Which mode of inheritance produces heterozygotes with phenotypes that differ from either homozygote but typically more closely resembles one homozygous phenotype than the other? A) complete dominance B) incomplete dominance C) codominance D) epistasis E) incomplete penetrance
B
Which mode of inheritance results in the phenotype of a heterozygote being indistinguishable from that of an organism homozygous for the dominant allele? A) complete dominance B) incomplete dominance C) codominance D) epistasis E) incomplete penetrance
A
Which mode of inheritance results in both alleles being detected equally in the heterozygous phenotype? A) complete dominance B) incomplete dominance C) codominance D) epistasis E) incomplete penetrance
C
A mutation results in an enzyme that is partially active compared to the wild-type allele. This type of "leaky" mutation is classified as A) null/amorphic B) hypomorphic C) hypermorphic D) neomorphic E) dominant negative
B
A mutation resulting in an inactive gene product is classified as A) null/amorphic B) hypomorphic C) hypermorphic D) neomorphic E) dominant negative
A
Two proteins interact to form a multimeric complex. When one of the proteins is mutated, there is a substantial loss of functional activity in the multimeric protein. This type of mutation is classified as A) null/amorphic B) hypomorphic C) hypermorphic D) neomorphic E) dominant negative
E
Many oncogenes result from mutations that cause excessive expression of a protein in cells where it is normally not expressed or is expressed at inappropriate times during development. This type of mutation can be described as A) hypermorphic B) dominant negative C) neomorphic D) hypomorphic E) amorphic
A
A mutation results in a gene product with a novel function that is not normally found in wild-type organisms. This type of mutation is known as A) neomorphic B) amorphic C) hypermorphic D) hypomorphic E) dominant negative
A
Which of the following is correct regarding individuals who are blood type AB? A) They do not carry the A or B antigen. B) They are the universal recipients. C) They express B-transferase that adds N-acetylgalactosamine to the H antigen. D) They carry both the anti-A and anti-B antibodies. E) Their blood cells clump when they receive blood from an individual with the genotype IAi.
B
A man with blood type A (whose mother was blood type O) has children with a woman that has blood type AB. The man and the woman are also heterozygous for the H antigen. What is the probability that they will have a child with blood type A? A) 3/8 B) 1/2 C) 0 D) 1/8 E) 3/4
A
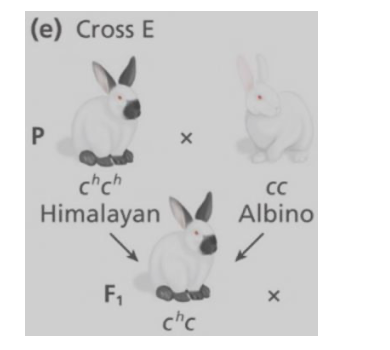
The parental cross between a rabbit with the Himalayan phenotype (genotype chch) and an albino rabbit (genotype cc) results in F1 rabbits that all have the Himalayan phenotype (genotype chc).
If the resulting F1 rabbits are crossed, what proportion of the F2 offspring will have the Himalayan phenotype and what causes the hypomorphic ch allele to be unstable and result in the distinctive fur pattern?
A) 1/2; complementation B) 3/4; complementation C) 1/4; temperature
D) 3/4; temperature E) 1/2; temperature
D
What type of allele is often detected as a distortion in segregation ratios, where one class of expected progeny is missing? A) incompletely penetrant allele B) temperature-sensitive allele C) partially dominant allele D) lethal allele E) dominant negative allele
D
You discover a new allele of a gene important for tail formation in mice. WT mice have long tails, but mice heterozygous for the allele have short tails. When you cross two heterozygous mice together, you obtain a 2:1 ratio of short-tailed mice to long-tailed mice. None of the short-tailed progeny are homozygous. What type of allele results in short tails? A) partially dominant allele B) dominant negative allele C) incompletely penetrant allele D) lethal allele E) temperature-sensitive allele
D
The amount of enzyme activity in a cell that is homozygous for a mutant allele is 400 units. The amount of enzyme activity in a cell homozygous for the WT allele is 200 units. The amount of enzyme activity in a heterozygote is 300 units. What type of allele is the mutant allele? A) dominant negative B) hypomorphic C) neomorphic D) hypermorphic E) null/amorphic
D
The amount of enzyme activity in a cell that is homozygous for a mutant allele is 400 units. The amount of enzyme activity in a cell homozygous for the WT allele is 200 units. The amount of enzyme activity in a heterozygote is 300 units. What is the dominance relationship between the WT and mutant allele for the phenotype of amount of enzyme per cell? A) The mutant allele is dominant. B) The WT and mutant alleles are codominant. C) The WT and mutant alleles show incomplete dominance. D) The WT allele is dominant. E) It is impossible to determine from the information given.
C
The amount of enzyme activity in a cell that is homozygous for a mutant allele is 0 units. The amount of enzyme activity in a cell homozygous for the WT allele is 200 units. The amount of enzyme activity in a heterozygote is 0 units. What type of allele is the mutant allele? A) hypermorphic B) hypomorphic C) null/amorphic D) neomorphic E) dominant negative
E
Which phenomenon explains differences in the inheritance patterns of the appearance of a chin beard between males and females of certain species of goats, even when their genotypes are the same? A) variable expressivity B) lethal allele C) sex-influenced trait D) sex-limited trait E) incomplete penetrance
C
In certain goat breeds, appearance of a chin beard is a sex-influenced trait. Recall that bearding is inherited as an autosomal trait determined by two alleles, B₁ and B₂, and females must be homozygous for the bearded allele, B₂, to have a beard. What genotypes must a bearded billy goat (male) and a beardless female goat have if they have a bearded female offspring? A) The bearded billy goat could be heterozygous or homozygous for the bearded allele, while the beardless female must be heterozygous for the bearded allele. B) The bearded billy goat could be heterozygous or homozygous for the bearded allele, while the beardless female must be homozygous for the bearded allele. C) Both the bearded billy goat and beardless female must be heterozygous for the bearded allele. D) Both the bearded billy goat and beardless female must be homozygous for the bearded allele. E) The bearded billy goat must be heterozygous for the bearded allele, while the beardless female must be homozygous for the bearded allele.
A
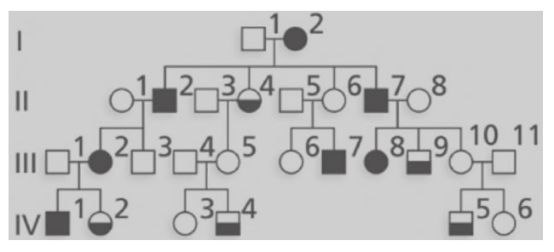
Brachydactyly type D is human autosomal dominant condition in which
the thumbs are 19) abnormally short and broad. In most cases, both
thumbs are affected, but occasionally just one
thumb is
involved. The pedigree above shows a family in which brachydactlyly
type D is
segregating. Filled circles and squares represent
females and males who have involvement of both thumbs. Half-filled in
symbols represent family members with just one thumb affected?
There is evidence of variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance in this family. Which individu most likely nonpenetrant for the trait?
A) IV-1 B) III-11 C) IV-5 D) III-10 E) II-4
D

Brachydactyly type D is human autosomal dominant condition in which
the thumbs are 20) abnormally short and broad. In most cases, both
thumbs are affected, but occasionally just one
thumb is
involved. The pedigree above shows a family in which brachydactlyly
type D is
segregating. Filled circles and squares represent
females and males who have involvement of both thumbs. Half-filled in
symbols represent family members with just one thumb affected?
There is evidence of variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance in this family. Which individu most likely nonpenetrant for the trait?
A) III-11 B) III-5 C) IV-1 D) IV-5
E) II-4
B
King George III of England and other members of the royal family were afflicted with a series of strange, seemingly unrelated symptoms including abdominal pain, rapid pulse, convulsions, and insanity. It has been determined that he likely suffered from porphyria, caused by a mutation in a single allele. What is the genetic term describing the alteration of multiple, distinct traits of an organism by a mutation in a single gene? A) codominance B) incomplete penetrance C) incomplete dominance D) epistasis E) pleiotropy
E
Gene interactions in which an allele of one gene modifies or prevents expression of alleles of another gene is known as A) incomplete penetrance B) incomplete dominance C) epistasis D) pleiotropy E) codominance
C
Bateson and Punnett crossed two white-flowered lines and saw all purple flowers in the F1 generation. They concluded this was an example of complementary gene interactions because a cross of the F1 plants yielded what ratio in the F2 generation? A) 0 purple to 16 white B) 7 purple to 9 white C) 8 purple to 8 white D) 16 purple to 0 white E) 9 purple to 7 white
E
The 9:6:1 ratio seen in the dihybrid cross of summer squash indicates what genetic relationship between the two genes controlling fruit shape? A) recessive epistasis B) dominant epistasis C) complementary gene interaction D) dominant gene interaction E) dominant suppression
D
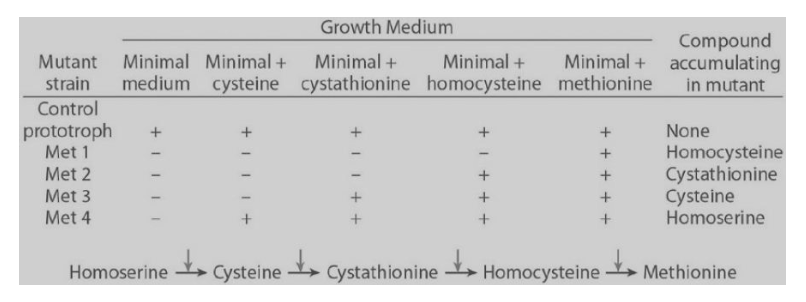
In the biosynthetic pathway for conversion from homoserine to methionine, you identify a 25) Neurospora crassa double mutant Met1/Met2. This mutant will grow only if which supplement(s) are added to the minimal media?
A) homoserine only B) cysteine only
C) homocysteine only
D) methionine only
E) cystathionine and homocysteine
D

Which step is catalyzed by the enzyme responsible for the Met 2 mutant?
A) methionine → homoserine
B) homoserine → cysteine
C) cysteine → cystathionine
D) cystathionine → homocysteine E) homocysteine → methionine
D
Wild-type bacteria can grow on minimal medium. Four mutants that cannot grow on minimal medium but can grow on minimal medium supplemented with the nutrient "H" are isolated. It is suspected that metabolites T, P, and A are in the biochemical pathway for synthesis of H, so each mutant is tested for ability to grow on minimal medium supplemented with these metabolites: A. Mutant 1: can grow on minimal medium supplemented with T, but not P or A B. Mutant 2: is unable to grow on minimal medium supplemented with T, P, or A C. Mutant 3: is able to grow on minimal medium supplemented with A or T, but not P D. Mutant 4: can grow on minimal medium supplemented with T, P, or A. Which of the following is NOT consistent with this information? A) Mutant 4 blocks a step before all the metabolites B) Mutant 3 blocks the conversion of metabolite P → metabolite A C) Mutant 2 blocks a step right before metabolite H D) Mutant 3 will cause a build up of metabolite T E) Mutant 1 will cause a build up of metabolite A
B
Wild-type bacteria can grow on minimal medium. Four mutants that cannot grow on minimal medium but can grow on minimal medium supplemented with the nutrient "H" are isolated. It is suspected that metabolites T, P, and A are in the biochemical pathway for synthesis of H, so each mutant is tested for ability to grow on minimal medium supplemented with these metabolites: A. Mutant 1: can grow on minimal medium supplemented with T, but not P or A B. Mutant 2: is unable to grow on minimal medium supplemented with T, P, or A C. Mutant 3: is able to grow on minimal medium supplemented with A or T, but not P D. Mutant 4: can grow on minimal medium supplemented with T, P, or A. Which of the following is NOT consistent with this information? A) Mutant 2 blocks a step right before metabolite H B) Mutant 1 blocks the conversion of metabolite T → metabolite H C) Mutant 1 will cause a build up of metabolite A D) Mutant 4 blocks a step before all the metabolites E) Mutant 3 blocks the conversion of metabolite P → metabolite A
B
Independent assortment predicts a 9:3:3:1 ratio with four different phenotypes in the F2 progeny. If the alleles are epistatic, what would you predict? A) no change in the 9:3:3:1 ratio B) fewer than four phenotypes C) 1/3 of the progeny with the dominant phenotypes and 2/3 recessive D) more than four phenotypes E) heterozygotes with a novel phenotype between the dominant and recessive homozygotes
B
Two pure-breeding mutant plants produce white flowers. When they are crossed, all of the progeny have wild-type purple flowers. What does this genetic complementation tell you? A) The two lines exhibit different mutations in the same gene. B) The allele is pleiotropic. C) The allele exhibits incomplete dominance. D) The genes are part of two distinct biosynthetic pathways. E) More than one gene is involved in determining the phenotype.
E
You are looking at the color of feathers in ducks and find that yellow ducks (Y) are dominant to green ducks (y). However, a second gene, H, controls whether the color will be expressed in the feathers. If the duck is hh, the duck will always be white, because the pigment does not go into feathers. What ratio of phenotypes would you expect following a dihybrid cross? A) 9:6:1 B) 12:3:1 C) 9:3:4 D) 15:1 E) 13:3
C
In sheep, coat color is influenced by two genes. Gene A influences pigment production, while gene B produces black or brown pigment. If two heterozygous white sheep resulted in 12 white sheep, 3 black sheep, and 1 brown sheep, which genotype(s) of the white sheep explain this data? A) The white sheep must all be A_B_. B) The white sheep must all be aabb. C) The white sheep could be A_B_ or aabb. D) The white sheep could be A_B_ or aaB_. E) The white sheep could be A_B_ or A_bb.
E
A certain species of morning glories produces flowers that are blue, red, or purple. Two pure-breeding purple lines are crossed and produce F1 progeny that all make blue flowers. The F1 are allowed to self and produce 320 F2 progeny with the following distribution: 185 blue, 115 purple, and 20 red. Which of the following is NOT consistent with this information? A) Analysis of the F1 and F2 progeny phenotypes suggests epistasis. B) The pure-breeding parental parents are homozygous recessive for mutations in two different genes. C) Dominant gene interaction appears to result in a 9:6:1 ratio. D) Red-flowering plants are homozygous recessive for both genes. E) Blue-flowering plants are either A_bb or aaB_.
B
Deafness is caused by recessive mutations in any one of at least five genes. Two deaf individuals have nine children, all of whom have normal hearing. Which of the following can you conclude? A) The parents have the same mutated protein involved in inner ear development. B) The parents have mutations in different genes. C) The mutations are codominant to the normal allele. D) The mutations are incompletely dominant to the normal allele. E) The parents have mutations in the same gene.
B
In yeast, there are three gene products required to synthesize the amino acid lysine. You cross two haploid lysine auxotrophs to form a diploid. The diploid fails to grow on plates lacking lysine. Which of the following can you definitively conclude? A) The haploid strains must belong to the complementation group encoding the first enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway. B) The haploid strains have identical mutations in the same genes. C) The haploid strains have mutations in different genes. D) The haploid strains have identical mutations in different genes. E) The haploid strains have mutations in the same gene.
E
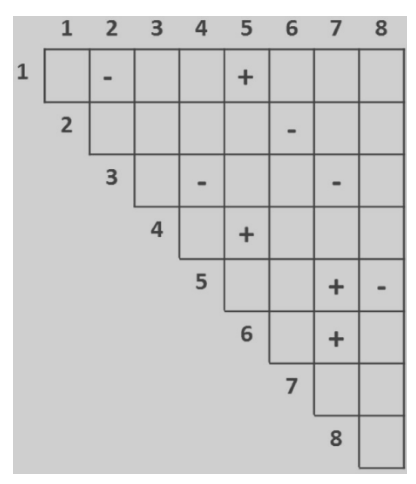
Complementation tests of distinct recessive mutants, 1 through 8,
produce the data in the matrix 36) below. A plus (+) indicates
complementation, meaning the phenotype of the combined alleles
is
wild type, and a minus (-) indicates a failure to complement
meaning that a mutant phenotype resu Assume that the missing mutant
combinations would yield data consistent with the entries that are
How many complementation groups are formed by these eight
mutants?
A) 5 B) 6 C) 3 D) 4 E) 2
C