Character
Varieties with distinct heritable features such as the color of a flower. 2 alleles
Traits
Character variants (such as purple or white flowers)
True breeding
Producing offspring with the same trait. An organism must be homozygous. Referred to as P generation.
P generation
Parental (always F1=offspring true breeding). True breeding parents.
F1
Offspring. Hybrid offspring
F2 generation
When F1 individuals self-pollinate or cross- pollinate with other F1 hybrids.
F1*F1=F2 generation
Hybridization
The mating, or crossing, of two true breeding varieties.
Alleles are always found where?
On the homologous chromosome located on the locus
Allele
Alternative form of gene
Dominant allele
If two alleles at a locus differs then the dominant one determines the appearance of the organism. Example Dd, so the Bigger D will be the dominant
Recessive allele
Has no noticeable affect on the organisms appearance. Example Dd, so the smaller d will be recessive
Law of Segregation
The two alleles for a heritable character separate (segregate) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes.
Homozygous
An organism with two identical alleles for a character
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a gene
Phenotype
physical appearance
- PP and Pp plants have the same phenotype (purple) but different genotypes
Genotypes
Genetic makeup
- PP and Pp plants have the same phenotype (purple) but different genotypes
Monohybrids
The F1 offspring produced in this cross were monohybrids, individuals that are heterozygous for one character
Monohybrid cross
A cross between monohybrids
Dihybrids
Crossing two true-breeding parents differing in two characters. in the F1 generation, heterozygous for both characters
Law of independent assortment
Two or more enes sort independent of one another. States that each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation
Complete dominance
occurs when phenotypes of the heterozygote and dominant homozygote are identical
Multiplication rule
the probability that two or more independent events will occur together is the product of their individual probabilities
Incomplete Dominance
the phenotype of F1 hybrids is somewhere between the phenotypes of the two parental varieties. This is basically a mixture. Genotype takes on a mixture of both the dominant allele and recessive allele one allele red and the other White...both colors mix to make pink.
CoDominant
two dominant alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways
Pleitropy
Most genes have a phenotypic effects. ***Gives out several phenotypes
Epistasis
***Several alleles affect one phenotype.
Dihybrid crosses always gives you a phenotypic ratio of what?
9:3:3:1
1) What do we mean when we use the terms monohybrid cross and
dihybrid cross?
A) A monohybrid cross involves a single
parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
B) A
monohybrid cross produces a single progeny, whereas a dihybrid cross
produces two progeny.
C) A dihybrid cross involves organisms
that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross
involves only one.
D) A monohybrid cross is performed for one
generation, whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two
generations.
E) A monohybrid cross results in a 9:3:3:1 ratio
whereas a dihybrid cross gives a 3:1 ratio.
Answer: C
A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one.
Why did the F₁ offspring of Mendel's classic pea cross always look
like one of the two parental varieties?
A) No genes interacted
to produce the parental phenotype.
B) Each allele affected
phenotypic expression.
C) The traits blended together during
fertilization.
D) One phenotype was completely dominant over
another.
E) Different genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
Answer: D
One phenotype was completely dominant over another
Monohybrid always gives you a phenotypical ratio of what?
3:1
Norm of Reaction
Influenced by the enviornment
When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a single
trait with a heterozygote, what is the chance of producing an
offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
Answer: C
50%
How many unique gametes could be produced through independent
assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 32
E) 64
Answer: B
8
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a recessive human disorder in which an
individual cannot appropriately metabolize a particular amino acid.
The amino acid is not otherwise produced by humans. Therefore, the
most efficient and effective treatment is which of the following?
A) Feed them the substrate that can be metabolized into this
amino acid.
B) Transfuse the patients with blood from unaffected
donors.
C) Regulate the diet of the affected persons to severely
limit the uptake of the amino acid.
D) Feed the patients the
missing enzymes in a regular cycle, such as twice per week.
E)
Feed the patients an excess of the missing product.
Answer: C
Regulate the diet of the affected persons to severely limit the uptake of the amino acid
An obstetrician knows that one of her patients is a pregnant woman
whose fetus is at risk for a serious disorder that is detectable
biochemically in fetal cells. The obstetrician would most reasonably
offer which of the following procedures to her patient?
A) CVS
B) ultrasound imaging
C) amniocentesis
D) blood
transfusion
E) X-ray
Answer: C
amniocentesis
Why does recombination between linked genes continue to occur?
A) Recombination is a requirement for independent assortment.
B) Recombination must occur or genes will not assort
independently.
C) New allele combinations are acted upon by
natural selection.
D) The forces on the cell during meiosis II
always result in recombination.
E) Without recombination there
would be an insufficient number of gametes.
Answer: C
New allele combinations are acted upon by natural selection
In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the
heterozygous (Rr) offspring of red (RR) and white (rr) homozygotes.
Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of
1 red:2 roan:1 white?
A) red × white
B) roan ×
roan
C) white × roan
D) red × roan
E) The answer
cannot be determined from the information provided.
Answer: B
roan × roan
Recombination between linked genes comes about for what reason?
A) Nonrecombinant chromosomes break and then rejoin with one another.
B) Independent assortment sometimes fails.
C) Linked genes travel together at anaphase.
D) Crossovers between these genes result in chromosomal exchange.
Answer D
Crossovers between these genes result in chromosomal exchange.
Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions. Which of the following might then occur to make the cancer worse?
A) an increase in nondisjunction
B) expression of inappropriate gene products
C) a decrease in mitotic frequency
D) failure of the cancer cells to multiply
Answer B
expression of inappropriate gene products
Which of the following provides an example of epistasis?
A) Recessive genotypes for each of two genes (aabb) results in
an albino corn snake.
B) The allele b17 produces a dominant
phenotype, although b1 through b16 do not.
C) In rabbits and
many other mammals, one genotype (cc) prevents any fur color from
developing.
D) In Drosophila (fruit flies), white eyes can be
due to an X-linked gene or to a combination of other genes.
E)
In cacti, there are several genes for the type of spines.
Answer: C
In rabbits and many other mammals, one genotype (cc) prevents any fur color from developing.
One possible result of chromosomal breakage is for a fragment to join
a nonhomologous chromosome. What is this alteration called?
A)
deletion
B) transversion
C) inversion
D)
translocation
E) duplication
Answer: D
translocation
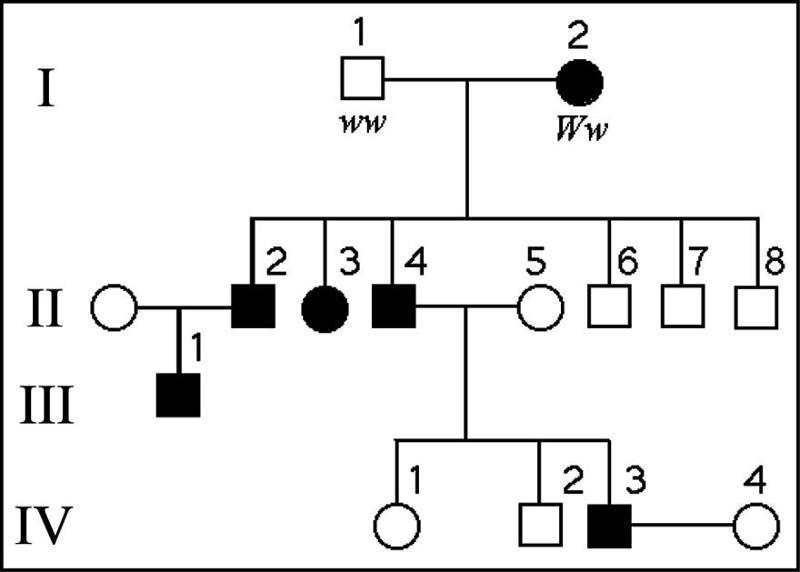
The following question refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 for
a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W.
Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
41) What is the likelihood that the progeny of IV-3 and IV-4
will have the trait?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D)
75%
E) 100%
Answer: C
50%
Which of the following statements is true of linkage?
A) The
closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a
crossover will occur between them.
B) The observed frequency of
recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a
maximum value of 100%.
C) All of the traits that Mendel
studied–seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others–are due to
genes linked on the same chromosome.
D) Linked genes are found
on different chromosomes.
E) Crossing over occurs during
prophase II of meiosis.
Answer: A
The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.

This a map of four genes on a chromosome (See Image)
51) Between which two genes would you expect the highest
frequency of recombination?
A) A and W
B) W and E
C)
E and G
D) A and E
E) A and G
Answer: E
A and G
Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails (T)
are dominant to long tails (t). What fraction of the progeny of
crosses BbTt × BBtt will be expected to have black fur and long tails?
A) 1/16
B) 3/16
C) 3/8
D) 1/2
E) 9/16
Answer: D
1/2
The following question refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 for
a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W.
Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
40) What is the genotype of individual II-5?
A) WW
B) Ww
C) ww
D) WW or ww
E) ww or Ww
Answer: C
ww
Which of the following is true of aneuploidies in general?
A) A
monosomy is more frequent than a trisomy.
B) 45 X is the only
known human live-born monosomy.
C) Some human aneuploidies have
selective advantage in some environments.
D) Of all human
aneuploidies, only Down syndrome is associated with mental
retardation.
E) An aneuploidy resulting in the deletion of a
chromosome segment is less serious than a duplication.
Answer: B
45 X is the only known human live-born monosomy
A couple has a child with Down syndrome. The mother is 39 years old
at the time of delivery. Which of the following is the most probable
cause of the child's condition?
A) The woman inherited this
tendency from her parents.
B) One member of the couple carried a
translocation.
C) One member of the couple underwent
nondisjunction in somatic cell production.
D) One member of the
couple underwent nondisjunction in gamete production.
E) The
mother had a chromosomal duplication.
Answer: D
One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in gamete production
What does a frequency of recombination of 50% indicate?
A) The
two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes.
B)
All of the offspring have combinations of traits that match one of the
two parents.
C) The genes are located on sex chromosomes.
D) Abnormal meiosis has occurred.
E) Independent
assortment is hindered.
Answer: A
The two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes.
) Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, the pancreas, the digestive
system, and other organs, resulting in symptoms ranging from breathing
difficulties to recurrent infections. Which of the following terms
best describes this?
A) incomplete dominance
B) multiple
alleles
C) pleiotropy
D) epistasis
E) codominance
Answer: C
pleiotropy
In humans, clear gender differentiation occurs, not at fertilization,
but after the second month of gestation. What is the first event of
this differentiation?
A) formation of testosterone in male
embryos
B) formation of estrogens in female embryos
C)
anatomical differentiation of a penis in male embryos
D)
activation of SRY in male embryos and masculinization of the gonads
E) activation of SRY in females and feminization of the gonads
Answer: D
activation of SRY in male embryos and masculinization of the gonads
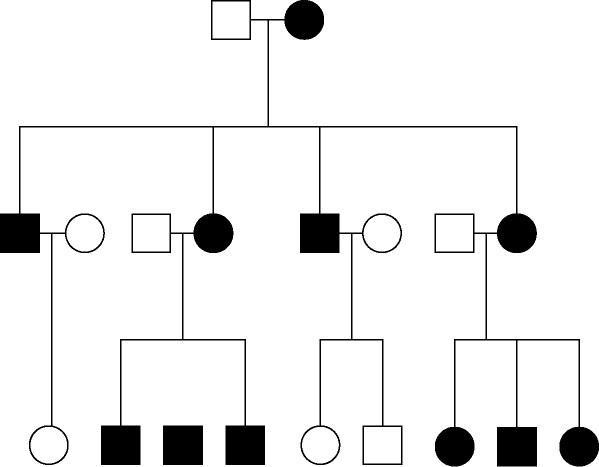
The pedigree in Figure 15.3 shows the transmission of a trait in a
particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is
most likely
A) mitochondrial.
B) autosomal recessive.
C) sex-linked dominant.
D) sex-linked recessive.
E)
autosomal dominant.
Answer: A
mitochondrial
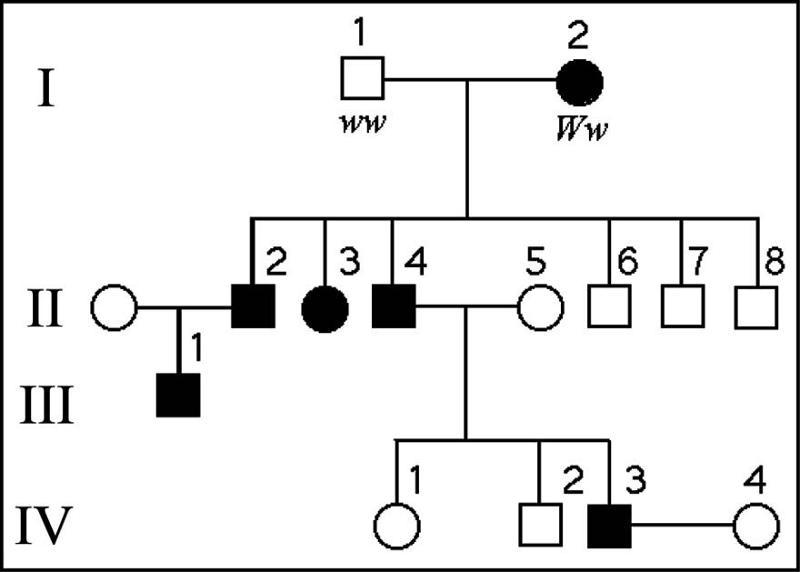
The following question refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 for
a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W.
Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
42) What is the probability that individual III-1 is Ww?
A) 3/4
B) 1/4
C) 2/4
D) 2/3
E) 1
Answer: E
1
Of the following human aneuploidies, which is the one that generally
has the most severe impact on the health of the individual?
A)
47, +21
B) 47, XXY
C) 47, XXX
D) 47, XYY
E)
45, X
Answer: A
47, +21
When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a single
trait with a heterozygote, what is the chance of producing an
offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
Answer: C
50%
Males are more often affected by sex-linked traits than females
because
A) male hormones such as testosterone often
alter the effects of mutations on the X chromosome.
B) female
hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of
mutations on the X chromosome.
C) X chromosomes in males
generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females.
D)
males are hemizygous for the X chromosome.
E) mutations on the
Y chromosome often worsen the effects of X-linked mutations.
Answer: D
males are hemizygous for the X chromosome
SRY is best described in which of the following ways?
A) a gene present on the X chromosome that triggers female
development
B) an autosomal gene that is required for the
expression of genes on the Y chromosome
C) a gene region present
on the Y chromosome that triggers male development
D) an
autosomal gene that is required for the expression of genes on the X
chromosome
E) a gene required for development, and males or
females lacking the gene do not survive past early childhood
Answer: C
a gene region present on the Y chromosome that triggers male development
What is a syndrome?
A) a characteristic facial appearance
B) a group of traits, all of which must be present if an
aneuploidy is to be diagnosed
C) a group of traits typically
found in conjunction with a particular chromosomal aberration or gene
mutation
D) a characteristic trait usually given the
discoverer's name
E) a characteristic that only appears in
conjunction with one specific aneuploidy
Answer: C
a group of traits typically found in conjunction with a particular chromosomal aberration or gene mutation
How many unique gametes could be produced through independent
assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 32
E) 64
Answer: B
8
When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result?
A) The gene involved is on the Y chromosome.
B) The gene involved is on the X chromosome.
C) The gene involved is on an autosome, but only in males.
D) Other male-specific factors influence eye color in flies.
Answer B
The gene involved is on the X chromosome
Which of the following is the best statement of the use of the
addition rule of probability?
A) the probability that two or
more independent events will both occur
B) the probability that
two or more independent events will both occur in the offspring of one
set of parents
C) the probability that either one of two
independent events will occur
D) the probability of producing
two or more heterozygous offspring
E) the likelihood that a
trait is due to two or more meiotic events
Answer: C
the probability that either one of two independent events will occur
Why did the F₁ offspring of Mendel's classic pea cross always look
like one of the two parental varieties?
A) No genes interacted
to produce the parental phenotype.
B) Each allele affected
phenotypic expression.
C) The traits blended together during
fertilization.
D) One phenotype was completely dominant over
another.
E) Different genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
Answer: D
One phenotype was completely dominant over another.
A nonreciprocal crossover causes which of the following products?
A) deletion only
B) duplication only
C)
nondisjunction
D) deletion and duplication
E) duplication
and nondisjunction
Answer: D
deletion and duplication
In certain plants, tall is dominant to short. If a heterozygous plant
is crossed with a homozygous tall plant, what is the probability that
the offspring will be short?
A) 1
B) 1/2
C) 1/4
D) 1/6
E) 0
Answer: E
0
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses
with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous
recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second
gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous
recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all.
61) The
relationship between genes S and N is an example of
A)
incomplete dominance.
B) epistasis.
C) complete
dominance.
D) pleiotropy.
E) codominance.
Answer: B
Humanoids on the newly explored planet Brin (in a hypothetical galaxy
in ~50 years from the present) have a gene structure similar to our
own, but many very different plants and animals.
73)
Marfan syndrome in humans is caused by an abnormality of the
connective tissue protein fibrillin. Patients are usually very tall
and thin, with long spindly fingers, curvature of the spine, sometimes
weakened arterial walls, and sometimes ocular problems, such as lens
dislocation. Which of the following would you conclude about Marfan
syndrome from this information?
A) It is recessive.
B) It
is dominant.
C) It has a late age of onset (> 60).
D)
It is pleiotropic.
E) It is epistatic.
Answer: D
It is pleiotropic
What is the reason that linked genes are inherited together?
A)
They are located close together on the same chromosome.
B) The
number of genes in a cell is greater than the number of chromosomes.
C) Chromosomes are unbreakable.
D) Alleles are paired
together during meiosis.
E) Genes align that way during
metaphase I of meiosis.
Answer: A
They are located close together on the same chromosome
The centimorgan (cM) is a unit named in honor of Thomas Hunt Morgan.
To what is it equal?
A) the physical distance between two linked
genes
B) 1% frequency of recombination between two genes
C) 1 nanometer of distance between two genes
D) the
distance between a pair of homologous chromosomes
E) the
recombination frequency between two genes assorting independently
Answer: B
1% frequency of recombination between two genes
An ideal procedure for fetal testing in humans would have which of
the following features?
A) the procedure that can be performed
at the earliest time in the pregnancy
B) lowest risk procedure
that would provide the most reliable information
C) the
procedure that can test for the greatest number of traits at once
D) a procedure that provides a three-dimensional image of the
fetus
E) a procedure that could test for the carrier status of
the fetus
Answer: A
the procedure that can be performed at the earliest time in the pregnancy
What is the source of the extra chromosome 21 in an individual with
Down syndrome?
A) nondisjunction in the mother only
B)
nondisjunction in the father only
C) duplication of the
chromosome
D) nondisjunction or translocation in either parent
E) It is impossible to detect with current technology.
Answer: D
nondisjunction or translocation in either parent
What do we mean when we use the terms monohybrid cross and dihybrid
cross?
A) A monohybrid cross involves a single parent,
whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
B) A monohybrid
cross produces a single progeny, whereas a dihybrid cross produces
two progeny.
C) A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are
heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only
one.
D) A monohybrid cross is performed for one generation,
whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two generations.
E) A
monohybrid cross results in a 9:3:3:1 ratio whereas a dihybrid cross
gives a 3:1 ratio.
Answer: C
A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one
Which of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance?
A) pink flowers in snapdragons
B) the ABO blood group in
humans
C) Huntington's disease in humans
D) white and
purple flower color in peas
E) skin pigmentation in humans
Answer: E
skin pigmentation in humans
At which phase(s) is it preferable to obtain chromosomes to prepare a
karyotype?
A) early prophase
B) late telophase
C)
anaphase
D) late anaphase or early telophase
E) late
prophase or metaphase
Answer: E
late prophase or metaphase
Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of
inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century?
A)
Individuals inherit particular chromosomes attached to genes.
B) Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and in
turn segregate during meiosis.
C) Homologous chromosomes give
rise to some genes and crossover chromosomes to other genes.
D)
No more than a single pair of chromosomes can be found in a healthy
normal cell.
E) Natural selection acts on certain chromosome
arrays rather than on genes.
Answer: B
Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and in turn segregate during meiosis.
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses
with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous
recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second
gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous
recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all.
62) A cross
between a true-breeding sharp-spined cactus and a spineless cactus
would produce
A) all sharp-spined progeny.
B) 50%
sharp-spined, 50% dull-spined progeny.
C) 25% sharp-spined, 50%
dull-spined, 25% spineless progeny.
D) all spineless progeny.
E) It is impossible to determine the phenotypes of the progeny.
Answer: A
A cross between a true-breeding sharp-spined cactus and a spineless cactus would produce
Two plants are crossed, resulting in offspring with a 3:1 ratio for a
particular trait. What does this suggest?
A) that the parents
were true-breeding for contrasting traits
B) that the trait
shows incomplete dominance
C) that a blending of traits has
occurred
D) that the parents were both heterozygous for a single
trait
E) that each offspring has the same alleles for each of
two traits
Answer: D
that the parents were both heterozygous for a single trait
Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans.
Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son. What are
the genotypes of the parents?
A) XcXc and XcY
B) XcXc and
XCY
C) XCXC and XcY
D) XCXC and XCY
E) XCXc and XCY
Answer: E
XCXc and XCY
Mendel's second law of independent assortment has its basis in which
of the following events of meiosis I?
A) synapsis of homologous
chromosomes
B) crossing over
C) alignment of tetrads at
the equator
D) separation of homologs at anaphase
E)
separation of cells at telophase
Answer: C
alignment of tetrads at the equator
Which of the following is known as a Philadelphia chromosome?
A) a human chromosome 22 that has had a specific
translocation
B) a human chromosome 9 that is found only in one
type of cancer
C) an animal chromosome found primarily in the
mid-Atlantic area of the United States
D) an imprinted
chromosome that always comes from the mother
E) a chromosome
found not in the nucleus but in mitochondria
Answer: A
a human chromosome 22 that has had a specific translocation
Which of the following is a function of a poly-A signal sequence?
A) It adds the poly-A tail to the 3' end of the mRNA.
B)
It codes for a sequence in eukaryotic transcripts that signals
enzymatic cleavage ~1035 nucleotides away.
C) It allows the 3'
end of the mRNA to attach to the ribosome.
D) It is a sequence
that codes for the hydrolysis of the RNA polymerase.
E) It adds
a 7-methylguanosine cap to the 3' end of the mRNA.
Answer: B
It codes for a sequence in eukaryotic transcripts that signals enzymatic cleavage ~1035 nucleotides away.
A frameshift mutation could result from
A) a base insertion
only.
B) a base deletion only.
C) a base substitution
only.
D) deletion of three consecutive bases.
E) either an
insertion or a deletion of a base.
Answer: E
either an insertion or a deletion of a base.
Which of the following does not occur in prokaryotic eukaryotic gene
expression, but does in eukaryotic gene expression?
A) mRNA,
tRNA, and rRNA are transcribed.
B) RNA polymerase binds to the
promoter.
C) A poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of an mRNA and
a cap is added to the 5' end.
D) Transcription can begin as soon
as translation has begun even a little.
E) RNA polymerase
requires a primer to elongate the molecule.
Answer: C
A poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of an mRNA and a cap is added to the 5' end.
What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding
the strands that make up DNA?
A) The twisting nature of DNA
creates nonparallel strands.
B) The 5' to 3' direction of one
strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
C) Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA
strands.
D) One strand is positively charged and the other is
negatively charged.
E) One strand contains only purines and the
other contains only pyrimidines.
Answer: B
The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
Which of the following help(s) to hold the DNA strands apart while
they are being replicated?
A) primase
B) ligase
C)
DNA polymerase
D) single-strand binding proteins
E) exonuclease
Answer: D
single-strand binding proteins
Accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a
polypeptide depends on specificity in the
A) binding of
ribosomes to mRNA.
B) shape of the A and P sites of ribosomes.
C) bonding of the anticodon to the codon.
D) attachment of
amino acids to tRNAs.
E) bonding of the anticodon to the codon
and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs.
Answer: E
bonding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs
Cytosine makes up 42% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an
organism. Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this
sample will be thymine?
A) 8%
B) 16%
C) 31%
D)
42%
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.
Answer: A
8%
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging
strand during DNA replication?
A) It synthesizes RNA nucleotides
to make a primer.
B) It catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres.
C) It joins Okazaki fragments together.
D) It unwinds the
parental double helix.
E) It stabilizes the unwound parental DNA.
Answer: C
It joins Okazaki fragments together
Which of the following variations on translation would be most
disadvantageous for a cell?
A) translating polypeptides directly
from DNA
B) using fewer kinds of tRNA
C) having only one
stop codon
D) lengthening the half-life of mRNA
E) having
a second codon (besides AUG) as a start codon
Answer: A
translating polypeptides directly from DNA
There are 61 mRNA codons that specify an amino acid, but only 45
tRNAs. This is best explained by the fact that
A) some tRNAs
have anticodons that recognize four or more different codons.
B)
the rules for base pairing between the third base of a codon and tRNA
are flexible.
C) many codons are never used, so the tRNAs that
recognize them are dispensable.
D) the DNA codes for all 61
tRNAs but some are then destroyed.
E) competitive exclusion
forces some tRNAs to be destroyed by nucleases.
Answer: B
the rules for base pairing between the third base of a codon and tRNA are flexible
Which of the following would you expect of a eukaryote lacking
telomerase?
A) a high probability of somatic cells becoming
cancerous
B) production of Okazaki fragments
C) inability
to repair thymine dimers
D) a reduction in chromosome length in
gametes
E) high sensitivity to sunlight
Answer: D
a reduction in chromosome length in gametes
The figure represents tRNA that recognizes and binds a particular
amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine). Which codon on the mRNA
strand codes for this amino acid?
A) UGG
B) GUG
C)
GUA
D) UUC
E) CAU
Answer: D
UUC
Which of the following sets of materials are required by both
eukaryotes and prokaryotes for replication?
A) double-stranded
DNA, four kinds of dNTPs, primers, origins
B) topoisomerases,
telomerases, polymerases
C) G-C rich regions, polymerases,
chromosome nicks
D) nucleosome loosening, four dNTPs, four rNTPs
E) ligase, primers, nucleases
Answer: A
double-stranded DNA, four kinds of dNTPs, primers, origins
To repair a thymine dimer by nucleotide excision repair, in which
order do the necessary enzymes act?
A) exonuclease, DNA
polymerase III, RNA primase
B) helicase, DNA polymerase I, DNA
ligase
C) DNA ligase, nuclease, helicase
D) DNA polymerase
I, DNA polymerase III, DNA ligase
E) endonuclease, DNA
polymerase I, DNA ligase
Answer: E
endonuclease, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase
Which of the following investigators was/were responsible for the
following discovery?
In DNA from any species, the amount of
adenine equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine equals
the amount of cytosine.
A) Frederick Griffith
B) Alfred
Hershey and Martha Chase
C) Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty, and
Colin MacLeod
D) Erwin Chargaff
E) Matthew Meselson and
Franklin Stahl
Answer: D
Erwin Chargaff
Transcription in eukaryotes requires which of the following in
addition to RNA polymerase?
A) the protein product of the
promoter
B) start and stop codons
C) ribosomes and tRNA
D) several transcription factors (TFs)
E) aminoacyl synthetase
Answer: D
several transcription factors (TFs)
When the function of the newly made polypeptide is to be secreted
from the cell where it has been made, what must occur?
A) It must
be translated by a ribosome that remains free of attachment to the ER.
B) Its signal sequence must target it to the ER, from which it
goes to the Golgi.
C) It has a signal sequence that must be
cleaved off before it can enter the ER.
D) It has a signal
sequence that targets it to the cell's plasma membrane where it causes
exocytosis.
E) Its signal sequence causes it to be encased in a
vesicle as soon as it is translated.
Answer: B
Its signal sequence must target it to the ER, from which it goes to the Golgi
What is a ribozyme?
A) an enzyme that uses RNA as a substrate
B) an RNA with enzymatic activity
C) an enzyme that
catalyzes the association between the large and small ribosomal
subunits
D) an enzyme that synthesizes RNA as part of the
transcription process
E) an enzyme that synthesizes RNA primers
during DNA replication
Answer: B
an RNA with enzymatic activity
In his transformation experiments, what did Griffith observe?
A) Mutant mice were resistant to bacterial infections.
B)
Mixing a heat-killed pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living
nonpathogenic strain can convert some of the living cells into the
pathogenic form.
C) Mixing a heat-killed nonpathogenic strain of
bacteria with a living pathogenic strain makes the pathogenic strain
nonpathogenic.
D) Infecting mice with nonpathogenic strains of
bacteria makes them resistant to pathogenic strains.
E) Mice
infected with a pathogenic strain of bacteria can spread the infection
to other mice.
Answer: B
Mixing a heat-killed pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living nonpathogenic strain can convert some of the living cells into the pathogenic form.
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation in a gene?
A) It
changes an amino acid in the encoded protein.
B) It has no
effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein.
C) It
introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
D) It alters
the reading frame of the mRNA.
E) It prevents introns from being excised.
Answer: C
It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA
Individuals with the disorder xeroderma pigmentosum are
hypersensitive to sunlight. This occurs because their cells are
impaired in what way?
A) They cannot replicate DNA.
B)
They cannot undergo mitosis.
C) They cannot exchange DNA with
other cells.
D) They cannot repair thymine dimers.
E) They
do not recombine homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Answer: D
They cannot repair thymine dimers.
For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the
Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to
label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They
reasoned that each nucleotide has only one phosphate and two to five
nitrogens. Thus, labeling the nitrogens would provide a stronger
signal than labeling the phosphates. Why won't this experiment work?
A) There is no radioactive isotope of nitrogen.
B)
Radioactive nitrogen has a half-life of 100,000 years, and the
material would be too dangerous for too long.
C) Avery et al.
have already concluded that this experiment showed inconclusive
results.
D) Although there are more nitrogens in a nucleotide,
labeled phosphates actually have 16 extra neutrons; therefore, they
are more radioactive.
E) Amino acids (and thus proteins) also
have nitrogen atoms; thus, the radioactivity would not distinguish
between DNA and proteins.
Answer: E
Amino acids (and thus proteins) also have nitrogen atoms; thus, the radioactivity would not distinguish between DNA and proteins.
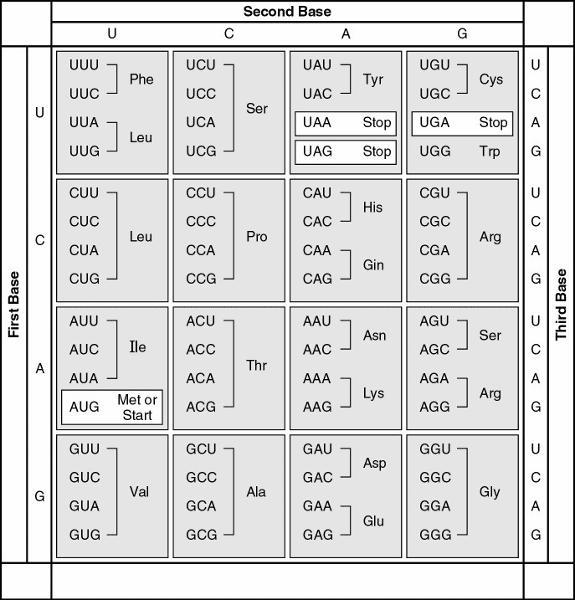
65) What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the
following mRNA codon sequence?
5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
A) met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
B) met-glu-arg-arg-glu-leu
C) met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
D) met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
E) met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
Answer: D
met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
What is the function of the release factor (RF)?
A) It
separates tRNA in the A site from the growing polypeptide.
B) It
binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA.
C) It
releases the amino acid from its tRNA to allow the amino acid to form
a peptide bond.
D) It supplies a source of energy for
termination of translation.
E) It releases the ribosome from the
ER to allow polypeptides into the cytosol.
Answer: B
It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA
What is the function of GTP in translation?
A) GTP energizes
the formation of the initiation complex, using initiation factors.
B) GTP hydrolyzes to provide phosphate groups for tRNA binding.
C) GTP hydrolyzes to provide energy for making peptide bonds.
D) GTP supplies phosphates and energy to make ATP from ADP.
E) GTP separates the small and large subunits of the ribosome at
the stop codon.
Answer: A
GTP energizes the formation of the initiation complex, using initiation factors
At a specific area of a chromosome, the sequence of nucleotides below
is present where the chain opens to form a replication fork:
3'
C C T A G G C T G C A A T C C 5'
An RNA primer is formed
starting at the underlined T (T) of the template. Which of the
following represents the primer sequence?
A) 5' G C C T A G G 3'
B) 3' G C C T A G G 5'
C) 5' A C G T T A G G 3'
D)
5' A C G U U A G G 3'
E) 5' G C C U A G G 3'
Answer: D
5' A C G U U A G G 3'
It became apparent to Watson and Crick after completion of their
model that the DNA molecule could carry a vast amount of hereditary
information in which of the following?
A) sequence of bases
B) phosphate-sugar backbones
C) complementary pairing of
bases
D) side groups of nitrogenous bases
E) different
five-carbon sugars
Answer: A
sequence of bases
Why do histones bind tightly to DNA?
A) Histones are positively
charged, and DNA is negatively charged.
B) Histones are
negatively charged, and DNA is positively charged.
C) Both
histones and DNA are strongly hydrophobic.
D) Histones are
covalently linked to the DNA.
E) Histones are highly
hydrophobic, and DNA is hydrophilic.
Answer: A
Histones are positively charged, and DNA is negatively charged.
A particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is AAA.
The anticodon on the tRNA that binds the mRNA codon is
A) TTT.
B) UUA.
C) UUU.
D) AAA.
E) either UAA or TAA,
depending on first base wobble.
Answer: C
UUU.
Which of the following help(s) to hold the DNA strands apart while
they are being replicated?
A) primase
B) ligase
C)
DNA polymerase
D) single-strand binding proteins
E) exonuclease
Answer: D
single-strand binding proteins
A transcription unit that is 8,000 nucleotides long may use 1,200
nucleotides to make a protein consisting of approximately 400 amino
acids. This is best explained by the fact that
A) many noncoding
stretches of nucleotides are present in mRNA.
B) there is
redundancy and ambiguity in the genetic code.
C) many
nucleotides are needed to code for each amino acid.
D)
nucleotides break off and are lost during the transcription process.
E) there are termination exons near the beginning of mRNA.
Answer: A
many noncoding stretches of nucleotides are present in mRNA
Which of the following can be determined directly from X-ray
diffraction photographs of crystallized DNA?
A) the diameter of
the helix
B) the rate of replication
C) the sequence of
nucleotides
D) the bond angles of the subunits
E) the
frequency of A vs. T nucleotides
Answer: A
the diameter of the helix
What is the function of DNA polymerase III?
A) to unwind the
DNA helix during replication
B) to seal together the broken ends
of DNA strands
C) to add nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing
DNA strand
D) to degrade damaged DNA molecules
E) to
rejoin the two DNA strands (one new and one old) after replication
Answer: C
to add nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing DNA strand
Why might a point mutation in DNA make a difference in the level of
protein's activity?
A) It might result in a chromosomal
translocation.
B) It might exchange one stop codon for another
stop codon.
C) It might exchange one serine codon for a
different serine codon.
D) It might substitute an amino acid in
the active site.
E) It might substitute the N-terminus of the
polypeptide for the C-terminus.
Answer: D
It might substitute an amino acid in the active site
Accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a
polypeptide depends on specificity in the
A) binding of
ribosomes to mRNA.
B) shape of the A and P sites of ribosomes.
C) bonding of the anticodon to the codon.
D) attachment of
amino acids to tRNAs.
E) bonding of the anticodon to the codon
and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs.
Answer: E
bonding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs.
If a cell were unable to produce histone proteins, which of the
following would be a likely effect?
A) There would be an
increase in the amount of "satellite" DNA produced during
centrifugation.
B) The cell's DNA couldn't be packed into its
nucleus.
C) Spindle fibers would not form during prophase.
D) Amplification of other genes would compensate for the lack of
histones.
E) Pseudogenes would be transcribed to compensate for
the decreased protein in the cell.
Answer: B
The cell's DNA couldn't be packed into its nucleus.
In an experimental situation, a student researcher inserts an mRNA
molecule into a eukaryotic cell after he has removed its 5' cap and
poly-A tail. Which of the following would you expect him to find?
A) The mRNA could not exit the nucleus to be translated.
B) The cell recognizes the absence of the tail and
polyadenylates the mRNA.
C) The molecule is digested by
restriction enzymes in the nucleus.
D) The molecule is digested
by exonucleases since it is no longer protected at the 5' end.
E) The molecule attaches to a ribosome and is translated, but
more slowly.
Answer D
The molecule is digested by exonucleases since it is no longer protected at the 5' end
A frameshift mutation could result from
A) a base insertion
only.
B) a base deletion only.
C) a base substitution
only.
D) deletion of three consecutive bases.
E) either an
insertion or a deletion of a base.
Answer: E
either an insertion or a deletion of a base.
The leading and the lagging strands differ in that
A) the
leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of
the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the
opposite direction.
B) the leading strand is synthesized by
adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the
lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end.
C) the lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the
leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately
stitched together.
D) the leading strand is synthesized at twice
the rate of the lagging strand.
Answer: A
the leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction.
A mutation results in a defective enzyme A. Which of the following
would be a consequence of that mutation?
A) an accumulation of A
and no production of B and C
B) an accumulation of A and B and
no production of C
C) an accumulation of B and no production of
A and C
D) an accumulation of B and C and no production of A
E) an accumulation of C and no production of A and B
Answer: A
an accumulation of A and no production of B and C
A new DNA strand elongates only in the 5' to 3' direction because
A) DNA polymerase begins adding nucleotides at the 5' end of the
template.
B) Okazaki fragments prevent elongation in the 3' to
5' direction.
C) the polarity of the DNA molecule prevents
addition of nucleotides at the 3' end.
D) replication must
progress toward the replication fork.
E) DNA polymerase can only
add nucleotides to the free 3' end.
Answer: E
DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the free 3' end.
Which of the following is a function of a signal peptide?
A) to
direct an mRNA molecule into the cisternal space of the ER
B) to
bind RNA polymerase to DNA and initiate transcription
C) to
terminate translation of the messenger RNA
D) to translocate
polypeptides across the ER membrane
E) to signal the initiation
of transcription
Answer: D
to translocate polypeptides across the ER membrane
Which of the following statements describes chromatin?
A)
Heterochromatin is composed of DNA, whereas euchromatin is made of DNA
and RNA.
B) Both heterochromatin and euchromatin are found in
the cytoplasm.
C) Heterochromatin is highly condensed, whereas
euchromatin is less compact.
D) Euchromatin is not transcribed,
whereas heterochromatin is transcribed.
E) Only euchromatin is
visible under the light microscope.
Answer: C
Heterochromatin is highly condensed, whereas euchromatin is less compact
Polytene chromosomes of Drosophila salivary glands each consist of
multiple identical DNA strands that are aligned in parallel arrays.
How could these arise?
A) replication followed by mitosis
B) replication without separation
C) meiosis followed by
mitosis
D) fertilization by multiple sperm
E) special
association with histone proteins
Answer: B
replication without separation
The nitrogenous base adenine is found in all members of which group?
A) proteins, triglycerides, and testosterone
B) proteins,
ATP, and DNA
C) ATP, RNA, and DNA
D) α glucose, ATP, and
DNA
E) proteins, carbohydrates, and ATP
Answer: C
ATP, RNA, and DNA
How do we describe transformation in bacteria?
A) the creation
of a strand of DNA from an RNA molecule
B) the creation of a
strand of RNA from a DNA molecule
C) the infection of cells by a
phage DNA molecule
D) the type of semiconservative replication
shown by DNA
E) assimilation of external DNA into a cell
Answer: E
assimilation of external DNA into a cell
The tRNA shown in the figure has its 3' end projecting beyond its 5'
end. What will occur at this 3' end?
A) The codon and anticodon
complement one another.
B) The amino acid binds covalently.
C) The excess nucleotides (ACCA) will be cleaved off at the
ribosome.
D) The small and large subunits of the ribosome will
attach to it.
E) The 5' cap of the mRNA will become covalently bound.
Answer: B picture
The amino acid binds covalently
During splicing, which molecular component of the spliceosome
catalyzes the excision reaction?
A) protein
B) DNA
C) RNA
D) lipid
E) sugar
Answer: C
RNA
What is the function of topoisomerase?
A) relieving strain in
the DNA ahead of the replication fork
B) elongating new DNA at a
replication fork by adding nucleotides to the existing chain
C)
adding methyl groups to bases of DNA
D) unwinding of the double
helix
E) stabilizing single-stranded DNA at the replication fork
Answer: A
relieving strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork
Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a DNA strand in the 5' → 3'
direction?
A) primase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA
polymerase III
D) topoisomerase
E) helicase
Answer: C
DNA polymerase III
Which of the following nucleotide triplets best represents a codon?
A) a triplet separated spatially from other triplets
B) a
triplet that has no corresponding amino acid
C) a triplet at the
opposite end of tRNA from the attachment site of the amino acid
D) a triplet in the same reading frame as an upstream AUG
E) a sequence in tRNA at the 3' end
Answer: D
a triplet in the same reading frame as an upstream AUG
An Okazaki fragment has which of the following arrangements?
A)
primase, polymerase, ligase
B) 3' RNA nucleotides, DNA
nucleotides 5'
C) 5' RNA nucleotides, DNA nucleotides 3'
D) DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III
E) 5' DNA to 3'
Answer: C
DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III
Which of the following does not occur in prokaryotic eukaryotic gene
expression, but does in eukaryotic gene expression?
A) mRNA,
tRNA, and rRNA are transcribed.
B) RNA polymerase binds to the
promoter.
C) A poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of an mRNA and
a cap is added to the 5' end.
D) Transcription can begin as soon
as translation has begun even a little.
E) RNA polymerase
requires a primer to elongate the molecule.
Answer: C
A poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of an mRNA and a cap is added to the 5' end.
Wild type
found normally in nature
Where is SRY gene found?
Y chromosome only
Recombination frequency equation
Add Recombiant offspring(last 2) x 100
Total offspring
17% crossover will occur ***Not linked
16% under ***Linked
Cant go over 50
Topoisomerase
Untwists the DNA
Leading Strand
Continuous
Helicase
Unzips DNA-breaks hydrogen bond between the two strands of DNA
Single Strand Binding Protein
Protector
Primase
primer (RNA mucleotides) needs the primer to start DNA replication
Dna Pol III
5
DNA ligase
its going to come in and seal in the gaps.