Anatomically, the spinal cord is part of the _________, and the spinal nerves are part of the _________.
CNS; PNS
What is the term for the expanded segment of the spinal cord where nerves exit that serve the shoulder and upper limbs?
Cervical Enlargement
Which of the spinal meninges is the outermost, dense, collagenous layer?
Dura Mater
The collection of dorsal and ventral roots that continues through the vertebral canal and resembles a horse's tail is the __________.
Cauda Equina
Which part of the gray matter in the spinal cord contains somatic and visceral sensory nuclei?
The posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei.
Which is/are composed of myelinated fibers carrying information toward the brain?
ascending tracts
What term is given to the projections of gray matter toward the outer surface of the spinal cord?
The term horns is given to the projections of gray matter toward the outer surface of the spinal cord and includes the anterior gray horns, posterior gray horns, and lateral gray horns.
The connective tissue that wraps bundles of axons into fascicles is the __________.
perineurium
A bilateral region of skin that in innervated by a single pair of spinal nerves is a __________.
Dermatome
What plexus includes the phrenic nerve, a nerve that controls the diaphragm?
Cervical plexus
What plexus includes the ulnar nerve?
Brachial Plexus
In what pattern of neural processing does one neuron synapse with several neurons?
Divergence
In what pattern of neural processing do several neurons synapse on one neuron?
Convergence
What is the first step of a reflex?
the arrival of a stimulus and the activation of a receptor
Which type of reflex is genetically or developmentally acquired?
Innate reflexes
What is the term for a reflex where the sensory neuron synapses directly on the motor neuron?
Monosynaptic Reflex
What type of reflex is initiated by increasing the length of a muscle and will cause that muscle to contract?
Stretch Reflex
What reflex causes the movement of a body part away from a stimulus?
Withdrawal reflex
Which reflex will cause a motor response on the side opposite the stimulus?
crossed extensor reflex
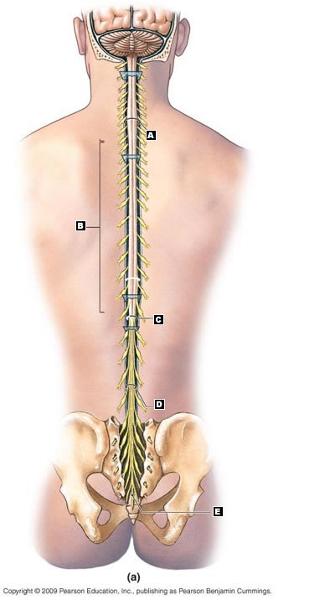
Label the parts of the adult spinal cord.
A. Cervical Enlargement
B. Thoracic Spinal Nerves
C. Conus Medullaris
D. Cauda Equina
E. Filum Terminale
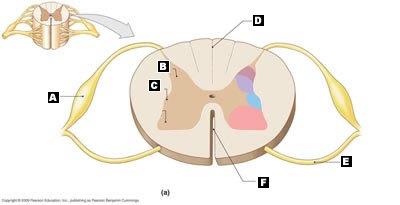
Label the parts of the sectional view of the spinal cord.
A. Dorsal Root Ganglion
B. Posterior Gray Horn
C. Lateral Gray Horn
D. Posterior Median Sulcus
E. Ventral Root
F. Anterior Median Fissure
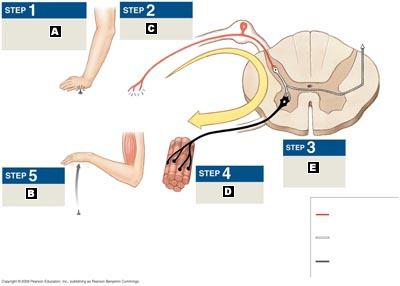
Label the steps in a reflex arc.
A. Arrival of stimulus and activation of receptor.
B. Response by effector.
C. Activation of sensory neuron.
D. Activation of motor neuron.
E. Information processing in the CNS.
Monitors external tension produced during a muscular contraction and prevents tearing or breaking of the tendon.
Tendon Reflex
A form of withdrawal reflex in which the muscles of a limb contract to move the limb away from a source of stimulation.
Flexor Reflex
A monosynaptic reflex that prevents excessive stretching of skeletal muscles.
Stretch Reflex
A polysynaptic reflex in which the motor response occurs on the side opposite the stimulus.
Crossed Extensor Reflex
Relay information from one side of the spinal cord to the other before reaching its destination in the gray matter.
Gray commissures
A collection of neuron cell bodies, neuroglia and unmyelinated axons.
Gray Matter
CNS nucleus
A collection of neuron cell bodies with a common function and a discrete anatomical boundary.
Bundles of axons in the CNS that are relatively uniform with respect to diameter, myelination and conduction speed.
Tracts
Conducts information from peripheral receptors to processing centers in the brain.
Sensory Pathways
Delivering information from the CNS motor control centers to the effecter organs.
Motor Pathways
The filum terminale and spinal nerves in the lumbar and sacral regions are called the __________.
Cauda Equina
The membranes surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord are the __________.
Meninges
The space between the arachnoid and pia mater is filled with __________.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
The dorsal root ganglion contains the __________ of __________ neurons.
cell bodies; sensory
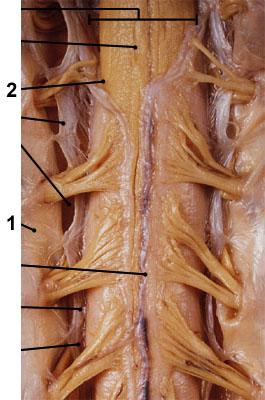
Which labeled structure is continuous with the dura mater of the brain?
Label 1
In the spinal cord, the gray horns contain __________.
visceral and somatic sensory and motor nuclei
The most important branch of the cervical plexus is the __________ nerve, which innervates the diaphragm.
phrenic
The branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate the __________.
laryngeal muscles
The median nerve of the brachial plexus innervates the __________.
flexor muscles of the forearm
Susan is doing hip extension movements during an exercise class. Which plexus and which nerve(s) is she using to contract the gluteus maximus muscle?
sacral plexus and inferior gluteal nerve
Ryan was in a car accident and has suffered injury to the dorsal root of his C7 spinal nerve on his left side. Which structure would he likely have difficulty receiving sensations from after this injury?
his left index finger
Which of the nerves innervates the sphincter muscles controlling defecation and urination?
pudendal nerve
Which term describes the action of the neural circuit when collateral branches of axons extend back and further stimulate presynaptic neurons?
reverberation
The reflex that complements a withdrawal reflex, making compensatory adjustments on the side of the body opposite that which receives the stimulus, is the __________ reflex.
crossed extensor
Sherry runs a feather along the sole of her 10-year-old brother's foot. His toes immediately curl in response to the touch. What type of reflex has just occurred?
Plantar Reflex
surrounds each myelinated axon and its Schwann cells
endoneurium
True statements about the peripheral distribution of spinal nerves.
-The largest branch from a spinal nerve is the ventral ramus.
-White rami communicantes carry information toward the sympathetic ganglia.
-Rami communicantes are nerve branches to and from sympathetic chain ganglia near the spinal cord.
These nerves arrive from cervical plexus.
phrenic nerve, supraclavicular nerve, greater auricular nerve
Method by which reflexes can be classified.
-the site where information processing occurs
-the nature of the resulting motor response
-the complexity of the neural circuit
Which of the following reflexes prevent(s) you from falling when you slip in a puddle of water in your kitchen?
polysynaptic
crossed extensor
contralateral
All of the listed responses are correct. ****
The patellar reflex __________.
-causes a rapid increase and then decline in the muscle tone of the quadriceps
-is an example of a monosynaptic reflex and a stretch reflex
-is triggered by stretching of the quadriceps muscles
True/False. The cauda equina is composed of the long ventral and dorsal roots of spinal segments L2 to S5.
True. Caudal to the conus medullaris, the spinal cord is evident as long fibrous roots called the cauda equina.
True/False. A sensory message entering the spinal cord enters the dorsal side of the spinal cord, while the motor response exits the ventral side.
True. A sensory message entering the spinal cord enters the dorsal side of the spinal cord, while the motor response exits the ventral side.
There are three complex, interwoven networks of compound nerve trunks called plexuses that branch into peripheral nerves; in descending order, these are the cervical plexus, the brachial plexus, and the __________ plexus.
lumbosacral
The largest nerve in the body is the sciatic nerve, which arises from the __________ plexus.
sacral
The best-known example of a monosynaptic reflex is the __________ reflex.
stretch
The withdrawal of CSF from the subarachnoid space is a called a __________.
spinal tap
In the CNS, the tracts that link the brain with the rest of the body are composed of __________.
sensory and motor pathways
The dorsal root of a spinal nerve is the site for ______________ neurons, whereas the ventral root is the site of ___________ neurons.
sensory; motor
The cervical enlargement of the spinal cord supplies nerves to the __________.
shoulder girdle and arms
The area of the spinal cord that surrounds the central canal and is dominated by the cell bodies of neurons and glial cells is the __________.
gray matter
The posterior gray horns of the spinal cord contain __________.
somatic and visceral sensory nuclei
The delicate connective tissue fibers that surround individual axons of spinal nerves comprise a layer called the __________.
endoneurium
The trapezius muscle is innervated by nerves from which plexus?
cervical
The brachial plexus innervates the __________.
shoulder girdle and arm
Parallel processing is the "neural circuit" in which __________.
several neurons or neuronal pools process the same information at one time
When sensory information is relayed from one part of the brain to another, the pattern is called __________.
serial processing
The goal of information processing during a neural reflex is the selection of __________.
an appropriate motor response and the activation of specific motor neurons
Consider the steps of a reflex arc. Which step follows information processing?
activation of a motor neuron
The sensory receptors in the stretch reflex are the __________.
muscle spindles
When one set of motor neurons is stimulated, those controlling antagonistic muscles are inhibited. This statement illustrates the principle of __________.
reciprocal inhibition
The highest level of motor control involves a series of interactions that occur __________.
in centers in the brain that can modulate or build on reflexive motor patterns
The designation C3 relative to the spinal cord refers to the __________.
third cervical segment
April stubs her left hallux as she is walking to the kitchen at night. Which nerve and which plexus are involved in the sensation of pain sent to her brain?
fibular nerve and sacral plexus
Spinal nerves are classified as mixed nerves because they contain __________.
both sensory and motor fibers
The epidural space is an area that contains __________.
loose connective tissue, blood vessels, and adipose tissue
In the spinal cord, the cerebrospinal fluid is found within the __________.
central canal and subarachnoid space
The dura mater attaches itself at its base to the skeletal system through the __________.
coccygeal ligament
The axons in the white matter of the spinal cord that carry sensory information up toward the brain are organized into __________.
ascending tracts
In reference to the vertebral column, C2 refers to the cervical nerve that __________.
precedes vertebra C2
The white ramus is the branch of a spinal nerve that consists of __________.
myelinated preganglionic axons
Unmyelinated fibers that innervate glands and smooth muscles in the body wall or limbs form the __________.
gray ramus
The lumbo-sacral plexus that supplies the pelvic girdle and the leg includes the spinal nerves __________.
T12–S4
Pain receptors are the __________.
dendrites of sensory neurons
Reflexive removal of a hand from a hot stove and blinking when the eyelashes are touched are examples of __________.
innate reflexes
Why are the most complicated responses produced by polysynaptic responses?
The interneurons can control several different muscle groups.
Several neurons synapsing on a single postsynaptic neuron are __________.
convergence
The activity occurring in the Golgi tendon organ involves __________.
the stretching of the collagen fibers and stimulation of the sensory neuron
In an adult, CNS injury is suspected if there is __________.
a positive Babinski reflex
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), __________.
A. neuron cell bodies are located in ganglia
B. spinal nerves connect to the spinal cord
C. cranial nerves connect to the brain
D. All of the listed responses are correct. (*)
Inferior to the lumbar enlargement; a region where the spinal cord becomes tapered and conical.
Conus Medullaris
___ matter is the region of integration and command initiation, and ___ matter carries information from place to place.
Gray; white
____, located only in the thoracic and lumbar segments, contain visceral motor nuclei.
Lateral gray horns
The _____ posterior to and anterior to the central canal contain axons that cross from one side of the cord to the other before they reach an area in the gray matter.
Gray Commissures
Functional groups of interconnected neurons are called _______.
Neuronal Pools