Nucleotide
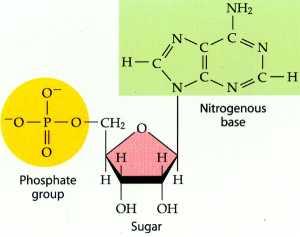
the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA/RNA) that consists of a phosphate group, a five carbon sugar, and a nitrogen base.
DNA
(Deoxyribonucleic acid)
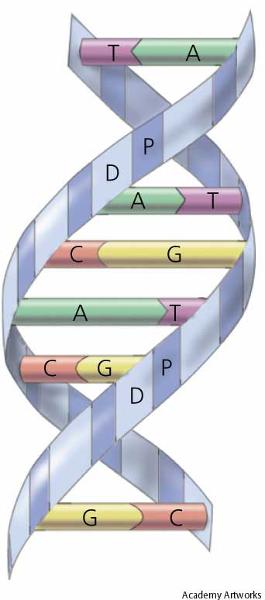
Nucleic acid in each cell that contains genetic information.
Double stranded helix
Contains sugar deoxyribose
Double Helix

The structure of DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides bonded together and twisted to form a double stranded helix shape.
Hydrogen Bonds
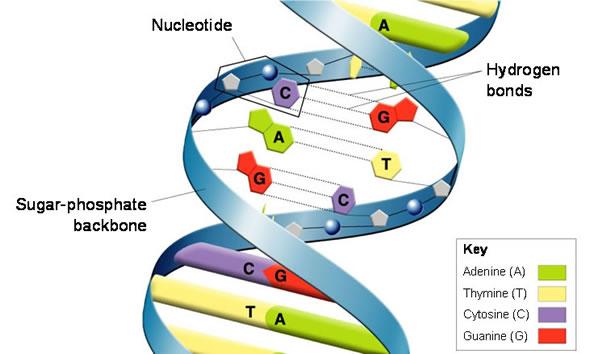
Weak bonds between nitrogen bases that hold the 2 DNA strands together.
Deoxyribose
The 5 carbon sugar found in the nucleotides that make up DNA.
Nitrogen Bases
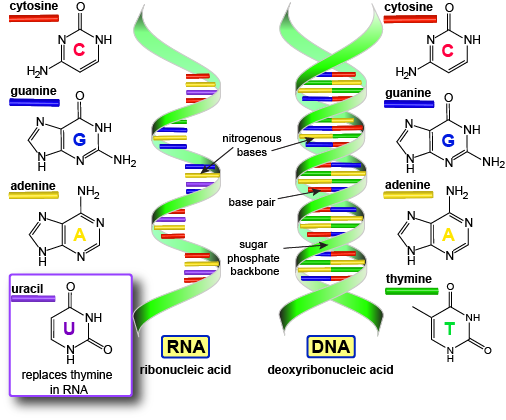
Nitrogen bases are part of a nucleotide. DNA has adenine, THYMINE, guanine, and cytosine. RNA has adenine, URACIL, guanine and cytosine.
Complementary Base Pairing Rules
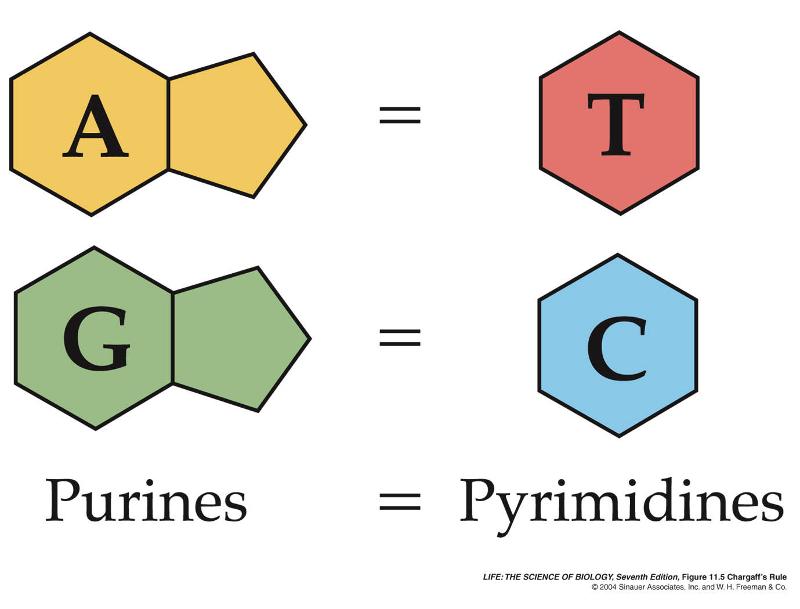
Bases always bond together in specific pairs:
Adenine with Thymine (DNA) or Uracil (RNA)
Cytosine with Guanine
RNA
(Ribonucleic acid)
Nucleic acid that uses the instructions stored in DNA to make proteins.
Usually single stranded
Contains sugar ribose
3 Type of RNA
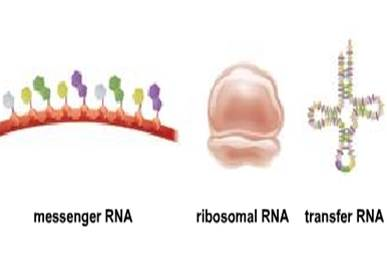
Messenger RNA (mRNA) -copy of DNA, made during transcription and used in translation, contains codons to code for specific amino acids.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - wrapped with proteins to form ribosomes, used in translation
Transfer RNA (tRNA) - shaped like t, contains anticodon to match up with codon on mRNA, carries amino acids to make proteins during translation.
Messenger RNA
(mRNA)
Single stranded RNA molecule that is a copy of DNA's genetic code. Contains codons. Made through transcription.
Ribosomal RNA
(rRNA)
Type of RNA that combines with many small proteins to make up a ribosome.
Transfer RNA
(tRNA)
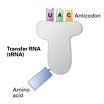
Type of RNA that carries amino acids coded for in mRNA to make proteins. Contains anticodon.
Transcription
1st process used to make proteins. Copies info in DNA and make a mRNA. Occurs in the nucleus.
DNA strands separate to expose 1 gene. RNA nucleotides are brought in to match up with exposed bases on DNA, following complementary base pair rules.
Translation
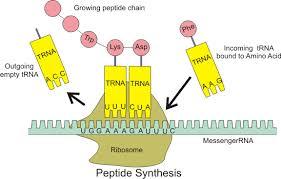
Process that makes proteins. Instructions carried by mRNA are read by rRNA. Amino acids are brought in by tRNA and are assembled to make protein strand.
Uses all 3 types of RNA.
Occurs in cytoplasm
Codon
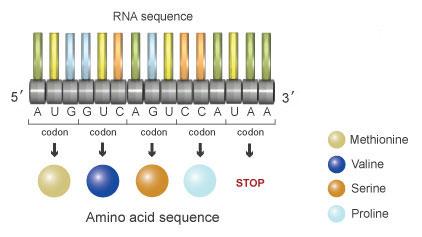
A sequence of 3 bases on mRNA that codes for a single amino acid.
Anticodon

3 bases on a tRNA molecule that complementary matchs a specific codon on a mRNA molecule, assuring that the correct amino acid is incorporated in a protein.
Amino Acids
The building block of proteins. Amino Acids are bonded together with peptide bonds to form a protein molecule and are assembled during translation.
Ribosomes
Composed of RNA and proteins. Makes proteins by translating the information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) into a polypeptide.
Genetic Code
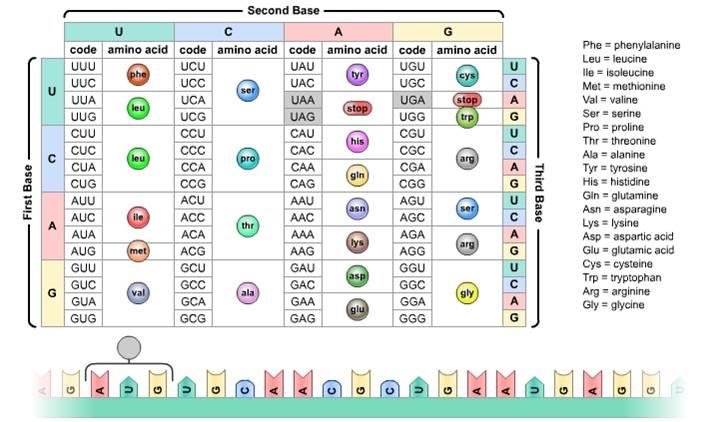
Triplets or codons of DNA sequences that code for a specific amino acid. It is the code that determines the amino acid sequence of proteins.
Chromosome
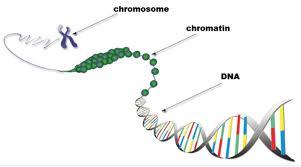
DNA strand wrapped around proteins.
Gene
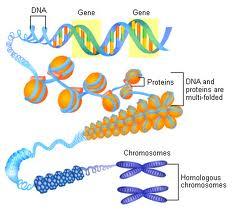
Segment on DNA that codes for a protein and directs the development of some inherited traits.
Gene Expression
Activation of a gene to produce a protein.
Recombinant DNA
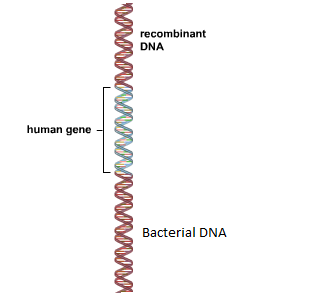
Type of DNA molecule that is created in a laboratory and incorporates the DNA of two or more organisms.
Plasmid
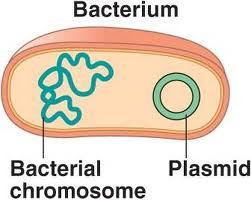
A single, circular piece of bacterial DNA that is separate from the main chromosome. Usually where DNA from other organisms is inserted for genetic engineering.
Genomics
The study of the whole genome or entire set of DNA in an organism.
Genome

The full set of DNA in an organism's cells.
Mutations
Random changes in DNA sequence. Can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect.
Point or Substitution Mutations
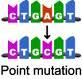
Mutations that only change 1 base in DNA sequence.
Missense Mutations
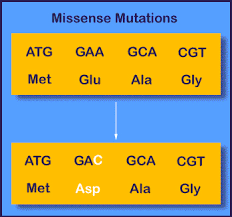
Type of point mutation where 1 base is changed causing a substitution of amino acid in protein, which causes change in protein structure.
Nonsense Mutations
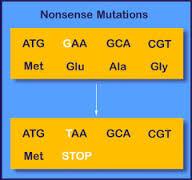
Type of point mutation where 1 base is changed causing a premature stop in protein production.
Silent Mutation
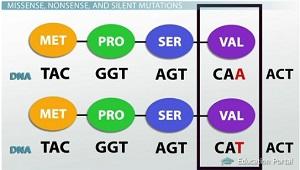
Type of point mutation where 1 base is change, but it codes for the same amino acid as original so the amino acid sequence is not changed.
Frameshift Mutations
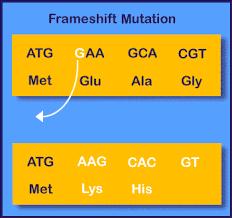
Mutation of DNA where multiple bases which results in every codon is changed after addition or deletion.
Deletion
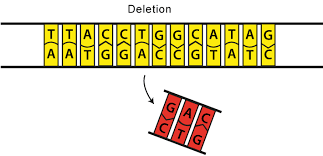
Mutation of DNA or in chromosome genes where bases are removed or deleted.
Insertion
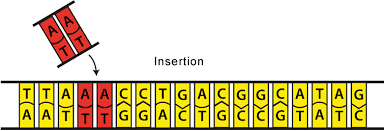
Mutation of DNA where bases or in chromosome genes are added or inserted.
Duplication
Chromosomal mutation where part of the chromosome is copied or duplicated.
Translocation
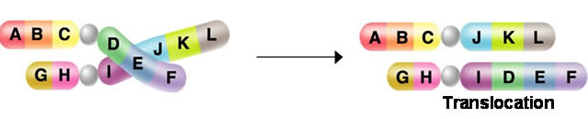
Chromosomal mutation where part of a chromosome is transferred to a non homologous chromosome.
Inversion
Chromosomal mutation where a part of a chromosome is reversed.
Nondisjunction
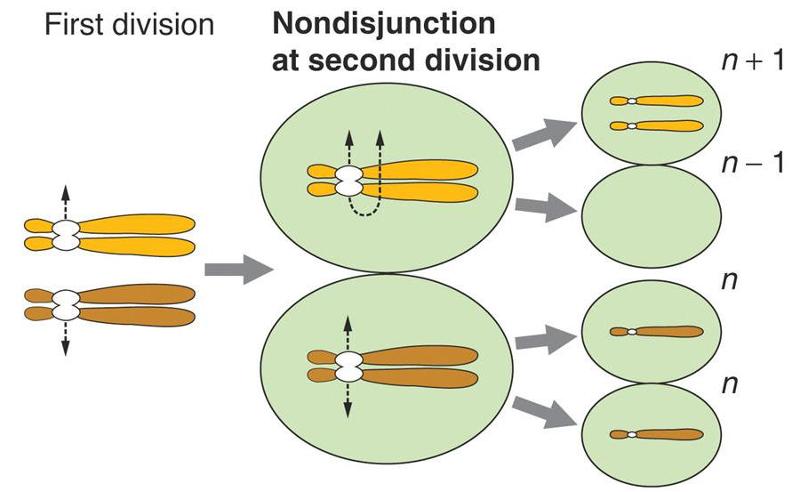
Chromosomal mutation where chromosomes do not separate properly during meiosis resulting in 1 cell having an extra chromosome and 1 cell missing a chromosome.
Biotechnology
Use of living systems and organisms to develop or make useful products.
Cloning
The process of producing genetically identical individuals.
DNA Fingerprinting
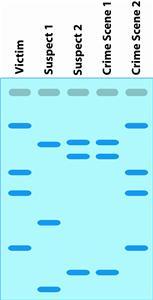
A test usded to identify and evaluate the DNA of a person's cells - creates a DNA profile that can be used to identify individuals.
DNA Sequencing

The process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule.
Electrophoresis
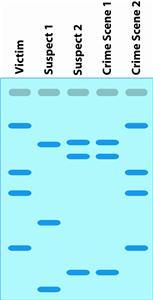
A technique used to separate and sometimes purify macromolecules. Used in DNA fingerprinting to separate fragments of of DNA based on size to get a DNA profile.
Gene Splicing
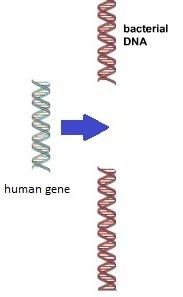
Used in genetic modification which involves cutting a gene from one organism and pasting it into the DNA of another organism to form recombinant DNA.
Gene Therapy
The use of DNA as a drug to treat disease by delivering therapeutic DNA into a patient's cells.
Genetic Engineering
Manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology.
Genetically Modified Organisms
(GMOs)
Organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
(PCR)

A biotechnology technique that copies a specific DNA sequence to produce millions of copies of that DNA sequence
Restriction Enzymes
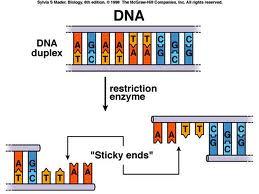
Enzymes that cuts DNA at or near a specific nucleotide sequence. Used to form recombinant DNA.
Selective Breeding
Also known as artificial selection. Process of breeding plants and animals for particular genetic traits.
Stem Cells
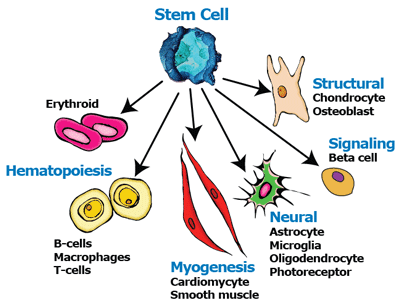
Undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into specialized cells.
Transgenic Organisms
Organism whose genetic characteristics have been altered using the techniques of genetic engineering.