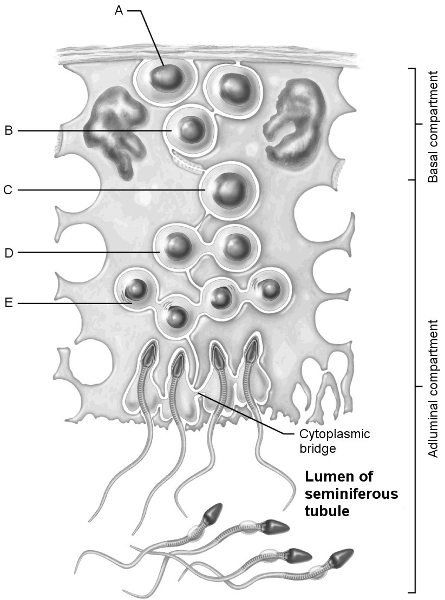
Match the following:
1. Stem Cell
2. First cells w n number of chromosomes
3. Type B spermatagonia
4. Early Spermatids
5. Primary spermatocyte
1. A
2. D
3. B
4. E
5. C
The dartos and cremaster muscles are important to the integrity of the male reproductive system. Which of the following is true about the role they play?
A) They contract to push sperm along the ductus deferens.
B) They regulate the temperature of the testes.
C) They are responsible for penile erection.
D) They contract to allow ejaculation.
B.
The ability of sperm cells to move along the ductus deferens is due to ________.
A) gravity
B) peristaltic contractions
C) enzymatic activity
D) hormonal action
B.
The most important risk for testicular cancer in young males is ________.
A) smoking
B) a diet high in fat
C) undescended testes
D) sexually transmitted infections
C.
Which of the following glands are responsible for 70% of the synthesis of semen?
A) the seminal vesicles
B) the bulbourethral glands
C) the prostate
D) the pituitary
A.
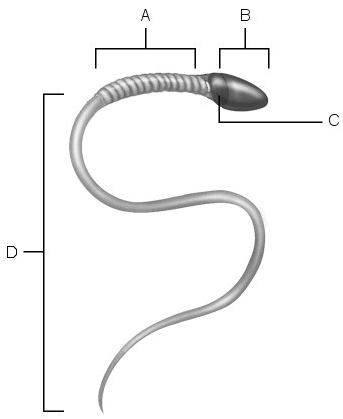
Label the following:
1. acrosome
2. location of the mitochondria
3. midpiece
4. location of nucleus
5. area of compacted DNA
6. flagellum
1. B
2.A
3.A
4.C
5.C
6.D
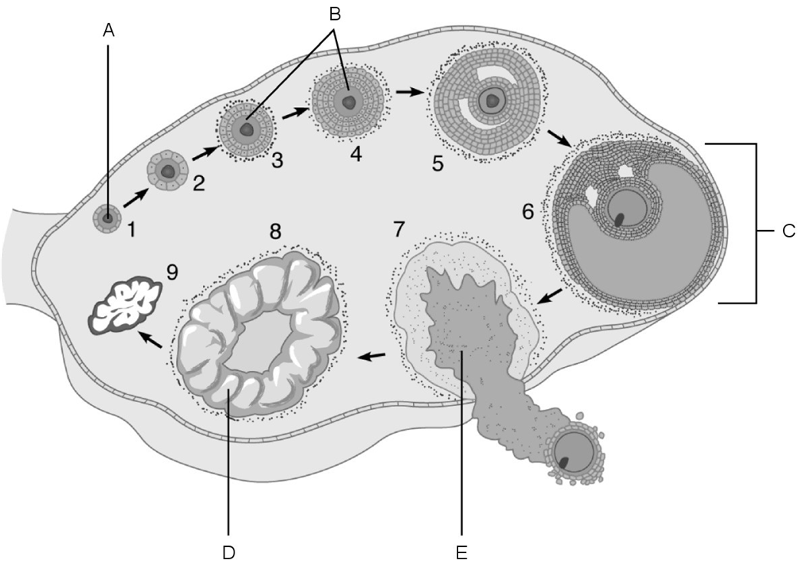
Match the following:
1) The stage called ovulation.
2) Vesicular (Graafian) follicle.
3) Primary follicles.
4) Primordial follicle.
5) Corpus luteum.
6) Mature follicle.
1.E
2.C
3.B
4.A
5.D
6.C
T/F
It is necessary for the testes to be kept below body temperature.
T
T/f
The prostate atrophies as a man ages, and it usually causes no health problems.
F
T/F
When a couple is having difficulty conceiving a child, it is necessary to investigate the sperm
of the male.
T
T/F
When it is cold, the scrotum pulls away from the body.
F
T/F
The amount of testosterone and sperm produced by the testes is dependent on the influence of
FSH alone.
F
T/F
Ovarian follicles contain mature eggs.
F
T/F
Sexually transmitted infections are the most important cause of reproductive disorders.
T
T/F
The smaller cell produced by oogenesis meiosis I, called the first polar body, is essentially a
packet of discarded nuclear material.
T
T/F
A human egg or sperm contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
F
T/F
The Pap smear is a test to detect cancerous changes in cells of the cervix.
T
T/F
The testis is divided into seminiferous tubules which contain lobules that produce sperm and the ejaculatory duct that allows the sperm to be ejected from the body.
F
Which of the following hormones controls the release of the anterior pituitary gonadotropins?
A)LH
B)FSH
C)GnRH
D)testosterone
C
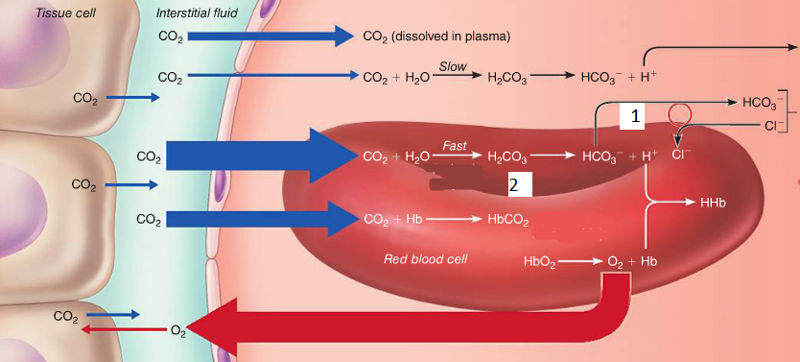
The reactions in this figure are taking place at which region?
a) tissues
b) lungs
c) hair
d) atoms
A
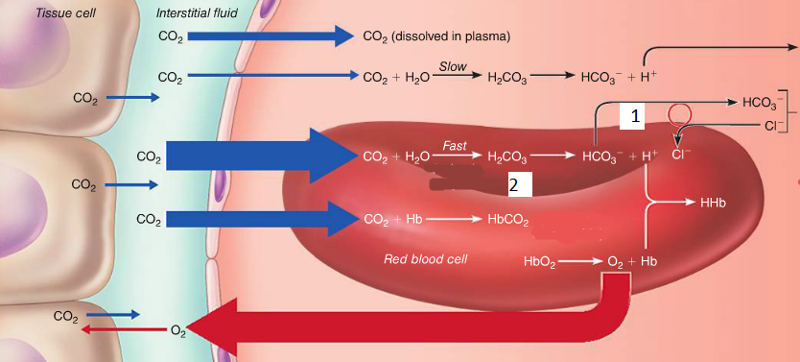
The chloride shift occurs at which number?
a.1
b.4
c.5
d.3
A
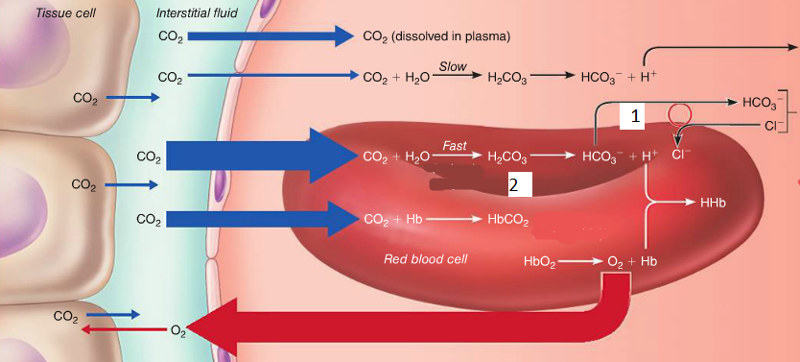
Where in the figure is carbonic acid quickly dissociated?
a. 1
b. 3
c. 2
d. 4
C
What is the formula for cardiac output?
CO = HR X SV
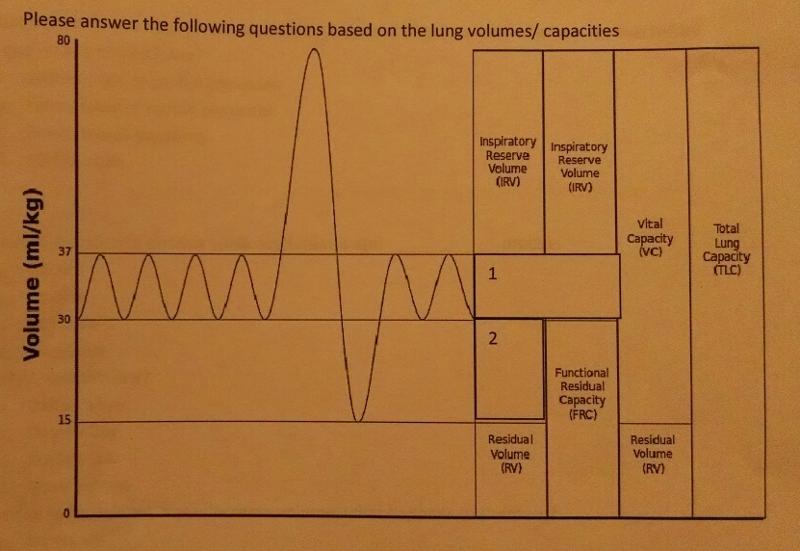
The tidal number is represented by which number?
1
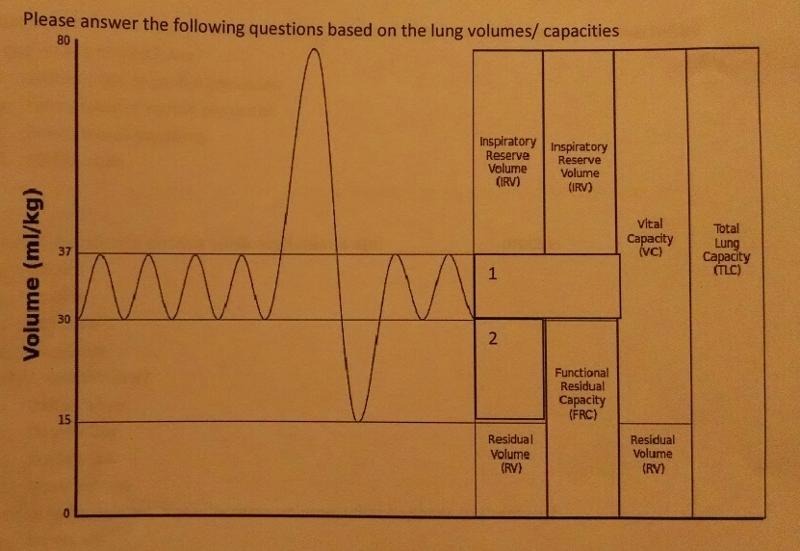
Expiratory reserve volume is represented by which number?
2
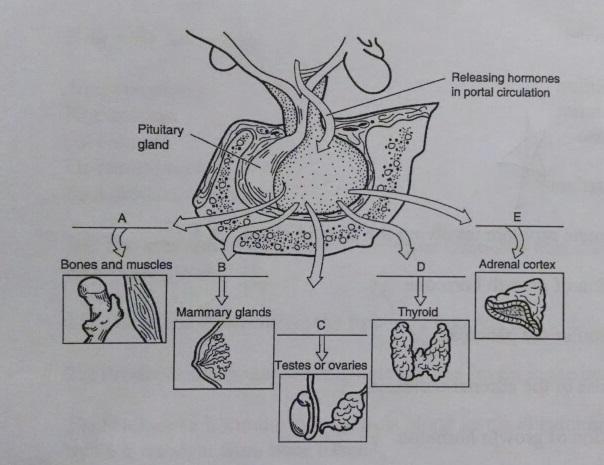
Match the following hormones w their targets:
1. Growth Hormone
2. FSH
3. Prolactin
4. Adrenocorticotropin Hormone
5. TSH
1.A
2.C
3.B
4.E
5.D
An autoimmune problem involving the thyroid gland.
Graves' disease
Hyposecretion of growth hormone
pituitary dwarfism
hyposecretion of the pancreas
diabetes mellitus
hyposecretion of adrenal cortex
Addison's disease
hypersecretion of growth hormone
acromegaly
Match:
1. produces glucocorticoids
2. produces epinephrine
3. produces aldosterone
4. excess hormone levels result in Cushing's syndrome
5. Hormones mimic sympathetic nervous system neurotransmitters
6. produces androgens
1.B
2.D
3.A
4.B
5.D
6.C
What is the formula for carbonic acid base balance system?
CO2+H2O-->H2CO3-->HCO3+H+Cl
Spermatogenesis
-production of sperm
-begins at puberty
-occurs in the seminiferous tubules
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) Stimulates...
the pituitary to release adrenocorticotropic
hormone (ACTH)
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) Stimulates...
the pituitary to release luteinizing hormone
(LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Stimulates...
the pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating
hormone (TSH)
Growth hormone-releasing hormone Stimulates...
the release of growth hormone (GH) from the
(GHRH) pituitary
Somatostatin Inhibits...
the release of GH from the pituitary
Dopamine Inhibits...
the release of prolactin from the pituitary
ACTH Stimulates
the release of hormones from the adrenal cortex
LH
In women, stimulates the production of sex hormones (i.e., estrogens) in the ovaries as well as during ovulation;
in men, stimulates testosterone production in the testes
FSH
In women, stimulates follicle development; in men, stimulates sperm production
TSH
Stimulates the release of thyroid hormone
GH
Promotes the body’s growth and development
Prolactin
Controls milk production (i.e., lactation)
Vasopressin
Helps control the body’s water and electrolyte levels
Oxytocin
Promotes uterine contraction during labor and activates milk ejection in nursing women
Cortisol
Helps control carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism;
protects against stress
Aldosterone
Helps control the body’s water and electrolyte regulation
Testosterone
Stimulates development of the male reproductive organs,
sperm production, and protein anabolism
Estrogen (produced by the follicle)
Stimulates development of the female reproductive organs
Progesterone (produced by the corpus luteum)
Prepares uterus for pregnancy and mammary glands for lactation
Thyroid hormone (i.e., thyroxine [T4]
and triiodothyronine [T3])
Controls metabolic processes in all cells
Calcitonin
Helps control calcium metabolism (i.e., lowers calcium levels in the blood)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Helps control calcium metabolism (i.e., increases calcium levels in the blood)
Insulin
Helps control carbohydrate metabolism (i.e., lowers blood
sugar levels)
Glucagon
Helps control carbohydrate metabolism (i.e., increases
blood sugar levels)