Ecology
The study of ecosystems or how organisms interact with each other and their environment.
Biosphere
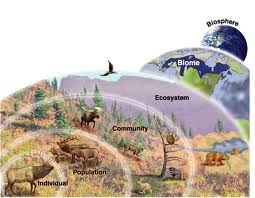
Largest level or organization. The zone of life on earth that includes all living things.
Population

A group of the same species of individuals living in the same area and interacting with each other in some way.
Community

Populations of different species that live in a specific location.
Ecosystem

A community or group of organisms living and interacting with other and their environment (non living factors)
Exponential Growth
Unchecked reproduction of a population of organisms. Occurs when each individual in a population reproduces, the offspring reproduce, and then the offpring of the offspring reproduce.
Carrying Capacity
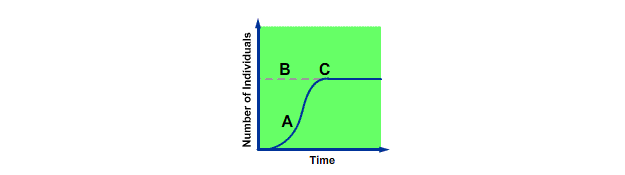
The largest population that a given ecosystem can support at any time. It is determined by the availability of resources.
Biotic Factors
Living things or things associated with or the result from the activities of living organisms in an ecosystem.
Abiotic Factors
Nonliving thing in an ecosystem such as rocks, soil, climate, etc.
Trophic Level
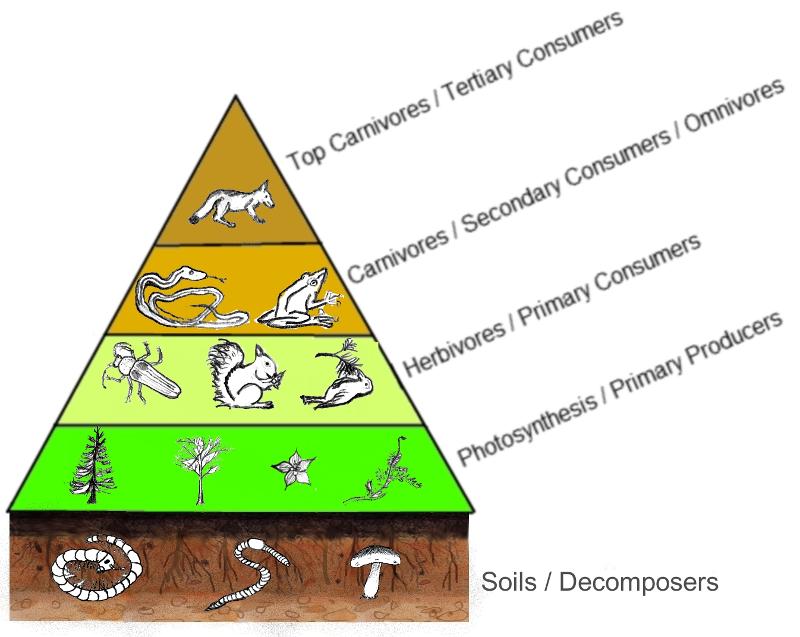
A producing or feeding level in a food chain.
Producer
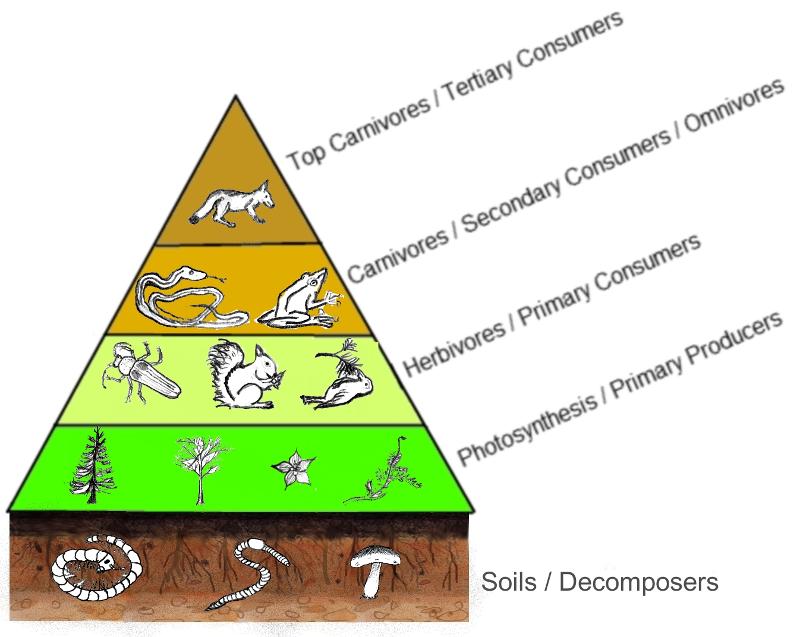
1st trophic level in organization. Plants and other photosynthetic organisms that produce glucose (converts sun energy into chemical energy). Also known as autotroph.
Food Chain
The pathway along with food/energy is transferred from one organism to another.
Food Web
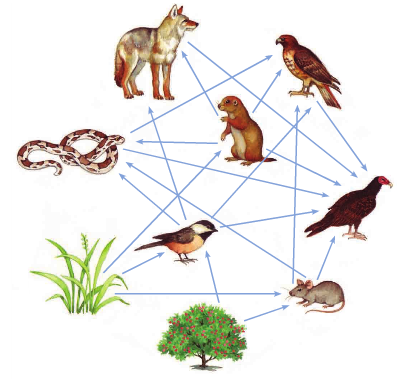
Shows flow of energy in all of the interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
Consumer
An organism that eats other organisms or are heterotrophs.
- Primary consumer - herbivores, eats producers
- Secondary consumer - eats primary consumers
- Tertiary consumer - eats secondary consumer
Keystone Species
Species that plays a key role in maintaining ecosystem stability.
Biome
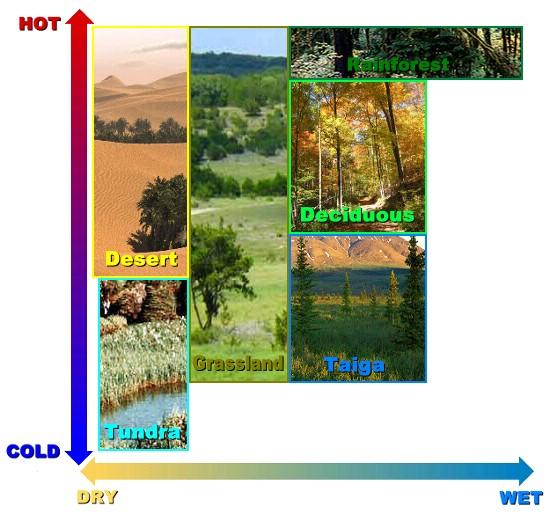
A large area dominated by characteristic plants and animals, such as a rain forest, desert, or tundra. Determined by participation and temperature. It is the broadest level of ecological classification within the biosphere.
Biodiversity
The variety of species and total number of individuals of each of species living in a defined area. An important indicator in how healthy and well-functioning an ecosystem is.
Limiting Factors
Limits the potential for a population to grow exponentially due to the availability of resources such as food, water and predators.
Heterotroph
Organisms that eat other organisms for energy. Also known as consumers.
Autotroph
Organisms that produces its own food either by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Also known as a producer.
Aquatic Ecosystem
An ecosystem in water - can be marine (saltwater) or freshwater ecosystems.
Terrestrial Ecosystem
Ecosystem found on land. 6 main types:
- Tundra
- Taiga
- Temperate Deciduous forest
- Tropical Rain Forest
- Grassland
- Desert
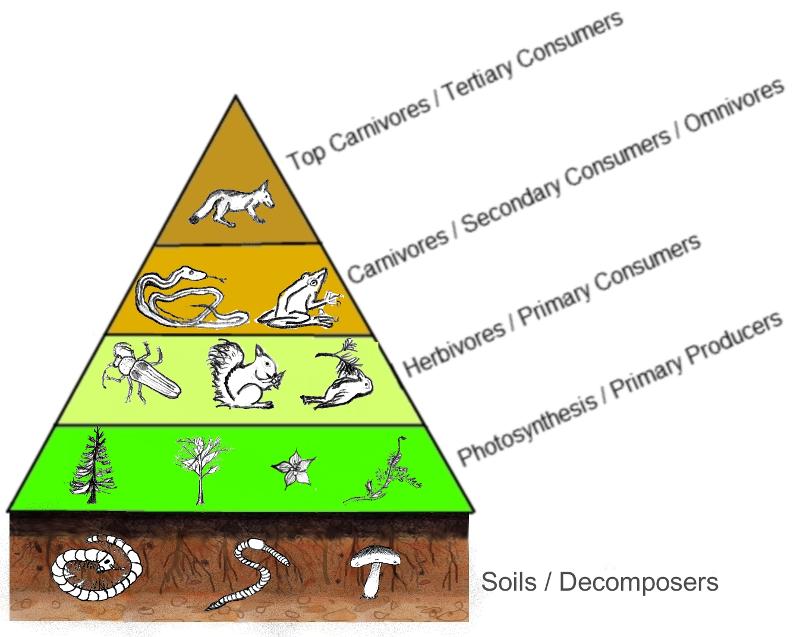
Ecological Pyramid
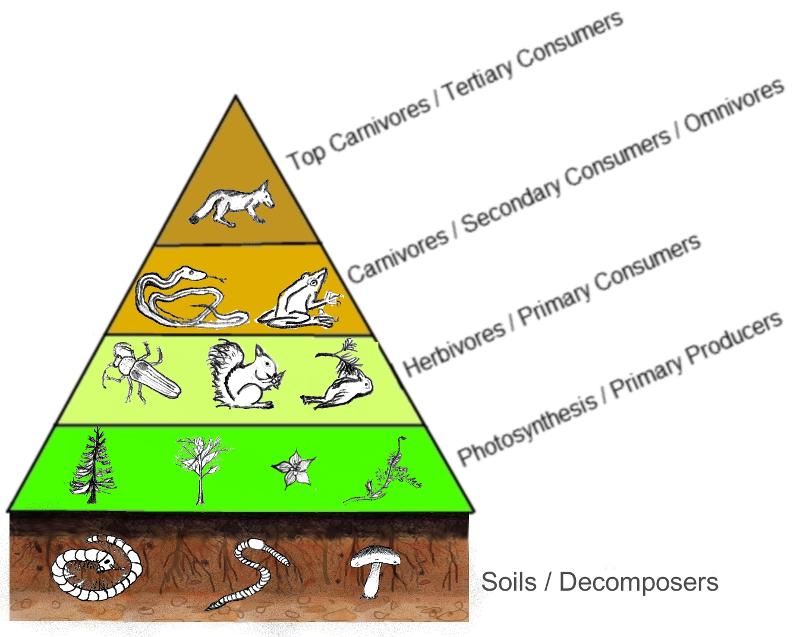
A graphical model that is shaped like a pyramid to show how the energy flows through a food chain.
Energy Pyramid
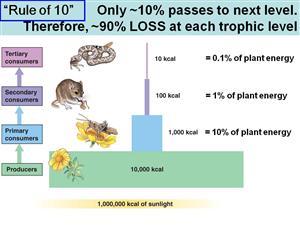
A graphical representation of the total amount of chemical energy present at each trophic level of an ecosystem.
10% rule
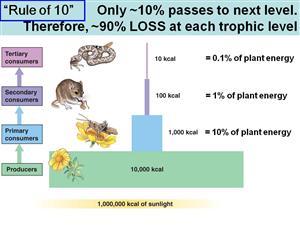
Used to explain energy flow in energy pyramids. In each trophic level, 90% of the available energy is used by that level and 10% moves up to the next level when they are eaten.
Primary Succession
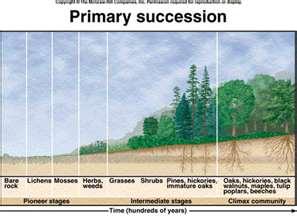
The change in species composition in a defined area over time, starting on ground that has no living things on it.
Pioneer Species
First plants or animals to inhibit bare land.
Succession
When ecosystems change over time through the progressive replacement of species.
Secondary Succession
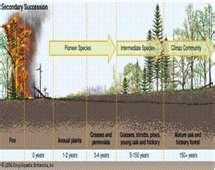
Changes in plant and animals life in an established ecosystem, can only occur after an ecosystem is in place.
Climax Community
A stable, long-lasting community that results from succession.
Non native species
Organisms that have invaded established ecosystems and disturbs the balance of the ecosystems. Also known as invasive species.
Water Cycle
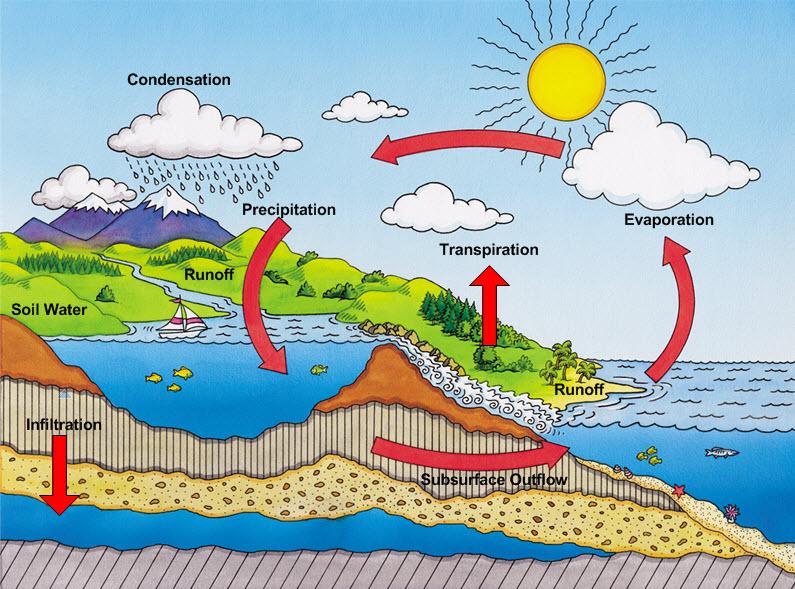
How water is stored and moved between land, air, and living things.
Condensation
Part of water cycle where water vapor condenses into liquid water by clinging to dust or other small particles suspended in the atmosphere, forming clouds
Evaporation
Part of the water cycle where liquid water changes to water vapor due to heat from the sun.
Transpiration
Part of the water cycle where a plant loses water to the atmosphere through the surface of its leaves.
Respiration

Processes in which organisms exchanges gases with its environment. Part of the water cycle because animals exhale water vapor into the air during respiration.
Decomposer
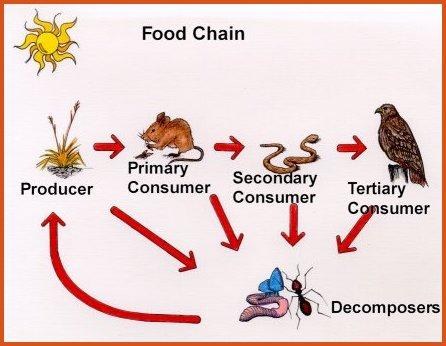
Organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that consume very small bits of organic matter from dead organisms and breaks them down into chemicals that are recycled back into the environment.
Symbiosis
The relationship between two different kinds of living things that live together and depend on each other. Three kinds:
- Mutalistic
- Parasitic
- Commensalistic
Mutalism
Type of symbiosis where both organisms in the relationship benefit.
Parasitism
Type of symbiosis where one organism benefits (parasite) at the expense of the other (host).
Commensalism
Type of symbiosis where one organism benefits and the other is not affected.
Nitrogen Cycle
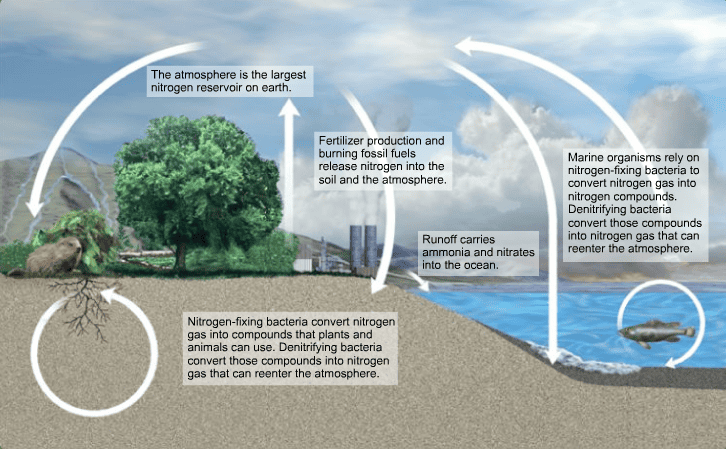
Cycle where nitrogen changes into different chemical forms. Atmosphere is largest reservoir of nitrogen, but is not useable so it needs to be converted into useable forms for organism.
Nitrogen Fixing

Conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonia and nitrates by bacteria. Bacteria form symbiotic relationship with plants to provide usable nitrogen for plants.
Denitrification
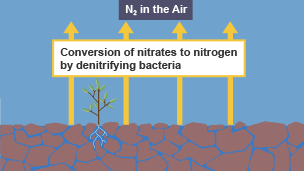
The conversion of nitrate to gaseous nitrogen by bacteria, which then enters the atmosphere. These bacteria use nitrogen compounds instead of oxygen for their processes of respiration.
Carbon Cycle
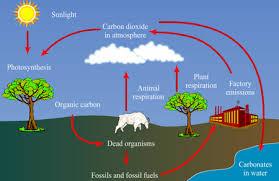
Processes that recycle carbon, one of the most important elements on earth, between earth's soil, atmosphere, and organisms.
Oxygen Cycle
Processes that cycle of oxygen between air, land, and organisms.
Renewable Resources
Resources that regenerate or regrow fast enough for us to keep using them. Ex: radiant energy, livestock, wind and water.
Nonrenewable Resources
Resources which either cannot be renewed at all or take such a long time to renew that people cannot depend on the renewal. Ex: oil and fossil fuels.
Greenhouse Effect
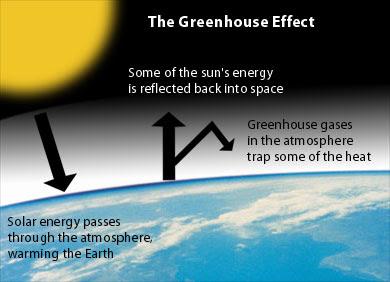
The process in which the atmosphere reflects radiation bouncing off earth's surface.
Greenhouse gases
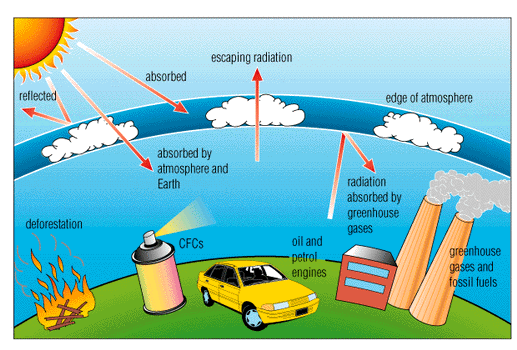
Gasses in the atmosphere which trap radiant energy, such as carbon dioxide. Increased greenhouse gases are thought to be causing global warming.
Pollution
The presence of harmful materials in the environment.
Competition
An interaction between organisms or species, in which fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another
Predation
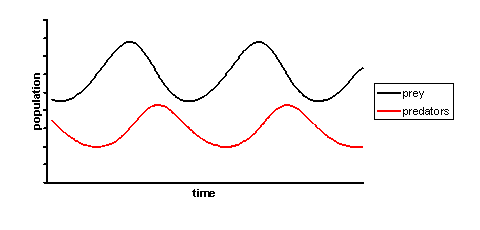
Where a predator feeds on a prey. Population size of the predator affect the population size of the prey and vise versa.