
Betty Friedan
Betty Freidan argued that college-educated women should have more opportunities to work outside the home and family, in order to provide them with the opportunity to exercise all their talents. This book helped inspire the "second wave" of feminism--more concerned with professional and personal issues than with political and legal ones.

William Levitt/Levittown (PARENT)
A mass-produced suburban housing development in New York which came to represent post-WWII suburbanization. The development consisted of cheaply produced, identical houses which would be bought by middle class families.

Billy Graham (BHATIA)
Graham was a well known Baptist minister. He is well known for his strong oratory skills and how this was able to help persuade massive audiences across the nation to accept Christ.

Alfred Kinsey (BHATIA)
Author of two books on sexual behavior and statistics on the topic. These books turned out to be best sellers but raised controversy because of the moral issues surrounding them. As a result of the complaints, the government stopped the funding of Kinsey's work.

Thurgood Marshall (VEERAMANI)
Thurgood Marshall was the first African American appointed as a Justice of the Supreme Court. He earned that position as Chief Counsel of the NAACP, who argued a large number of cases before the Supreme Court - mostly notably in Brown vs. Board of Education (Topeka).

Earl Warren (ROSS)

Earl Warren was the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court during the 1950s and 1960s. Warren's court expanded civil rights and ruled many important civil rights cases as unconstitutional. Brown v. the Board of Education and Engel v. Vitale were two very important cases that came in front of Warren's court.
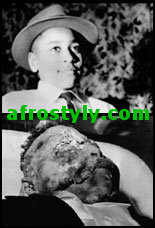
Emmett Till (VEERAMANI)
Emmett Till was a fourteen-year-old African American boy who allegedly whistled at a white woman, which caused the white men in the town to find a reason to lynch (murder) him. Till was originally from the North, just visiting with relatives, and was not accustomed to the extreme white supremacy found in the South. His murderers were acquitted of all supposed crimes.

Rosa Parks (ROSS)
Rosa Parks, an African-American woman, is famed for having not given up her bus seat to a white man in 1955. Parks was arrested, and her actions led to the bus boycott led by Martin Luther King Jr. in Montgomery, Alabama. The boycott ultimately led to desegregation legislation and a greater expansion of the civil rights movement.

Martin Luther King, Jr. (ROSS)
Martin Luther King Jr. is probably the best known Civil Rights leader of all time. King championed nonviolence and direct confrontation as the best way for blacks to receive their rights. King was also the chairman of the SCLC (Southern Christian Leadership Conference.) King's "I Have a Dream" speech was given at the March on Washington in 1963, which he helped organized.

"Kitchen Debate" (VEERAMANI)
The Kitchen Debate was the first high profiled meeting between the Soviet Union and the US since the Geneva Summit in 1955. It was basically a continuing dialogue (via interpreters) between Krushchev and Nixon at the opening of the American National Exhibition at Sokolniki Park in Moscow on July 24, 1959. For the exhibit, a full scale American house was built that Nixon claimed anyone in America could afford. It was stocked with many new appliaces that 'made life easier' which Krushchev ridiculed.
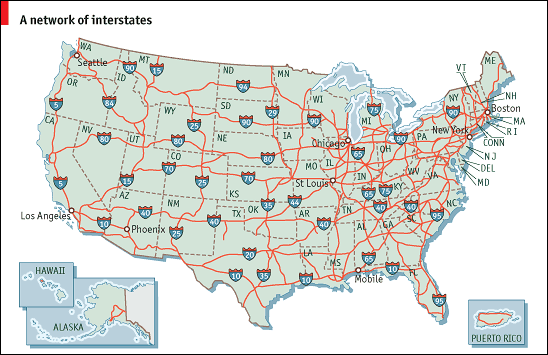
Interstate Highway and Defense Act of 1956 (SALTZMAN)
Initiated during the Eisenhower administration, the Interstate Highway and Defense Act of 1956 had many benefits, including an easier way for the American defense system to travel cross-country, a burst in economic growth (making it easier to travel further distances), and an increase in many industries including those of construction, automobiles, trucking, fast food, and motels. Consequences included: passing over small towns, increase in air pollution, and declining railways.

"Brinksmanship" (ANDERSON)
Brinksmanship was the name coined by Secretary of State Dulles to describe America's nuclear weapons policies. The US developed continually more advanced nuclear arms that were meant to intimidate the Soviets and keep them from attacking America; this was called "brinksmanship" because the US was going to the brink of war with these new weapons.

Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD) (ANDERSON)
MAD was the standoff brought on by both Soviet and American fears that, if either nation instigated a nuclear attack, the other would produce just as much destruction. It was described by Winston Churchill as a "mutual balance of terror."

Domino Theory (VEERAMANI)
The Domino Theory was first brought up by Harry Truman in the wake of WWII, when Turkey and Greece were resisting Communist takeover. It was a term used to describe the ripple effect Communism would have - if it struck one country, it was apt to strike other suscpetible countries near it. Eisenhower also used this term in relation to Communism in Vietnam during their revolution for freedom against France.

Geneva Accords (ROSS)
The Geneva Accords were the 1954 decision to divide Vietnam at the seventeenth north latitude. North Vietnam became nationalist while SOuth Vietnam was a Western-influenced government. The Geneva Accords also provided free elections in Vietnam.

SEATO (ROSS)
SEATO (Southeast Asia Treaty Organization 1954-1977) was created as a response to communism in Southeast Asia after France left Indochina. The original members included the US, Britain, France, Pakistan, Thailand, and the Philippines. SEATO was meant to justify American troops in Vietnam.
United Fruit Company (VEERAMANI)
The United Fruit Company (UFC) was a US corporation whose annual profits were twice the size of the Guatemalan government's profits. Arbenz, the ruler of Guatemala in the 50s, sought to compensate the United Fruit company for land they owned but didn't cultivate to give to poor peasants. The UFC did not approve of this, so they worked with the CIA to organize an coup of the Guatemalan government.

Eisenhower Doctrine (SALTZMAN)
Similar to the Truman Doctrine, the Eisenhower Doctrine stated that America will assist any Middle Eastern nation "against armed aggression from any country controlled by international communism." It was passed in March 1957 and was first used for Jordan and later Lebanon.

Sputnik (VEERAMANI)
The Sputnik was the first man-made satellite to orbit the Earth. It was launched by the Soviet Union, who beat the United States because of the US's failure to launch their own satellite before the Soviet Union (it exploded).

NASA (SALTZMAN)
NASA (the National Aeronautics and Space Administration) was established in July 1958 by President Eisenhower. It was created in response to the USSR's fast growing space development, starting off with their launch of Sputnik. A portion of the federal budget was set aside for the development of NASA and the government pushed for more development in the space industry.

U-2 Incident (ROSS)
In 1960, Eisenhower sent a U-2 plane into the Soviet Union with the intention of spying. The Soviets shot down the plane, and Eisenhower admitted to intent to spy. The incident was greatly embarrassing to the US and marked the progressively worsening Soviet-US relations.

Military-Industrial Complex (BHATIA)
The reference made by President Dwight D. Eisenhower towards the danger of the US Army joining with larger industries to make bigger, more powerful weapons. Eisenhower warned the American public of the total control that may imposed by this collaboration.

The Affluent Society (BHATIA)
The term given by leading economist John Kenneth Galbraith to describe the higher standard of living many Americans enjoyed due to the increase in jobs, income, benefits, and economic improvement.
Sun Belt (VEERAMANI)
The Sun Belt was West and Southwest area of the United States where both the population and business sector were growing, which resulted in a revitalized economy and new suburban development.

Operation Wetback (SALTZMAN)
Operation Wetback happened during 1954. It was a series of raids in which more than a million Mexican who did not possess documentation were deported and some incidents of mistaken identity occurred as well. These raids left Mexican-Americans feeling unwelcome and threatened.
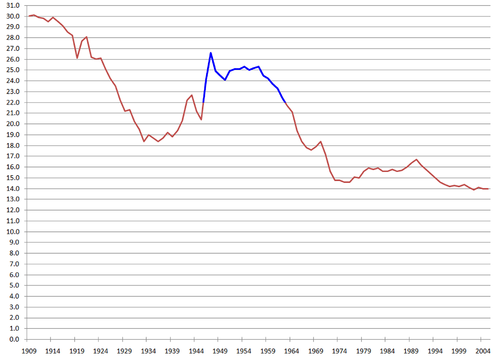
Baby Boom Generation (VEERAMANI)
The Baby Boom Generation consists of people who were born between 1946 and 1964 (post WWII). This sector of the public makes up a large part of the population - 20 percent. In the years immediately after the war, the dramatic increase in population created a large demand for consumer goods - which rejuvenated the economy.

Beat Generation (BHATIA)
The Beats were a popular writing group who influenced the lives of the younger generation. These people were commonly dissented as some had thought them to be controversial.

Brown v. Board of Education (ROSS)
Brown v. Board of Education was a Supreme Court case during the Warren times that challenged the "separate but equal" decision of the Plessy v. Ferguson case. Judge Earl Warren ruled that separate but equal facilities was not constitutional and demanded states to integrate schools. The South did not cooperate and made the integration nearly impossible.

Central High School/Little Rock Nine (BHATIA)
Little Rock Nine was a group of African American Students who were to integrate the Central High School located Little Rock, Arkansas. While in this school, the faced harassment from the public, and the students. At one point, the Governor of Arkansas had even sent for troops to block the school from these students just because he didn't want integration of the school.

Montgomery Bus Boycott (VEERAMANI)
The Montgomery Bus Boycott was a civil disobedience action mobilized by the WPC because of Rosa Park's unjust arrest for failure to give up her seat to a white man. It called for African Americans in Montgomery to stay off the public transport systems, which would take away a large amount of business from the bus companies, and force them to change the law.

SCLC (BHATIA)
The group formed by mostly Southern African American minsters whose main goal was to contribute ideas as to how to integrate the south. These people appointed the young, Martin Luther King as their spokesman.