What is the correct order for the application of Koch's postulates?
I. Inoculate suspect agent into test subject and observe that subject develops disease of interest
II. Isolate and culture suspect agent in the laboratory
III. Find suspect agent is every case of disease of interest but not in healthy hosts
IV. Recover and isolate suspect agent from test subject
a. IV, I, II, III
b. I, II, III, IV
c. III, I, IV, II
d. III, II, I, IV
E. IV, I, III, II
d. III, II, I, IV
Recombination of genetic material between homologous chromosomes occurs during:
a. late prophase II of meiosis
b. prophase of mitosis
c. metaphase I of meiosis
d. metaphase of mitosis
e. early prophase I of meiosis
e. early prophase I of meiosis
Which of the following is a cell type produced during sexual reproduction in fungi?
a. haustoria
b. pneumocyst
c. sporanglospore
d. dikaryon
e. mycorrhiza
d. dikaryon
Which of the following is a particle found in the nucleus of an atom and that has no electrical charge?
a. neutron
b. element
c. proton
d. electron
e. isotope
a. neutron
Which of the following are magnifying lenses?
a. dark-field stops
b. objectives
c. oculars
d. condensers
e. both objectives and the oculars
e. both the objectives and the oculars
Members of the genus Chlamydia are:
a. classified with the deeply branching bacteria
b. thermophiles
c. endospore-formers
d. intracellular parasites
e. gram-positive bacteria
D. intracellular parasites
Which of the following types of animal viruses requires RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase to be replicated?
a. retroviruses
b. -ssRNA viruses
c. +ssRNA viruses
d. ssDNA viruses
e. dsDNA viruses
b. -ssRNA viruses
Anna is conducting an experiment using a pH indicator that is red at low pH, green at neutral pH, and purple at high pH. She starts with a green solution. When she adds compound X to her solution it turns purple. The she as compound Z to the solution and it turns green. She adds more Z and the solution remains green. These observations suggest X is _____ and Z is _____.
a. a base; a buffer
b. a base; a strong acid
c. an acid; a base
d. an acid; a buffer
e. a buffer; a base
a. a base; a buffer
Zones of clearing in cell cultures that are the result of virus infection are called plaques. Sometimes “cloudy plaques” are seen on bacterial cultures infected with bacteriophage. What type of viral infection might cause this appearance?
a. prion
b. lytic
c. transducing
d. viroid
e. lysogenic
e. lysogenic
Which of the following statements concerning glycolysis is TRUE?
a. glycolysis occurs in the cell membrane of bacteria
b. glycolysis is an alternative to fermentation
c. ribulose 5-phosphate is an intermediate of glycolysis
d. glycolysis produces ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
e. glycolysis both requires the input of ATP and produces ATP
e. glycolysis both requires the input of ATP and produces ATP
Which of the following is an accurate description of a virion?
a. the protein portion of a viral particle
b. an infectious particle of protein and nucleic acid outside a host cell
c. a population of infectious particles
d. the nucleic acid of a viral pathogen inside a host cell
e. the nucleic acid of a viral pathogen
b. an infectious particle of protein and nucleic acid outside a host cell
The _____ is the entire interwoven mass of one multicellular fungal organism.
a. mycelium
b. pseudoplasmodium
c. sporangium
d. conidiophore
e. hyphae
a. mycelium
You are performing an experiment in your chemistry lab class. The directions advise caution because the reaction is exothermic. Which of the following is the hazard the directions warn about?
a. the reaction will generate radiation
b. the reaction may cause the container to become dangerously hot
c. the reaction may cause the container to freeze and break
d. the reaction will produce a noxious vapor
e. the reaction will generate enough light to require eye protection
b. the reaction may cause the container to become dangerously hot
Aristotle was an early natural philosopher who formulated the
a. scientific method
b. theory of natural selection
c. germ theory of disease
d. theory of "magic bullets"
e. theory of spontaneous generation (abiogenesis)
e. theory of spontaneous generation (abiogenesis)
When mitosis occurs without cytokinesis, which of the following is produced?
a. chromatids
b. coenocytes
c. cysts
d. macronuclei
e. merozoites
b. coenocytes
The Gram-negative diplococci _____ are pathogenic members of the Betaproteobacteria that infect mammalian mucous membranes.
a. Streptococcus
b. Haemophilus
c. Neisseria
d. Coxiella
e. Listeria
c. Neisseria
Small circular RNA molecules without capsids are characteristics of
a. plasmids
b. viroids
c. viruses
d. prions
e. viruses and prions
b. viroids
Which of the following statements concerning prokaryotic flagella is TRUE?
a. Treponema is an example of a bacterium that has a tuft of polar flagella
b. Prokaryotic flagella are anchored in cytoplasm
c. Prokaryotic flagella rotate like a drive shaft
d. a "run" results form clockwise movement of the flagellum
e. Prokaryotic flagella are composed of tubulin
c. Prokaryotic flagella rotate like a drive shaft
A microorganism found living under conditions of high _____ is a barophile.
a. salt concentrations
b. pH values
c. hydrostatic pressure
d. carbon dioxide levels
e. oxygen concentrations
c. hydrostatic pressure
Which of the following is an INCORRECT pairing?
a. quaternary structures; two or more polypeptides
b. primary structure; amino acid sequence
c. tertiary structure; covalent bonds
d. secondary structure; disulfide bridges
e. secondary structure; B-pleated sheets
d. secondary structure; disulfide bridges
Lasers are used to generate the images produced by ____ microscopes.
a. phase-contrast
b. atomic force
c. fluorescent
d. confocal
e. both confocal and atomic force
b. atomic force
All of the following are ways in which cells regulate metabolism EXCEPT:
a. use of the same coenzymes for anabolic and catabolic reactions that share substrate molecules
b. synthesis of a catabolic enzyme only when its substrate is available
c. isolation of various enzymes within membranous organelles
d. feedback inhibition by end products
e. synthesis or degradation of membrane transport proteins
a. use of the same coenzymes for anabolic and catabolic reactions that share substrate molecules
Pleomorphic Gram-negative members of the Firmicutes that colonize mammalian respiratory mucous membranes are the:
a. Rickettsias
b. Actinobacteria
c. Clostridia
d. Mycobacteria
e. Mycoplasmas
e. mycoplasmas
The accumulation of glucose 6-phosphate inside a bacterial cell via phosphorylation of glucose is an example of
a. osmosis
b. diffusion
c. facilitated diffusion
d. group translocation
e. plasmolysis
d. group translocation
A reaction requires water as a reactant produces heat. What type of reaction is likely to be involved?
a. a synthesis reaction
b. a decomposition reaction
c. a hydrolysis reaction
d. an exchange reaction
e. the answer cannot be determined with the available information
b. a decomposition reaction
what was the first disease shown to be bacterial in origin?
a. yellow fever
b. anthrax
c. tuberculosis
d. malaria
e. cholera
b. anthrax
which of the following was NOT an aspect of Pasteur's experiments to disprove spontaneous generation?
a. the necks of the flasks he used were bent into an S-shape
b. the flasks he used were sealed with corks
c. he boiled the infusions to kill any microbes present
d. the flasks were free of microbes until they were opened
e. the flasks were incubated for very long periods of time
b. the flasks he used were sealed with corks
Which of the following questions largely stimulated the research of microbes during what is known as the Golden Age of Microbiology?
a. how are microns related?
b. what causes disease, and is spontaneous generation of microbes possible?
c. how should living organisms be classified?
d. how do genes work?
e. how can microorganisms be seen?
b. what causes disease, and is spontaneous generation of microbes possible?
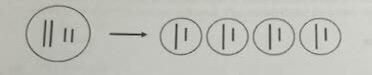
which process is represented by this figure?
a. budding
b. mitosis
c. meiosis
d. Schizogony
e. cytokinesis
c. meiosis
what functional groups are present in ALL amino acids?
a. carboxyl groups
b. amino groups
c. amino and carboxyl groups
d. amino and sulfhydryl groups
e. hydroxyl groups
b. amino groups
Which of the following is a feature shared by viruses and living organisms?
a. metabolic capability
b. responsiveness
c. possession of a genome that directs synthesis of materials necessary for replication
d. presence of cytoplasm
e. the ability to increase in size
c. possession of a genome that directs synthesis of materials necessary for replication
the genus Mycobacterium includes species responsible for
a. gastric ulcers
b. tuberculosis
c. food poisoning from contaminated dairy products
d. urinary tract infection
e. food poisoning from rice
b. tuberculosis
which of the following is an approach to preventing the formation of biofilms?
a. digesting matrix molecules
b. triggering the production of streamers
c. stimulating quorum sensing receptors
d. increasing quorum sensing
e. blocking the activity of carbohydrate catabolism
d. increasing quorum sensing
which of the following statements is TRUE concerning the fluid mosaic model?
a. small water soluble molecules move freely across the bilayer
b. the phospholipids form a rigid structure
c. membrane proteins are free to move in two dimensions in the bilayer
d. the integrated proteins are firmly cemented in place relative to each other
e. the phospholipids rotate across the bilayer from one fast to the other
c. membrane proteins are free to move in two dimensions in the bilayer
Safranin dye is used as the counterstain in _____ strain(s).
a. the endospore
b. the acid-fast
c. the Gram
d. the flagellar
e. both the Gram and the endospore
e. both the Gram and the endospore
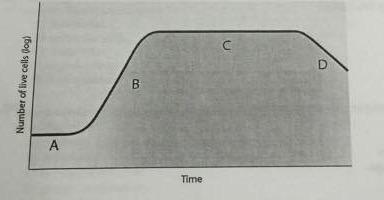
the correction sequence for the phases indicated by the letters A, B, C, and D is:
a. death phase, stationary phase, log phase, lag phase
b. stationary phase, lag phase, log phase, death phase
c. death phase, log phase, stationary phase, lag phase
d. log phase, stationary phase, lag phase, death phase
e. lag phase, log phase, stationary phase, death phase
e. lag phase, log phase, stationary phase, death phase
during which growth phase do antimicrobial drugs have the greatest inhibitory effect?
a. stationary phase
b. death phase
c. lag phase
d. log phase
e. the susceptibility is the same for all phases
d. log phase
which of the following is characteristic of proteins?
a. They are composed of carbohydrate
b. they have multiple layers of structural organization
c. they are primarily hydrophobic
d. they are composed of nucleic acids
e. their secondary structure is composed of B-helices
b. they have multiple layers of structural organization
which of the following statements concerning Koch's postulates is FALSE?
a. all of Koch's postulates must be satisfied before an organization can be shown to cause a particular disease
b. a suspected pathogen must be able to be grown in the laboratory
c. the suspected pathogen may not be present in all cases of the disease being studied
d. Koch's postulates involve the experimental infection of susceptible hosts
e. Koch's postulates cannot be used to demonstrate the cause of all diseases
c. the suspected pathogen may not be present in all cases of the disease being studied
A gram stain of a tissue sample from a patient shows Gram-negative spheres that can barely be resolved on the best light microscope. A transmission electron micrograph reveals the spheres have a double membrane but no cell wall. The intracellular parasites are likely to be a:
a. Rickettsia
b. Coxiella
c. Listeria
d. Chlamydia
e. Mycoplasma
d. Chlamydia
how is the HIV provirus different from a lambda-phage prophage?
a. all the offspring of a cell infected with a prophage will contain the virus
b. lambda phage-infected cells produce virus slowly over time
c. the HIV provirus is integrated permanently into the host cell's DNA
d. all subsequent generation of HIV-infected cells carry the provirus
e. the HIV provirus is inactive inside the host cell
c. the HIV provirus is integrated permanently into the host cell's DNA
if a microbiology lab student left the safranin out of the Gram stain procedure, what would be the result?
a. Gram-positive cells would be purple and Gram-negative cells would be colorless
b. Gram-positive cells would be pink and Gram-negative cells would be purple
c. Gram-positive cells would be colorless and Gram-negative cells would be purple
d. all cells would be pink
e. all cells would be purple
a. Gram-positive cells would be purple and Gram-negative cells would be colorless
a flexible, spiral-shaped bacterium is called a:
a. spirillum
b. sarcina
c. vibrio
d. coccobacillus
e. spirochete
e. spirochete
A laboratory protocol lists the following ingredients: 1 g sucrose, 16.4 g Na2HPO4, 1.5 g (NH4)3PO4, 0.02 g CaCO3, KNO3, water to 1 liter and autoclave. This recipe is for a __________ medium.
a. complex enrichment broth
b. defined broth
c. defined agar
d. complex broth
e. complex agar
b. defined broth
fungi called Deuteromycetes are not known to reproduce sexually. Nonetheless, most of them are considered members of the _____ on the bases of genetic sequences.
a. Ascomycota
b. Rhizaria
c. Basidiomycota
d. Zygomycota
e. Sporozoa
a. Ascomycota
which of the following molecules would be expected to cross the cytoplasmic membrane rapidly and without the use of transport proteins?
a. small hydrophobic molecules only
b. large molecules only
c. small hydrophilic molecules only
d. ions only
e. both ions and hydrophilic molecules
a. small hydrophobic molecules only
Hopanoids are found in _____ cytoplasmic membranes.
a. no
b. eukaryotic
c. archaeal
d. prokaryotic
e. bacterial
e. bacterial
Mites are responsible for the spread of:
a. helminth disease
b. Lyme disease
c. diseases caused by Rickettsias
d. malaria
e. diseases caused by Apicomplexans
c. diseases caused by Rickettsias
A unique feature of cytokinesis in algae is:
a. the new cell is pinched off by a ring of cell wall
b. the formation of a cell plate between daughter cells
c. that cytokinesis is delayed until several rounds of mitosis have occurred
d. the formation of a cleavage furrow
e. the unequal division of the cytoplasm
b. the formation of a cell plate between daughter cells
which of the following is found only in eukaryotic cells?
a. DNA
b. cytoplasmic membrane
c. ribosomes
d. cytoplasm
e. nuclear envelope
e. nuclear envelope
the type(s) of bonds produced with atoms share electrons equally is/are
a. an ionic bond
b. a nonpolar covalent bond
c. a hydrogen bond
d. a polar covalent bond
e. both polar covalent and ionic bonds
b. a nonpolar covalent bond
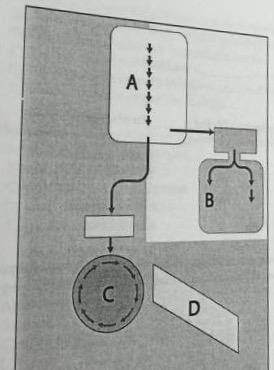
identify the processes of glucose metabolism represented in Figure 5-1.
a. A= fermentation, B= glycolysis, C= Krebs cycle, D= electron transport chain
b. A= glycolysis, B= fermentation, C= Krebs cycle, D= electron transport chain
c. A= glycolysis, B= Krebs cycle, C= fermentation, D= electron transport chain
d. A= glycolysis, B= Krebs cycle, C= electron transport chain, D= fermentation
e. A= electron transport chain, B= Krebs cycle, C= glycolysis, D= fermentation
b. A= glycolysis, B= fermentation, C= Krebs cycle, D= electron transport chain
Students in a microbiology lab are provided plates of medium to use in their bacterial culturing. The growth of organisms that can metabolize mannose sugar will result in the agar turning yellow, while the agar color remains unchanged if the mannose is not metabolized. The plates contain a ___________ medium.
a. selective
b. differential
c. reducing
d. transport
e. defined
b. differential
a measurement of a microbe is reported as 1 x 10-6m, also known as
a. nanometers (nm)
b. micrometers (um)
c. yards
d. centimeters (cm)
e. millimeters (mm)
b. micrometers (um)
during the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from pyruvic acid, _____ is produced.
a. FADH2
b. acetic acid
c. H2O
d. NADH
e. ATP
d. NADH
identification of bacteria in the laboratory usually begins with the _____ for placement in one of two large groups of bacteria.
a. Koch's stain
b. Gram stain
c. Petri stain
d. Ehrlich magic test
e. Pasteur fermentation test
b. Gram stain
One mechanism by which viruses may cause cancer is to interrupt the genetic regulatory sequences of repressor proteins. Which of the following types of viruses is most likely to be involved in causing cancer by this mechanism?
a. +ssRNA viruses
b. dsRNA viruses
c. -ssRNA viruses
d. retroviruses
e. both =ssRNA and -ssRNA viruses
d. retroviruses
which of the following is a property of water?
a. it is a nonpolar molecule
b. it is liquid in a very narrow temperature range
c. it is not a common reactant in metabolic reactions
d. it is not a good solvent
e. it has a high capacity for heat
e. it has a high capacity for heat
why does immersion oil improve resolution?
a. it increases numerical aperture and maintains a uniform light speed
b. it decreases the working distance
c. it increases the angle of refraction of the light
d. it increases the numerical aperture
e. it allows light to travel at a uniform speed on its way to the lens
a. it increases numerical aperture and maintains a uniform light speed
the acid-fast stain is used to stain
a. bacteria with capsules
b. endospores
c. bacteria lacking cell walls
d. bacteria with waxy cell walls
e. living bacteria
d. bacteria with waxy cell walls
Chloroplasts differ from mitochondria in that the former have
a. 70S ribosomes
b. DNA
c. thylakoids
d. two lipid bilayers
e. cristae
c. thylakoids
what is one of the most difficult aspects of studying animal viruses?
a. the use of animals to study the viruses is unethical in the eyes of many
b. the viruses are extremely dangerous to handle
c. the viruses are hard to obtain
d. the use of animals is expensive, and unethical to many people
e. the study requires expensive facilities
d. the use of animals is expensive, and unethical to many people
which of the following would NOT normally be found as a component of a cell's nucleic acids?
a. adenine deoxyribonucleotides
b. adenine ribonucleotides
c. thymine deoxyribonucleotides
d. uracil deoxyribonucleotides
e. cytosine ribonucleotides
d. uracil deoxyribonucleotides
simple eukaryotes that carry out oxygenic photosynthesis and reproduce by means of alternation of generations are known as
a. arachnids
b. algae
c. slime molds
d. fungi
e. euglenids
b. algae
Lipid-soluble molecules would be expected to cross the cytoplasmic membrane by which of the following processes?
a. group translocation
d. diffusion
c. active transport
d. facilitated diffusion
e. osmosis
d. diffusion
plant cell walls are composed of _____ held together by _____.
a. fatty acids; polar covalent bonds
b. peptidoglycan; ionic bonds
c. amino acids; peptide bonds
d. polysaccharides; hydrogen bonds
e. disaccharides; hydrophobic interactions
d. polysaccharides; hydrogen bonds
how are prions different from all other known infectious agents?
a. They cause neurological problems
b. they can be destroyed by incineration
c. they cannot reproduce outside a cell
d. they act as slow viruses
e. they lack nucleic acid
e. they lack nucleic acid
Lipid A is a component of
a. lipopolysaccharides
b. bacterial glycocalyces
c. cytoplasmic membranes
d. plant cell walls
e. mycolic acid
a. lipopolysaccharides
An epidemiologist is investigating a new disease and observes what appear to be bacteria inside tissue cells in clinical samples from victims. The scientist wants to try to isolate the bacteria in the lab. What culture conditions are most likely to be successful?
a. inoculation of cell cultures
b. culturing on blood agar plates
c. inoculation of a minimal medium broth
d. inoculation of EMB plates
e. incubation in an anaerobic culture system
a. inoculation of cell cultures
which of the following statements concerning endocytosis and exocytosis is TRUE?
a. these processes occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
b. endocytosis is a form of passive transport, whereas exocytosis is a form of active transport
c. wastes products and secretions are exported from the cell during endocytosis
d. endocytosis produces a structure called a food vesicle
e. phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis in which liquids are brought into the cell
b. endocytosis is a form of passive transport, whereas exocytosis is a form of active transport
which of the following is an INCORRECT pairing?
a. contrast; staining techniques
b. numerical aperture; curved glass
c. dark field; high contrast
d. magnification; refraction of radiation
e. electron beams; shorter wavelength
b. numerical aperture; curved glass
some bacteria have an outer layer composed of _____ that protects them from desiccation and allows them to adhere to surfaces.
a. polysaccharides
b. waxes
c. polypeptides
d. nucleotides
e. either polypeptides or polysaccharides
e, either polypeptides or polysaccharides
the valence of an atom represents its
a. ability to interact with other atoms
b. electronegativity
c. ability to interact with water
d. radioactivity
e. ability to attract electrons
a. ability to interact with other atoms
how many ATP molecules can theoretically be produced from the NADH generated by the catabolism of a molecule of glucose during aerobic respiration?
a. 36
b. 38
c. 4
d. 34
e. 30
e. 30
the anaerobic Clostridium species are troublesome pathogens in part because of their capacity for
a. biofilm production
b. rapid reproduction
c. high salt tolerance
d. endospore production
e. oxygen production
d. endospore production
Pasteur's experiments on fermentation laid the foundation for:
a. abiogenesis
b. antisepsis
c. industrial microbiology
d. epidemiology
e. immunology
c. industrial microbiology
what is the major product of the Calvin-Benson cycle that can then be used to form glucoses?
a. adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
b. ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
c. NADPH
d. carbon dioxide (CO2)
e. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
e. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
which of the following products of glucose catabolism is a substrate for fatty acid synthesis?
a. succinyl-CoA
b. acetyl-CoA
c. pyruvic acid
d. oxaloacetate
e. phosphoglyceric acid
b. acetyl-CoA
the filamentous water molds are no longer classified with the true fungi because:
a. they are never diploid
b. their cell walls are composed of cellulose
c. they have cell walls composed of cellulose and motile spores with two flagella
d. they produce motile spores with two types of flagella
e. they have cell walls composed of chitin and are never diploid
c. they have cell walls composed of cellulose and motile spores with two flagella
changes in temperature or pH can cause enzymes to lose activity. what is a common feature of these two effects?
a. temperature and pH change the activation energy of the reaction
b. temperature and pH affect the rate of substrate binding
c. temperature and pH change the ionization state of cofactors
d. temperature and pH both induce an enzyme to lose its precise three-dimensional shape
e. there is no common mechanism of temperature and pH effects on enzyme activity
d. temperature and pH both induce an enzyme to lose its precise three-dimensional shape
which of the following statements concerning the characteristics of life is FALSE?
a. organisms may not exhibit all of the characteristics of life at all times
b. reproduction can occur asexually or sexually in living things
c. reproduction is defined as an increase in the size of an organism
d. living things store metabolic energy in the form of chemicals such as ATP
e. viruses have some, but not all, of the characteristics of living things
c. reproduction is defined as an increase in the size of an organism
Virus replication results in the death of the cell in _____ infection(s).
a. a lysogenic
b. a latent
c. a persistent
d. a lytic
e. both latent and persistent
d. a lytic
Parasitic worms, even meters-long tapeworms, are studied in microbiology because:
a. diagnosis usually involves microscopic examination of patient samples
b. no one else wants to study them
c. the Gram stain can be used to identify them
d. they are parasites
e. Leeuwenhoek first discovered them
a. diagnosis usually involves microscopic examination of patient samples
A microbiologist inoculates a growth medium with 100 bacterial cells/ml. if the generation time of the species is 1 hour, and there is no lag phase, how long will it be before the culture contains more than 10,000 cells/ml?
a. 2 hours
b. 7 hours
c. 3 hours
d. 24 hours
e. 10 hours
b. 7 hours
unstained cells that lack pigment are best observed on the _____ microscope.
a. scanning electron
b. phase-contrast
c. transmission electron
d. bright-field
e. scanning tunneling
b. phase-contrast
the rules of naming organisms are called:
a. taxonomy
b. classification
c. binomials
d. nomenclature
e. identification
d. nomenclature
which of the following is an accurate description of viruses?
a. they are acellular obligatory parasites
b. they are typically about the size of a prokaryotic cells
c. they are visible with a light microscope
d. they are the smallest known cells
e. they are composed of protein only
a. they are acellular obligatory parasites
the Gram-positive occurs _____ grows in irregular clusters and is frequently found in the human nasal cavity. When it invades other parts of the body it can cause serious disease.
a. Clostridium perfringens
b. Bacillus thuringiensis
c. Helicobacter pylori
d. Escherichia coli
e. Staphylococcus aureus
e. Staphylococcus aureus
at temperatures higher than the maximum growth temperature for an organism,
a. hydrogen bonds within molecules are broken
b. membranes become too fluid for proper functions
c. hydrogen bonds are broken and proteins are permanently denatured
d. hydrogen bonds are broken, proteins are denatured, and membranes become too fluid
e. proteins are permanently denatured
d. hydrogen bonds are broken, proteins are denatured, and membranes become too fluid
Which of the following statements about fungi is INCORRECT?
a. molds are multicellular
b. yeasts are unicellular
c. fungi are eukaryotes
d. fungi have a cell wall
e. fungi are photosynthetic
e. fungi are photosynthetic
prions cause disease in:
a. mammals
b. bacteria
c. fungi
d. plants
e. birds
a. mammals
The development of a cancerous cell is said to require "multiple hits." this means:
a. multiple oncogenic viruses infect the cell at the same time
b. multiple cell cycle regulators are inactivated at once
c. the cell must be infected with several different types of viruses to be transformed
d. several protoncogenes are activated at the same time
e. a series of separate events over time lead to the loss of cell cycle regulation
e. a series of separate events over time lead to the loss of cell cycle regulation
the process known as _____ is a mechanism of release for enveloped viruses.
a. budding
b. lytic replication
c. latency
d. persistent infection
e. metastasis
a. budding
Rocky Mountain spotted fever is causes by Gram-negative tiny bacilli that are intracellular parasites. they are in the genus:
a. Bordetella
b. Coxiella
c. Acetobacter
d. Rickettsia
e. Enterococcus
d. Rickettsia
microorganisms characterized by the absence of a nucleus are called:
a. fungi
b. viruses
c. eukaryotes
d. prokaryotes
e. pathogens
d. prokaryotes
isomerases catalyze reactions in which:
a. atoms in biomolecules are rearranged
b. groups are transferred from one molecule to another
c. biomolecules are oxidized or reduced
d. biomolecules are broken into their components parts
e. biomolecules are assembled from smaller molecules
a. atoms in biomolecules are rearranged
which of the following lipids has the lowest ratio of hydrogens to carbons?
a. monounsaturated fats
b. polyunsaturated fats
c. both saturated and monounsaturated fats
d. saturated fats
e. saturated, unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats have equal ratios of hydrogens to carbons
b. polyunsaturated fats
the production of NADH takes place during the _____ stage(s) of glycolysis.
a. lysis
b. energy-conservation
c. energy-investment
d. lysis and energy-investment
e. energy-investment and energy-conservation
b. energy-conservation
which of the following is unique to archaea?
a. pili
b. LPS
c. fimbriae
d. peptidoglycan
e. hami
e. hami
a species of the genus Streptococcus is the leading cause of:
a. contaminated milk and meat
b. tuberculosis
c. food poisoning from rice
d. "flesh-eating" bacterial infections
e. urinary tract infections
d. "flesh-eating" bacterial infections