Which of the following is true concerning the number and type of
permanent teeth?
A) There are 32 permanent teeth, and the wisdom
teeth are the last to emerge.
B) There are 27 permanent teeth,
and the first molars are usually the last to emerge.
C) The
number of permanent teeth is always equal to the number of primary
teeth.
D) The number of upper permanent teeth is not equal to
the number of lower permanent teeth.
A) There are 32 permanent teeth, and the wisdom teeth are the last to emerge.
The salivary glands are composed of which two types of secretory
cells?
A) goblet cells and squamous epithelial cells
B)
parietal cells and glial cells
C) serous cells and mucous cells
D) cuboidal epithelium and ciliated columnar cells
C) serous cells and mucous cells
In addition to storage and mechanical breakdown of food, the stomach
________.
A) initiates protein digestion and denatures proteins
B) is the first site where absorption takes place
C) is
the only place where fats are completely digested
D) is the first
site where chemical digestion of starch takes place
A) initiates protein digestion and denatures proteins
Hydrochloric acid is secreted by which of the secretory cells of the
stomach?
A) chief cells
B) parietal cells
C) serous
cells
D) mucous neck cells
B) parietal cells
There are three phases of gastric secretion. The cephalic phase
occurs ________.
A) before food enters the stomach and is
triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
B) immediately after food
enters the stomach, preparing the small intestine for the influx of a
variety of nutrients
C) at the end of a large meal, and the
juices secreted are powerful and remain in the GI tract for a long
period of time
D) when the meal is excessively high in acids and
neutralization is required
A) before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
Gastrin is a digestive hormone that is responsible for the
stimulation of acid secretions in the stomach. These secretions are
stimulated by the presence of ________.
A) starches and complex
carbohydrates
B) protein and peptide fragments
C) simple
carbohydrates and alcohols
D) fatty acids
B) protein and peptide fragments
You have just eaten a meal high in complex carbohydrates. Which of
the following enzymes will help to digest the meal?
A) gastrin
B) amylase
C) cholecystokinin
D) trypsin
B) amylase
The enzymatic breakdown of any type of food molecule is called
________.
A) diffusion
B) active transport
C)
hydrolysis
D) denatured
C) hydrolysis
Parietal cells of the stomach produce ________.
A) mucin
B) pepsinogen
C) hydrochloric acid
D) rennin
C) hydrochloric acid
Which of the following is not a phase of gastric secretion?
A)
cephalic
B) gastric
C) intestinal
D) enterogastric
D) enterogastric
Chief cells ________.
A) occur in the intestine
B)
produce HCl
C) are found in the basal regions of the gastric
glands
D) produce mucin
C) are found in the basal regions of the gastric glands
The ________ contains lobules with sinusoids (lined with macrophages)
that lead to a central venous structure.
A) liver
B)
spleen
C) pancreas
D) stomach
A) liver
The terminal portion of the small intestine is known as the ________.
A) duodenum
B) ileum
C) jejunum
D) pyloric sphincter
B) ileum
Digestion of which of the following would be affected the most if the
liver were severely damaged?
A) lipids
B) carbohydrates
C) proteins
D) starches
A) lipids
Important peritoneal folds do not include the ________.
A)
omenta
B) peritoneum
C) mesentery
D) round ligament
D) round ligament
________ is (are) not important as a stimulus in the gastric phase of
gastric secretion.
A) Distension
B) Carbohydrates
C)
Peptides
D) Low acidity
B) Carbohydrates
The function of the goblet cells is to ________.
A) absorb
nutrients from digested food and store them for future use
B)
produce mucus that protects parts of the digestive organs from the
effects of powerful enzymes needed for food digestion
C) secrete
buffers in order to keep the pH of the digestive tract close to
neutral
D) provide protection against invading bacteria and
other disease-causing organisms that enter the digestive tract in food
B) produce mucus that protects parts of the digestive organs from the effects of powerful enzymes needed for food digestion
Nervous control of gastric secretion is provided by ________.
A) somatic neurons in the spinal cord
B) the vagus nerve
and enteric plexus
C) the rubrospinal tracts
D) the
reticulospinal and vestibulospinal tracts
B) the vagus nerve and enteric plexus
Which of the following produce intrinsic factor?
A) parietal
cells
B) zymogenic cells
C) mucous neck cells
D)
enteroendocrine cells
A) parietal cells
Which of the following enzymes is specific for proteins?
A)
dextrinase
B) amylase
C) trypsin
D) lipase
C) trypsin
Surgical cutting of the lingual frenulum would occur in which part of
the body?
A) tongue
B) esophagus
C) nasal cavity
D) salivary glands
A) tongue
The layer of the digestive tube that contains blood vessels,
lymphatic nodes, and a rich supply of elastic fibers is the ________.
A) mucosa
B) submucosa
C) muscularis externa
D) serosa
B) submucosa
What stomach secretion is necessary for normal hemoglobin production
in RBCs?
A) HCl
B) pepsinogen
C) intrinsic factor
D) gastric lipase
C) intrinsic factor
Select the correct statement about the regulation of gastric
secretion.
A) Vagus stimulation of the stomach results in
decreased secretion of gastric juice.
B) The presence of food in
the stomach prevents hormonal control of gastric secretion.
C)
Gastric secretion can be stimulated before food has entered the mouth.
D) Gastric secretion is enhanced by very low pH (below a pH of 2).
C) Gastric secretion can be stimulated before food has entered the mouth.
Select the correct statement about digestive processes.
A)
Enterogastrone is a hormone that helps increase gastric motility.
B) Pepsin is an enzyme produced by the stomach for the purpose
of starch digestion.
C) Chyme entering the duodenum can decrease
gastric motility via the enterogastric reflex.
D) All commonly
ingested substances are significantly absorbed by the mucosa of the stomach.
C) Chyme entering the duodenum can decrease gastric motility via the enterogastric reflex
Select the correct statement about absorption.
A) Eighty
percent of ingested materials have been absorbed by the end of the
large intestine.
B) Carbohydrates diffuse across the villus
epithelium and are then actively transported into blood
capillaries.
C) If intact proteins are transported across the
villus epithelium, an immune response may be generated.
D) Amino
acid transport is linked to chloride transport.
C) If intact proteins are transported across the villus epithelium, an immune response may be generated.
You have just eaten french fries, buttered toast, ice cream, and
whole milk. Which of the following glands would be active in helping
you to digest this food?
A) the pancreas
B) the buccal
glands
C) the thyroid gland
D) the parotid glands
A) the pancreas
A baby is admitted to the hospital with a history of projectile
vomiting after each feeding. On examination, it is found that the
sphincter controlling food passage from the stomach to the duodenum is
thickened and does not open readily. Because of the baby's loss of
gastric juice, his blood probably indicates ________.
A)
acidosis
B) ketosis
C) alkalosis
D) dysphagia
C) alkalosis
Which of these is not part of the splanchnic circulation?
A)
hepatic portal vein
B) inferior vena cava
C) superior
mesenteric artery
D) celiac artery
B) inferior vena cava
There are some 20 known pathogens found in the large intestine; our
Ig ________ antibody-mediated response restricts them from going
beyond the mucosa and causing problems.
A) D
B) A
C)
M
D) E
B) A
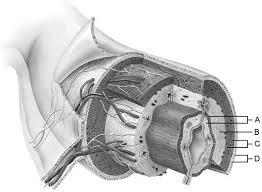
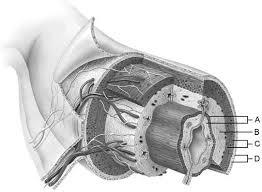
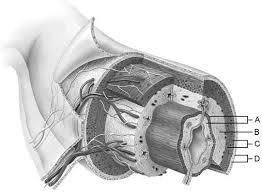
Mucosa
A
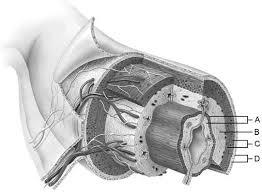
Duodenal glands found here
B
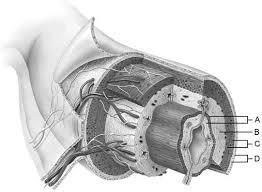
Smooth muscle layer.
C
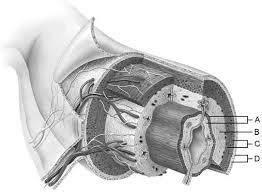
Serosa.
D
Area of the lamina propria
A
Continuation of the mesentery
D
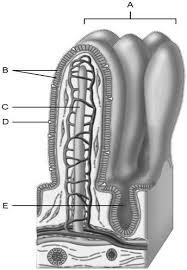
Absorptive cells that line the intestinal tract
B
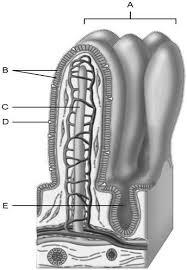
Cell type specialized to secrete mucus into the lumen of the intestinal tract.
D
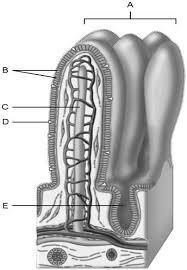
Wide lymph capillary located in the villus.
C
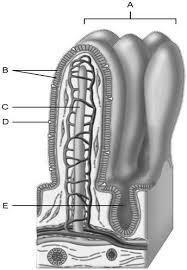
Paneth cells are found here.
E
A fluid secreted into the small intestine during digestion that
contains cholesterol, emulsification agents, and phospholipids is
________.
A) bile
B) pancreatic juice
C) intestinal
juice
D) gastric juice
A) bile
Which of the following is not characteristic of the large intestine?
It ________.
A) does not contain villi
B) exhibits
external muscular bands called teniae coli
C) is longer than the
small intestine
D) has haustra
C) is longer than the small intestine
How are most nutrients absorbed through the mucosa of the intestinal
villa?
A) simple diffusion
B) facilitated diffusion
C) active transport driven directly or indirectly by metabolic
energy
D) bulk flow
C) active transport driven directly or indirectly by metabolic energy
Paneth cells ________.
A) are more common in the ileum than in
the jejunum
B) are absorptive cells in the small intestine
C) secrete enzymes that kill bacteria
D) are located next
to the lacteal in a villus
C) secrete enzymes that kill bacteria
Chemical digestion in the small intestine involves ________.
A)
a significant amount of enzyme secretion by the intestinal mucosa
B) cholecystokinin (CCK), an intestinal hormone responsible for
gallbladder contraction
C) secretions from the spleen that
contain all enzymes necessary for complete digestion
D) bile
salts that help emulsify carbohydrates so that they can be easily
digested by enzymatic action
B) cholecystokinin (CCK), an intestinal hormone responsible for gallbladder contraction
Select the correct statement about electrolyte absorption.
A)
Chlorine ion absorption is coupled to glucose and amino acid
transport.
B) Potassium moves across the epithelium by active
transport.
C) If vitamin B is not present, calcium is not
absorbed.
D) Iron and calcium are absorbed mostly by the duodenum.
D) Iron and calcium are absorbed mostly by the duodenum
The ingestion of a meal high in fat content would cause which of the
following to occur?
A) Severe indigestion would occur, caused by
the lack of sufficient digestive enzymes.
B) This type of food
would cause secretion of gastrin to cease, causing digestive upset.
C) Bile would be released from the gallbladder to emulsify the
fat in the duodenum.
D) The acid secretions from the stomach
would be sufficient to digest this food.
C) Bile would be released from the gallbladder to emulsify the fat in the duodenum.
Which hormone causes an increased output of enzyme-rich pancreatic
juice and stimulates gallbladder contraction to release bile?
A)
gastrin
B) secretin
C) cholecystokinin CCK
D)
gastric inhibitor peptide
C) cholecystokinin CCK
Which of these is not a component of saliva?
A) lysozyme
B) a cyanide compound
C) defensins
D) nitric oxide
D) nitric oxide
The mechanical and chemical receptors that control digestive activity
are located ________.
A) in the glandular tissue that lines the
organ lumen
B) in the walls of the tract organs
C) in the
pons and medulla
D) only in the esophagus because this is the
only part of the tract that needs to change to accommodate food passage
B) in the walls of the tract organs