__________ are receptors that can respond to changes in pressure.
Photoreceptors
Chemoreceptors
Nociceptors
Mechanoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
Pressure, pain, and temperature receptors in the skin are ________.
proprioceptors
interoceptors
mechanoreceptors
exteroceptors
exteroceptors
Potentially damaging stimuli that result in pain are selectively detected by ________.
nociceptors
interoceptors
proprioceptors
photoreceptors
nociceptors
Which receptors adapt most slowly?
smell receptors
nociceptors
touch receptors
pressure receptors
nociceptors
Feeling a gentle caress on your arm would likely involve all of the following except ________.
Meissner's corpuscles
tactile discs
Pacinian corpuscles
hair follicle receptors
Pacinian corpuscles
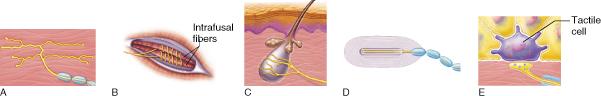
Which of the receptor types above might function as a nociceptor?
A
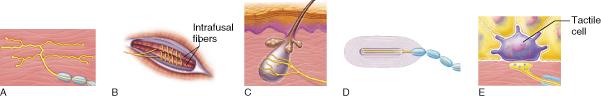
Which of the receptor types pictured function as exteroceptors?
A,C,D,E
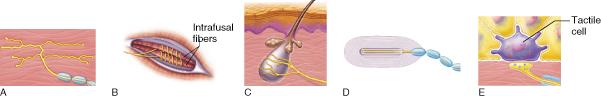
Which of the receptor types pictured function exclusively as proprioceptors?
B
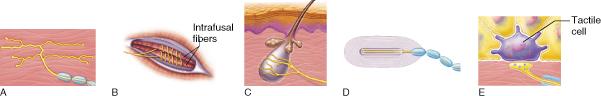
Which of the receptor types contribute to the sense of touch by responding to deep pressure stimuli?
D
Pacinian corpuscles can be exteroceptors, interoceptors, or proprioceptor,
True
False
T
Which of the following is not a way that sensory receptors are classified?
location in the body
structural complexity
sensitivity to a stimulus
type of stimulus detected
sensitivity to a stimulus
Which type of sensory receptor allows us to feel an insect landing on our skin?
chemoreceptor
thermoreceptor
mechanoreceptor
nociceptor
mechanoreceptor
Which of the following is NOT used to classify sensory receptors?
the number of dendritic endings present
the type of stimulus they detect
location
structural complexity
the number of dendritic endings present
Which of the following is composed of encapsulated nerve endings?
tactile discs
muscle spindles
free nerve endings of sensory neurons
hair follicle receptors
muscle spindles
The first level of neural integration in the somatosensory system is the __________ level.
receptor
abstraction
perceptual
circuit
receptor
__________ do NOT exhibit the property of adaptation.
Tonic receptors
Phasic receptors
Photoreceptors
Sensory receptors
Tonic receptors
In the somatosensory system there are no third-order neurons in the cerebellum.
True
False
T
Which of the following is not a main level of neural integration in the somatosensory system?
receptor
perceptual
circuit
segmental
segmental
Which of the following is an incorrect statement regarding the occurrence of a sensation?
The stimulus energy must occur within the receptor's receptive field.
The stimulus energy must match the specificity of the receptor.
A generator potential in the associated sensory neuron must reach threshold.
The stimulus energy must be converted into the energy of a graded potential
called a transduction potential.
The stimulus energy must be converted into the energy of a graded potential
called a transduction potential
Select the correct definition.
Magnitude estimation is the simplest level of sensation.
Spatial discrimination allows us to recognize textures.
Pattern recognition allows us to see a familiar face.
Perceptual detection is the ability to detect how much stimulus is applied to the body.
Pattern recognition allows us to see a familiar face.
All processing at the circuit level going up to the perceptual level must synapse in the ________.
pons
thalamus
reticular formation
medulla
thalamus
Which of the following is not an aspect of sensory perception?
magnitude estimation
feature abstraction
visceral identification
spatial discrimination
pattern recognition
visceral identification
Transduction refers to conversion of ________.
presynaptic nerve impulses to postsynaptic nerve impulses
afferent impulses to efferent impulses
stimulus energy into energy of a graded potential
receptor energy to stimulus energy
stimulus energy into energy of a graded potential
Three main levels of neural integration operate in the somatosensory system. Which level involves processing in the sensory areas of the cerebral cortex?
circuit level
receptor level
perceptual level
integrative level
perceptual level
Why might an individual experience the phenomenon known as "referred pain"?
Because the eyes may detect an injury before it is sensed, the brain creates referred sensations of pain before there is an authentic sensory stimulus.
Visceral pain afferents travel along the same pathways as somatic pain fibers.
Sensory nuclei in the thalamus become overwhelmed and send impulses to the wrong sensory cortex.
When the pain associated with an injury is severe, the brain will shut down certain cognitive functions as a defense mechanism.
Visceral pain afferents travel along the same pathways as somatic pain fibers.
Nerves that only carry impulses away from the central nervous system (CNS) are called __________.
afferent nerves
mixed nerves
motor nerves
sensory nerves
motor nerves
__________ are collections of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Myelin sheaths
Fascicles
Nuclei
Ganglia
Ganglia
The hyperalgesia that is common in phantom limb pain could be blocked if a new drug was developed that could prevent (without triggering any side-effects) the ______.
diffusion of calcium ions through NMDA receptors
release of enkephalins
binding of enkephalins to NMDA receptors
diffusion of enkephalins across synaptic clefts
diffusion of calcium ions through NMDA receptors
Nerves that carry impulses toward the CNS only are ________.
motor nerves
afferent nerves
efferent nerves
mixed nerves
afferent nerves
After axonal injury, regeneration in peripheral nerves is guided by ________.
Wallerian cells
dendrites
Schwann cells
Golgi organs
Schwann cells
Regeneration within the CNS ________.
is promoted by growth inhibitors and glial scars
typically allows axonal sprouting of 20 mm
is prevented due to growth-inhibiting proteins of oligodendrocytes
is more successful than with the PNS
is prevented due to growth-inhibiting proteins of oligodendrocytes
Select the statement that is most correct.
Ganglia are collections of neuron cell bodies in the spinal cord that are associated with efferent fibers.
The dorsal root ganglion is a motor-only structure.
The cell bodies of afferent ganglia are located in the spinal cord.
Ganglia associated with afferent nerve fibers contain cell bodies of sensory neurons.
Ganglia associated with afferent nerve fibers contain cell bodies of sensory neurons.
Which connective tissue layer directly surrounds each axon in a nerve?
perineurium
epineurium
endomysium
endoneurium
endoneurium
Choose the FALSE statement about nerves.
Nerve axons are surrounded by a loose connective tissue layer called the endoneurium.
Nerves vary in size.
Nerves consist of parallel bundles of myelinated and nonmyelinated axons.
The majority of a nerve's bulk is due to axons.
The majority of a nerve's bulk is due to axons.
There are __________ pairs of cranial nerves.
6
8
10
12
14
12
The majority of the cranial nerves attach to the __________.
spinal cord
cerebellum.
brain stem.
forebrain
brain stem.
Spinal nerves are all classified as __________.
mixed nerves
afferent nerves
sensory nerves
motor nerves
mixed nerves
The glossopharyngeal nerve is the only cranial nerve that contains sensory fibers.
True
False
False
The only cranial nerves to extend beyond the head and neck region are the vagus nerves.
True
False
True
External strabismus and ptosis could be caused by damage to the oculomotor nerve.
True
False
T
The ________ nerve is not a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
ophthalmic
maxillary
mandibular
cervical
cervical
Bell's palsy is ________.
characterized by paralysis of facial muscles
often caused by inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
characterized by loss of vision
characterized by partial paralysis of diaphragm muscles
characterized by paralysis of facial muscles
Mixed cranial nerves containing both motor and sensory fibers include all except which of the following?
olfactory
facial
oculomotor
trigeminal
olfactory
The cranial nerves that have neural connections with the tongue include all except the ________.
trochlear
trigeminal
glossopharyngeal
facial
trochlear
Problems in balance may follow trauma to which nerve?
vestibulocochlear
trigeminal
abducens
accessory
vestibulocochlear
A fracture of the ethmoid bone could result in damage to which cranial nerve?
accessory
olfactory
glossopharyngeal
vagus
olfactory
A patient who received a blow to the side of the skull exhibits the following signs and symptoms on that side of the face: he is unable to close his eye, and the corner of his mouth droops. Which cranial nerve has been damaged?
glossopharyngeal
facial
accessory
hypoglossal
facial
David, an aspiring baseball player, was struck on the left side of his face with a fastball pitch. He was not wearing a safety helmet. His zygomatic arch was crushed, as well as parts of the temporal bone. Following the accident and reconstructive surgery, he noted that his left lower eyelid was still drooping and the corner of his mouth sagged. What nerve damage did he sustain?
Trigeminal nerve damage on his left side
Facial nerve damage on his left side
Trigeminal nerve damage on his right side
Facial nerve damage on his right side
Oculomotor nerve damage on his left side
Facial nerve damage on his left side
A nurse is asked about the cause of the excruciating pain of tic douloureux. How should the nurse answer?
The excruciating pain is caused by damage to the optic nerve, resulting in anopsias.
The excruciating pain is caused by damage to the vestibulocochlear nerve, resulting in nerve deafness.
The excruciating pain is caused by inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Pressure on the trigeminal nerve root can turn normal stimuli, like tooth brushing, into painful stimuli.
The excruciating pain is caused by paralysis of the facial muscle, a condition called Bell's palsy.
The excruciating pain is caused by inflammation of the facial nerve. The nerve is constantly transmitting pain signals to the brain.
The excruciating pain is caused by inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Pressure on the trigeminal nerve root can turn normal stimuli, like tooth brushing, into painful stimuli.
The second cranial nerve forms a chiasma at the base of the brain for partial crossover of neural fibers.
True
False
T
The cranial nerve with a cervical origin (spinal cord) is the ________.
vagus
hypoglossal
accessory
glossopharyngeal
accessory
Which of the following cranial nerves carries only sensory information?
oculomotor
olfactory
trigeminal
abducens
olfactory
Which cranial nerve transmits information about our sense of equilibrium?
abducens
vagus
vestibulocochlear
optic
vestibulocochlear
The phrenic nerve serves the __________.
shoulder
neck
diaphragm
ear
diaphragm
In carpal tunnel syndrome, the __________ is compressed.
radial nerve
axillary nerve
median nerve
musculocutaneous nerve
median nerve
Hiccups could occur if there was irritation or damage to the ______.
dorsal rami of spinal nerves associated with the C3-C5 region of the spinal cord
afferent neurons of spinal nerves associated with the C3-C5 region of the spinal cord
cutaneous branches of rami associated with the C3-C5 region of the spinal cord
motor branches of ventral rami associated with the C3-C5 region of the spinal cord
motor branches of ventral rami associated with the C3-C5 region of the spinal cord
The brachial plexus can be palpated at the lower lateral border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Injury to the brachial plexus could cause weakness or paralysis to all of the following EXCEPT the ______.
deltoid muscle
biceps brachii muscle
sternocleidomastoid muscle
muscles that flex the wrist and fingers
sternocleidomastoid muscle
In carpal tunnel syndrome, there may be tingling and numbness in the thumb due to compression of the ______.
thumb muscles
cutaneous branches of the median nerve
muscular branches of the posterior cord that supply the median nerve
None of the listed responses is correct.
cutaneous branches of the median nerve

Which of the following statements is true?
The effects of neurotransmitters released by parasympathetic postganglionic neurons are always inhibitory.
The effects of neurotransmitters released by somatic motor neurons may be either stimulatory or inhibitory.
The effects of neurotransmitters released by sympathetic postganglionic neurons are always stimulatory.
The effects of neurotransmitters released from either sympathetic or parasympathetic postganglionic neurons may be stimulatory or inhibitory.
The effects of neurotransmitters released from either sympathetic or parasympathetic postganglionic neurons may be stimulatory or inhibitory.

Which of the following is the site of the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine?
terminus of a somatic motor neuron
terminus of a parasympathetic postganglionic neuron
within the ganglia of the sympathetic division
within the ganglia of the parasympathetic division
terminus of a sympathetic postganglionic neuron
terminus of a sympathetic postganglionic neuron

The circular structures shown within both pathways B and C represent which of the following?
tracts
rami
nuclei
ganglia
ganglia
A joint and the muscle that moves that joint tend to be innervated by different nerves.
True
False
F
CNS nerve fibers lack the intrinsic capacity to regenerate, while PNS nerve fibers are able to regenerate.
True
False
T
Which reflex is triggered when a stranger suddenly grasps your arm?
stretch reflex
plantar reflex
tendon reflex
crossed-extensor reflex
crossed-extensor reflex
Which reflex is important for maintaining muscle tone?
flexor reflex
stretch reflex
tendon reflex
crossed-extensor reflex
stretch reflex

Increased nerve impulse activity in the neuron labeled A will generally result in ______.
the contraction of the both muscles labeled F and G
the relaxation of the both muscles labeled F and G
the relaxation of the muscle labeled F
the relaxation of the muscle labeled G
the relaxation of the muscle labeled G
n a crossed-extensor reflex, if the right arm was grabbed it would flex and the left arm would ________.
extend
adduct
abduct
also flex
extend
A reflex that causes muscle relaxation and lengthening in response to muscle tension is called a ________.
crossed-extensor reflex
flexor reflex
plantar reflex
Golgi tendon reflex
Golgi tendon reflex
The patellar "knee jerk" reflex is an example of a(n) ________.
crossed-extensor reflex
stretch reflex
extensor thrust reflex
stress reflex
stretch reflex
Reciprocal inhibition means that while one sensory nerve is stimulated, another sensory neuron for synergistic muscles in the same area is inhibited and cannot respond.
True
False
F
A knee-jerk reflex that is unusually strong may be caused by ______.
inhibition of reciprocal inhibition
transmission of excitatory signals from the brain to the neurons that form the femoral nerve
suppression of muscle spindle activity in the lower limb
enhancement of activity in the antagonistic muscles
transmission of excitatory signals from the brain to the neurons that form the femoral nerve
Anatomically, all general sensory receptors are encapsulated nerve endings.
True
False
F
Inborn or intrinsic reflexes are ________.
autonomic only
rapid, predictable, and can be learned responses
involuntary, yet may be modified by learned behavior
always mediated by the brain
involuntary, yet may be modified by learned behavior

Which of the following muscles might be represented by that labeled F in the figure during the patellar (knee jerk) reflex?
rectus femoris
tibialis anterior
soleus
biceps femoris
rectus femoris

The nerve fibers labeled B and C are both classified as which of the following?
alpha efferent fibers
type Ia fibers
type II fibers
gamma efferent fibers
alpha efferent fibers

The synapse between which of the following two neurons is a part of a monosynaptic reflex arc?
B and C
A and D
A and B
A and B

What is the specific function of the structure labeled E?
increasing tension of the antagonistic muscle
increasing tension of the surrounding muscle
determination of muscle tension
determination of muscle length
determination of muscle length

figure below, which letter points to an afferent neuron?
A
B
C
D
A
Which of the following is the correct simple spinal reflex arc?
effector, afferent neuron, integration center, efferent neuron, receptor
receptor, efferent neuron, integration center, afferent neuron, effector
receptor, afferent neuron, integration center, efferent neuron, effector
effector, efferent neuron, integration center, afferent neuron, receptor
receptor, afferent neuron, integration center, efferent neuron, effector
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
True
False
f
Which of the following does NOT occur as people age?
Peripheral nerves die off.
Reflexes occur more slowly.
Sensory receptors atrophy.
Muscle tone in the face and neck starts to decrease.
Peripheral nerves die off.
What parts of the brain ultimately plan and coordinate complex motor activities?
cerebrum and basal nuclei
cerebrum, cerebellum, and basal nuclei
cerebellum and basal nuclei
cerebrum and cerebellum
cerebellum and basal nuclei
The cerebellum and basal nuclei are involved in regulating motor activity, starting
and stopping movements, and coordinating postural movements.
True
False
T
The knee-jerk reflex is an example of a __________.
stretch reflex
tendon reflex
flexor reflex
superficial reflex
stretch reflex
Somatic reflexes activate __________.
cardiac muscle
glands
skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
skeletal muscle
Which structure is involved in the segmental level of motor control?
cerebellum
brain stem
basal nuclei
spinal cord
spinal cord
Which of the following lists the hierarchy of motor control from lowest to highest level of control?
precommand level, projection level, segmental level
projection level, precommand level, segmental level
segmental level, projection level, precommand level
segmental level, precommand level, projection level
segmental level, projection level, precommand level
The thickest and longest nerve in the body is the __________.
pudendal nerve
femoral nerve
obturator nerve
sciatic nerve
sciatic nerve
The primary nerve that controls breathing is found in which nerve plexus?
sacral
lumbar
brachial
cervical
cervical
What type of nerve fibers are found in the ventral ramus of a spinal nerve?
autonomic only
both sensory and motor
sensory only
motor only
both sensory and motor
A fall or an improperly delivered gluteal injection could result in ________.
neurofibromatosis
phantom limb pain
postpoliomyelitis muscular atrophy
sciatica
sciatica
Which nerve is compressed in carpal tunnel syndrome?
radial
median
axillary
ulnar
median
Ralph sustained a leg injury in a bowling accident and had to use crutches. Unfortunately, he never took the time to learn how to use them properly. After two weeks of use, he noticed his fingers were becoming numb. Then he noticed his arms were getting weaker and had a tingling sensation. What could be his problem?
Compression of the musculocutaneous nerve (in the region of the armpit) may cause temporary cessation of nervous transmission, often called "Saturday night paralysis."
Compression of the median nerve (in the region of the armpit) may cause temporary cessation of nervous transmission, often called "Saturday night paralysis."
Pulling on the brachial plexus is causing weakness in the muscles of his arms, and may lead to paralysis.
Compression of the radial nerve (in the region of the armpit) may cause temporary cessation of nervous transmission, often called "Saturday night paralysis."
The median nerve is being compressed, making it difficult to pick up small objects, and resulting in the tingling sensations in his fingers.
Compression of the radial nerve (in the region of the armpit) may cause temporary cessation of nervous transmission, often called "Saturday night paralysis."
If the ventral root of a spinal nerve were cut, what would be the result in the tissue or region that nerve supplies?
a complete loss of sensation and movement
a complete loss of voluntary movement
loss of neither sensation nor movement but only of autonomic control
complete loss of sensation
a complete loss of voluntary movement
The flexor muscles in the anterior arm (biceps brachii and brachialis) are innervated by what nerve?
radial
median
ulnar
musculocutaneous
musculocutaneous
The sciatic nerve is a combination of which two nerves?
pudendal and posterior femoral cutaneous
posterior femoral cutaneous and tibial
pudendal and common fibular
common fibular and tibial
common fibular and tibial
Striking the "funny bone" is actually stimulation of (or injury to) the ________.
radial nerve
ulnar nerve
median nerve
sciatic nerve
ulnar nerve
Spinal nerves exiting the cord from the level of L4 to S4 form the ________.
sacral plexus
femoral plexus
thoracic plexus
lumbar plexus
sacral plexus
A major nerve of the lumbar plexus is the ________.
iliohypogastric
sciatic
femoral
ilioinguinal
femoral
Starting at the spinal cord, the subdivisions of the brachial plexus are (in order):
trunks, divisions, cords, and roots
roots, divisions, cords, and trunks
divisions, roots, trunks, and cords
roots, trunks, divisions, and cords
roots, trunks, divisions, and cords
The posterior side of the thigh, leg, and foot is served by the ________ nerve.
common fibular
obturator
tibial
femoral
tibial
Which of the following nerves does not arise from the brachial plexus?
ulnar
phrenic
radial
median
phrenic
The obturator nerve branches from the sacral plexus.
True
False
False
Irritation of the phrenic nerve may cause diaphragm spasms called hiccups.
True
False
t
Dorsal and ventral rami are similar in that they both contain sensory and motor fibers.
True
False
t
Dermatomes are skin segments that relate to sensory innervation regions of the spinal nerves.
True
False
t
The dorsal ramus consists only of motor fibers bringing information to the spinal cord.
True
False
f
The musculocutaneous nerve is a major nerve of the brachial plexus.
True
False
t
The meningeal branch of a spinal nerve actually reenters the vertebral canal to innervate the meninges and blood vessels.
True
False
t
Sciatica has no direct affect on ______.
perception of sensory information from the skin that covers the front of the leg
perception of sensory information from the skin that covers the back of the leg
control of the adductor longus
control of the semimembranosus
control of the adductor longus
herniated lumbar disc could interfere with ______.
skin sensations from the lateral thigh
skin sensations from the medial thigh
adduction of the thigh
All of the listed responses are correct.
All of the listed responses are correct.
If "wrist drop" were to appear, there would also be an increased probability of ______.
inability to extend the forearm
inability to flex the fingers
inability to pronate the forearm
inability to contract the biceps brachii
inability to extend the forearm
Damage to the ulnar nerve could result in the inability to ______.
supinate or pronate the forearm
flex the wrist
extend the forearm
All of the listed responses are correct.
flex the wrist