Under which condition will the metabolic activity in a sea urchin egg most likely be activated even in the absence of sperm? A) abnormally high levels of carbonic acid in the cytosol B) abnormally low levels of extracellular oxygen C) injection of calcium ions into the cytosol D) depletion of its ATP supplies
C
The formation of the fertilization envelope in a sea urchin egg is most directly stimulated by an increase in the cytosolic concentration of which of the following ions? A) calcium ions B) hydrogen ions C) potassium ions D) sodium ions
A
Contact between signaling molecules on a sperm membrane with receptor molecules on an oocyte membrane will most directly result in which of the following responses? A) mitosis B) membrane depolarization C) vitellogenesis D) an acrosomal reaction
B
Which of the following answers best describes a feature of the plasma membrane of a sea urchin egg that is required for fertilization? A) It is located outside of the fertilization membrane. B) It releases calcium, which initiates the fast block to polyspermy. C) It has receptor molecules that specifically bind to acrosomal proteins. D) It is a mesh of proteins crossing through the cytosol of the egg.
C
Release of the acrosomal contents during fertilization most directly results in which of the following events? A) blocking polyspermy B) helping propel more sperm toward the egg C) digesting the protective jelly coat on the surface of the egg D) triggering the completion of meiosis by the sperm
C
Which of the following statements best describes the function of the vitelline layer in a newly fertilized sea urchin egg? A) It lifts away from the egg and hardens to form a fertilization envelope. B) It secretes hormones that enhance steroidogenesis by the ovary. C) It reduces the loss of water from the egg and prevents desiccation. D) It provides most of the nutrients used by the zygote.
A
In sea urchins, which of the following pairs of events most directly results in the short-lasting "fast block" and the longer-lasting "slow block" to polyspermy, respectively? A) the acrosomal reaction and vitellogenesis B) the cortical reaction and the formation of yolk protein C) formation of the jelly coat and the vitellin membranes D) membrane depolarization and the cortical reaction
D
Treating an oocyte with a chemical that binds calcium and magnesium ions will block ________. A) the acrosomal reaction B) fusion of sperm and egg nuclei C) the fast block to polyspermy D) formation of the fertilization envelope
D
In mammalian eggs, the receptors for sperm are found in which of the following locations? A) mitochondrial membrane B) plasma membrane C) nuclear envelope D) cell wall
B
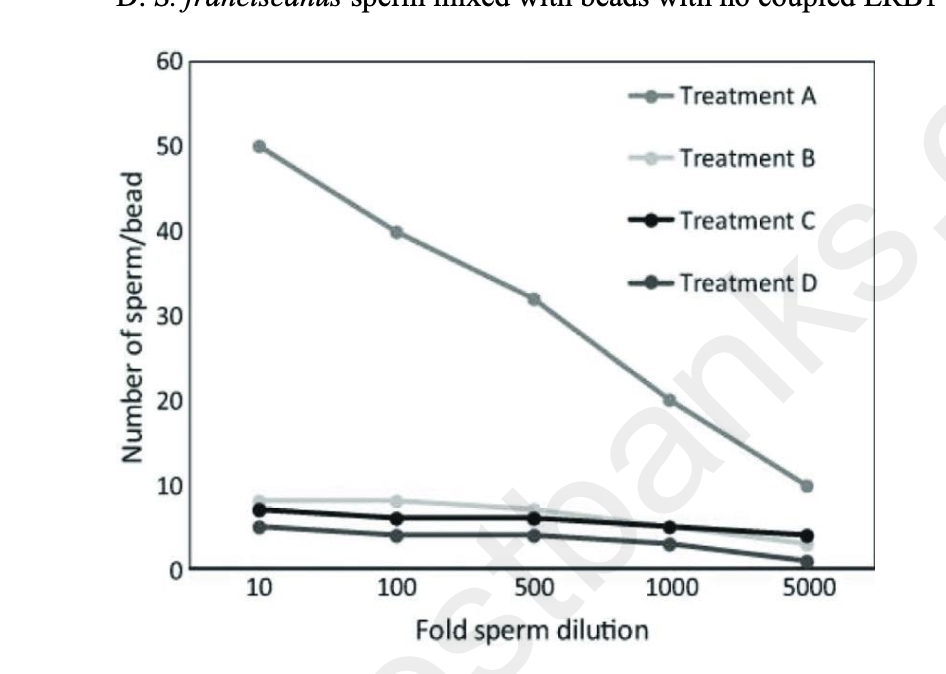
Use the following information to answer the question.
In an investigation into sperm-oocyte binding, researchers isolated the egg receptor protein,
ERB1, from the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. ERB1 binds to the sperm acrosomal
protein, bindin, during fertilization. The researchers coupled the ERB1 receptor from S.
purpuratus to plastic microbeads and then mixed the ERB1-coupled beads with sperm from S.
purpuratus or from the related species, S. franciscanus. A summary of the treatment mixtures
and a graph of the results are shown.
Treatments:
A: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1-coupled beads
B: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with beads with no coupled ERB1 protein
C: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1 beads
D: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with beads with no coupled ERB1 protein
Based on the description of the experiment, which of the treatments would be considered a
negative-control treatment for S. purpuratus sperm binding?
A) Treatment A
B) Treatment B
C) Treatment C
D) Treatment D
B
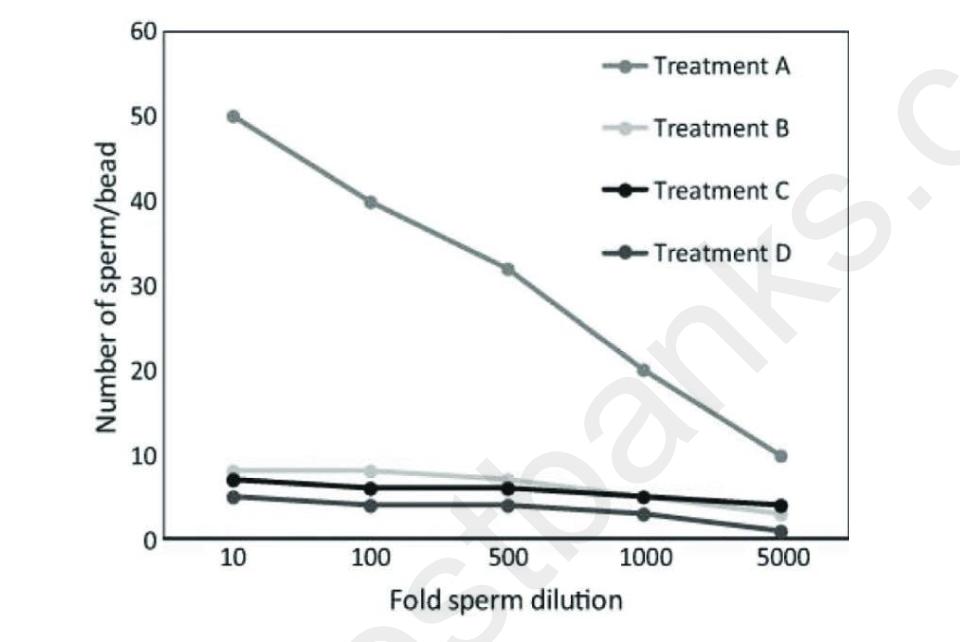
Use the following information to answer the question.
In an investigation into sperm-oocyte binding, researchers isolated the egg receptor protein,
ERB1, from the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. ERB1 binds to the sperm acrosomal
protein, bindin, during fertilization. The researchers coupled the ERB1 receptor from S.
purpuratus to plastic microbeads and then mixed the ERB1-coupled beads with sperm from S.
purpuratus or from the related species, S. franciscanus. A summary of the treatment mixtures
and a graph of the results are shown.
Treatments:
A: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1-coupled beads
B: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with beads with no coupled ERB1 protein
C: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1 beads
D: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with beads with no coupled ERB1 protein
Which of the following conclusions is most consistent with the data?
A) Plastic beads do not bind at all to sperm from either species of sea urchin.
B) ERB1 prevents S. franciscanus sperm from binding the beads.
C) Sperm from S. purpuratus bind to beads more if ERB1 is present than if ERB1 is not present.
D) S. franciscanus and S. purpuratus are the same species.
C
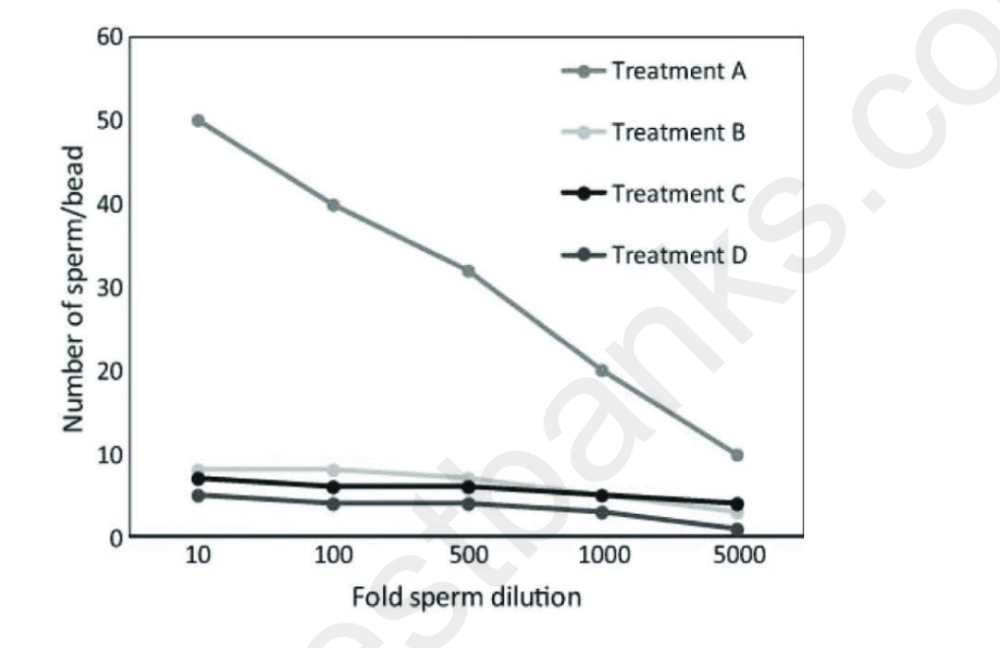
Use the following information to answer the question.
In an investigation into sperm-oocyte binding, researchers isolated the egg receptor protein,
ERB1, from the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. ERB1 binds to the sperm acrosomal
protein, bindin, during fertilization. The researchers coupled the ERB1 receptor from S.
purpuratus to plastic microbeads and then mixed the ERB1-coupled beads with sperm from S.
purpuratus or from the related species, S. franciscanus. A summary of the treatment mixtures
and a graph of the results are shown.
Treatments:
A: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1-coupled beads
B: S. purpuratus sperm mixed with beads with no coupled ERB1 protein
C: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with S. purpuratus ERB1 beads
D: S. franciscanus sperm mixed with beads with no coupled ERB1 protein
Which of the following is a broader implication from the observations of the experiment?
A) In sea urchins, fertilization of eggs by sperm is dependent upon species-specific protein
interactions.
B) Only some species of sea urchins use receptor proteins on their eggs to bind sperm.
C) Protein-coated plastic beads should not be used to test sperm binding to eggs.
D) S. franciscanus is probably not a sea urchin, but must be some other type of organism.
A
Which of the following is true about human eggs at the moment of sperm penetration? A) They use flagellar propulsion to move from the ovary to the oviduct. B) They are still located within the ovary. C) They are covered by a thin layer of calcium carbonate that prevents desiccation. D) They are still surrounded by follicular cells.
D
Which of the following is the largest cell involved in frog reproduction? A) an egg B) a blastomere in the vegetal pole C) a blastomere in the animal pole D) one of the products of the first cleavage
A
Which of the following correctly describes a difference between the vegetal pole of a frog zygote and the animal pole? A) The vegetal pole has a higher concentration of yolk. B) The blastomeres originate only in the vegetal pole. C) The vegetal pole cells undergo mitosis, but not cytokinesis. D) The polar bodies bud from this region.
A
In which of the following pairs of organisms does holoblastic cleavage typically occur? A) humans and fish B) sea urchins and birds C) sea urchins and humans D) birds and fish
C
Which of the following correctly describes the sequence of developmental milestones in chordates? A) blastula → gastrula → cleavage B) cleavage → gastrula → blastula C) cleavage → blastula → gastrula D) gastrula → blastula → cleavage
C
Which of the following structures is formed before the others during frog development? A) blastopore B) mouth C) blastocoel D) anus
C
In some rare salamander species, all individuals are females. Reproduction relies on those females having access to sperm from males of another species. However, the resulting embryos receive no genetic contribution from the males. Given this information, what is the role of sperm in reproduction in this species? A) The sperm allow morphogenesis to proceed. B) Sperm trigger egg activation. C) Cell differentiation is initiated by the sperm. D) Sperm are necessary to produce a diploid zygote.
B
The cortical reaction of sea urchin eggs is required for which of the following events in fertilization? A) forming a fertilization envelope B) producing a fast block to polyspermy C) releasing hydrolytic enzymes from the sperm D) generating an electrical impulse from the egg
A
Which of the following correctly describes the order of events of early development from earliest to latest? A) first cell division → synthesis of embryo's DNA begins → acrosomal reaction → cortical reaction B) cortical reaction → synthesis of embryo's DNA begins → acrosomal reaction → first cell division C) cortical reaction → acrosomal reaction → first cell division → synthesis of embryo's DNA begins D) acrosomal reaction → cortical reaction → synthesis of embryo's DNA begins → first cell division
D
Which of the following types of embryos displays meroblastic cleavage, extraembryonic membranes, and a primitive streak? A) an insect B) an amphibian C) a bird D) a sea urchin
C
During which stage of development do cells in a triploblastic embryo move to new positions to establish the three germ tissue layers? A) determination B) cleavage C) induction D) gastrulation
D
Which of the following options describes the correct outer-to-inner sequence of tissue layers in a post-gastrulation vertebrate embryo? A) endoderm → ectoderm → mesoderm B) mesoderm → endoderm → ectoderm C) ectoderm → mesoderm → endoderm D) ectoderm → endoderm → mesoderm
C
Which of the following outcomes would most likely occur if gastrulation was blocked? A) cleavage would not occur in the zygote B) embryonic germ layers would not form C) the blastula would not be formed D) the blastopore would form above the gray crescent in the animal pole
B
What does the archenteron of the developing sea urchin eventually develop into? A) blastocoel B) heart and lungs C) digestive tract D) brain and spinal cord
C
Which of the following correctly describes gastrulation in frog embryos? A) causes the ectoderm and endoderm layers to invert B) occurs along the primitive streak in the animal hemisphere C) proceeds by involution as cells roll over the lip of the blastopore D) occurs within the inner cell mass that is embedded in the large amount of yolk
C
Which of the following correctly matches a structure with the germ layer from which it is derived? A) The mesoderm gives rise to the notochord. B) The endoderm gives rise to the hair follicles. C) The ectoderm gives rise to the liver. D) The mesoderm gives rise to the lungs.
A
The primitive streak in a bird embryo is the functional equivalent to which of the following structures? A) the lip of the blastopore in the frog B) the archenteron in a frog C) the notochord in a mammal D) neural crest cells in a mammal
A
Which of the following is required for development in all vertebrate animals? A) a large supply of yolk B) an aqueous environment C) extraembryonic membranes D) a primitive streak
B
The eggs of which of the following organisms contains the least amount of yolk? A) bird B) frog C) eutherian mammal D) reptile
C
What is a human embryo called at the time of implantation? A) blastocyst B) gastrula C) fetus D) zygote
A
Which of the following structures releases enzymes that initiate implantation of an embryo in the endometrium? A) inner cell mass B) endoderm C) mesoderm D) trophoblast
D
Thalidomide, now banned for use as a sedative during pregnancy, was used in the early 1960s by many women in their first trimester of pregnancy. Some of these women gave birth to children with limb and organ deformities. Which of the following processes did the drug most likely influence? A) early cleavage divisions B) differentiation of bone tissue C) morphogenesis D) gastrulation
C
The migratory neural crest cells give rise to which of the following structures? A) the brain B) the spinal cord C) a variety of peripheral neural and non-neural structures D) the lining of the lungs and of the digestive tract
C
Which of the following is a result of gastrulation in animals? I) The archenteron is formed. II) The body axes are established. III) The germ layers are formed. A) I only B) III only C) I and III only D) I, II, and III
C
Cell migration occurs extensively as part of which of the following processes? A) organogenesis, but not gastrulation or cleavage B) cleavage, but not gastrulation or organogenesis C) gastrulation and cleavage D) gastrulation and organogenesis
D
Which of the following cellular structures is usually reorganized when a cell changes shape? A) nucleus B) cytoskeleton C) extracellular matrix D) Golgi apparatus
B
Which correctly matches the organ with its embryonic source? A) adrenal medulla–endoderm B) nervous system–mesoderm C) kidney–mesoderm D) skin–endoderm and mesoderm
C
Which of the following structures is the embryonic precursor to the human spinal cord? A) notochord B) neural tube C) mesoderm D) archenteron
B
Which of the following processes reduces the size of a tadpole's tail during metamorphosis? A) regeneration B) apoptosis C) oxidative phosphorylation D) redifferentiation
B
Which of the following terms applies to a morphogenetic process whereby cells extend themselves, making the mass of the cells narrower and wider? A) convergent extension B) induction C) invagination D) involution
A
Which of the following is common to the development of birds and mammals? A) the formation of an embryonic epiblast and hypoblast B) the formation of an embryonic trophoblast C) the formation of an embryonic yolk plug D) the formation of an embryonic gray crescent
A
Which of the following occurs to the blastocoel during frog development? A) becomes the archenteron B) gives rise to the endoderm C) gives rise to the placenta D) is replaced by the expanding archenteron
D
Which of the following correctly matches an extraembryonic membrane with its function? A) amnion–waste disposal B) chorion–nutrient storage C) allantois–waste storage D) yolk sac–gas exchange
C
Which of the following contributions of the extra embryonic membranes was crucial for the colonization of land by vertebrate organisms? A) extraembryonic membranes provide an aqueous environment for embryo development B) extraembryonic membranes provide nutrients that produce energy for development C) extraembryonic membranes direct morphogenesis within the embryo D) extraembryonic membranes give rise to crucial organ systems, like the heart and brain
A
Suppose that during gastrulation in humans, a protease is present such that the enzymes released by the trophoblast cannot function. What is the most likely immediate outcome of this situation? A) The embryo will not implant into the endometrium. B) The blastocyst will not form. C) Cleavage will not occur. D) Organogenesis will not occur.
A
Which of the following is most likely to occur if an amphibian zygote is manipulated so that the first cleavage plane fails to divide the gray crescent? A) the daughter cell with the entire gray crescent will die B) both daughter cells will develop normally, because amphibians are totipotent at this stage C) only the daughter cell with the gray crescent will develop normally D) both daughter cells will develop abnormally
C
Which of the following were Hans Spemann and colleagues studying when they developed the concept of the "organizer" in amphibian embryos? A) medial cells between the optic cups B) anterior terminus of the notochord C) lateral margins of the neural tube D) dorsal lip of the blastopore
D
Which of the following is an adult organism that has fewer than 1,000 cells? A) chickens, Gallus domesticus B) African clawed frogs, Xenopus laevis C) fruit flies, Drosophila melanogaster D) nematodes, Caenorhabditis elegans
D
Which of the following are found in developmental precursors to the gonadal tissues of Caenorhabditis elegans? A) proteins of maternal origin B) high concentrations of potassium ions C) T tubules for the propagation of action potentials D) P granules of mRNA and protein
D
Which of the following is a primary external factor in determining the polarity of the body axes in chick embryos? A) light B) oxygen availability C) gravity D) moisture
C
Which of the following processes determines the arrangement of organs and tissues in their characteristic places in 3-D space? A) pattern formation B) differentiation C) determination D) organogenesis
A
Which of the following processes will be disrupted if the apical ectodermal ridge is surgically removed from an embryo? A) positional information for limb-bud pattern formation B) guidance signals needed for correct gastrulation C) unequal cytokinesis of blastomeres D) the developmental substrate for the kidneys
A
Identical twins are possible in humans because ________. A) cytoplasmic determinants are distributed unevenly in unfertilized eggs B) extraembryonic cells interact with the zygote nucleus C) early blastomeres can form a complete embryo if isolated D) the gray crescent divides the dorsal-ventral axis into new cells
C
Cells transplanted from the neural tube of a frog embryo to the ventral part of another embryo develop into nervous system tissues. Which of the following claims about the transplanted cells is most consistent with the results? A) the cells were totipotent B) the cells were determined C) the cells were differentiated D) the cells were mesenchymal
B
In 1924, Hans Spemann and Hilde Mangold transplanted a piece of tissue from the dorsal lip of an amphibian embryo to the ventral side of another embryo. The transplanted piece of tissue influenced the formation of the notochord and neural tube. What observation justifies the claim of embryonic induction? A) The transplanted tissue induced multiple limbs to develop on the ventral side of the recipient embryo. B) The transplanted tissue inhibited normal cell division on the dorsal side of the recipient embryo that lead to its death. C) The transplanted tissue had no effect on either the ventral or dorsal side of the recipient embryo. D) The transplanted tissue induced the formation of a second notochord and neural tube on the ventral side of the developing embryo.
D
Just prior to the onset of gastrulation in an embryo, the "organizer" cells are specified. What would you expect in the developing embryo if the specification of these cells were experimentally blocked? A) There would be no effect on development. B) Gastrulation would not occur, and normal development would cease. C) The body axes would develop normally, but the embryo would not grow appendages. D) The embryo would not develop an intestine, but all other organs and tissues would develop normally.
B
Researchers were investigating the effects of bicoid in fruit fly development. They injected bicoid mRNA into the posterior end of a normally developing embryo. What result would they most likely observe? A) The embryo would develop with a normal anterior end and anterior structures on the posterior end. B) The embryo would develop with a normal posterior end and posterior structures on the anterior end. C) The embryo would develop with anterior structures on the posterior end and posterior structures on the anterior end. D) The embryo would develop with a normal anterior end and a normal posterior end.
A
Suppose that a female fruit fly's egg with a bicoid mutation is fertilized by a male's sperm with a Sneaky gene mutation. Both mutations make nonfunctional proteins. What would be the most likely outcome? A) a normal embryo would develop B) an embryo would not be able to develop C) an embryo would develop with a normal posterior end and with posterior structures on the anterior end D) an embryo would develop with a normal anterior end and with anterior structures on the anterior end
B
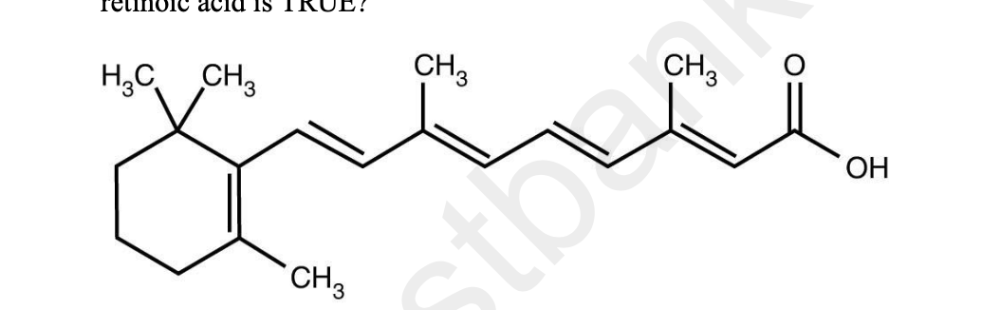
Retinoic acid (a metabolite of vitamin A) plays a key role in vertebrate development,
differentiation, and organogenesis. Retinoic acid is produced in cells via redox reactions
catalyzed by enzymes. The structure of retinoic acid is shown below. What statement regarding
retinoic acid is TRUE?
A) Retinoic acid is a morphogen and it likely binds to intracellular receptors.
B) Retinoic acid is a maternal effect gene and it likely binds to intracellular receptors.
C) Retinoic acid is a morphogen and it likely binds to membrane receptors.
D) Retinoic acid is a maternal effect gene and it likely binds to membrane receptors.
A
Retinoic acid (a metabolite of vitamin A) plays a key role in vertebrate development, differentiation, and organogenesis. Researchers have determined that one type of RAR receptor is found at high levels in muscles, but not in neurons. How can you explain these findings? A) Muscle cells, but not neurons, contain the gene for the RAR receptor. B) The RAR receptor gene is expressed in muscle cells but not neurons. C) Neurons can produce retinoic acid, so they do not need RARs for development. D) RAR transcripts are hydrolyzed by lysosomes in neurons but not in muscle cells.
B
In C. elegans, P granules act as cytoplasmic determinants to assist with the development of the posterior end of the organism. Suppose that P granules were abnormally found in both the anterior and posterior ends of a developing C. elegans organism. What would you expect to observe? A) The embryo would develop with a normal anterior end and anterior structures on the posterior end. B) The embryo would develop with a normal posterior end and posterior structures on the anterior end. C) The embryo would develop with anterior structures on the posterior end and posterior structures on the anterior end. D) The embryo would develop with a normal anterior end and a normal posterior end.
B
The cortical reaction of sea urchin eggs functions directly in ________. A) the formation of a fertilization envelope B) the production of a fast block to polyspermy C) the generation of an electrical impulse by the egg D) the fusion of egg and sperm nuclei
A
Which of the following is common to the development of both birds and mammals? A) holoblastic cleavage B) epiblast and hypoblast C) trophoblast D) gray crescent
B
The archenteron develops into ________. A) the mesoderm B) the endoderm C) the placenta D) the lumen of the digestive tract
D
What structural adaptation in chickens allows them to lay their eggs in arid environments rather than in water? A) extraembryonic membranes B) yolk C) cleavage D) gastrulation
A
If an egg cell were treated with EDTA, a chemical that binds calcium and magnesium ions, ________. A) the acrosomal reaction would be blocked B) the fusion of sperm and egg nuclei would be blocked C) the fast block to polyspermy would not occur D) the fertilization envelope would not form
D
In humans, identical twins are possible because ________. A) extraembryonic cells interact with the zygote nucleus B) convergent extension occurs C) early blastomeres can form a complete embryo if isolated D) the gray crescent divides the dorsal-ventral axis into new cells
C
Cells transplanted from the neural tube of a frog embryo to the ventral part of another embryo develop into nervous system tissues. This result indicates that the transplanted cells were ________. A) totipotent B) determined C) differentiated D) mesenchymal
B