Heartburn is most often felt in the ____.
epigastric region
A transverse plane ____.
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
The plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts is called the ____.
frontal plane
Determines the set point and appropriate response in a negative feedback system.
control center
Provides the means to respond to the stimulus in a negative feedback system.
effector
Cervical refers to the ____.
neck
Pedal refers to the ____.
foot
Homeostatic imbalance has occurred when a person ____.
becomes ill
The ____ cavity contains the bladder and rectum.
pelvic
Which internal organ is NOT housed in the ventral body cavity?
spinal cord
The abdominal regions that are lateral to the hypogastric region.
iliac
Listening to heart and breathing sounds with a stethoscope is ____.
auscultation
Lungs are located in the ____ cavities
pleural, ventral, and thoracic
Given these levels of organization: a) cell, b) chemical, c) organelle, d) organ, e) tissue. Choose the arrangement that lists the levels of organization in the correct order from smallest to largest.
chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ
____ is considered the "father of physiology." He was the first to propose that all parts of the body are served by a vein, artery, and nerve.
Erasistratus
Pollex is _____ to carpal.
distal
The term _____ refers to the arm.
brachial
Internal body temperature averages 37 C but fluctuates from 36.5 to 37.5 C. A body temperature of 37 C can therefore be considered the ____ for this variable.
set point
The anatomical position is characterized by all of the following except _____.
palms turned posteriorly
Which of the following imaging devices would best identify blockages in arteries that supply the brain or heart wall?
DSA
____ is a chemical reaction that breaks bonds between the monomers in a polymer (e.g., polysaccharide), and this process ____ water.
Dehydration synthesis ... utilizes
Which of the following lipids in your diet are thought to decrease the risk of heart disease?
omega-3 fatty acids
Human blood has a pH of about ___ and this is slightly ____.
7.4 ... basic
Prostaglandins are ____.
lipids
Which of the following molecules' major function is to provide a ready, easily used source of cellular fuel?
carbohydrates
The single most abundant protein in the body is ____.
collagen
Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscles in the form of ____.
glycogen
Which of the following is NOT true of proteins?
They are the molecular carriers of coded hereditary information.
A "chain" of 25 amino acids is best referred to as a relatively ____.
small polypeptide
Strands of RNA are made from ____ (units), and they are produced via the ____ of a water molecule between each two units.
nucleotides ... "removal"
The coiling of the protein chain backbone into an alpha helix is referred to as the ____ structure.
secondary
Glycogen is a _____ composed of ____.
polysaccharide ... glucose
The genetic information is coded in DNA by the ____.
sequence of the nucleotides
The four elements that make up about 96% of body matter are ____.
carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
The _____ structure of a protein is the sequence of ____.
primary ... amino acids
Which statement about enzymes is false?
Enzymes raise the activation energy needed to start a reaction.
A phospholipid is usually ____.
partially hydrophilic and partially hydrophobic
Sucrose is a ____.
disaccharide
An example of a protein that functions in transport is ____.
hemoglobin
Triglycerides and steroids are ____.
hydrophobic
Once solid material is phagocytized and taken into a vacuole, which of the following statements best describes what happens?
A lysosome combines with the vacuole and digests the enclosed solid material.
Which of the following statements is most correct regarding the intracellular chemical signals known as "second messengers?"
Cyclic AMP and calcium are second messengers.
Which of the following correctly lists the relative abundance of membrane lipids from the most abundant to the least abundant?
phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids
In osmosis, net movement of water occurs toward the solution with the lower solute concentration.
false
Which of the following is a principle of the fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure?
Phospholipids form a bilayer that is largely impermeable to water-soluble molecules.
Which of the following is a function of a plasma membrane protein?
molecular transport through the membrane
Cell junctions that promote the coordinated activity of cells by physically binding them together into a cell community include all of the following except ________.
microvilli
Peroxisomes ____.
are able to detoxify substances by enzymatic action
Which structures are fingerlike projections that greatly increase the absorbing surface of cells?
microvilli
The ____ is a coating of glycoproteins and glycolipids on the surface of a cell that can be involved in cell recognition.
glycocalyx
A red blood cell placed in pure water would ____.
swell and burst
Which of the following statements is correct regarding diffusion?
The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion.
Which of the following correctly matches a cell structure with its function?
Nucleoli ... Dense spherical bodies in the nucleus that are the synthesis site for ribosomal RNA.
Which of the following is a concept of the cell theory?
A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
Which of the following correctly matches the term with its definition?
Cholesterol ... Plasma membrane lipid that improves the rigidity of the plasma membrane and increases the membrane's impermeability to water.
Which of the following correctly matches the term with its definition?
Osmosis ... The movement of water across a selectively permeable plasma membrane from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
Which of the following correctly matches the substance(s) with the method that would move it into a cell?
Large particles, bacteria, or cellular debris ... Phagocytosis
Which of the following structures is correctly matched with its function?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ... Lipid synthesis
The active transport of sodium ions across the cell membrane which then provides a diffusion gradient for the transport of glucose, is an example of ____.
secondary active transport
Most of the molecules in the cell membrane that serve as receptors, gates, and carriers are _____.
proteins
Which of the following correctly matches a membrane to its location?
Serous ... makes up the pleura and pericardium
Inability to absorb digested nutrients and secrete mucus might indicate a disorder in which tissue?
simple columnar
The shape of the external ear is maintained by ____.
elastic cartilage
Which statement best describes connective tissue?
usually contains a large amount of matrix
____ epithelium appears to have two or three layers of cells, but all the cells are in contact with the basement membrane.
Pseudostratified columnar
Which of the following is TRUE about the mode of secretion by exocrine glands?
Secretory cells of merocrine glands are not altered by the secretory process.
Matrix is ____.
protein fibers and ground substance
Which of the following is NOT connective tissue?
muscle
Select the correct statement regarding epithelia.
Stratified epithelia are present where protection from abrasion is important.
The presence of lacunae and calcium salts would indicate ____ tissue.
osseous
Glands, such as the thyroid, that secrete their products directly into the blood rather than through ducts are classified as ____.
endocrine
What type of connective tissue has matrix composed almost entirely of parallel collagen fibers and is found in tendons and ligaments?
dense regular
Ovarian follicles and seminiferous tubules (of the testes) are lined with ____ epithelium.
stratified cuboidal
Glands that release an oily substance on the skin surface are ____.
sebaceous
Striated, branched cells with intercalated discs are characteristic of ____.
cardiac muscle
____ covers the outer surface of the lungs.
Visceral pleura
____ membranes form the lining of joint cavities.
synovial
____ tissue covers external and internal surfaces of the body and forms most glands.
epithelial
____ epithelium forms the lining of respiratory airways.
Pseudostratified columnar
Fibrocartilage is found in ____.
disks between the vertebrae
The ____ are muscles attached to the hair follicles which can cause "goose bumps" when they contract?
arrector pili
Fingernails are ____.
a modification of the epidermis
Changes in the color of skin are often an indication of a homeostatic imbalance. Which of the following changes would suggest that a patient is suffering from Addison's disease?
The skin takes on a bronze or metallic appearance.
Diaphoresis refers to secretions from ____ glands that help to cool the body.
sudiferous glands
A needle would pierce the epidermal layers of the forearm in which order?
corneum, granulosum, spinosum, basale
Despite its apparent durability, the dermis is subject to tearing. How might a person know that the dermis has been stretched and/or torn?
The appearance of visible, silvery-white scars is an indication of stretching of the dermis.
Select the correct statement concerning skin cancer.
Melanomas are rare but must be removed quickly to prevent them from metastasizing.
Melanocytes and keratinocytes work together in protecting the skin from UV damage because the role of the keratinocytes is to ____.
accumulate the melanin granules on their superficial portion, forming a pigment barrier that protects DNA from UV radiation
What is the first threat to life from a massive third-degree burn?
dehydration
Water loss through the epidermis could cause a serious threat to health and well-being. Which of the following protects us against excessive water loss through the skin?
Lamellated granules of the cells of the stratum granulosum (a glycolipid that is secreted into extracellular spaces).
Apocrine glands, which begin to function at puberty under hormonal influence, seem NOT to be useful in thermoregulation. Where would we find these glands in the human body?
in the axillary and anogenital area
Melanocytes are ____.
in contact with cells in the stratum basale
Eyebrow hairs are always shorter than hairs on your head (scalp) because ____.
eyebrow follicles are only active for a few months of the year
The epidermis consists of four to five layers of cells, each layer with a distinct role to play in the health, well-being, and functioning of the skin. Which of the following layers is responsible for cell division and replacement?
stratum basale
Which of the following touch receptors is found in the epidermis?
Merkel cells
The integumentary system is protected by our immune system through the action of cells that arise from bone marrow and migrate to the epidermis. Which of the following cells serve this immune function?
dendritic cells
The dermis has two major layers; which of the following constitutes 80% of the dermis and is responsible for the tension lines in the skin?
reticular layer
The ____ glands are modified apocrine glands that secrete a waxy material.
ceruminous
A large amount of the body's stored fat is located in the _____.
hypodermis
Which of the following skin conditions is correctly matched with its cause?
porphyria ... an inherited metabolic disorder
Both compact bone and a medullary cavity are present in the ____ bones.
diaphysis of long
The ____ are layers of calcified matrix that appear as concentric rings in a cross-section of bone.
lamellae
____ are found in both compact and spongy bone.
lacunae, caniliculi, lamellae
____ ossification produces flat bones of the skull and ____ ossification produces long bones.
Intramembranous ... endochondral
Bones of the axial skeleton include ____.
occipital, parietal, & atlas
Examples of long, short, flat & irregular bones are ____, respectively.
humerus, carpals, sternum & vertebrae
The fundamental structural unit of compact bone is the ____.
osteon
Bone growth that increases bone width or diameter occurs primarily ____.
on the bone surface under the periosteum
The endosteum is ____ tissue that ____.
connective ... lines medullary cavities
During childhood, an increase in the length of long bones occurs via ____ growth at the ____.
interstitial ... epiphyseal plate
Trabeculae occur ____ bones.
inside flat
Blood vessels and nerve fibers pass through the ____ of each osteon.
central canal
____ marrow is the site of blood-forming (stem) cells. This type of marrow is most abundant in ____.
Red ... young children
The fusion of marrow stem cells produces the ____ which are located on the bone surface and can remove bone as needed.
osteoclasts
Epiphyses are the ____.
ends of long bones
Little cavities occupied by osteocytes in mature bone are ____.
lacunae
Little canals that connect adjacent lucunae in bone are ____.
canaliculi
In middle-aged adults, ___ marrow is found primarily in the bones of the axial skeleton whereas ___ marrow is found primarily in the long bones of the limbs.
red ... yellow
Within the epiphyseal plate, cartilage grows on the ____ side and new bone is formed on the ____ side.
epiphyseal ... diaphyseal
Ossification is produced by the ____.
osteoblasts
Which of the following glands or organs produces hormones that tend to decrease blood calcium levels?
thyroid
Which hormone increases osteoclast activity to release more calcium ions into the bloodstream?
calcitrol
Bones are constantly undergoing resorption for various reasons. Which of the following cells accomplishes this process?
osteoclast
In bone formation, a deficiency of growth hormone will cause _____.
decreased proliferation of the epiphyseal plate cartilage
Factors in preventing (or delaying) osteoporosis include _____.
drinking fluoridated water
What kind of tissue is the forerunner of long bones in the embryo?
hyaline cartilage
When blood calcium levels become too low, ____ promotes the transfer of calcium from ____.
parathyroid hormone ... bone to blood
Which of the following would NOT be a potential cause of hypocalcemia?
underactive thyroid C cells
____ is the softening of bones in adults due to vitamin D or calcium deficiency.
Osteomalacia
Which of the following would NOT tend to increase levels of calcium in the blood?
increased activity of osteoblasts
The ligaments that protect the alignment of the femoral and tibial condyles and limit the movement of the femur anteriorly and posteriorly are called ____.
cruciate ligaments
In the classification of joints, which of the following is TRUE?
All synovial joints are freely movable.
When a ballerina points the toes, the ankle movement is known as ____.
plantar flexion
Connective tissue sacs lined with synovial membranes that act as cushions in places where friction develops are called ____.
bursae
Fibrous joints are classified as ____.
sutures, syndesmoses, and gomphoses
A synovial cavity, articular cartilage, synovial membrane, and ligaments are present in a ____.
hinge joint
Football players often sustain lateral blows to the extended knee. Which of the ligaments is/are often damaged as a result?
medial collateral, medial meniscus, and anterior cruciate
Which of these joint types affords uniaxial movement?
hinge
Which of the following statements defines synchondroses?
cartilaginous joints where hyaline cartilage unites the ends of bones
Menisci refer to ____.
semilunar cartilage pads
Articulations permitting only slight degrees of movement are ____.
amphiarthroses
Bending your head back until it hurts is an example of ____.
hyperextension
An interosseus fibrous joint is present between the ____.
radius and ulna along its length
____ are cartilaginous joints.
Synchondroses
The terms inversion and eversion pertain only to movements at the ____.
feet
Synarthrotic joints ____.
permit essentially no movement
The shoulder joint is a good example of a(n) ____ synovial joint.
multiaxial
On the basis of structural classification, which joint is fibrous connective tissue?
syndesmosis
When one is moving a limb away from the median plane of the body along the frontal plane, it is called ____.
abduction
A joint united by dense fibrocartilaginous tissue that permits a slight degree of movement is a ____.
symphysis
The muscle cell membrane is called a(n) ____.
sarcolemma
Smooth muscles that function somewhat like skeletal muscles but are controlled by autonomic nerves and hormones are _____ muscles.
multiunit
Which of the following is NOT a usual result of cross-training exercise?
a significant increase in the number of muscle cells
____ is used by muscle cells to convert ADP to ATP.
Creatine phosphate
Which of the following surrounds a muscle fascicle?
perimysium
Most skeletal muscles contain ____.
a mixture of slow-oxidative, fast-oxidative, and fast-glycolytic fibers
During muscle contraction, ____ heads attach to active sites on the ____ to form cross-bridges.
myosin ... actin
In an isotonic contraction, the muscle ____.
changes in length and moves the "load"
After nervous stimulation of the muscle cell has ceased, the calcium ____.
level in the sarcoplasm declines
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical with many nuclei.
Which of the following does NOT correctly match a muscle fiber band with its appropriate feature?
Does not decrease in width during muscle contraction. --- I band
Which of the following does NOT correctly match a muscle fiber type with its appropriate feature?
Contain abundant amounts of glycogen. --- Slow-oxidative
Rigor mortis occurs because ____.
ATP is required to release the attached actin and myosin molecules
The functional role of the T tubules is to ____.
inititate excitation-contraction coupling via conduction of action potentials
A motor unit is ____.
a nerve and the fibers that it controls
Myoglobin ____.
holds a reserve supply of oxygen in muscle cells
An elaborate network of membranes in skeletal muscle cells that functions in calcium storage is the ____.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Situation in which the contraction of an isolated muscle becomes stronger due to an increase in stimulus frequency. Partial relaxation occurs between muscle twitches.
summation
A bundle (group) of muscle cells forms a ____ in skeletal muscle.
muscle fascicle
____ is a neurotransmitter released at motor end plates (neuromuscular junctions) by the axonal endings of neurons.
Acetylcholine
In what way does the interior surface of a cell membrane of a resting (nonconducting) neuron differ from the external environment? The interior is ____.
negatively charged and contains less sodium
Ciliated CNS neuroglia that play an active role in moving the cerebrospinal fluid are called ____.
ependymal cells
The sympathetic and parasympathetic are subdivisions of the ____.
autonomic nervous system
Immediately after an action potential has peaked (finished the depolarization phase), which cellular gates open to cause repolarization?
potassium
Which of the following does NOT correctly match a term with its description?
Depolarization --- Period during which sodium ions diffuse out of the neuron due to a change in permeability for these ions.
An efferent neuron ____.
carries motor output from the CNS to an effector
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is best associated with ____.
hyperpolarization
The sodium-potassium pump ____ the cell for every ____ the cell.
pumps three sodium ions outside ... two potassium ions inside
The substance released at axon terminals (knobs) to propagate a nervous impulse is called a(n) ____.
neurotransmitter
Schwann cells are functionally similar to ____.
oligodendrocytes
The part of a neuron that conducts impulses away from its cell body is called a(n) ____.
axon
An excitatory neurotransmitter secreted by motor neurons innervating skeletal muscle is ____.
acetylcholine
The point at which an impulse from one nerve cell is communicated to another nerve cell is the ____.
synapse
The term central nervous system refers to the ____.
brain and spinal cord
"Change in local potential producing slight depolarization" best describes ____.
an excitatory postsynaptic potential
A neuron with which of the following features would transmit action potentials at the fastest speed?
large diameter axon with myelin
Most neurons are ____ with one axon and many dendrites.
multipolar
During the depolarization phase of an action potential in a neuron, ____ gates open and these ions move ____ the cell.
Na+ ... into
The ___ of action potentials that travel through a sensory neuron codes for stimulus intensity.
frequency
List the following events of synaptic transmission in the correct sequence: (A) neurotransmitter binds to receptor on receiving cell, (B) excess neurotransmitter is reabsorbed into sending cell, (C) action potential occurs in sending cell, (D) neurotransmitter is released from vesicles in sending cell, (E) local potential is generated in receiving cell.
C, D, A, E, B
The spinal cord has gray matter on the ____.
inside, white matter on the outside, and a ventral motor root
The brain stem consists of the ____.
midbrain, medulla, and pons
The subarachnoid space lies between what two layers of meninges?
arachnoid and pia
The brain area that regulates activities which control the state of wakefulness or alertness of the cerebral cortex is the ____.
reticular formation
An individual accidentally transected the spinal cord between T1 and L1. This would result in ____.
paraplegia
The hypothalamus ____.
is the thermostat of the body since it regulates temperature
Cell bodies of the sensory neurons of the spinal nerves are located in ____.
the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord
Which of the following correctly matches a brain area with its function or description?
This brain area associates experiences necessary for the production of abstract ideas, judgment, and conscience. --- Prefrontal area
The area of the cortex that is responsible for sensations of the full bladder and the feeling that your lungs will burst when you hold your breath too long is the _____.
visceral sensory area
The vital centers for the control of heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure are located in the ____.
medulla
Spastic paralysis suggests involvement of the ____.
upper motor neurons
The primary auditory cortex is located in the ____.
temporal lobe
Which of the following correctly matches a brain lobe with its function?
Seat of intelligence, abstract reasoning. --- Frontal
The blood-brain barrier is effective against ____.
metabolic waste such as urea
Spinocerebellar tracts ____.
carry proprioceptive inputs to the cerebellum
Which of the following is not a midbrain structure?
third ventricle
Which of the following would you NOT find in normal cerebrospinal fluid?
red blood cells
The white matter of the spinal cord is composed of ____.
both sensory & motor neurons
Molecular changes in post-synaptic neurons such as an increase in NMDA receptors and release of nitric oxide to enhance signal transmission is primarily associated with forming ____ memory.
long-term
The spinal cord ends at the level of ____.
L1
Transduction refers to the conversion of ____.
stimulus information (energy) to afferent nerve impulses
A reflex that causes muscle relaxation and lengthening in response to muscle contraction is called a ____.
Golgi tendon reflex
In a crossed extensor reflex, if the right arm were grabbed it would flex and the left arm would _____.
extend
Which of the following correctly matches a reflex with its function or attribute?
Checks the integrity of the spinal cord and dorsal rami at the level of T8 to T12. --- Abdominal
Irritation of a major nerve of this plexus may cause hiccups.
cervical plexus
Which of the following is FALSE about the integration center of a reflex arc?
There are always multiple synapses with chains of interneurons.
The "knee jerk" reflex is an example of a(n) ____.
stretch reflex
Bell's palsy is ____.
characterized by paralysis of facial muscles
Which of the following numbers of pairs of spinal nerves is correct?
12 thoracic
Mixed cranial nerves containing both motor and sensory fibers include all except which of the following?
oculomotor
Problems in balance may follow trauma to which nerve?
vestibulocochlear
Receptors for ____ are NOT free nerve endings.
heavy touch
Which of the following correctly matches a cranial nerve with its function or attribute?
Helps to regulate blood pressure and digestion. --- Vagus
Potentially damaging stimuli that result in pain are selectively detected by ____.
nociceptors
A simple spinal reflex goes along which of the following reflex arcs?
receptor, afferent neuron, integration center, efferent neuron, effector
A patient who received a blow to the side of the skull exhibits the following signs and symptoms on that side of the face: he is unable to close his eye, and the corner of his mouth droops. Which cranial nerve has been damaged?
facial
Feeling a gentle caress on your arm would likely involve all of the following except ____.
Pacinian corpuscles
Meissner's corpuscles are ____.
mechanoreceptors
Which of the following correctly matches a nerve plexus with its function or attribute?
Trauma to a nerve of this plexus may cause wrist drop. --- Brachial
The cranial nerves that have neural connections with the tongue include all except the ____.
trochlear
The "resting and digesting" division of the autonomic nervous system is the ____.
parasympathetic division
In contrast to the somatic nervous system, the autonomic nervous system ____.
has two efferent neurons
Which of the following correctly matches an ANS motor fiber with its neurotransmitter?
Postganglionic parasympathetic -- Acetylcholine
Autonomic ganglia contain ____.
the cell bodies of postganglionic motor fibers
The site(s) of origin of the preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system is (are) the ____.
brain stem and the sacral region of the spinal cord
The parasympathetic nervous system is characterized by peripheral ganglia near the ____.
organs and by short postganglionic fibers
Erection of the penis or clitoris ____.
is primarily under parasympathetic control
The autonomic nervous system ____.
is controlled by the hypothalamus and reticular formation
Preparing the body for the "fight-or-flight" response is the role of the ____.
sympathetic nervous system
Which of the following correctly matches a division of the ANS with one of its effects?
Decreases heart rate -- Parasympathetic
The secretions of the adrenal medulla act to supplement the effects of ____ stimulation.
sympathetic
Which of the following is NOT a result of parasympathetic stimulation?
increased vasoconstriction of most blood vessels
Over 90% of all parasympathetic fibers are derived from cranial nerve number ____.
X
Sympathetic responses generally are widespread because ____.
single preganglionic axons make multiple synapses with ganglionic neurons
Effects of the sympathetic division include all except ____.
dilation of the blood vessels serving the digestive viscera
Sympathetic fibers leave the spinal cord in the ____.
thoracic and lumbar regions
Which is a uniquely sympathetic function?
regulation of body temperature
A drug that might be used specifically to reduce heart rate in cardiac patients could be ____.
a beta-blocker
Albuterol stimulates dilation of bronchioles and thus acts as a ____ medication.
sympathomimetic
Emotions influence autonomic reactions (reflexes) primarily through integration in the ____.
hypothalamus
Which of the following correctly matches an eye or ear condition with its appropriate description?
An inflammation of the lining of the middle ear. -- Otitis media
Which of the following correctly matches an eye structure with its appropriate description?
Helps maintain the intraocular pressure; located in the anterior part of the eye. -- Aqueous humor
There are three layers of neurons in the retina. The axons of which of these neuron layers form the optic nerves?
ganglion cells
Light passes through the following structures in which order?
cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor
Motion sickness seems to ___.
result from a mismatch between visual and vestibular inputs
Which the following incorrectly matches an ear condition with its description?
Can result from the fusion of the auditory ossicles. -- Sensorineural deafness
The receptor for static equilibrium is the ___.
macula
What is the main function of the rods in the eye?
vision in dim light
During dark adaptation ___.
rhodopsin accumulates in the rods
Photoreceptors ___.
package visual pigment in membrane-bound discs, which increases the efficiency of light trapping
Which of the following incorrectly matches an eye structure with its description?
The vascular coat of the eyeball; deeply pigmented. -- Cornea
An essential part of the maculae involved in static equilibrium is (are) the ___.
otoliths
The ciliary body does not ___.
belong to the anterior chamber of the eye
Olfactory cells and taste buds are normally stimulated by ___.
substances in solution
The blind spot of the eye is where ___.
the optic nerve leaves the eye
Which of the following incorrectly matches a receptor with its location?
The receptors of olfaction are found in this structure. -- Vestibule.
Which of the following incorrectly matches an ear structure with its description?
A membrane that transmits sound vibrations to the auditory ossicles. -- Oval window
___ is a disorder of the olfactory nerves.
Anosmias
Which of the following incorrectly matches an ear structure with its description?
Separates external auditory canal from the middle ear. -- Round window
Receptors for hearing are located in the ___.
cochlea
What are the special senses in human?
vision, olfaction, gustation, hearing, equilibrium
How do the special senses in humans differ from general senses?
General senses are scattered throughout the body and have simple make up. Special senses have distinct receptors and have a complex make up.
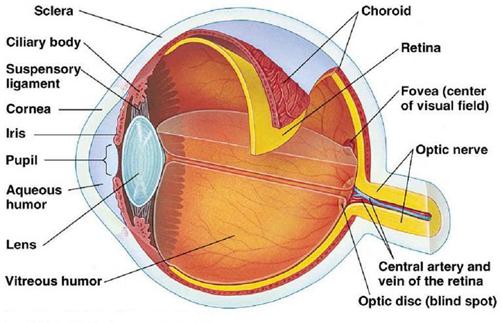
know this
What is the sequence of structures and fluids that light rays must pass through to reach the retina?
conjuctiva, cornea, anterior segment, margin of pupil, lens, ciliary body, ciliary process, ciliary zonule, posterior segment, retina.
Which of the eye structures does most of the refraction of light rays?
cornea
What is astigmatism?
a defect in the eye or in a lens caused by a deviation from spherical curvature, which results in distorted images, as light rays are prevented from meeting at a common focus.
How does the ANS control pupil diameter?
The parasympathetic controls constriction and the sympathetic controls dilation
How does the ANS control changes in lens shape during accommodation (how does the ciliary muscle change lens shape when viewing a near versus distant object)?
For near objects, the ciliary muscle relaxes and the lens flattens.
For distant objects, the ciliary muscle contracts and the lens bulges.
What are the layers of cells that constitute the retina?
horizontal, bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion cells
In which direction does light pass through these cell layers in the retina?
horizontal, bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion??
Which neurons of the retina form the optic nerve?
ganglion cells
How do rods and cones differ anatomically?
Rods contain rhodopsin; they are for black and white.
Cones contain retinal; they are for colors.
What is the outer segment?
contains visual pigment molecules
What is photodissociation?
bleaching of visual pigments
What is rhodopsin?
visual pigment made of retinal and opsin
What is retinal?
protein derived from vitamin A
What is opsin?
protein that helps make up rhodopsin and is activated by light.
Why is vitamin A important for vision?
retinal comes from vitamin A
What vision problem occurs as a result of vitamin A deficiency?
night blindness
What is responsible for dark adaptation?
rhodopsin
How are action potentials (nerve impulses) generated in the optic nerve when light strikes the photoreceptors?
phototransduction closes the Na channels; no release of inhibitory neurotransmitter
What are the types of cones?
red, green, blue
How do the different types of cones differ?
Each type contains retinal attached to different types of opsin
red(560 nm), green(530 nm), blue(420 nm)
What anatomical features of the retina are responsible for producing high visual sensitivity?
rods
What anatomical features of the retina are responsible for producing high visual acuity?
cones
What are the relative distribution of rods and cones in the retina?
way more rods than cones
What is the extent of neuronal convergence from these photoreceptors to the ganglion cells?
Extensive neuronal convergence from rods; no neuronal convergence from cones.
What is myopia?
nearsightedness
What is hyperopia?
farsightedness
What produces conditions of myopia?
the eye is too long
What produces conditions of hyperopia?
the eye is too short
How do corrective lenses compensate for myopia?
concave lenses
How do corrective lenses compensate for hyperopia?
convex lenses
What is glaucoma?
inadequate drainage of aqueous humor
What produces glaucoma?
high intraocular pressure damages optic nerve
What is cataract?
inadequate delivery of nutrients to deeper lens fibers
What produces cataract?
clumping of crystallin proteins
What types of receptors are responsible for the sense of taste?
taste buds aka taste cells or taste hairs
What types of receptors are responsible for the sense of olfaction?
olfactory cells
How are taste receptors stimulated?
dissolved molecules bind to protein receptors
How are olfaction receptors stimulated?
volatile molecules bind to protein receptors
How many different odors can humans distinguish?
more than 1 trillion
How many different tastes can humans distinguish?
five
What are the tastes that humans can distinguish?
salty, sweet, sour, bitter, savory
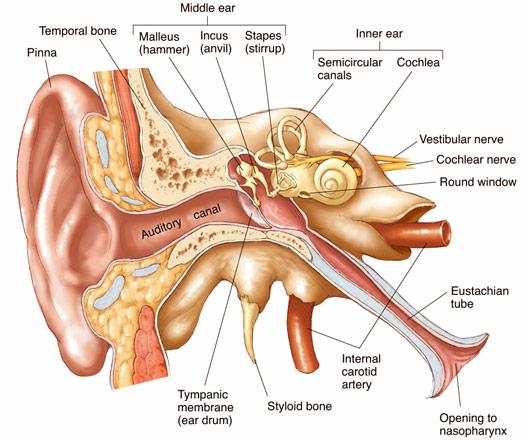
know this
What structures are located in the outer ear region?
auditory canal, tympanic membrane
What structures are located in the middle ear region?
tympanic membrane, auditory tube, oval window
What structures are located in the inner ear region?
oval window, cochlea, auditory tube
What is the sequence of events that leads to generation of action potentials in cochlear nerve?
Sound waves vibrate tympanic membrane, the vibration moves ossicles, stapes move oval window, pressure waves created in fluid inside cochlea, pressure waves in cochlear fluid move the basilar membrane, hair cells in spiral organ are bent, bending of hair cells opens K+ channels of sterocilia, K+ inflow --> depolarization --> Ca influx --> release of glutamate --> APs in cochlear nerve fibers
What are the sensory receptor cells for hearing?
cochlear hair cells
Where are the sensory receptor cells for hearing located?
cochlea of the inner ear
How does transduction occur in hearing receptors?
outer modify responsiveness of inner
What is the reflex mechanism for preventing damage to hearing receptor cells when you are exposed to very loud sounds?
stapedius and tensor tympani limit movements from loud sounds
How does the ear detect differences in pitch of sound?
high pitch stimulates basilar membrane close to the oval window
low pitch stimulates basilar membrane farther from oval window
What types of problems can lead to conduction deafness?
auditory canal blockage, inflamed middle ear, abnormal bone growth near middle ear, damage to tympanic membrane
What types of problems can lead to sensorineural deafness?
loss of cochlear hair cells
Which structures of the inner ear are involved in sensory perception for balance?
hair cells in the inner ear
What are the sensory receptor cells for balance?
hair cells, visual receptors, somatic receptors(proprioceptors)
Where are the sensory receptor cells for balance located?
ear, eyes, neck, trunk, limbs
What are the stimuli for the balance (vestibular) receptors in these structures?
gravity and inertia
What are the motor responses for vestibular information?
reflexive eye movements, motion sickness
What are the anatomical and functional links between the endocrine system and nervous system?
hypothalamus and adrenal medulla
What is an endocrine glad?
gland that secretes hormones into the bloodstream
What is a hormone?
chemical that alters the activity of specific cells
What is a target cell?
specific cell targeted by hormones
How do paracrine regulators differ from hormones?
a paracrine regulator is a target cell near the secreting cell
How do autocrine regulators differ from hormones?
an autocrine regulator is a target cell that is also the secreting cell
What are the chemical classes of hormones?
polypeptides, steroids, amines
Lipid-soluble hormones mode of transport to the bloodstream
cytoplasm or nucleus
Water-soluble hormones mode of transport to the bloodstream
2nd messenger system
Lipid-soluble ability to pass through the cell membranes of target cells
directly trigger cell response
Water-soluble ability to pass through the cell membranes of target cells
indirectly trigger cell response via signal transduction
Lipid-soluble location of receptors at target cells
inside target cells
Water-soluble location of receptors at target cells
surface of target cells
How do lipid-soluble hormones typically affect target cells?
alter gene transcription and protein production
How do water-soluble hormones typically affect target cells?
alter membrane transport, enzyme activation, or gene transcription
Examples of lipid-soluble hormones
cortisol and thyroxine
Examples of water-soluble hormones
insulin and epinephrine
How can a single hormone have multiple effects?
different receptor types produce different responses
What are tissues that produce hormones?
endocrine tissues
What are organs that produce hormones?
endocrine glands
Anatomy of the anterior pituitary
pars distalis, Pars tuberalis, Pars intermedia
Function of the anterior pituitary
hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones control release of hormones from anterior pituitary
Anatomy of the posterior pituitary
Pars nervosa, Infundibular stalk
Function of the posterior pituitary
neurosecretory cells of hypothalamus release hormones from posterior pituitary
Eight hormones released from the anterior pituitary (with their target cells and functions)
tropic, FSH, LH, TSH, ACTH, Prolactin, MSH, GH
Two hormones released from the posterior pituitary (with their target cells and functions)
oxytocin and ADH (vasopressin)
thyroid gland
T3 and T4; regulate metabolic rate and proper growth and development
calcitonin; lowers blood calcium
parathyroid gland
parathyroid hormone; increases blood calcium and completes vitamin D synthesis in kidneys
pancreas
insulin; lowers blood glucose
glucagon; raises blood glucose
thymus
thymosin; controls maturation of T cells
adrenal medulla
epinephrine and norepinephrine; promote fight-or-flight response
adrenal cortex
aldosterone and cortisol; increase blood glucose and pressure
pineal gland
melatonin; regulates daily and seasonal rhythms and controls the reproductive system
ovaries
estrogen and progesterone; control development of sex traits and reproduction
testes
testosterone; controls development of sex traits and sex drive
small intestines
secretin and CCK; stimulate pancreas to release bicarbonate and enzymes, and stimulates gall bladder to contract
kidney
erythropoieten; increases red blood cell production
placenta
HCG; maintains endometrium during pregnancy
What are the stress responses of glucocorticoids?
Proteins and fats broken down and converted to glucose, leading to increased blood glucose.
Partial suppression of immune system.
What are the stress responses of mineralocorticoids?
Retention of sodium ions and water by kidneys.
Increased blood volume and pressure.
What are the stress responses of epinephrine and norepinephrine?
glycogen broken down to glucose; increased blood glucose.
increased blood pressure, breathing rate, and metabolic rate.
Change in blood flow patterns.
What is the role of a second messenger in hormone action?
It relays a hormone's message inside a target cell.
Which one of the following endocrine organs does not actually manufacture hormones but, rather, stores hormones produced elsewhere?
posterior pituitary
A doctor might give an expectant mother _____ to stimulate uterine contractions (induce labor).
oxytocin
The regulation of water volume in the blood involves which hormone?
ADH
How does the hypothalamus control the secretion of growth hormone (GH) from the anterior pituitary?
The hypothalamus produces a releasing hormone that stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete GH.
Which of the following hormones specifically act(s) to trigger secretion of hormones by another endocrine gland?
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
The mammary glands of a pregnant female will begin to produce milk in response to changes in the level of which of the following hormones?
prolactin
Hyperthyroidism, typically characterized by a high metabolic rate and high blood pressure, might be expected when _____.
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration is high
Which of the following hormones have antagonistic effects?
insulin and glucagon
At night, the _____ secretes _____ than during the day.
pineal gland ... more melatonin
Which of the following is a hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary?
oxytocin
FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone) are hormones known as _____.
gonadotropins
Which disorder is correctly matched with its cause?
pituitary dwarfism ... hyposecretion of growth hormone
If a diet is deficient in iodine, a goiter may form because _____.
low blood levels of T3 and T4 inhibit the negative feedback loop. An overload of TSH causes enlargement of the gland.
Every time you eat a cookie or candy bar, your blood sugar increases. This triggers an increase in the hormone _____.
insulin
Cortisol and estrogen are ____ hormones and thus the protein receptors for these hormones are ____ the target cells.
lipid soluble ... inside
The adrenal gland is ____ and secretes hormones such as ____.
near the kidney ... norepinephrine and corticosteroids
Which of the following INCORRECTLY matches hormone with its effect?
LH ... controls maturation of T cells
____ hormones such as ____ bind to receptors on the surface of target cells.
Water-soluble ...insulin
Calcitonin is secreted from the ____ and acts to ____ blood calcium.
thyroid gland ... decrease