Developed better nursing care in psychiatric hospitals & organized nursing services & educated programs in state mental hospitals in Illinois
Linda Richards
Called the first American psychiatric nurse
Linda Richards
One of Linda Richards most important contributions was her emphasis on what?
Assessing both physical & emotional needs of patients
The role of psychiatric nursing began to emerge in the early 1950's, but the following three problems affected psychiatric nurses:
Scarcity of qualified psych nurses
Underuse of their abilities
The fact that "very little real psychiatric nursing is carried out in otherwise good psychiatric hospitals & units"
Dr. Hildegard Peplau, who published the book, Interpersonal Relations in Nursing (1952), defined nursing as:
A significant, therapeutic process
6 interpersonal nursing roles identified by Dr. Peplau
Stranger
Resource person
Teacher
Leader
Surrogate
Counselor
The role assumed by both nurse & patient when they first meet
Stranger (Dr. Peplau)
Provides health information to a patient who has assumed the counselor role
Resource person (Dr. Peplau)
Helps the patient grow & learn from experience with the health care system
Teacher (Dr. Peplau)
Helps the patient participate in a democratically implemented nursing process
Leader (Dr. Peplau)
Assumes roles that have been assigned by the patient, based on significant past relationships
Surrogate (Dr. Peplau)
Helps the patient integrate the facts & feelings associated with an episode of illness into the patient's total life experience
Counselor (Dr. Peplau)
Jones' idea of the therapeutic community (1953) includes these ideas:
Patients should:
-Be active participants in care
-Be involved in daily unit problems
-Plan activities
-Develop unit rules
Along with Jones' publication of The Therapeutic Community, another significant development in psychiatry in the early 1950's was the use of:
Psychotropic drugs
Peplau's Interpersonal Techniques: The Crux of Psychiatric Nursing (1962) identified the heart of psychiatric nursing as the role of:
Counselor or psychotherapist
For this individual's contributions to psychiatric nursing, they are often referred to as the mother of psychiatric nursing
Dr. Hildegard Peplau
Made federal money available to states to plan, construct, & staff community mental health centers & resulted in a growing awareness of the value of treating people in the community & preventing hospitalization whenever possible.
The Community Mental Health Centers Act of 1963
An interpersonal process that promotes & maintains patient behavior that contributes to integrated functioning
Pyschiatric-mental health nursing
The five core mental health disciplines, per The Center for Mental Health Services
Psychiatric nursing
Marriage & family therapy
Psychiatry
Psychology
Social Work
This type of collaboration/relationship includes the elements of clinical competence, consumer-family advocacy, fiscal responsibility, interprofessional collaboration, social accountability, & legal-ethical parameters
Nurse-patient partnership
*Formerly the nurse-patient relationship
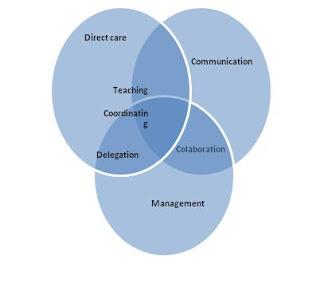
3 domains of contemporary psychiatric-mental health nursing practice
Direct care
Communication
Management
One strategy psychiatric nurses can use to enhance their growth is to participate in:
Support group/s
4 factors that help determine the level of a psychiatric nurses performance
Law
Nurse's qualifications
Practice setting
Personal initiative
In 1952, Hildegard Peplau defined the psychiatric nurse’s role as a:
Resource person, a teacher, a leader, and a counselor to patients.
The contribution of Linda Richards that remains a part of contemporary psychiatric nursing practice is the idea that:
Nurses should assess both the physical and the emotional needs of patients.
A nurse states, “I plan ways for patients assigned to me to participate in their own care and to be actively involved in all of the activities on the unit.” This approach demonstrates the concept of:
Therapeutic community
Hildegard Peplau’s classic article “Interpersonal Techniques: The Crux of Psychiatric Nursing” directed psychiatric nursing’s future growth by stating that the primary role of the psychiatric nurse was that of:
Counselor
When teaching the orientation portion of a psychiatric nursing course, which statement would the instructor be most likely to make to the students?
“The psychiatric nursing patient may be an individual, a family, a group, or even a community.”
For psychiatric nurses in the 1980s and 1990s, the scope of practice began to change to include:
New advances in the fields of psychobiology and technology.
During orientation to the inpatient psychiatric unit, new staff members are told, “Address all patients by their title and surname unless you are directed by the patient to do otherwise.” The belief that underlies this directive is that:
Every person is worthy of respect.
A psychiatric aide says, “I don't know why that patient does all that silly giggling and posturing. It’s senseless!” The best reply to this comment would address the psychiatric nursing principle that states:
All behavior is meaningful, arising from personal needs and goals.
The role of the psychiatric nurse in today’s contemporary practice settings is:
Centered on the nurse-patient partnership.
The primary opportunity provided by psychiatric clinical rotations for nursing students is an opportunity to:
Learn to work with patients with various psychiatric mental health issues.
Case supervision is a psychiatric nursing activity that falls within the nursing practice domain of:
Direct care
When one considers the roles and functions of psychiatric nursing, the overlap of communication and management roles is seen in the function of:
Collaboration
The major determinants of the roles in which a psychiatric nurse engages are:
State law and personal qualifications.
Nursing should increase its role in the advocating of funding for outcome studies because these studies:
Document quality, cost, and effectiveness of psychiatric nursing.
New opportunities for psychiatric nursing practice have emerged as psychiatric hospitals have changed from large institutions providing custodial care to:
Integrated clinical systems providing a full continuum of care.
A psychiatric nurse uses leadership skills to strengthen the profession by:
Working as a change agent advocating for patients, families, and communities.
In the 1960s, the psychiatric nurse began to shift to primary prevention and psychiatric nursing practice began to focus more on community care. This focus was initiated by which act?
The Community Mental Health Centers Act of 1963.
A nurse is contemplating a change from a medical-surgical nursing psychiatric nursing unit in a community hospital. Which intervention would help the nurse identify the supportiveness of the new unit?
A consistent daily patient assignment to help the nurse become more autonomous and daily reading assignments to be discussed with a preceptor daily.
It is essential that psychiatric nurses become aware of their ability in the area of positive political action. The nurse can best achieve this goal by:
Working on a city committee to help register local voters.
When considering psychiatric nursing roles and functions, in order to delegate effectively the nurse must have knowledge of the domains of: (Select all that apply.)
A. management
B. communication
C. direct care
D. teaching
E. collaboration
A. management
C. direct care
In the nurse-patient relationship, _____ _____ are respected
Differing values
The key therapeutic tool of the psychiatric nurse
Use of oneself (self-awareness)
A holistic nursing model of self-awareness includes these 4 interconnected components:
Psychological
Physical
Environmental
Philosophical
Concepts that are formed as a result of life experiences with family, friends, culture, education, work, and relaxation
Values
Concern for the welfare of others
Altruism
The 4 phases of the nurse-patient relationship
Preinteraction (before first contact; self-assessment; gather data & plan for interaction)
Introductory/Orientation (find out why patient sought out help)
Working (most of therapeutic work carried out; actual behavioral change is the focus)
Termination
Actual or concrete meaning of a word
Denotative
Implied or suggested meaning of a word
Connotative
Plays a major factor in the meaning of nonverbal behavior
Sociocultural background
Personal space generally consists of this distance range
1.5 - 4 ft
What eye level encourages greater communication?
Similar eye level
The structural model of communication has these 5 components
Sender
Message
Receiver
Feedback
Context (setting in which communication takes place)
If the sender is communicating the same message both verbally & nonverbally, it's called
Congruent communication
*If verbal & nonverbal differ, it's incongruent communication
The first rule of a therapeutic relationship
Listen to the patient
Encourages the patient to select topics to discuss
"What are you thinking about?"
"Can you tell me more about that?"
"What shall we discuss today?"
Broad openings
This communication tool shows that the nurse is listening
Restating
This communication technique can give the patient time to think & gain insights
Silence
This type of questioning has limited usefulness in the therapeutic relationship
Direct questioning (almost becomes interrogation)
An attempt by the nurse to make the patient aware of inconsistencies in feelings, attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors
Confrontation
*Requires high levels of empathy & respect to be effective
This occurs when the patient is encouraged to talk about things that are most bothersome
Catharsis
This technique can increase the patient's insight into human relations & deepen the ability to see the situation from another point of view
Role playing
A patient's reluctance or avoidance of talking about or experiencing troubling aspects of oneself
Resistance
A related benefit that a patient may experience as a result of their illness
Can be a cause of resistance (patient's avoidance of talking about troubling aspects of oneself)
Secondary gain
Unconscious response in which patients experience feelings & attitudes toward the nurse that were originally associated with other significant figures in their lives
Transference
Transference is characterized by the inappropriate intensity of the patient's response...
The two types that are problematic in the nurse-patient relationship include:
Hostile transference
Dependent reaction transference (submissive)
A novice nurse states, “Psychiatric nursing can’t be very difficult. After all, I believe in showing care and in mutual exchange with my friends.” The experienced nurse’s understanding of the difference between a social and a therapeutic relationship is primarily based on the:
Type of responsibility involved.
Which strategy can the nursing student use to foster authenticity in therapeutic relationships with patients?
Analyzing feelings associated with psychiatric clinical experience with the help of instructors and peers
A person who has always wished to care for “special children” adopts a biracial child and another child who has spina bifida. What is the highest step of the value clarification process that this person has achieved?
Doing something with the choice in a pattern of life
3 steps in the value clarification process
Choosing (freely, from alternatives, after considering consequences)
Prizing (being happy with choice, affirming it in public)
Acting (doing something repeatedly with choice in a pattern)
A nurse makes observations that a depressed patient is more energetic and is smiling much more. Still, the nurse shares with the unit manager that when thinking about the patient a sense of hopelessness surfaces. The nurse manager replies:
“Pay attention to your feelings. They can provide valuable clues about the patient’s feelings.”
A new nurse has the following thoughts: “How will I handle things if my patient walks away from me? How will I react if the patient is sexually provocative? How will I cope with a patient who cries?” These thoughts indicate that the nurse is engaged in:
Self-exploration
A nurse’s most appropriate initial action during the preinteraction phase of a relationship with a homosexual patient should be to:
Examine personal feelings about homosexuality.
A nurse engaged in the preinteraction phase of the nurse-patient relationship will:
Plan for the first interaction with the patient.
When asked to contrast social superficiality with therapeutic intimacy, an experienced nurse mentor explains to a new nurse that the termination component in therapeutic intimacy is:
Specified & agreed to.
Which task would be most appropriate to focus on during the introductory phase of work with a teenage patient with low self-esteem?
Mutual formulation of a contract
A patient admitted with a diagnosis of schizophrenia, paranoid type, coldly tells a nurse during the admission interview, “I am here because my family brought me here and locked me up.” The nurse’s best response would be:
“I see you are angry about being here. I hope that after we talk you will feel differently.”
A patient is admitted to the unit and complains of being depressed. The patient says, “I want to feel like my old self again.” Which nursing response will be most therapeutic?
“Tell me more so that I can better understand.”
In the initial sessions a patient frequently asks the nurse for money and expresses doubt about the nurse’s ability to help. Which principle provides guidance for the nurse in this situation?
Testing behavior is common during the introductory phase of a relationship.
*Testing behavior serves the purpose of exploring the nurse’s consistency and intent.
A young adult has been receiving treatment for an anxiety disorder. Which statement by the patient confirms that the nurse and patient are most likely entering the terminal phase of the therapeutic relationship?
“I don’t know whether I’ll be able to handle things alone.”
A psychiatric nurse will recognize which action as demonstration of resistance behavior?
A. Regularly referring to himself as a “loser”
B. Becoming tearful during every therapy session about abuse
C. Asking to postpone a therapy session until after visiting hours
D. Consistently describing his drug use as starting “a little while ago”
D. Consistently describing his drug use as starting “a little while ago”
During the working phase of the relationship, the nurse assesses that the patient may be demonstrating resistance. The most appropriate way to deal with this would be to:
Clarify, share observations, and reflect content and feelings with the patient.
A patient reports seeing a “frightening” face on the wall of the dayroom. A nurse attempts to calm her by providing an explanation for the flawed perception of what she saw. The nurse would implement this strategy by stating:
“The shadows of the tree outside the window make strange shapes on the dayroom walls.”
A patient says to a nurse, “My spouse and I get along just fine. We usually agree on everything.” The nurse observes nonverbal communication that disagrees with what the patient has verbally communicated. Which of the patient’s actions is incongruent with her statement?
Staring down at her shoes during the conversation
A nurse tells a patient who is feeling guilty about an infidelity to call the spouse and beg for forgiveness. According to the transactional model of communication, the nurse’s response originated from which state?
Parent
*The nurse’s statement can be construed as critical. The parent ego state consists of all the nurturing, critical, and prejudicial attitudes, behaviors, and experiences learned from other people, especially from parents and teachers.
According to transactional analysis theory, when a patient finally recognizes the importance of being medication-compliant, which type of transaction has occurred?
Complementary
*In this interaction the two parties are communicating from adult ego state to adult ego state. Communication flows smoothly between the sender and the receiver. The remaining options do not demonstrate such effective communication.
When the nurse suggests the patient communicate to her employer how overwhelmed she is by the workload, the patient responds, “Yes but I’ll get fired if I do that.” According to transactional analysis theory, this is an example of a(n) _____ transaction.
Ulterior
*This is an example of the “Why don’t you? Yes, but...” game. On the surface the game involves two adults solving problems; in reality, one person is using the child ego state to show what a bad parent the other person is.
A patient who is currently in an abusive marriage shares, “Some days I think it’s just not worth it. I’d be better off if we separated.” The nurse uses restating as a therapeutic communication technique when responding:
“You think you would be better off without your spouse?”
When a patient is late for three consecutive therapy sessions, the nurse implements perception sharing as a communication technique when stating:
“I feel that you aren’t ready to work on your problems.”
The therapeutic communication technique of suggesting is appropriate to use when it:
is used during the working stage to present alternative coping strategies.
A teenager being treated for oppositional defiance behavior states: “I wish my parents would stop treating me like an irresponsible child.” The nurse implements confrontation as a therapeutic technique when responding:
“You want to be treated like an adult, but is it adult-like when you skip school?”
Which statement is true of planning the timing for the use of confrontation?
A. Confrontation should never be used during the orientation phase of the relationship.
B. Confrontation is useful during the working phase to focus on specific patient discrepancies.
C. Confront patients with their limitations early in the relationship and with their assets later in therapy.
D. Confront patients when other therapeutic action dimensions have proven ineffective.
B. Confrontation is useful during the working phase to focus on specific patient discrepancies.
The nurse suspects that a client has a problem with the action dimension of immediacy when she states, “You can’t tell people very much about yourself; it gives them too much power over you.” The nurse responds:
“It’s reasonable for you to be suspicious of me until I’ve earned your trust.”
A chronically depressed patient has been diagnosed with having a dependent personality. The nurse suspects that the situation has resulted in dependence transference when the patient shares that:
“I know I can count on you to chart my course back to health. I will do whatever you say.”
A nurse tells the unit supervisor, “I’m having a difficult time empathizing with my patient especially since he is so unwilling to change. Talking with him makes me feel both frustrated and depressed.” The supervisor may suspect that the cause of the barrier in this nurse-client relation is the:
existence of countertransference on the part of the nurse.
*Countertransference is a therapeutic impasse created by the nurse’s specific emotional response to the qualities of the patient. This response is inappropriate to the content and context of the therapeutic relationship or inappropriate in the degree of intensity of emotion.
If the potential for suicide is suspected, what should the nurse do?
Ask the patient directly about thoughts of self-harm
The patient's apparent emotional tone
Affect
Absence of emotional expression
Flat affect
False sensory impressions or experiences
Hallucinations
False perceptions or false responses to a sensory stimulus
Illusions
A patient admitted for treatment of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus is withdrawn and tearful. The patient says, “I just want to be normal again.” The nurse determines there is a need for a psychiatric evaluation primarily to assist:
A. the patient in verbalizing distress about the disease.
B. in assessing the emotional factors affecting the patient’s present condition
C. in assessing priorities to be set for the patient’s overall nursing plan of care.
D. the patient in emotionally accepting the chronic nature of the disease.
B. in assessing the emotional factors affecting the patient’s present condition
Recall of events, information, and people from the distant past
Remote memory
Recall of events, information, and people from the past week or so
Recent memory
Recall of information or data to which a person was just exposed
Immediate memory
Recall of _____ events involves reviewing information from the patient's history
Remote events (testing remote memory)
How can we test immediate recall (memory)?
-Ask patient to repeat series of numbers either forward or backward within a 10-second interval
-Ask patient to remember 3 words (object, color, address) and then repeat these words 15 min later
The patient's understanding of the nature of one's problem or illness
Insight
This type of interviewing technique can assess a patient's readiness to change
Motivational interviewing
-Interactive & problem-solving
-Systematic & individualized way to achieve outcomes of nursing care
-Respects individual's autonomy & freedom to make decisions & be involved in nursing care
Nursing process
1) Describe what the psychiatric nurse does
2) Describe the context in which the psychiatric nurse performs these activities
1) Standards of Practice
2) Standards of Professional Performance
The 6 phases of the nursing process (as described by the Standards of Practice)
ADOPIE:
Assessment
Diagnosis
Outcomes Identification
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
In the _____ phase of the nursing process, information is obtained from the patient in a direct & structured manner through observations, interviews, & examinations
Assessment phase
+ Goal-directed method of communication
+ Should be focused, but open ended
+ Should progress from generic to specific, allowing spontaneous patient self-expression
Interviewing
*Assessment phase of nursing process
The nurse develop _____ in the diagnosis phase, which is a clinical judgement about individual, family, or community responses to actual or potential health problems/life processes
Nursing diagnosis
What is the subject of the nursing diagnosis?
Patient's behavioral response to stress
The _____ phase of the nursing process may include relieving symptoms or improving functional ability
Outcomes Identification phase
Mutually identifying _____ & expected _____ is an essential step in the therapeutic process
Goals, outcomes
In writing the goals of a nursing care plan, one should remember to classify them into the "ABCs," or 3 domains, of knowledge, which are:
Affective (feeling)
Behavioral (psychomotor)
Cognitive (thinking)
Patients aren't likely to commit to a goal or work toward attaining a goal in this situation
Stakes are too high or the payoffs too low
In the planning phase of the nursing process, a plan of care is developed. The goals within are prioritized. What type of goals always receive top priority?
Those that protect the patient from self-destructive impulses
If a goal/s answers the question of "what", then the _____ answers the questions of "how" & "why"?
Plan of care
*Planning phase of nursing process
The _____ phase of the nursing process is the actual delivery of nursing care to the patient & the patient's response to that care
Implementation phase
The psychiatric nurse helps the psychiatric patient do these 2 things:
1) Develop insight
2) Change behavior
What's the idea behind motivational interviewing?
-The patient will not learn new patterns until the motivation to change > the motivation to stay the same
-The nurse should help the patient see the negative consequences of current actions & that they do more harm than good
This type of supervision equates to one-on-one supervision, in which the supervisor meets individually with the nurse being supervised
Dyadic
This term encompasses the idea that nurses view themselves as members of an organized professional group or unit and that nurses trust, support, & demonstrate commitment to other nurses
Collegiality
Collaboration is the shared planning, decision making, problem solving, goal setting, & assumption of responsibilities by individuals who work together cooperatively & w/open communication. These 3 key ingredients are needed for effective collaboration:
1) Active involvement & ideas from each person
2) Respect for each person's input
3) Negotiations that build on each person's input to form new concepts
A continuous, active process that begins early in the nurse-patient relationship & continues throughout
Evaluation phase (nursing process)
What should happen when a psych patient who's prescribed drug therapy develops side effects that emerge after treatment?
They should be identified & appropriately treated as they appear
These drugs speed up the CYP-450 metabolizing system, thus decreasing the blood levels of drugs & potentially causing a lack of effectiveness of those drugs
Inducers
These drugs slow down the CYP-450 metabolizing system, thus increasing blood levels of drugs & potentially causing increased S/E or even toxicity from those drugs
Inhibitors
*Known as cytochrome P-450 inhibition
The study of how the body affects a drug
Pharmacokinetics
4 properties of pharmacokinetics (how body affects drugs)
Absorption (into bloodstream)
Distribution (how much gets into tissues)
Metabolism (how drug is altered - usually by liver - into active/inactive parts)
Elimination
How much of a drug reaches systemic circulation unchanged
Bioavailability
The point at which the plasma drug concentration remains relatively constant between doses because the amount of drug excreted equals the amount ingested
Steady state
*Occurs in about 5 half-lives of any given drug
Most antidepressants, some antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, and __1__ can inhibit the CYP-450 system, potentially causing toxicity of drugs
In contrast, St. John's wort and __2__ can markedly reduce psychotropic drug levels, rendering them ineffective
1) Grapefruit juice
2) Smoking cigarettes
The study of the effects of a drug on the body and, in particular, the interaction of a drug on the receptor that it's targeting
Pharmacodynamics
*Answers the question: What does the drug do once it gets where it's going?
A relative measure of the safety & toxicity of a drug
Therapeutic index
*Identifies what's the lowest dose to begin to produce a therapeutic effect for 50% of patients, and what's the highest dose at which a toxic effect is produced in the average patient
If a drug has a low therapeutic index, does it have a wide or narrow range between achieving the desired effect & toxicity?
Narrow - increased risk of toxicity requiring blood levels to be checked (i.e. Lithium)
The addition of another class of medication to supplement the effectiveness of the primary medication, usually done when the primary medicine (that which is prescribed to treat the target S/S of the patient's primary DX) falls short of expectation & needs a lil' sumpin' sumpin' added ;)
Augmentation
The use of multiple psychopharmacological meds in the treatment of psychiatric disorders
Polypharmacy
With the elderly, how should medication regimens begin?
Start low & go slow (titrate up after initial lower-than-adult dose)
Has the FDA approved any psychotropic medications for safe use during pregnancy?
No - so it's up to the provider & patient to look at risks vs benefits
These 3 biological threads can affect biological response to medications
Race
Ethnicity
Gender
For most psychotropic meds, women require _____ doses than men
Lower due to greater biological activity of drugs in system
A lack of _____ often results in lack of compliance to the medication treatment
Shared decision making
Know the 3 domains of contemporary psychiatric-mental health nursing practice, & the 4 functions which oftentimes overlap in the above domains (see figure on opposite side)
Suggesting is appropriate to use in the __1__ phase when you're attempting to present __2__
1) Working phase
2) Alternative coping strategies