
a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylic acid group at one end.
Fatty Acids
- the main form of sugar that circulates in the blood
- elect which reactions will usually be irreversible regarding chemical equilibrium in human bodies
- Glucose
- glucose to CO2 and H2O
- In a DNA molecule, guanine would connect to ________.
- An increased rate of breathing as a result of an increased buildup of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream would be best described as an example of
- cytosine
- excretion of metabolic waste
fatty molecules that dissolve poorly in water but dissolve well in a nonpolar solvent; fats and oils
Lipids
Apoptosis is programmed cell suicide; cancer cells do not undergo this process
TRUE
key information-carrying molecules in cells
nucleic acids
The coronal plane divides the body into _____ and _____ portions.
Posterior and anterior
The plane divides the body into left and right
portions.
MEDIAN OR MIDSAGITAL
TOWARDS THE POINT OF REFERENCE
PROXIMAL
The plane divides the body into front and back.
FRONTAL OR CORONAL
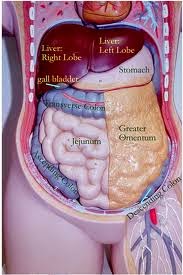
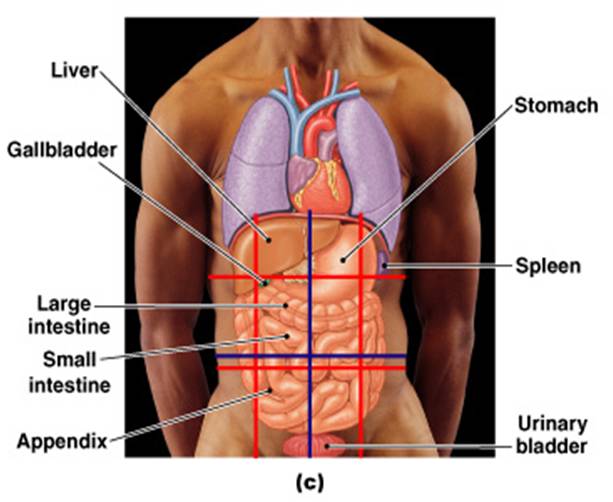
ORGANS FOUND IN THE ABDOMINAL
CAVITY
STOMACH, LIVER, SPLEEN, PANCREASE, PART OF THE LARGE INTENSITNE, PART OF SMALL INTESTINE.
DISTAL
AWAY FROM THE POINT OF REFERENCE
lateral
Towards the side
ORGANS FOUND IN THE PELVIC CAVITY
UTERUS, BLADDER, OVERIES
CORONAL
ANOTHER NAME FOR THE FRONTAL PLANE
SUPERFICIAL
TOWARDS THE SURFACE
What must happen before a cell can begin mitosis?
The chromosomes must be duplicated.
The centrosomes move away from each other and the nuclear envelope breaks up during which phase of mitosis?
prophase
The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell during which phase of mitosis?
Metaphase
The sister chromatids separate and begin moving toward opposite poles of the cell during which phase of mitosis?
Anaphase
The chromosomes arrive at the poles and nuclear envelopes form during which phase of mitosis?
Telophase
The spindle now can move into the center of the cell.
Kinetochores develop, which are linked to the chromosomes.
Prometaphase
The chemical symbol O=O means
the atoms are double bonded
What does CH4 mean?
There is one carbon and four hydrogen atoms.
- Which vesicular transport process occurs primarily in some white blood cells and macrophages?
- Engulfment of small particles.
- phagocytosis
An atom with a valence of 3 may have a total of ________ electrons.
NUMBER 13
AB → A + B is an example of a(n) ________ reaction. Answer:
Decomposition
Homogeneous, will not settle.
SOLUTIONS
Sucrose is a?
disaccharide
- ________ is the division of the cytoplasmic mass into two parts.
- Answer: At the end of the mitotic (M) phase, the cytoplasm divides in a process called ________.
- Cytokinesis
- WATER IS?
- The single most abundant chemical substance of the body, accounting for 60% to 80% of body weight, is
- What is the single most abundant chemical substance in the body? Answer:
- COMPOUND and MOLECULE ( H2O,)
- WATER
- WATER
Choose the anatomical topic and definition that is not correctly matched.
Cytology: study of the structures in a particular region.
Which of the following is an example of a suspension?
BLOOD
In which quadrant of the abdominopelvic cavity is the stomach located?
LEFT UPPER QUADRANT
eicosanoids
REGULATE INFLAMMATION
- Why must a normal body temperature be maintained in order for chemical reactions to be continued at life-sustaining rates?
- If body temperature is too low, chemical reactions slow and eventually stop. If body temperature is too high, chemical reactions speed up and body proteins lose their normal shape, resulting in loss of function.
What major chemical is responsible for apoptosis?
caspases
Energy that travels in waves. Part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
RADIANT ENERGY
Amino acids joining together to make a peptide is a good example of a(n) ______ reaction.
synthesis
molecule and compound
mean the same thing and can be used interchangeably.
A chemical bond is an energy relationship between outer electrons and neighboring atoms.
TRUE
Microtubules are hollow tubes made of subunits of the protein tubulin.
TRUE
In the compound H2CO3, what do the numbers 2 and 3 represent?
The 2 indicates that there are two hydrogen atoms in the compound and the 3 indicates that there are three oxygen atoms in the compound.
The most common extracellular ion is ________. Answer:
sodium
Which of the following is a function of a plasma membrane protein?
molecular transport through the membrane
A process by which large particles may be taken into the protection of the body by invaders like bacteria, or for disposing of old or dead cells is called phagocytosis
TRUE