Cilia
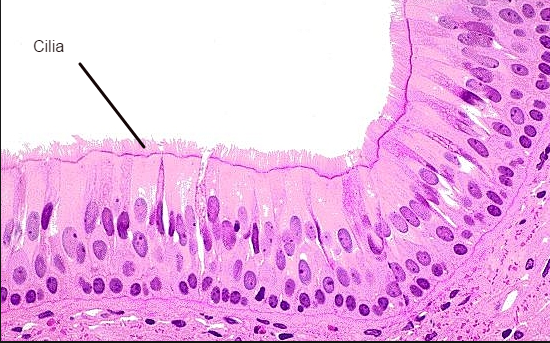
hair like or whip like structure often found on tissues with columnar -shape cell. They beat in unison to move fluids past the cell
Goblet cells
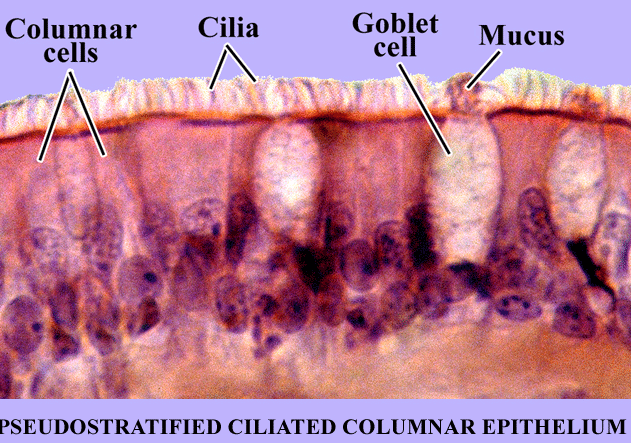
produce and secrete mucus, are also found in columnar-shaped cells
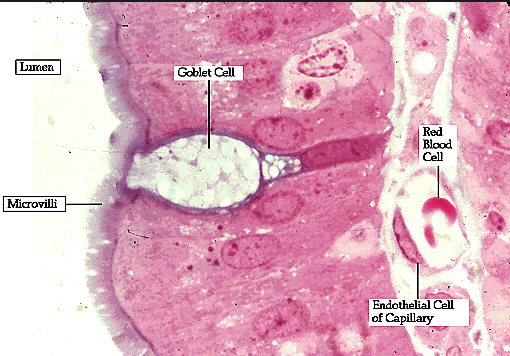
Epithelium with Microvilli
PSEUDO (ROOT WORD)
MEANS FALSE
Epithelia with two or more layers is called?
Epithelium tissues formed of two or more layers is called "stratified"The surface of the skin is stratified
Pseusdostratified
In a few locations of the body the epithelium tissue appears to be in layers or stratified but it is not is actually composed of one layer of cells.Each cell contacts the basement membrane , but the varying cell heights and nuclei location give the impression of multiple layers.These tissues are called pseudostratIfied. The main pseudostratified epithelium tissue is the pseudostratifies columnar epithelium .This tissue lines the upper and lower respiratory system.
Simple cuboidal epithelium location
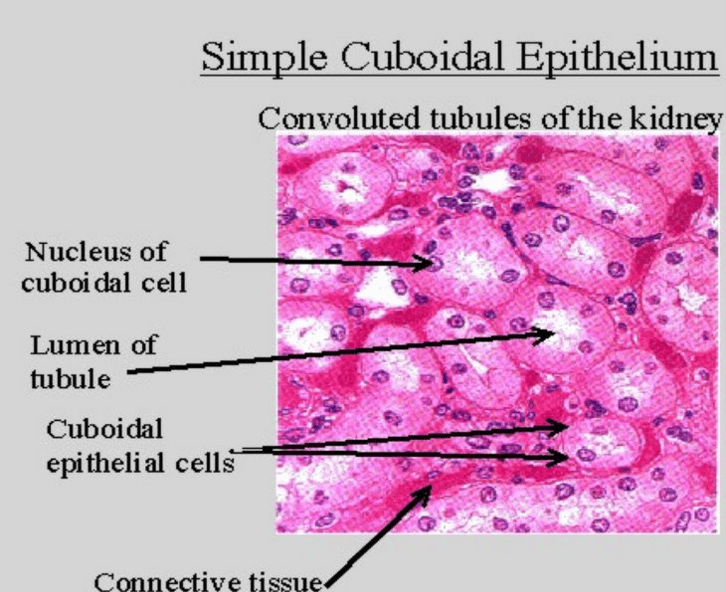
Lines the kidney ducts where exchange occurs
Where is simple Epithelial tissues located?
One layer epithelium is called simple and and are located in places not subjected to abrasion and where materials are exchanged between two areas of the body.
Epithelium that secret material
Serous membranes,,mucous membranes, epithelial cells of the digestive tract,kidneys and glands
Epithelium that serve as protection
skin and mucous membranes of the mouth , esophagus , vagina and rectum
What epithelium function in absorption of materials
epithelial of the digestive tract and and kidneys
Desmosome
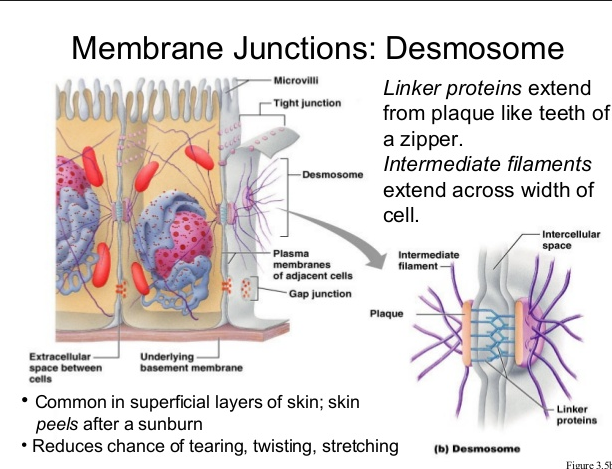
Cells might contain close fitting connections called tight junctions or rivet like connection called Desmosmes
Desmosomes are unctions that are structurally similar to a snap rather a zipper. They prevent cells from pulling apart by allowing tissues to resist mechanical stress.Desmosomes are found in the epidermis,cardiac muscle, and the cervix of the uterus.
Innervated
Since nerve ending tend to be plentiful in epithelial tissue , epithelial tissue are said to be innervated .In fact some epithelial tissues are important sensory organs because they have some many nerve endings
Avascular
Epithelial tissue are avascular which means that blood vessels do not penetrate between the epithelial cells
Basement membrane
On the opposite side of the lumen is the basement membrane that binds the epitelial tissue to the deeper tissuea thin, delicate membrane of protein fibers and glycosaminoglycans separating an epithelium from underlying tissue.
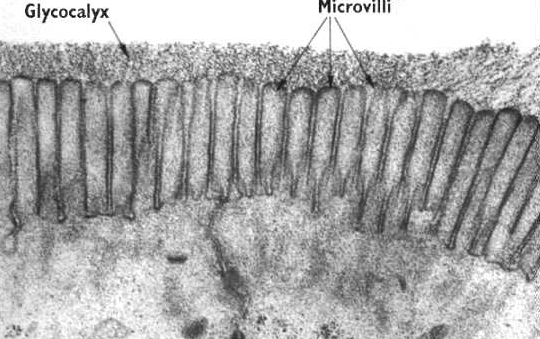
Microvilli
These are small finger like projections, about 1 µm in length, and 90nm or so in diameter. The microvilli are shorter and narrower than cilia. (Microvilli is the plural of microvillus.)
They contain bundles of parallel actin filaments held together into a bundle by cross-linking proteins called villin and fimbrin.
Lateral arms containing myosin I and calmodulin link the actin filament bundle to the plasma membrane.
Microvilli are present on the luminal surface of many epithelia, particularly those specialised for absorption.
Microvilli increase the area of the free surface of the epithelium available for absorption.
Extensions of the membrane that serve primarily to increase a cell's surface area and are specialized for absorption in epithelial cells of the intestines and kidney tubules
Lumen
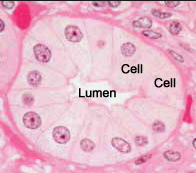
One side of the epithelial layer is always is contact with with a space.In this case of at the epidermis, this space is the outside of the body. If the the epithelia tissue is lining an internal space, the space is called the lumen.
BASAL LAMINA
Consist of Glycoproteins secreted by the epithelial cells,plus some fine collagen fibers.
INNERVATED
supply (an organ or other body part) with nerves
Reticular lamina
A layer of extra cellular material containing a fine network of collagen protein that belongs to the underlying connective tissue
Epithilium funcions
Protection. absorption,filtration,excretion, and sensory reception.
Simple epithelia
Consist of one single cell layer, found where absorption,secretion, and filtration occurs
Stratified Epithelia
Composed of two or more cell layers stacked on top of each other concentrate in high -abrasion areas where protection is important such skin surface and the lining of the mouth.
Simple esquamous epithelium
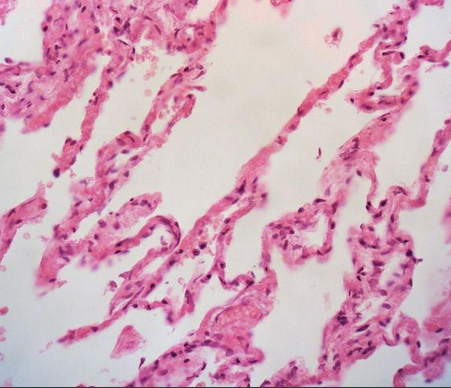
Single layer cell of flattened cells with disc-shape central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm(the simplest of the epithelia)
Allows material to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important, secrets lubricating substances in serosae.
Location:Kidney,glomeruli,,air sacs of lungs,lining of heart ,blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels ,ling of the ventral cavity
Simple cubodial epithelium
Single layer of cube like cells with large, spherical central nuclei.
Function:secretion and absorption.
Location:Kidney tubules,ducts and secretory portions of small glands,ovary surface.
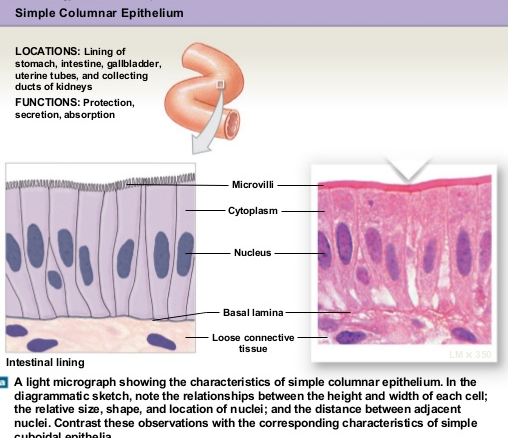
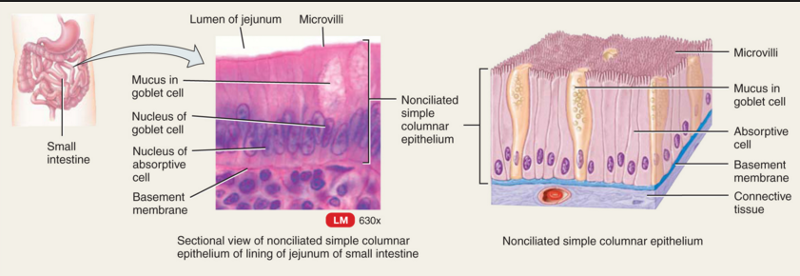
Simple columnar epithelium
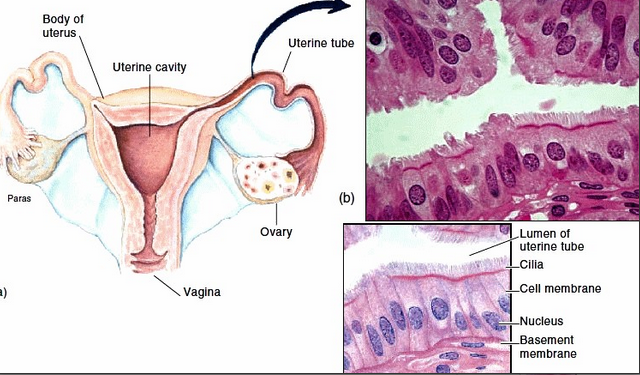
Description:Single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei,many cells bear microvilli, some bear cilia,layer may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands.
Function:Absorption, secretion of mucus,enzymes,and other substances,ciliated type,propels mucus(or reproductive cells)by ciliary action.
Location: Nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract(stomach to rectum)gallbladder and excretory ducts of some glands,ciliated variety lines small bronchi,uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus.
Ciliated columnar epithelium in the pulmonary system is interspersed with goblet cells that secrete mucous to form a mucosal layer apical to the epithelial layer.The rowing-like action of epithelial cilia work in tandem with goblet cells to propel mucus away from the lungs, preventing particulate matter from causing infection
Ciliated Simple columnar epithelium(ciliated kind)
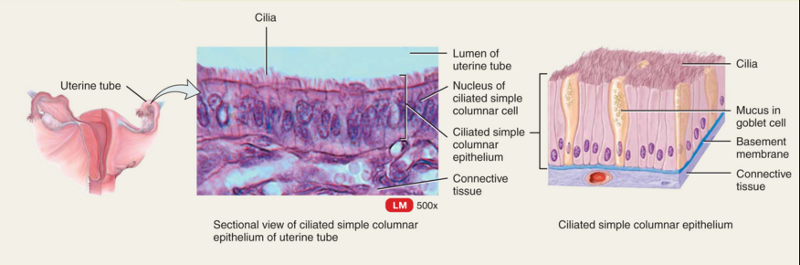
Simple columnar epithelium ( non ciliated )
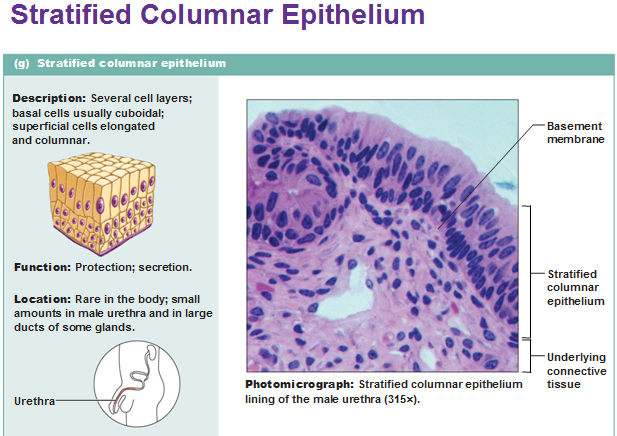
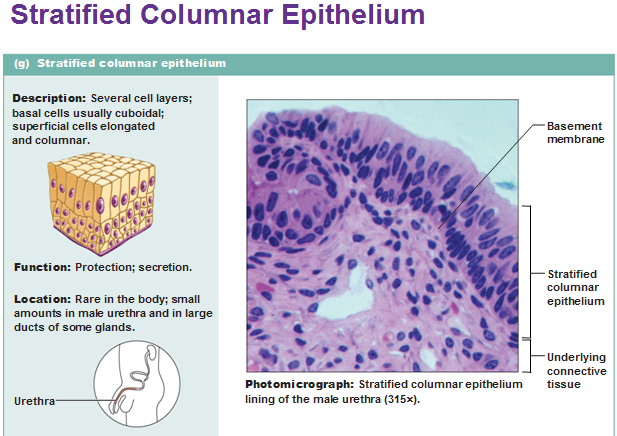
Stratified columnar epithelium
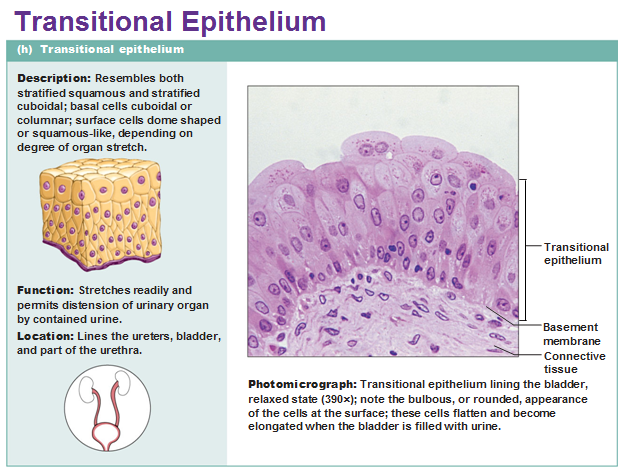
Tranditional epithelium
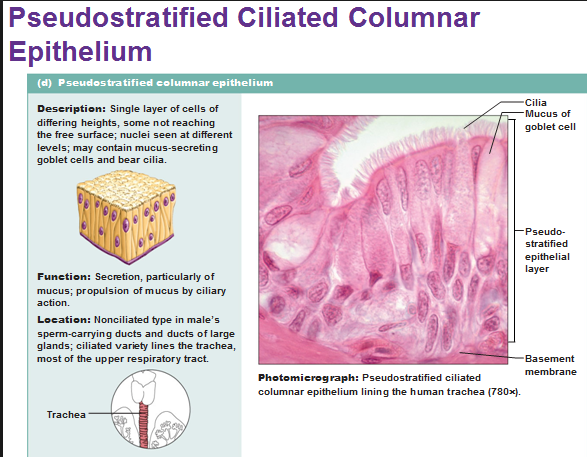
Pseudo stratified columnar epithelium
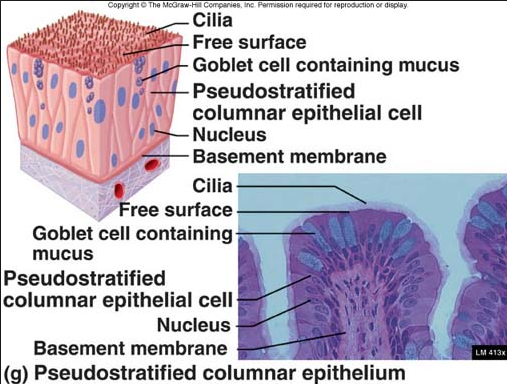
Single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface:nuclei seen at different levels , may contain mucus -secreting cells and bear cilia.
Function:Secrets substances particularly mucus,propulsion of mucus by ciliary action.
Location;:Nonciliated type in males' sperm carrying ducts and ducts of large glands , ciliated variety lines the trachea most of the upper respiratory tract.
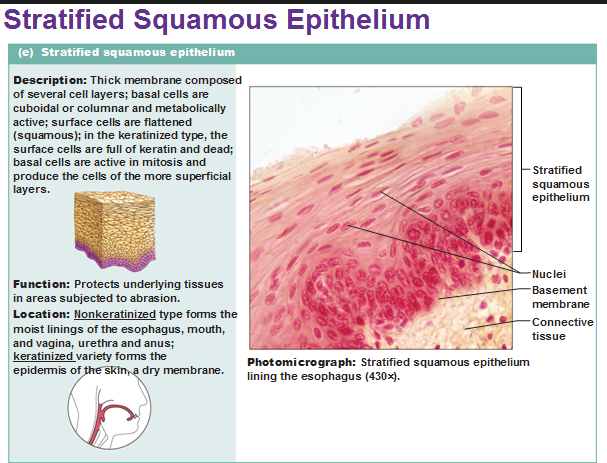
Stratified squamous epithelium
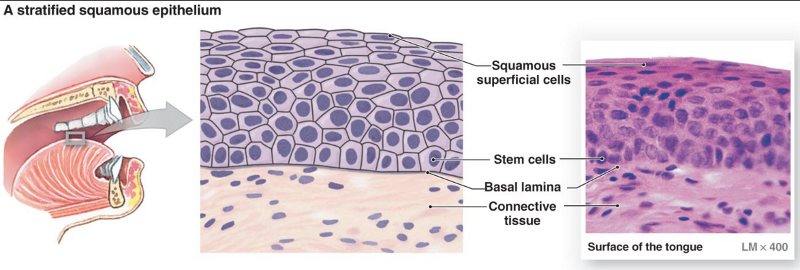
Thick membrane composed of several cell layers , basal cells are cuboidial or columnar and metabolically active , surface cells are flattened (squamous)in the keratinized type, the surface cells are full of keratin and dead,basals cells are active in mitosis and produce the cells of the more superficial layers.
Function:Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion.
location;Nonkeratinized type forms the moist things of the esophagus , mouth and vagina. Keratinized variety forms the epidermis of the skin a dry membrane.
Transitional epithelium in bladder
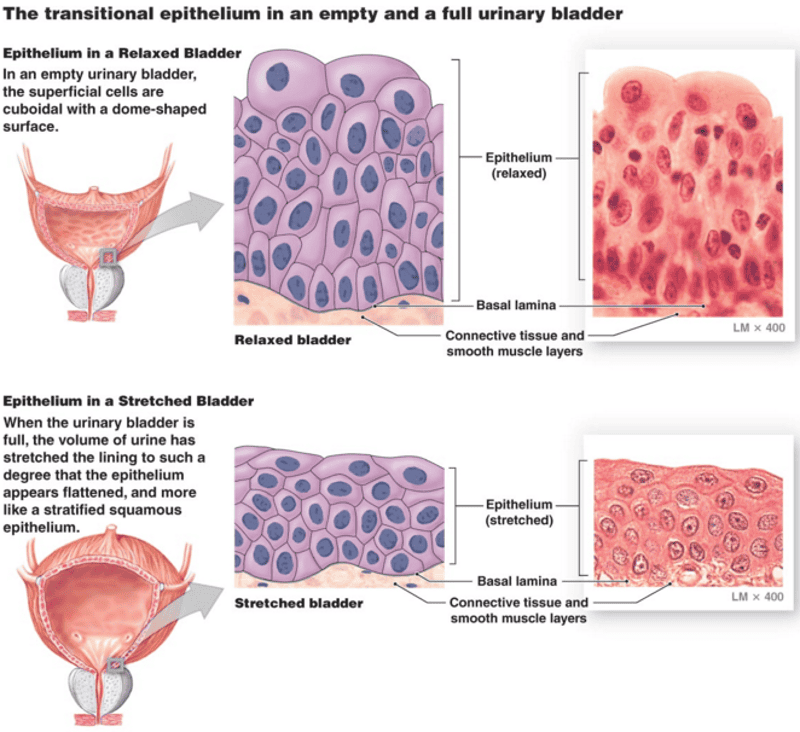
Transitional epithelium
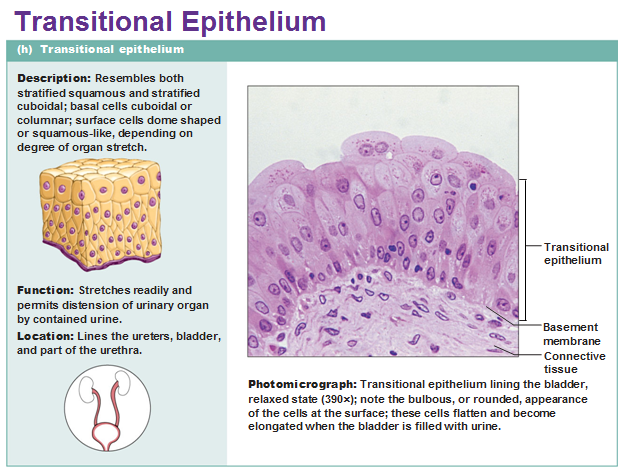
Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal ;basal cells cuboidal or columnar ; surface cells dome shaped or squamouslike depending on degree of organ stretch.
Function: Stretches readily ,permits stored urine to distend urinary organ.
Location;Lines the ureters,bladder, and part of the urethra.
Stratified squamous epithelium
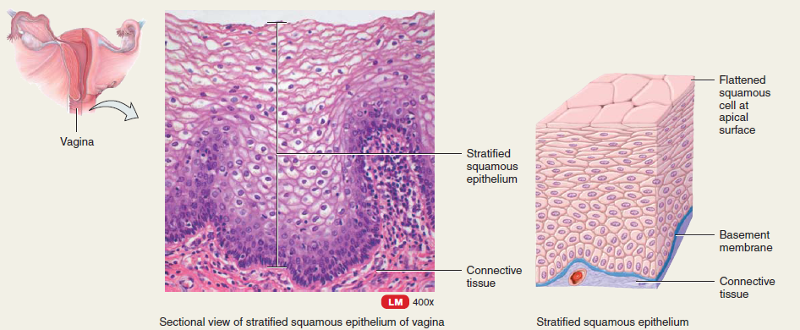
protects underlying areas subjected to abrasion(this kind here is non keratinized)
stratified columnar epithelia
Pseudotratified columnar epithelia
Stratified squamous epithelia
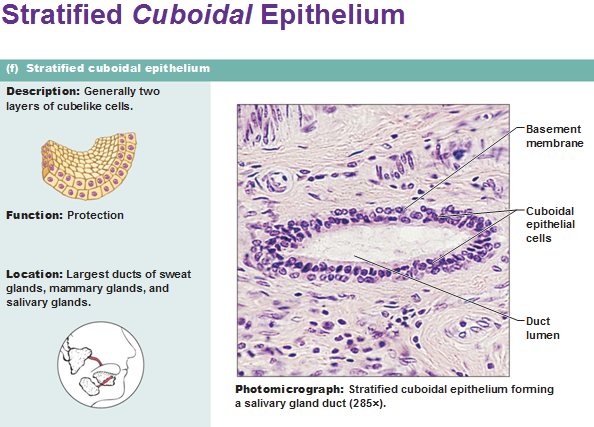
stratified cuboidal epithelium
vascularized
connective tissue is well vascularized so substances can easily pass from connective tissue blood vessels to the nearby epithelial cells
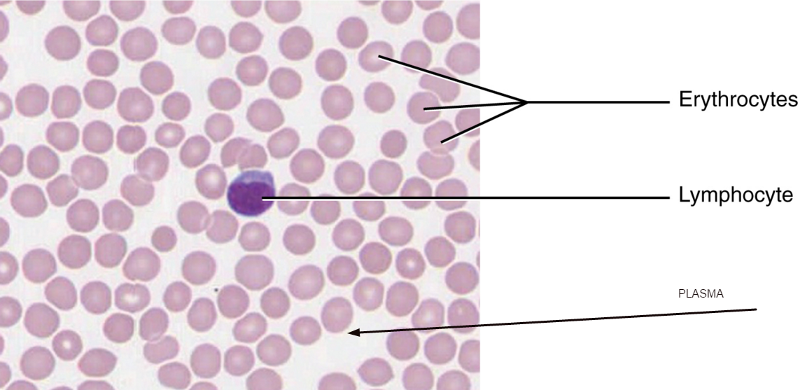
Blood
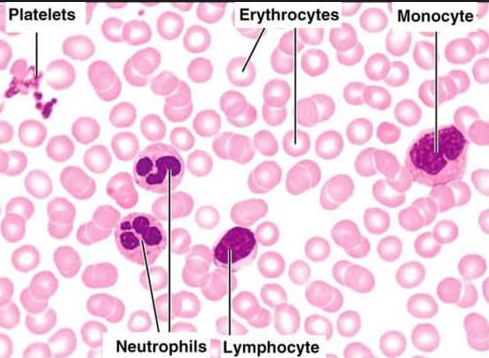

withe blood ells

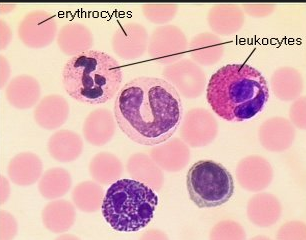
Red blood cells
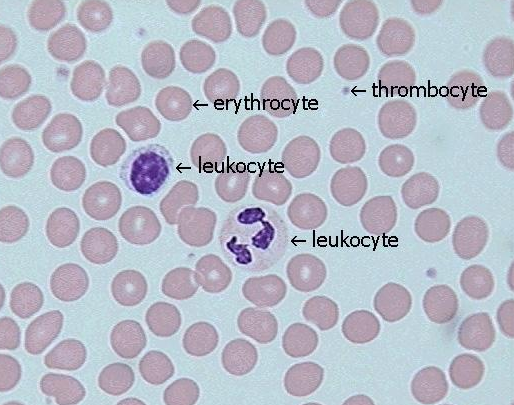
Erythrocytes
leukocytes
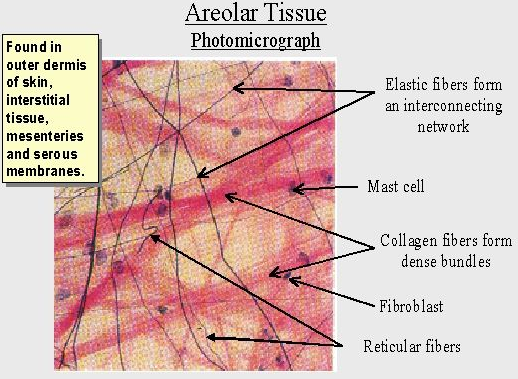
fibroblast

A fibroblast is a type of cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen,. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals.
Mast cell

a cell filled with basophil granules, found in numbers in connective tissue and releasing histamine and other substances during inflammatory and allergic reactions.
Macrophages
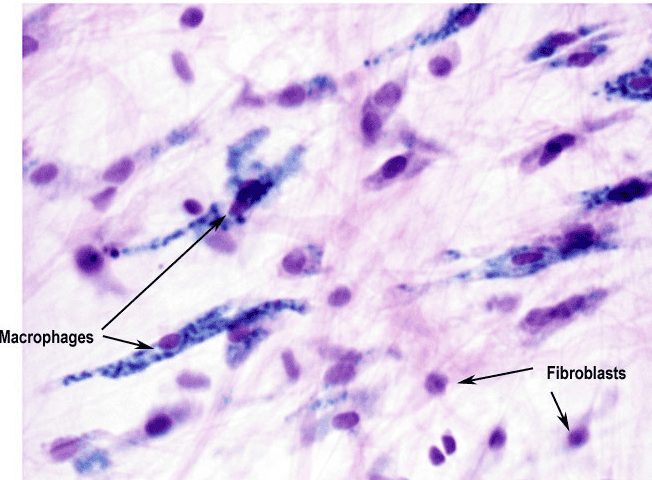
are a type of white blood cell that engulfs and digests cellular debris, foreign substances, microbes, cancer cells, and anything else that does not have the types of proteins specific to the surface of healthy body cells on its surface[1] in a process called phagocytosis. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues,[2] where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune cells such as lymphocytes. For example, they are important as antigen presenters to T cells. In humans, dysfunctional macrophages cause severe diseases such as chronic granulomatous disease that result in frequent infections.
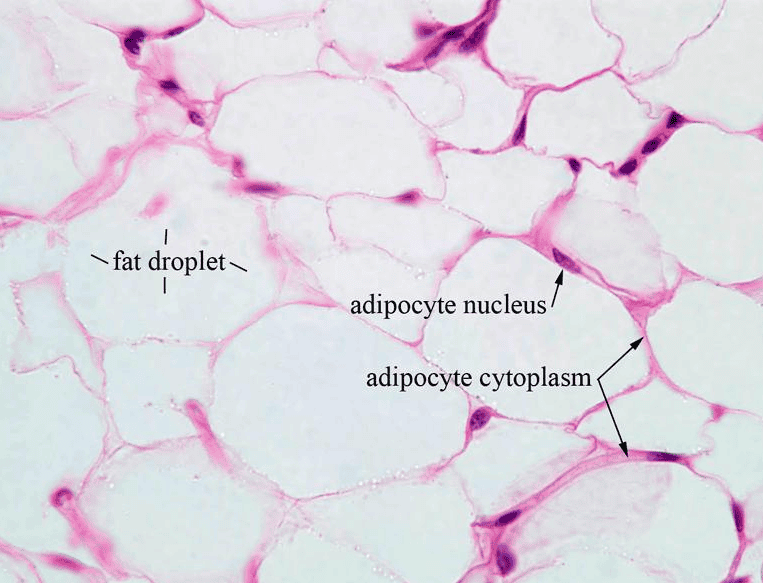
Adipocytes
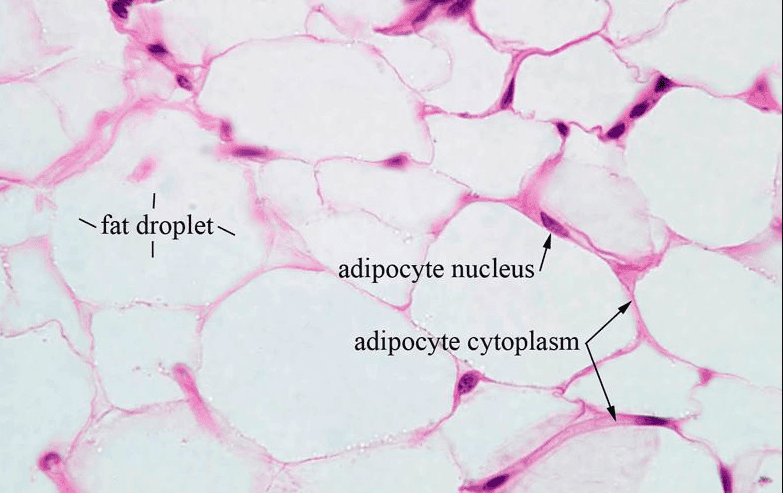
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat.
Osteocytes

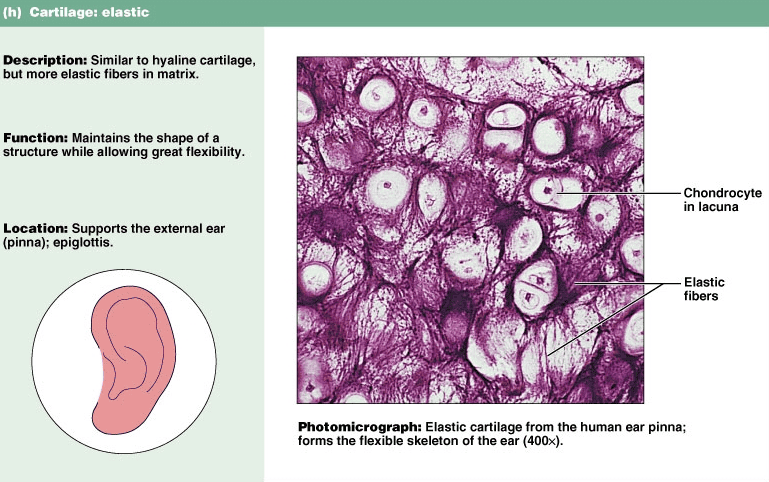
Chondrocytes
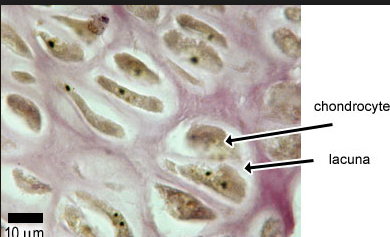
found in hyaline cartilage
Matrix
made up of ground substances and fibers, is created by cells found in the given connective tissue.
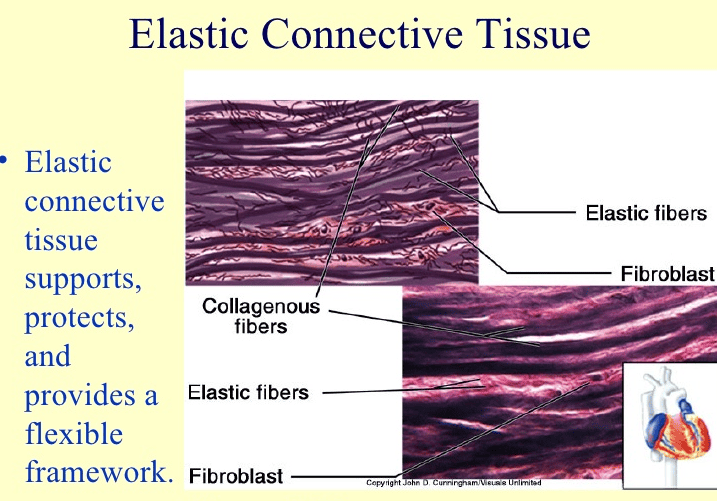
Elastic fibers
Are found aerolar connective tissue, elastic connective tissue, and elastic cartilage
Reticular fibers
Are within the reticular connective tissue and the aerola connective tissue
Collagen fibers
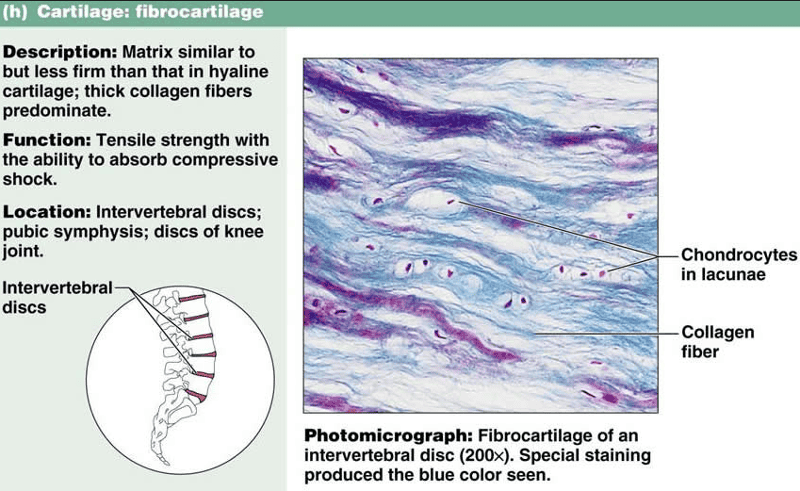
found on areolar connective ,dense regular connective tissue, dense irregular connective tissue , bone, fibrocartilage and hyline cartilage
AREOLAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Adipose Connective tissue
Reticular connective tissue

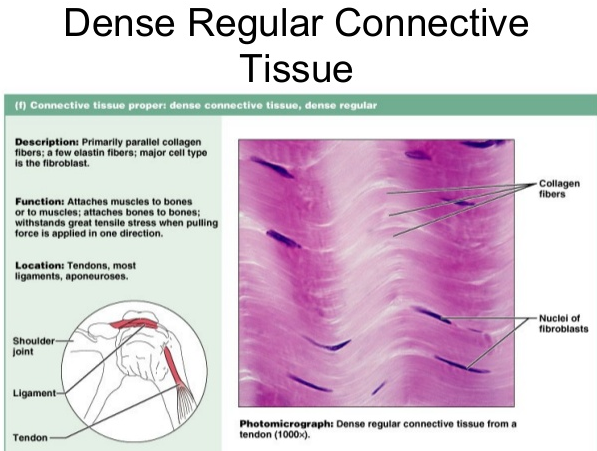
DENSE REGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE
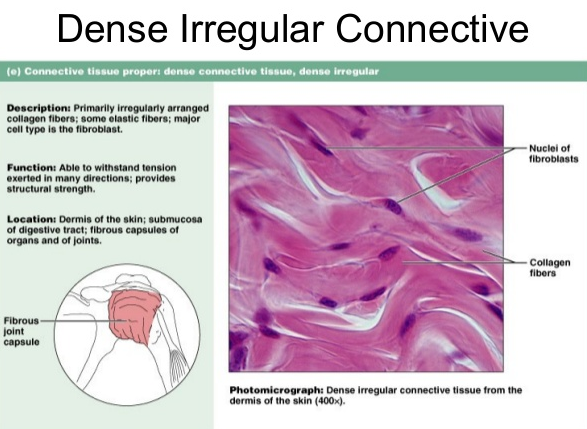
DENSE IRREGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE
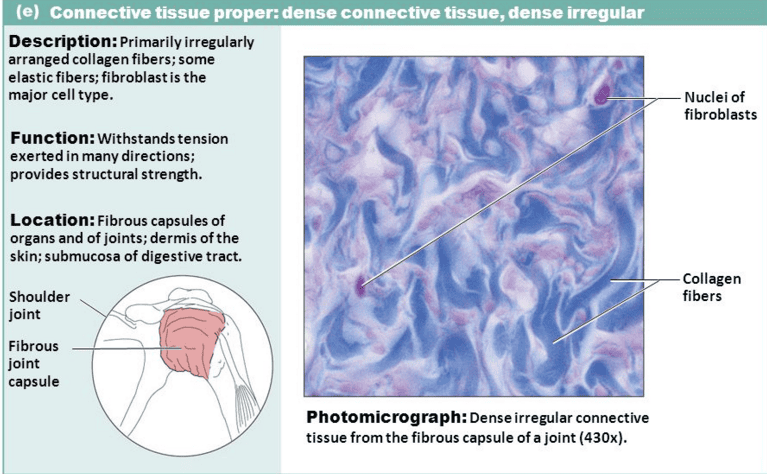
DENSE IRREGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE(BLUE)
DENSE ELASTIC CONNECTIVE TISSUE
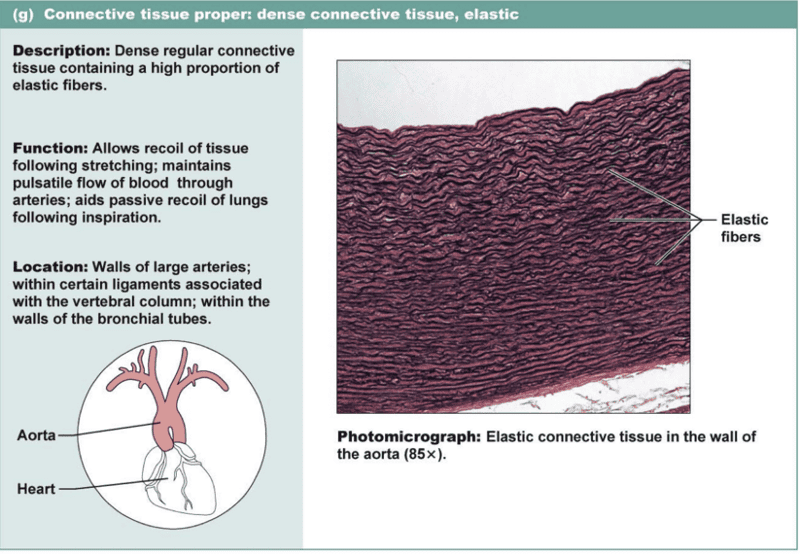
DENSE ELASTIC CONNECTIVE TISSUE
HYALINE CARTILAGE
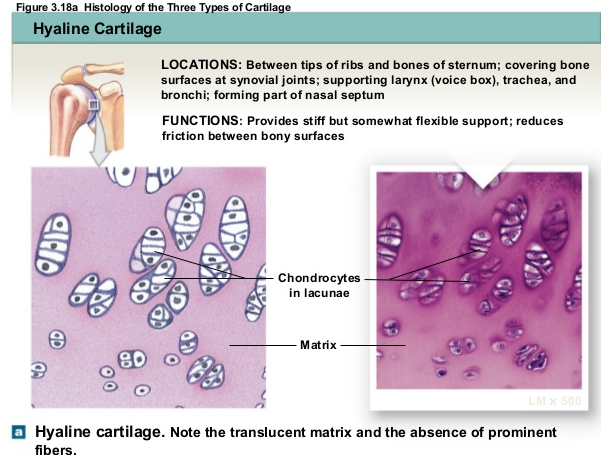
HYALINE CARTILAGE

ELASTIC CARTILAGE
FIBROCARTILAGE
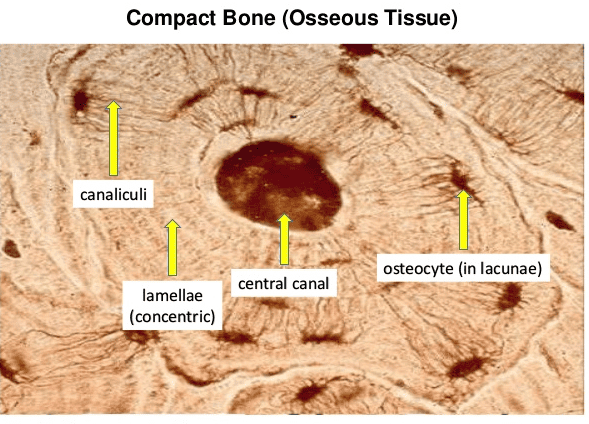
OSSEOUS TISSUE
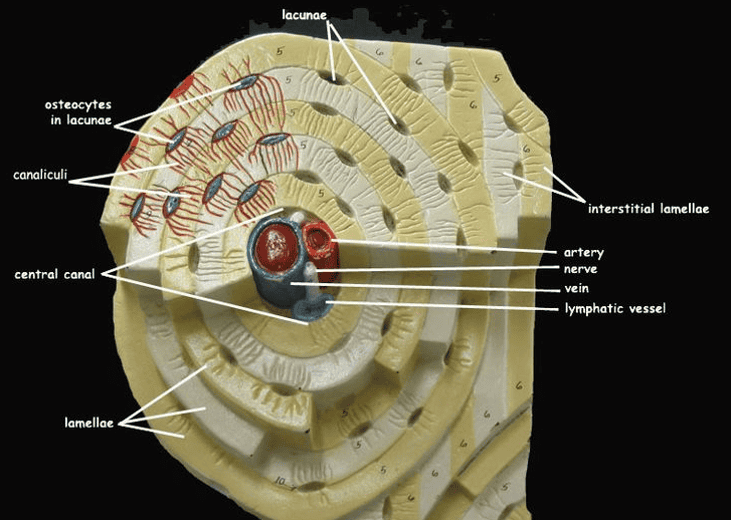
Osseous tissue
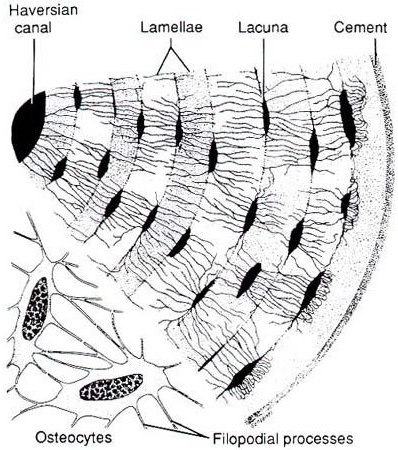
MORE OSSEOUS TISSUE
BLOOD
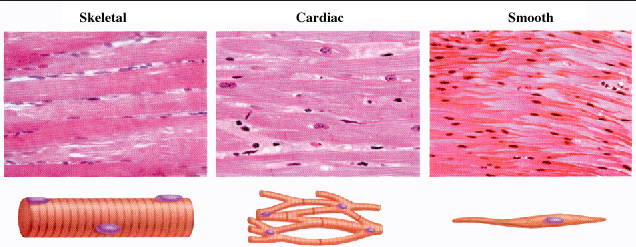
SKELETAL,CARDIAC,SMOOTH MUSCLE
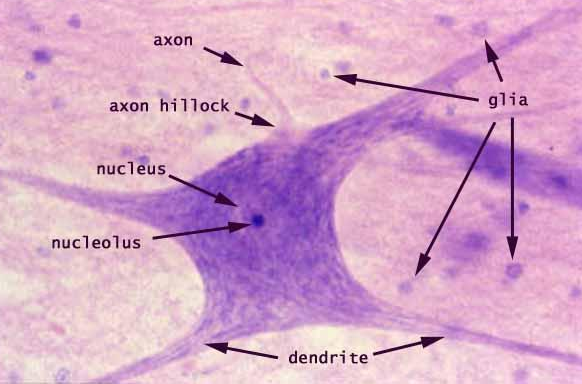
NERVOUS TISSUE
Cell cycle
A cell cycle is a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides. A cell spends most of its time in what is called interphase, and during this time it grows, replicates its chromosomes, and prepares for cell division. The cell then leaves interphase, undergoes mitosis, and completes its division.
Mitosis(noun: mitosis; plural noun: mitoses)Greek mitos ‘thread.’
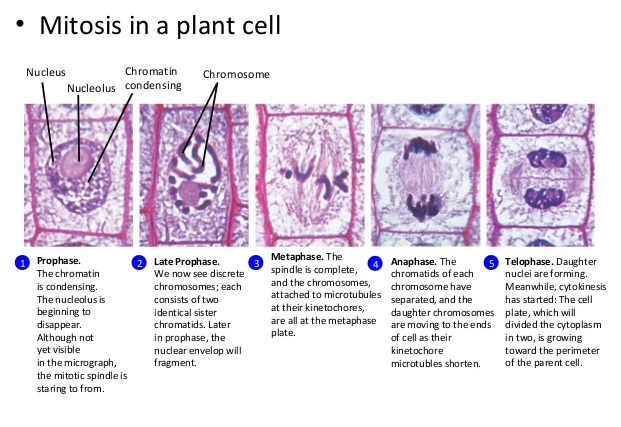
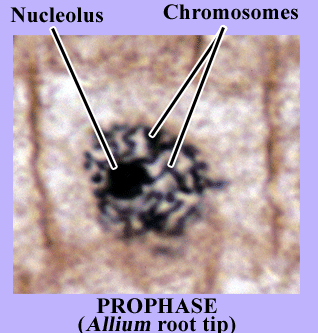
Cell cycle Mitosis(onion root) Prophase
In early prophase, the cell starts to break down some structures and build others up, setting the stage for division of the chromosomes.
- The chromosomes start to condense (making them easier to pull apart later on).
- The mitotic spindle begins to form. The spindle is a structure made of microtubules, strong fibers that are part of the cell’s “skeleton.” Its job is to organize the chromosomes and move them around during mitosis. In prophase, the spindle grows between the centrosomes as they move apart.
- The nucleolus (or nucleoli, plural), a part of the nucleus where ribosomes are made, disappears. This is a sign that the nucleus is getting ready to break down.
Prophase stages(early,mid and late prophase)
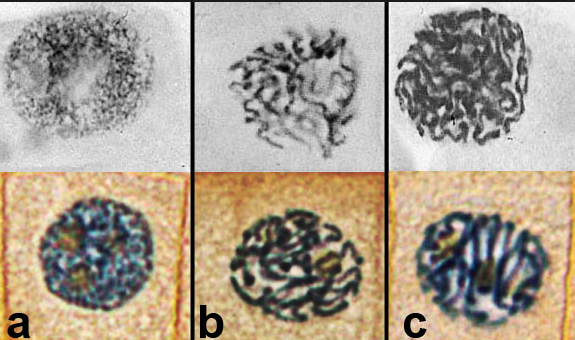
In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase), the mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes.
- The chromosomes finish condensing, so they are very compact.
- The nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing the chromosomes.
- The mitotic spindle grows more, and some of the microtubules start to “capture” chromosomes.
Metaphse
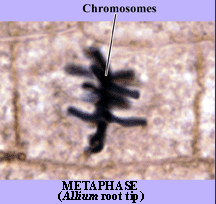
In metaphase, the spindle has captured all the chromosomes and lined them up at the middle of the cell, ready to divide.
- All the chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (not a physical structure, just a term for the plane where the chromosomes line up).
- At this stage, the two kinetochores of each chromosome should be attached to microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
Before proceeding to anaphase, the cell will check to make sure that all the chromosomes are at the metaphase plate with their kinetochores correctly attached to microtubules. This is called the spindle checkpoint and helps ensure that the sister chromatids will split evenly between the two daughter cells when they separate in the next step. If a chromosome is not properly aligned or attached, the cell will halt division until the problem is fixed.
Telophase

In telophase, the cell is nearly finished dividing, and it starts to re-establish normal internal structures as cytokinesis takes place.
- The mitotic spindle is broken down into its building blocks.
- Two new nuclei form, one for each set of chromosomes. Nuclear membranes and nucleoli reappear.
- The chromosomes begin to decondense and return to their “stringy” form.
metaphase

Anaphase

In anaphase, the sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell.
- Cohesin, the protein “glue” that holds the sister chromatids together, is broken down, allowing them to separate. Each is now considered its own chromosome. The microtubules attached to the chromosomes (kinetochore microtubules) get shorter, pulling chromosomes towards the poles.
- Microtubules not attached to chromosomes (non-kinetochore microtubules) elongate and push apart, separating the poles and making the cell longer.
All of these processes are driven by motor proteins, molecular machines that can “walk” along microtubule tracks and carry a cargo. In mitosis, motor proteins carry chromosomes or other microtubules as they walk.
prometaphase

interphase
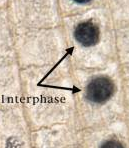
the interphase is the longste lasting stage of the cell cycle. Interphase is considered as the phase during which cells conduct their "normal" cellular functions, i.e. take up nutrients, grow, read DNA and produce proteins, and prepare themselves for the mitosis, in particular by replicating their DNA.
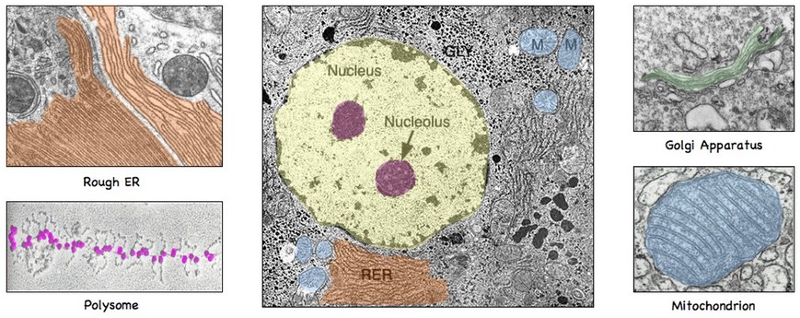
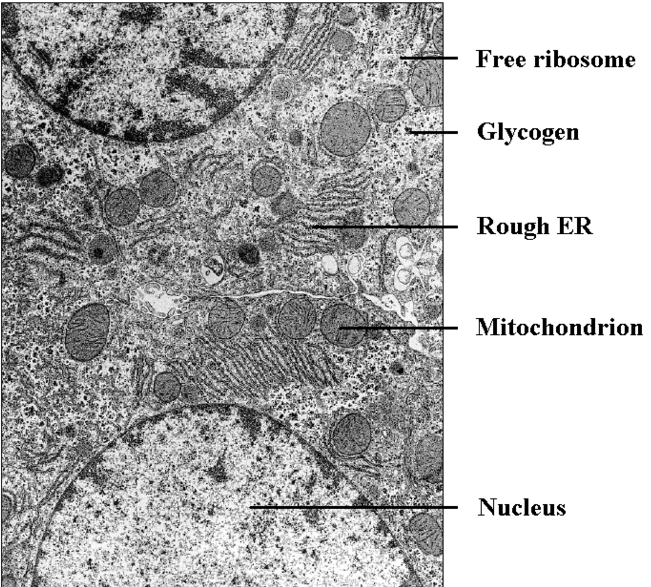
electron micro-graph image of cell

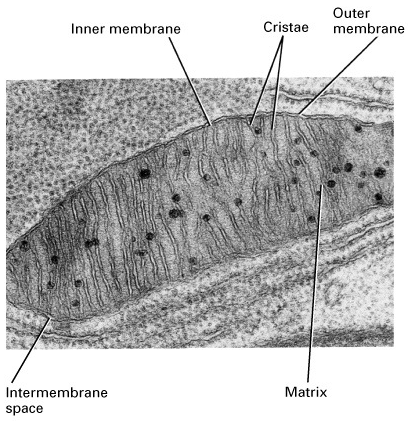
electron micro-graph image of Mitochondria
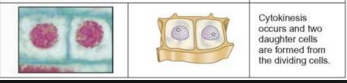
cytokinesis
Cytokinesis (kytos = hollow vessel = cell, and kinesis = movement): the two daughter cells become independent. During cytokinesis (example in Bellevalia) that follows up the actual mitosis, the cytoplasm of the daughter cells is divided by a cell membrane (and in plants also a cell wall) in two single compartments. In animal cells the separation of the new cells involves a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell membrane. In plants, this process is characterized by the formation and growth of a cell plate (example in Solanum sp.) that expands from the space between the two daughter nuclei towards the cell periphery. Sometimes remants of the spindle (phragmoplast) are involved in the attachment of this new wall.
Adipocytes
or adipose flat cell account for 90% of this tissue mass (almost pure trygliceride)