Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges
Meninges (3)
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid Mater
3. Pia mater
Meninges
1. Dura Mater
2. Arachnoid Mater
3. Pia Mater
1. (tough mother) most superficial layer
2. middle layer,
3. (soft mother) adheres tightly to tissues its protecting, (most deep layer)
Decussation
fancy term for crossing over
Isolateral
response goes in one side and leaves from the same side
Contralateral
response goes in one side and leaves from a different side
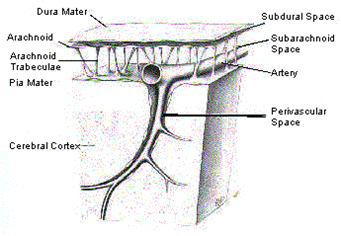
1. dura mater 2. arachnoid mater
3. arachnoid trebeculae 4. pea mater
5. cerebral cortex 6. subdural space
7. subarachnoid space 8. perivascular space
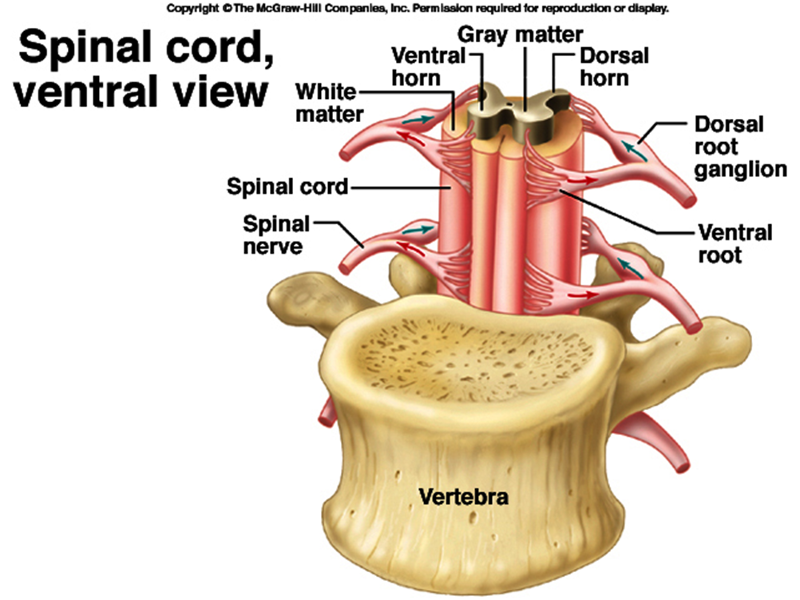
1. spinal nerve 2. spinal cord 3. white matter
4. ventral horn 5. gray matter 6. dorsal horn
7. dorsal root ganglion 7. ventral root
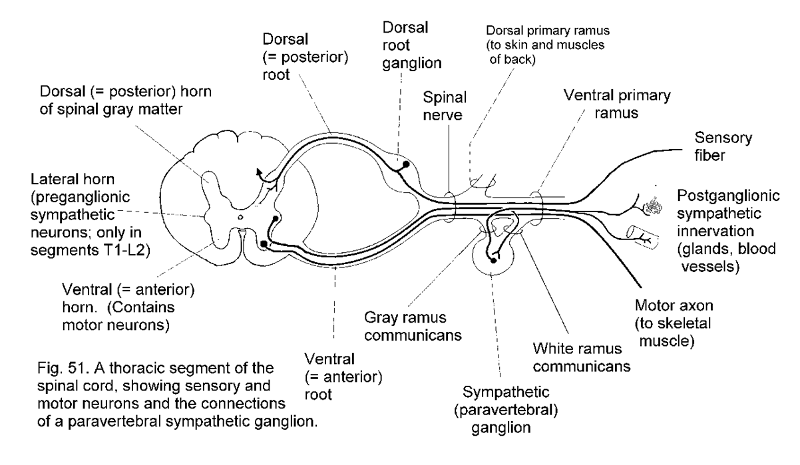
1. lateral horn (preganglionic sympathetic neurons, only in segments T1 - L2)
2. dorsal horn of gray matter 3. dorsal root
4. dorsal root ganglion 5. spinal nerve
6. Dorsal primary ramus (to skin and muscles)
7. ventral primary ramus 8. sensory fiber
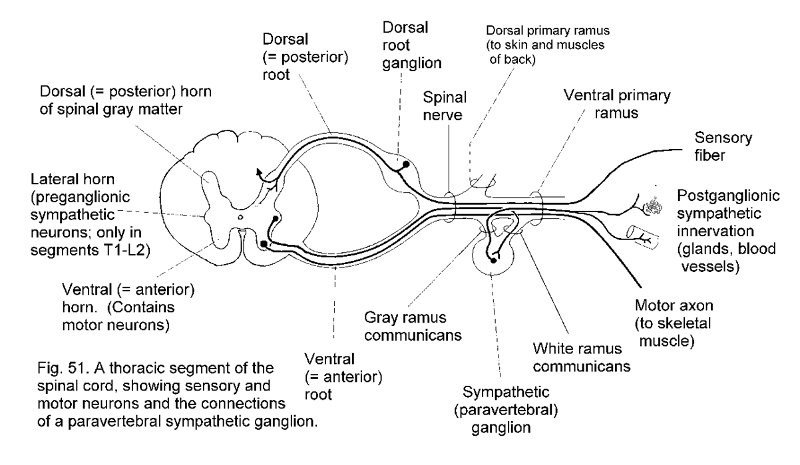
9. postgangionic sympathetic innervation (glands, blood vessels)
10. motor axon (to skeletal muscle)
11. white ramus communicans
12. sympathetic (paravertebral) ganglion
13. Gray ramus communicans
14. ventral root
15. ventral horn (contains motor neurons)
crossed extension reflex
one of the spinally mediated reflexes normally present in the first 2 months of life, demonstrated by the adduction and extension of one leg when the foot of the other leg is stimulated. When present in adults, it indicates hyperactive reflexes.
plexuses (4)
1. cerebral plexus
2. brachial plexus
3. lumbar plexus
4. sacral plexus
Dermatome
an area of the skin that is mainly supplied by a single spinal nerve
Chicken pox
-is not....
-it will...
-this is called...
-fully eradicated when you get better.
- hang out in the spinal cord until it senses you are weak and will then come out and reinfect an area in addults.
-shingles
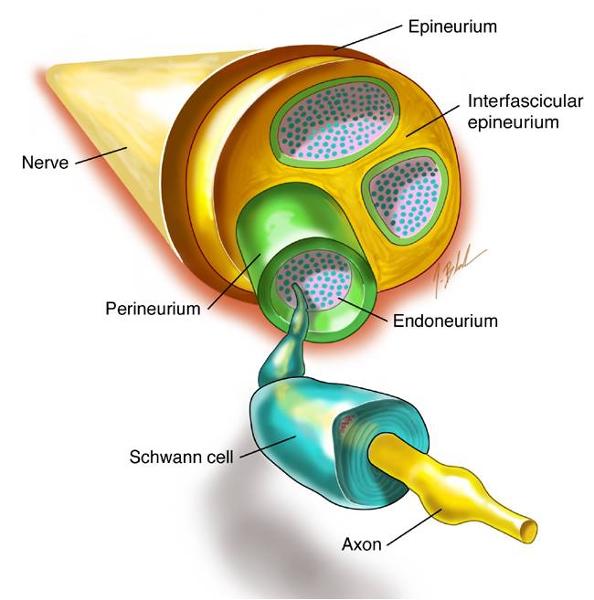
1. epineurium 2. interfascicular epineurium
3. endoneurium 4. axon
5. schwann cell 6. perineurium
1. How long is the brain developing?
2. which lobe is the last to develop?
A. this lobe is known for? (3)
1. till about 25 years old
2. frontal lobe
A. decision making, personality, religiosity
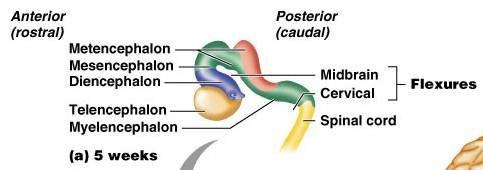
1. metensephalon 2. mesencephalon 3. diencephalon
4. telensephalon 5. myelencephalon 6. midbrain
7. cervical 8. flexures 9.spinal cord
10. 5 weeks
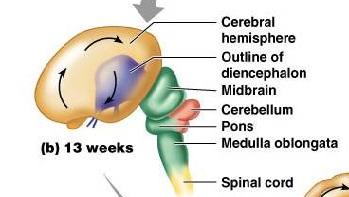
1. cerebral hemisphere 2. outline of diensephalon
3. midbrain 4. cerebellum 5. pons
6. medulla oblongata 7. spinal cord 8. 13 weeks
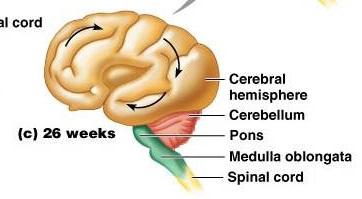
1. cerebral hemisphere 2. cerebellum
3. pons 4. medulla oblongata
5. spinal cord 6. 26 weeks
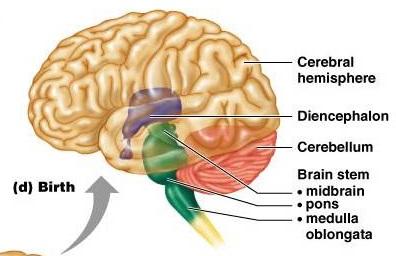
1. cerebral hemisphere 2. diencephalon
3. cerebellum 4. brain stem
5. midbrain 6. pons 7. medulla oblongata
-what is the cut off for an abortion?
-why?
- 26 weeks
- the cerebral cortex is now maid and they can now feel.
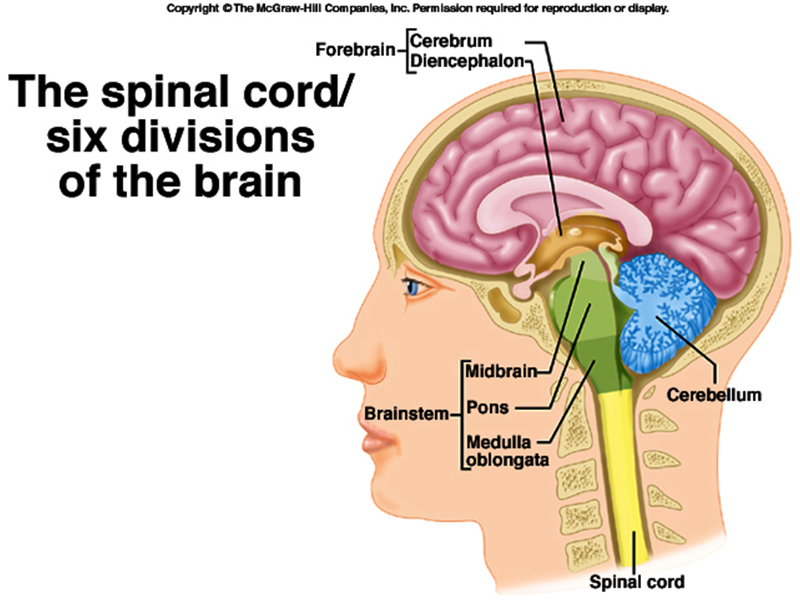
A. forebrain 1. cerebrum 2. diencephalon
B. brainstem 3. midbrain 4. pons
5. Medulla oblongata 6. cerebellum
C spinal cord
Cerebellum
functions (3)
1. Coordinates somatic motor function
2. Adjusts output of somatic motor centers resulting in smooth operation
Diencephalon
forms (3)
1. thalamus
2. hypothalamus
4.epithalamus
Midbrain (mesencephalon)
1. location
2. function (2)
1. superior portion of the brain stem
2. A. Processes visual and auditory data
B. Maintains consciousness and alertness
Pons
1. location
2. functions (2)
1. middle of the brain stem
2. A. Relays information to the thalamus and cerebellum
B. Regulates subconscious somatic and visceral motor centers
Medulla Oblongata
1. location
2. functions (2)
1. inferior portion of the brain stem
2. A. Relays information to the thalamus and brain stem
B. Regulates visceral function
cerebrum
functions (3)
1. Conscious thought processes
2. Memory storage
3. Conscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions
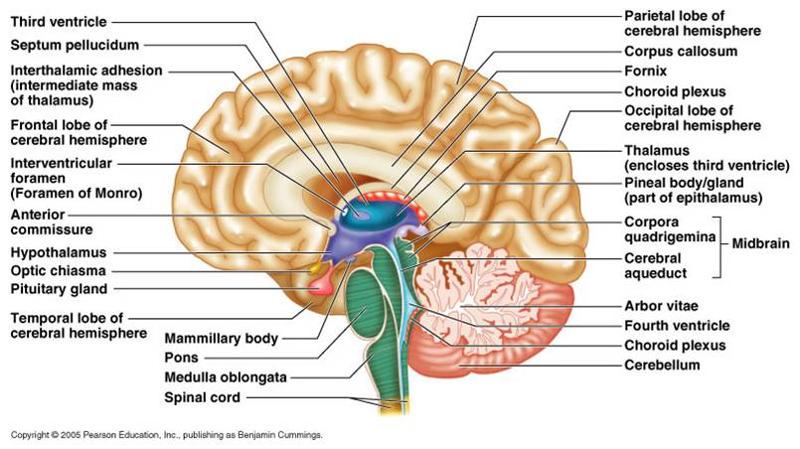
1. third ventricle 2. septum pellucidum
3. interthalamic adhesion 4. frontal lobe
5. anterior commissure 6. hypothalamus
7. optic chiasm 8. pituitary gland
9. temporal lobe 10. mammillary body
11. pons 12. medulla oblongata 13. spinal cord
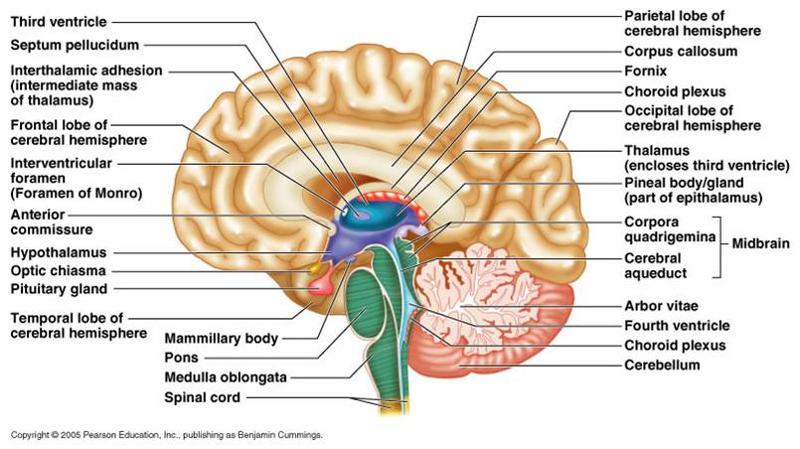
1. parietal lobe 2. corpus collosum
3. fornix 4. choroid plexus
5. occipital lobe 6. thalamus 7. pineal body/gand
8. corpora quadrigemina 9. cerebral aqueduct
10. midbrain 11. arbor vitae 12. fourth ventricle 13. choroid plexus 14. cerebellum
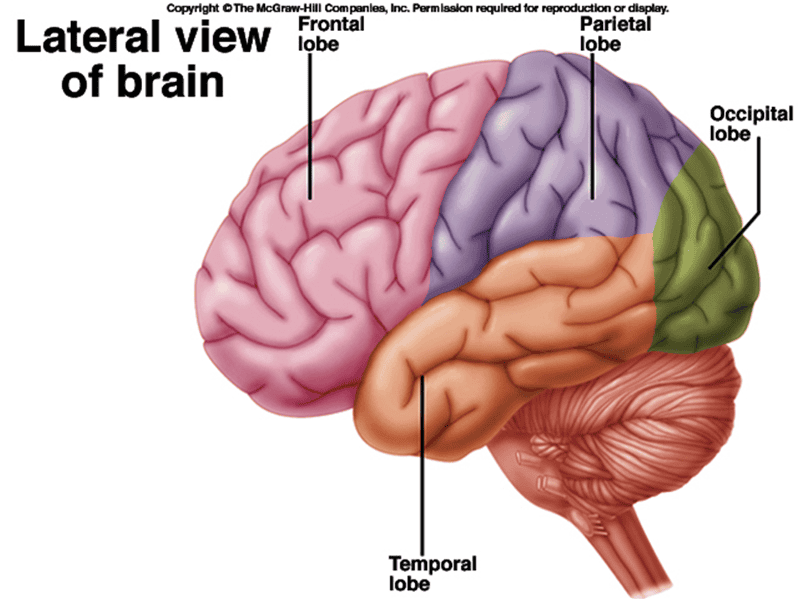
1. frontal lobe 2. parietal lobe
3. temporal lobe 4. occipital lobe
Frontal lobe
controls (6)
1. voluntary motor functions
2. concentration
3. verbal communication
4. decision making
5. planning
6. personality
Parietal lobe
controls (3)
1. general sensory functions
2. understanding speech
3. formulating words
temporal lobe
controls (2)
1. hearing
2. smell
occipital lobe
controls (3)
1. conscious perception of visual stimuli
2. integration of eye focusing movements
3. correlation of visual images w/ previous visual experiences
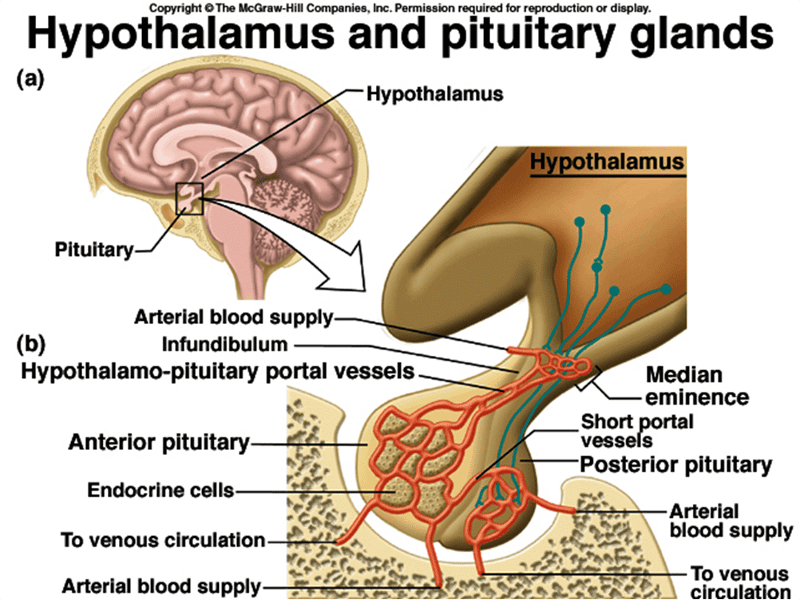
1. hypothalamus 2. pituitary
3. infundibulum 4. anterior pituitary gland
5. posterior pituitary gland
Divisions of the pituitary gland (2)
1. Anterior pituitary gland
2. Posterior pituitary gland
1. anterior pituitary grows...
2. posterior pituitary grows...
1. up (adrenohypothesis)
2. down (neurohypothysis)
cells and Hormones of the Anterior pituitary (1-3)
1. thyrotropic cells = thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
2. Mammotropic cells = prolactin (PRL)
3. corticotropic cells = Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
cells and hormones of the anterior pituitary (4-7)
4. somatotropic cells = growth hormone (GH)
5. Gonadotropic cells = follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
6. Gonadotropic cells - Luteinizing hormone (LH)
7. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
Hormones of the posterior piduitary
1. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
2. oxytocin
flow of fluid in the brain and spinal cord
1. lateral ventricles 2. third ventricle
3. fourth ventricle 4. subarachnoid space in brain and spinal cord.
what absorbs and reabsorbs cerebrospinal fluid?
Arachnoid villi
what happens to fluid flow while sleeping? why?
fluid flows at a faster rate. because cells in brain shrink while sleeping
what does Cerebrospinal fluid contain? what happens to it when you sleep?
nutrients and wastes. it replenishes
what happens when you have a concussion?
1. arachnoid is damages and cant reabsorb fluid.
2. brain swells
3. if pressure cant be released brain is forced into foramen magnum and will die
cranial nerves (12)
1. olfactory (I) 2. optic nerve (II)
3. oculomotor (III) 4. trochlear (IV)
5. trigeminal (V) 6. abducens (VI)
7. facial nerve (VII) 8. vestibulocochlear (VIII)
9. glossopharungeal (IX) 10. vagus (X)
11. hypoglossal (XII) 12. accessory (XII)
how does blood get to brain?
it gets diffused from blood vessels and CSF into the brain
hypophyseal portal system
provides a vascular pathway from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary gland
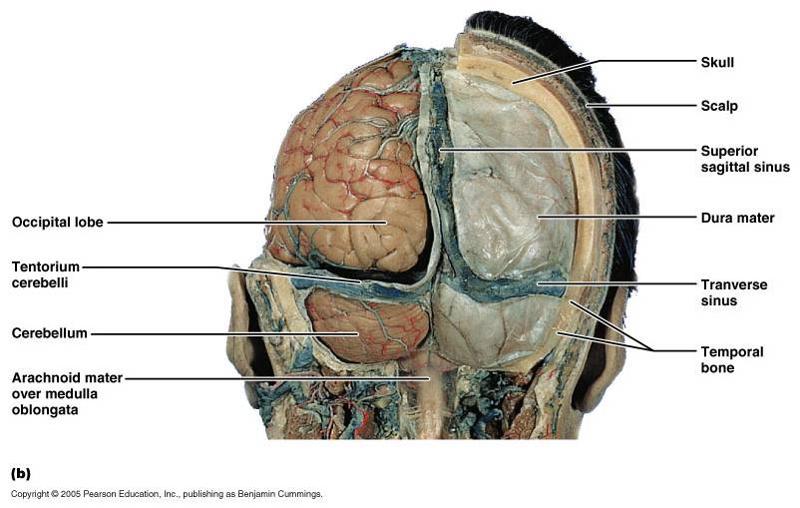
1. superior sagital sinus 2. transverse sinus
hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain
what is controlled by the limbic system
emotion and memory
the limbic system includes
1. cingulate gyrus 2. parahippocampal gyrus
3. hippocampus 4. amygdoid body
5. olfactory 6. fornix
7. anterior thalamic nuclei 8. habenular nuclei
9. septal nuclei 10. mammillary bodies
what is the reticular system? which does what?
activating systems. wakes you up
functions of:
1. olfactory
2. optic
3. oculomotor
4. trochlear
1. smell
2. vision
3. eyelid and eyeball movement
4. innervates superior oblique, turnes eye downward and laterally
functions of:
5. trigeminal
6. abducens
7. facial
8. vestibulocochlear
5. chewing, face + mouth touch + pain
6. turns eye laterally
7. controls most facial expressions, secretion of tears + saliva taste
8. hearing, equilibrium, sensation
9. glossopharyngeal
10. vagus
11. spinal accessory
12. hypoglossal
9. taste, senses carotid blood pressure
10. taste, senses aortic BP, slows heart rate, stimulates digestive organs
11. controls trapezius+ sternocleidomastoid, controls swallowing movements
12. controls tongue movements
primary sensory areas (4)
1. auditory cortex
2. somatosensory cortex
3. visual cortex
4. taste cortex
functions of:
1. frontal lobe (6)
2. parietal lobe (4)
3. occipital lobe (1)
4. temporal lobe (3)
1. reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
2. movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli
3. visual processing
4. perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory and speech
pathway for hearing (
tympanic membrane-> malleus-> incus-> stapes-> oval window-> cochlea-> auditory nerve-> auditory cortex-> ornike region-> frontal lobe
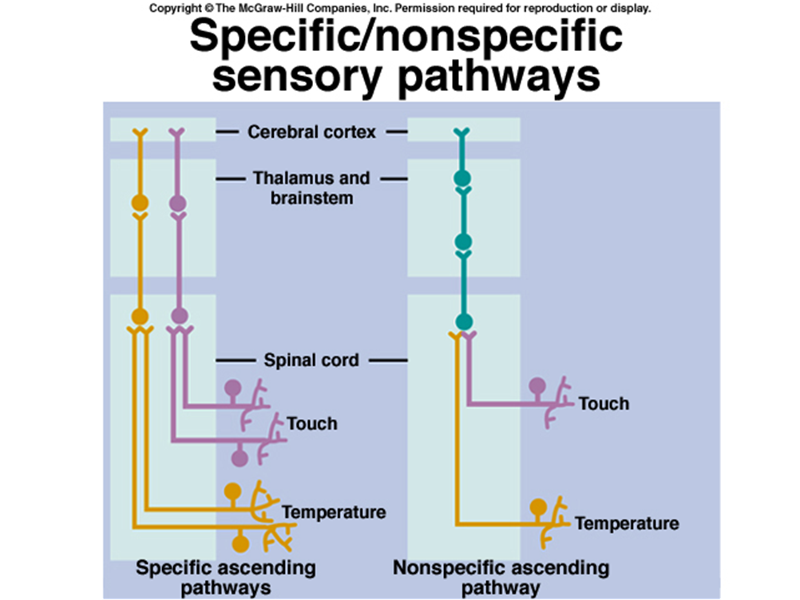
1. specific asscending pathway 2. cerebral cortex
3. spinal cord 4.touch 5. temperature
6. nonspecific ascending pathway 7. touch
8. temperature
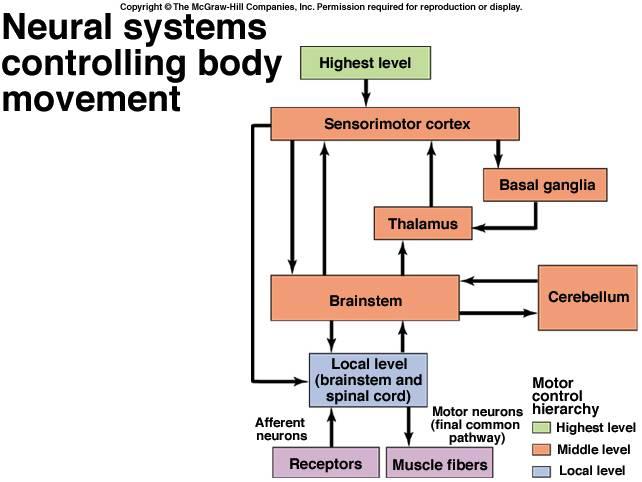
1. highest level 2. sensorimotor cortex
3. basal ganglia 4. thalamus
5. brainstem 6. cerebellum
7. local level (brainstem and spinal cord)
8. receptors 9. muscle fibers
10. highest level 11. middle level 12. local level
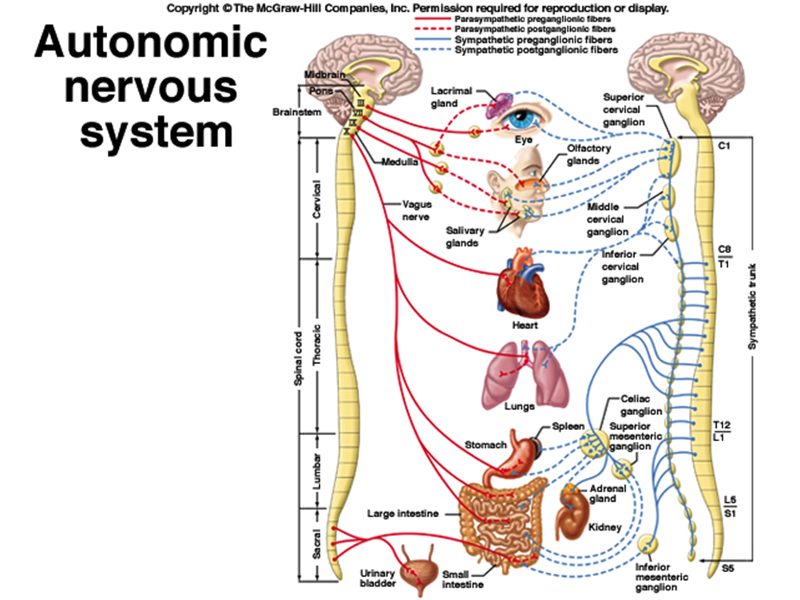
1. red = sympathetic
2. blue = parasympathetic
1. what causes the diaphragm to go down?
2. what causes the diaphragm to go up?
1. stimulating the phrenic nerve
2. once stimulation of the phrenic nerve stops
pulmonary Ventilation
1. movement of air into and out of respiratory system
Steps of respiration (5)
1. ventilation: exchange of air b/w atmosphere and alvioli by bulk flow
2. exchange of O2 + CO2 b/w alveolar air and blood in lun capillaries by diffusion.
3. transport of O2 +CO2 through pulmonary and systemic circulation by bulk flow
4. exchange of O2 + CO2 b/w blood in tissue capillaries and cells in tissues by diffusion
5. cellular utilization of )2 and production of CO2
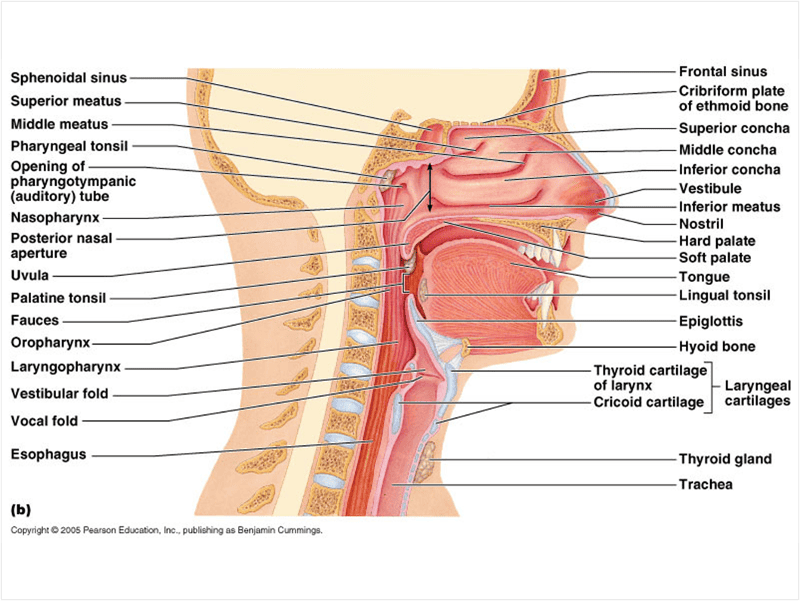
1. pharyngeal tonsil 2. nasopharynx
3. uvula 4. oropharunx
5. laryngopharynx 6. esophogus
7. epiglottis
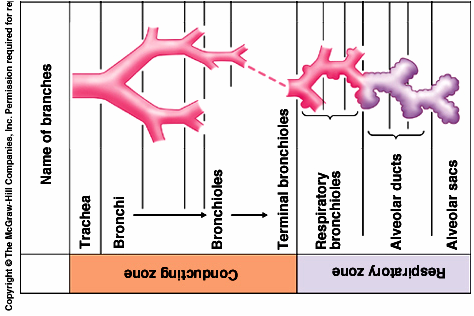
1. primary bronchi
2. secondary bronchi
3. tertiary bronchi
1. Conducting zone:
2. respiratory zone
1. transports air, little oxygen is absorbed
2. oxygen is absorbed
lungs have what kind of cells?
pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
what does the cilia in lungs do?
transports mucus to larynx where it is swallowed and digested
distinctions of
1. primary bronchi
2. secondary bronchi
3. tertiary bronchi
4. terminal bronchiole (3)
5. respiratory bronchioles
6. alveolar sacs
1. pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
2. smooth muscle begins to replace C cartilage
3. increased muscle replacing cartilage
4. nonciliated simple columnar to cuboidal epithelium, no cartilage, no goblet cells
5. epithelium begins to be squamous like
6. simple squamous epithelium, 2 types
Asthma
is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways.
nebulization
To treat with a medicated spray.
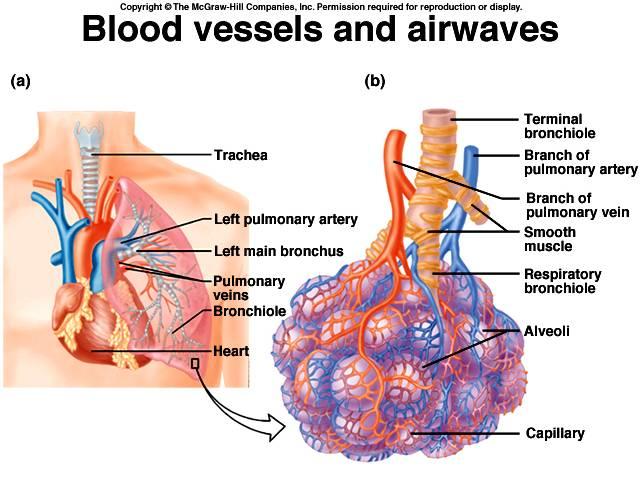
1. branch of pulmonary artery
2. branch of pulmonary vein
what decreases surface tension in alveoli?
surfactants
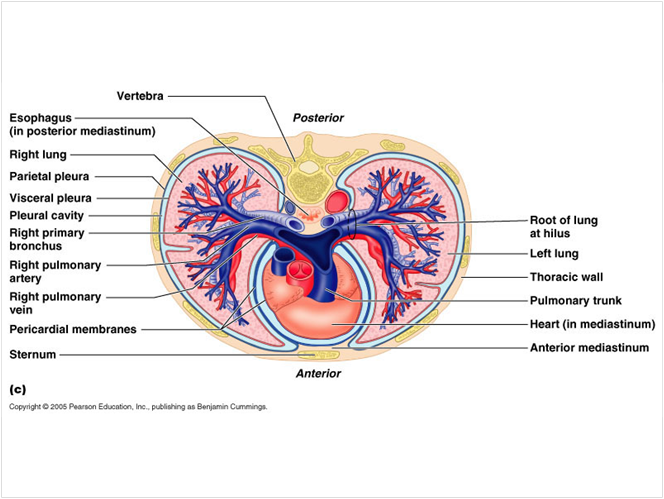
1. parietal pleura 2. visceral pleura
3. pericardial membranes 4. pleural cavity
5. thoracic wall 6. mediastinum
7. anterior mediastinum
Inspiration (7)
1. diaphragm and inspiratory intercostals contract
2. thorax expands
3. Pip becomes more subatmospheric
4. t Transpulmonary pressure
5. lungs expand
6. Palv becoms subatmospheric
7. air plows into alveoli
Expiration (1-4)
1. diaphragm and inspiratory intercostals stop contractin
2. chest wall recoils inward
3. Pip back toward preinspirarion value
4. transpulmonary pressure back toward preinspiration value
Expiration (5-8)
5. Lungs recoil toward preinspiration size
6. air in alveoli becomes compressed
7. Palv becomes greater than Patm
8. air flows out of lungs
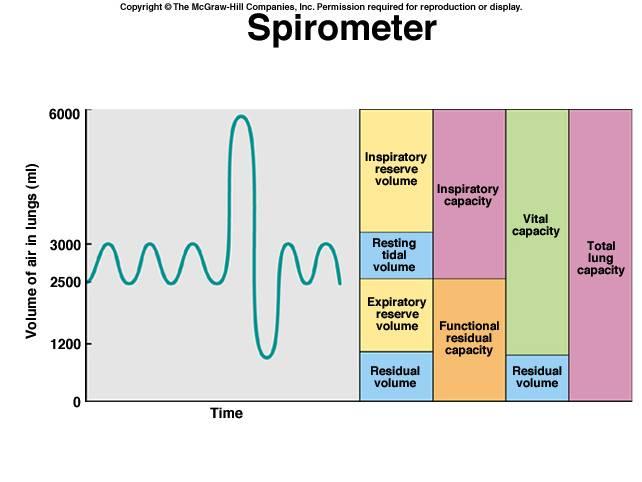
...
1. vital capacity
2. Title volume
1. the volume of air you can hold or expel when taking a forceful breath
2. the volume of air that you move into or out of lungs at rest, ~1/2 L for avg sized male
1. Barioreceptor
2. chemoreceptor
1. detect pressure change within body surfaces
2. detect chemicals/specific molecules dissolved in fluid; respond to odors and tastes in fluids
1. CO2 stimulates _____
2. smoking puts ____ making RBC's ____ efficient
1. chemoreceptors
2. CO2 and carbonmonoxide, less
alimentary canal
the tubular passage that extends from mouth to anus
1. what kind of muscle are sphincers made of?
2. which is not made of these?
1. smooth muscle
2. anal sphincter
retroperitoneal
Situated behind the peritoneum.
Accessory structures
1. physical (3)
2. secretory (3)
1. A. teeth
b. tongue
C. muscle
2. A. liver
B. gall bladder
C. pancreas
sphincters (4)
1. cardiac/esphogeal sphincter
2. pyloric sphincter
3. ileocecal valve
4. anal sphincter
peristalsis
the constant contraction of muscles to move things down a tube
1. mechanical digestion
2. chemical digestion
1. mechanical breakdown of food fromchewing and churning in stomach
2.chemical breakdown from saliva and other fluids
enteric nervous system
intrinsic nervous system of the gastrointestinal tract
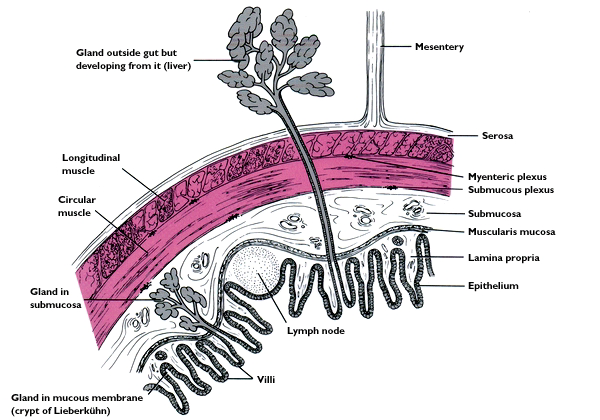
1. serosa 2. submucosa 3. muscularis mucosa
4. longitudinal muscle 5. circular muscle
1. pepsinogen
2. intrinsic factor
1. a substance that is secreted by the stomach wall and converted into the enzyme pepsin by gastric acid.
2. protein that helps your intestines absorb vitamin B12
cells of the stomach (4)
1. chief cells
2. parietal cells
3. goblet cells
4. enteroendocrine cells
function of:
1. chief cells
2. parietal cells
3. goblet cells
4. enteroendocrine cells
1. synthesize and secrete hormones = pepsinogen (converted to pepsin)
2. secretes HCl- + intrinsic factor
3. secretes acidic mucin (mucus)
4. secrete gastrin
1. pepsin
2. HCl-
3. intrinsic factor
4. gastrin
1. digests + denatures proteins
2. denatures proteins
3. helps with B12 absorption
4. hormones that enters blood + stimulates chief + parietal cells to secrete + contractile muscles of gastric music
Accessory structures (3)
1. pancreas
2. Gall bladder
3. liver
functions of:
1. pancreas
2. Gal bladder
3. liver
1. secretes enzymes that help break down food
2. holds bile produced in the liver until it is needed for digesting fatty foods
3. produces bile, detoxifies potentially harmful chemicals
cells of the pancreas (3)
1. exocrine cells
2. endocrine cells
3. duct cells
function of:
1. exocrine cells
2. duct cells
1. secretes enzymes
2. secrete bicarbonate
1. plicae circularis
2. lacteal
1. (circular folds) help increase surface area for better absorption + act as speed bumps to slow down movement of chyme
2. lymphatic capillaries
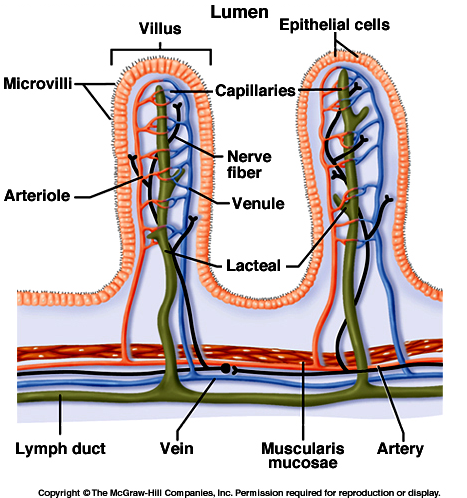
...
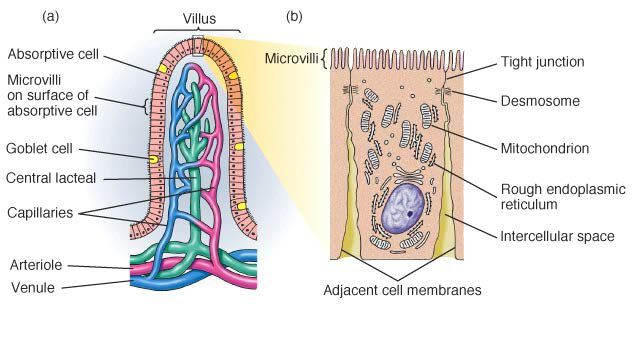
1. absorptive cells 2. goblet cells
3. central lacteal 4. capillaries
5. arteriole 6. tight junctions
7. desmosome 8. mitochondria
vernifoem appendix
most likely a resivior for immune cells
functions of colon
removes water, salt, and some nutrients forming stool
the kidneys are covered in _1_ for _2_
1. fat
2. protection
kidneys have both _1_ and _2_ functions
1. endocrine
2. exocrine
functions of the kidney (4)
1. producing hormones
2. absorbing minerals
3. filtering blood
4. producing urine
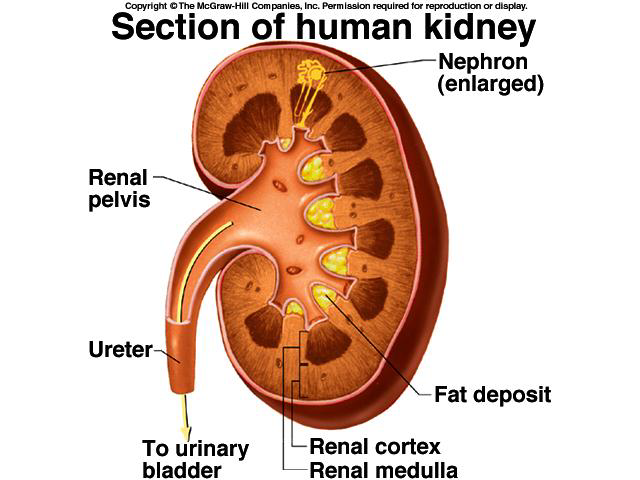
1. renal pelvis 2. prenal pyramid
2. cortex 4. medulla
kidney blood flow (11)
renal A.-> renal segmental A.-> lobar A.-> interlobar A-> arcuate A-> interlobular A-> afferent arteriole-> glomerulus-> efferent arteriole-> peritubular cappilaries
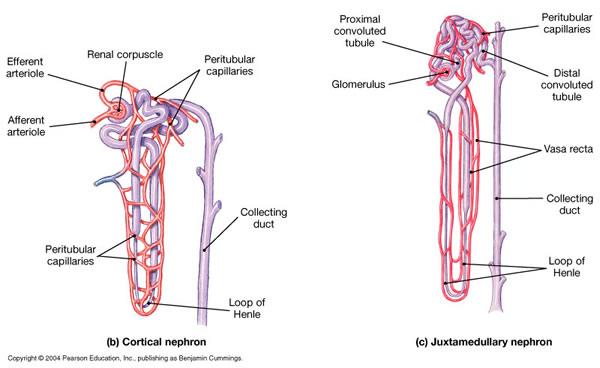
1. cortical nephron
2. juxtamedullary nephron
structure of a nephron:
1. renal corpuscle (2)
2. renal proximal tubule
3. loop of Henle
1. A. glomerulus B. boman's space
2. A. proximal convoluted tubule
B. proximal straight tubule
3. A. descending thin limb B. ascending thin limb
C. ascending thick limp
structure of a nephron
4. distal convoluted tubule
5. collecting duct system (3)
4. distal convoluted tubule
5. A. collecting tubule B. cortical collecting tubule C. medullary collecting duct
flow through the nephron (12)
glomerulus-> bowmans space in bowmans capsule-> proximal convoluted tubule-> proximal straight tubule-> descending thin limb of Henle's loop-> ascending thin limb of Henles loop-> ascending thick limb of henles loop-> distal convoluted tubule-> connecting tubule-> cortical collecting duct-> medulary collecting duct-> renal pelvis
Components of renal function (3)
1. glomerular filtration
2. tubular secretion
3. tubular reabsorption
podocyte
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
causes opening of aquaporons (water channels) which allows you to reabsorb more water
what does alcohol do to ADH?
it blocks it
renin
enzyme secreted by kidneys to increase blood sodium levels
ace inhibitor
a diuretic
mictrition
fancy word for peeing
atrial naturitic peptide
promotes salt and water excretion and lowers blood pressure
flow of urin (8)
from collecting duct-> papillary duct-> minor calyx -> majore calyx-> renal pelvis-> ureter-> urinary bladder->urethra
-evolutionarily we start out as__1__
-without any__2__ you will remain an __3__
1. female 2. hormones 3. nonviable female
1. XX=
2. XY=
3. Xo=
1. female
2. male
3. nonviable female
SRY segment
there are genes that differentiate you to develop testis
1. homologous
2. analogus
1. same embriological origin
2. same function ie. wing of a bat = wing of a bird
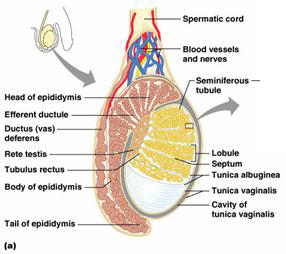
1. lobule 2. tunica albuginea
3. tunica vaginalis
where is perm produced?
lobules
sperm/ejaculant development
1. develops in testies
2. matures in epididymus
3. travels up vas deferens
4. most ejaculant liquid comes from seminal vessical
5. this meets in the ejaculatory duct with sperm
6. out through urethra
inguinal canal
the most common place for a male hernea
conceptis
The products of conception; that is, the embryo, chorionic sac, placenta, and fetal membranes.
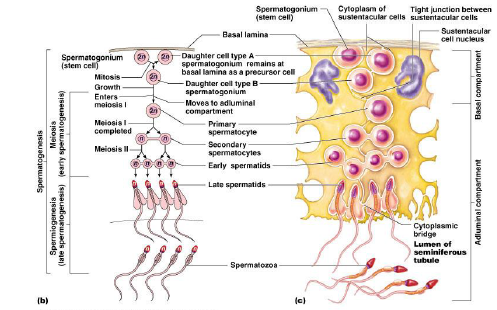
1. spermatogenisis 2. meiosis(early spermatogenisis
3. spermatogenisis (late spermatogenisis)
4. spermatogonium 5. mitosis 6. meiosis 1
7. meiosis 2 8. spermatosoa
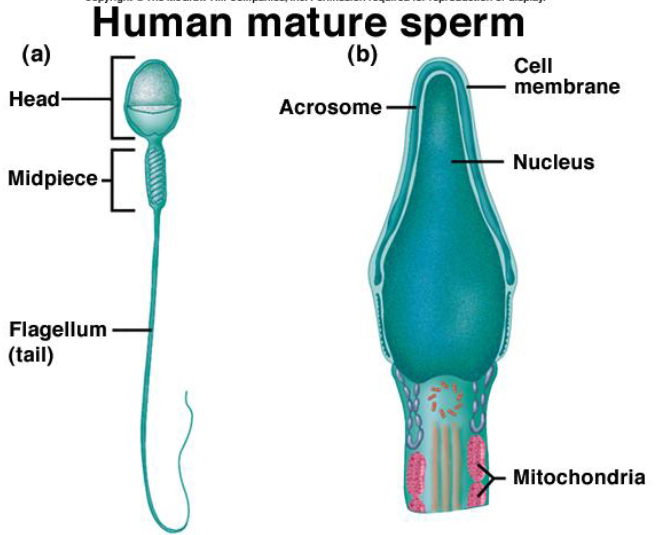
...
1. acrosome in sperm
2. mitochondria in sperm
1. has enzymes that helps penetrate the ovum
2. powers the tail of sperm
bunches of ovum are connected by___
gap junctions
layers of uterus (3) and cell types
1. endometrium (epithelium)
2. myometrium (muscle)
3. perimetrium
cycles your uterus goes through (2)
1. ovarian cycle
2. menstrual cycle
ectopic pregnancy
when an ovum implants anywhere its not supposed to
stages of mammary glands (5)
1. prior to pregnancy, ducts w/ few alveoli exist
2. in early pregnency, alveoli grow
3. in midpregnency, alveoli enlarge and acquire lumen
4. during lactation, alveoli dilate
5. after weaning, gland regresses
breast cancer- depending on __1__ of breast cancer can use __2__ to treat it
1. site
2. estrogens