Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as testosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because:
Intracellular receptors are present only in target cells.
GTPase activity is involved in the regulation of signal transduction because it:
Hydrolyzes GTP binding to G protein.

Match the key event of meiosis with the stages listed below. Tetrads of chromosomes are aligned at the equator of the spindle; alignment determines independent assortment.
B. II
testosterone functions inside a cell by:
binding with a receptor protein that enters the nucleus and activates specific genes.

Match the key event of meiosis with the stages listed below. Centromeres of sister chromatids disjoin and chromatids separate
A. II
What is a cleavage furrow?
A groove in the plasma membrane between daughter nuclei.
When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway?
signal molecule
What are scaffolding proteins?
large molecules to which several relay proteins attach to facillitate cascade effects
The function of phosphatases in signal transduction is best described as to:
inactivate protein kinases and turn off the signal transduction.
Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells?
E) A,B,C
-A) They do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
B) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle.
C) They are not subject to cell cycle controls.
Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → camp. Identify the second messenger.
camp.
In a human karyotype, chromosomes are arranged in 23 pairs. If one of these pairs is chosen, such as pair 14, which of the following do the two chromosomes of the pair have in common?
Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and traits coded for by their genes.
Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during:
meiosis I
After which checkpoint is the cell first committed to continue the cell cycle through M?
G1
Which of the following occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
synapsis of chromosomes.
Why do neurons and some other specialized cells divide infrequently?
They have been shunted into g0
The human X and Y chromosomes:
include genes that determine an individual's sex.
Adenylyl cyclase has the opposite effect of which of the following?
Phosphodiesterase
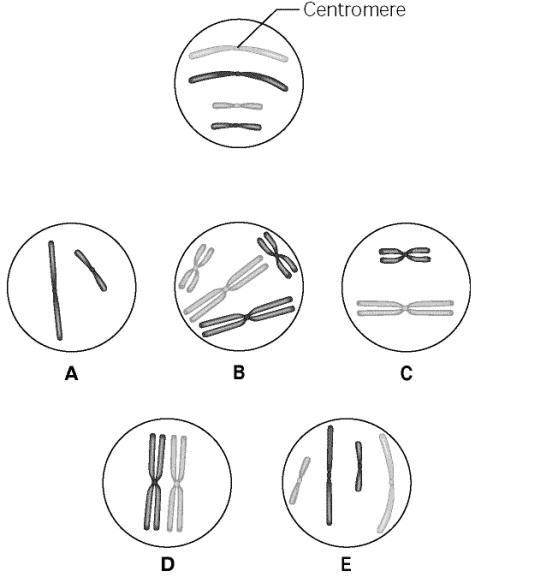
The top circle in Figure 12.1 shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is symbolized as black and the other haploid set is gray. The chromosomes in the top circle have not yet replicated
Choose the correct chromosomal condition for prometaphase of mitosis.
B
Which of the following is a protein maintained at constant levels throughout the cell cycle that requires cyclin to become catalytically active?
CDK
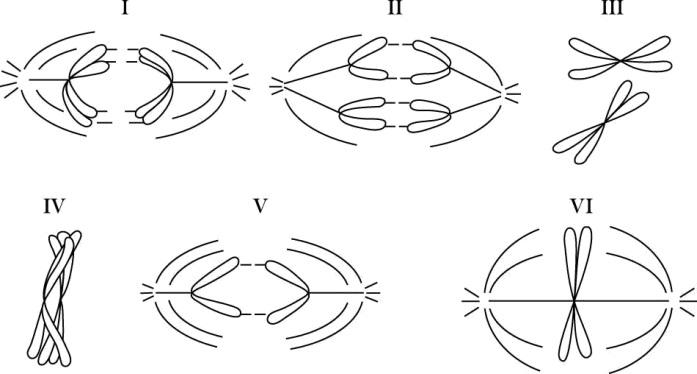
Refer to the drawings of a single pair of homologous chromosomes in Figure 13.2 as they might appear during various stages of either mitosis or meiosis.
Which diagram represents anaphase I of meiosis?
I
Which number represents dna synthesis?
II
Which of the following does not occur during mitosis?
replication of the DNA
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is:
a sperm
Density-dependent inhibition is explained by which of the following?
As cells become more numerous, the cell surface proteins of one cell contact the adjoining cells and they stop dividing.
Which of the following most accurately describes a cyclin?
It activates a CDK molecule when it is in sufficient concentration.
Why do chromosomes coil during mitosis?
to allow the chromosomes to move without becoming entangled and breaking
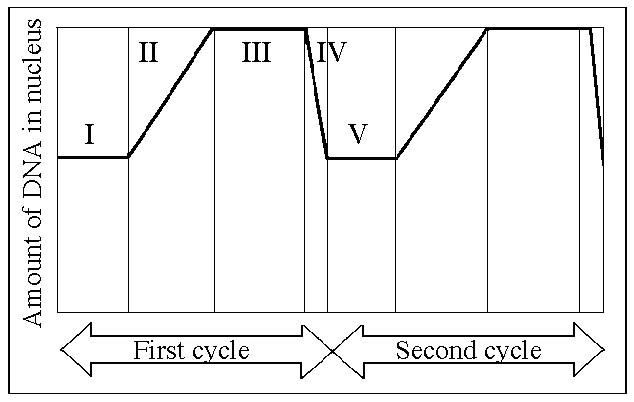
In the figure above, mitosis is represented by which numbered part(s) of the cycle?
IV
Which of the following is the best explanation for the fact that most transduction pathways have multiple steps?
Multiple steps provide for greater possible amplification of a signal.
For anaphase to begin, which of the following must occur?
Cohesin must be cleaved enzymatically.
Which of the following defines a genome?
The complete set of an organism's genes.
Independent assortment of chromosomes occurs.
The statement is true for meiosis I only.
The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is characterized by:
Dimerization and phosphorylation.
Which of the following happens at the conclusion of meiosis I?
Homologous chromosomes are separated.
Where do the microtubules of the spindle originate during mitosis in both plant and animal cells?
centrosome
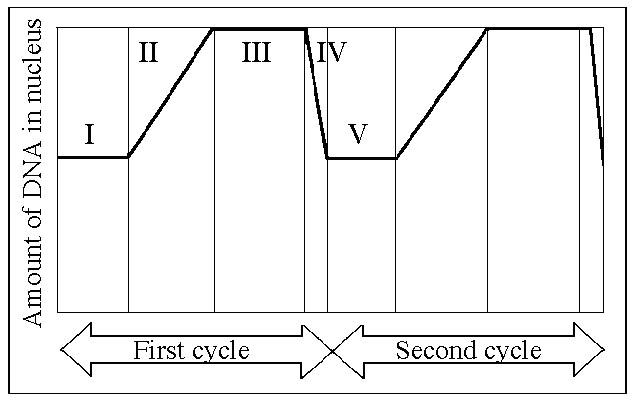
Measurements of the amount of DNA per nucleus were taken on a large number of cells from a growing fungus. The measured DNA levels ranged from 3 to 6 picograms per nucleus. In which stage of the cell cycle did the nucleus contain 6 picograms of DNA?
G2
After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is:
haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
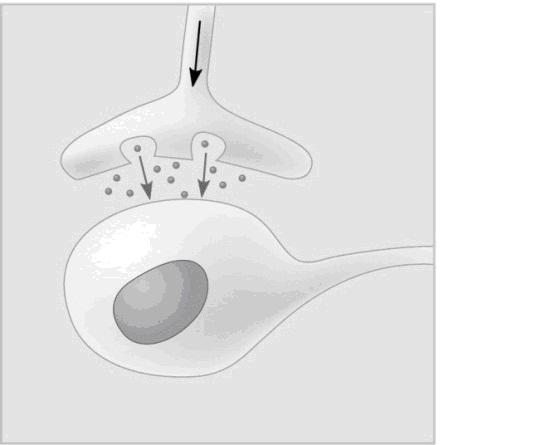
In the figure, the dots in the space between the two structures represent which of the following?
neurotransmitters
The centromere is a region in which:
Chromatids remain attached to one another until anaphase.
One of the major categories of receptors in the plasma membrane reacts by forming dimers, adding phosphate groups, and then activating relay proteins. Which type does this?
Receptor tyrosine kinases
A chemical reaction that has a positive ΔG is correctly described as:
endergonic
Which of the following is true for all exergonic reactions?
The reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy.
Which of the following is (are) true for anabolic pathways?
They consume energy to build up polymers from monomers.
Which temperature and pH profile curves on the graphs were most likely generated from analysis of an enzyme from a human stomach where conditions are strongly acid?
Curves 1 and 4
Reactants capable of interacting to form products in a chemical reaction must first overcome a thermodynamic barrier known as the reaction's:
Activation energy
Which of the following statements describes NAD+?
NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle.
The ATP made during glycolysis is generated by:
Substrate-level phosphorylation.
Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy
C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
Starting with one molecule of isocitrate and ending with fumarate, how many ATP molecules can be made through substrate-level phosphorylation (see Figure 9.2)?
1
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
A molecule of glucose.
When skeletal muscle cells undergo anaerobic respiration, they become fatigued and painful. This is now known to be caused by:
Buildup of lactate.
Why is glycolysis described as having an investment phase and a payoff phase?
It uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP.
Which curves on the graphs may represent the temperature and pH profiles of an enzyme taken from a bacterium that lives in a mildly alkaline hot springs at temperatures of 70°C or higher?
Curves 3 and 5
Phosphofructokinase is an allosteric enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, an early step of glycolysis. In the presence of oxygen, an increase in the amount of ATP in a cell would be expected to:
Inhibit the enzyme and thus slow the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
When you have a severe fever, what grave consequence may occur if the fever is not controlled?
Change in the tertiary structure of your enzymes.
For living organisms, which of the following is an important consequence of the first law of thermodynamics?
The organism ultimately must obtain all of the necessary energy for life from its environment.
Which of the following statements is representative of the second law of thermodynamics?
Cells require a constant input of energy to maintain their high level of organization.
What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules?
Catabolic pathways
In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate:
Two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced.
Which of the following produces the most ATP when glucose (C6H12O6) is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water?
Oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
The following question is based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in Figure 8.1.
Which of the following represents the activation energy required for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction in Figure 8.1?
B
An electron loses potential energy when it:
Shifts to a more electronegative atom.
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions 47-49.
In which step in Figure 9.1 is an inorganic phosphate added to the reactant?
C
Where does glycolysis take place in eukaryotic cells?
Cytosol
Which of the following is a statement of the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction:
Loses electrons and loses potential energy.
Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located?
Mitochondrial inner membrane
Which of the following statements is true concerning catabolic pathways?
They supply energy, primarily in the form of ATP, for the cell's work.
Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism?
It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions 47-49.
Which step in Figure 9.1 shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules?
B
Which of the following intermediary metabolites enters the citric acid cycle and is formed, in part, by the removal of a carbon (CO2) from one molecule of pyruvate?
Acetyl coa
According to the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis, which of the following is correct?
The binding of the substrate changes the shape of the enzyme's active site.
The active site of an enzyme is the region that:
Is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme.
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ into which location in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondrial intermembrane space
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions 47-49.
Which portion of the pathway in Figure 9.1 contains a phosphorylation reaction in which ATP is the phosphate source?
A
Which of the following occurs in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell?
Glycolysis and fermentation
In cellular respiration, the energy for most ATP synthesis is supplied by:
A proton gradient across a membrane.
Where is ATP synthase located in the mitochondrion?
Inner membrane
The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to:
Act as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water.
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent?
Glycolysis