After a hurricane damages a coral reef, some sea anemones regenerate into complete anemones. Which type of reproduction is this? A) hermaphroditism B) fission C) fragmentation D) parthenogenesis
C
Many aphid species switch between asexual and sexual reproduction. What is only used in sexual reproduction? A) mitosis B) meiosis C) parthenogenesis D) fission
B
Which process causes offspring of sexual reproduction to differ genetically from their parents? A) fertilization B) protein synthesis C) cytokinesis D) mitosis
A
Which organism reproduces by budding? A) lamprey B) bluefin tuna C) whiptail lizards D) stony corals
D
A female lizard lays viable eggs without mating. What type of reproduction is this? A) sexual B) budding C) fission D) parthenogenesis
D
What is evidence that parthenogenic whiptail lizards evolved from sexual ancestors? A) Male-like behaviors before ovulation B) Testes develop and regress C) Offspring are haploid D) Some have vestigial penis
A
When is sexual reproduction more likely than asexual reproduction? A) when food is abundant B) when survival conditions are bad C) when a male and female mate D) when finding a mate is hard
B
When is asexual reproduction more successful than sexual? A) pathogens are rapidly diversifying B) risk of overpopulation C) species spreads to diverse areas D) stable and favorable environment
D
Advantage of sexual reproduction? A) more of each parent’s genome passed B) more offspring C) greater genetic diversity D) lower mutation rate
C
What triggers Daphnia to switch to sexual reproduction? A) favorable conditions B) temperature stress C) increased food D) can't produce eggs
B
What is the cloaca in nonmammalian vertebrates? A) sperm-transfer device B) shared path for digestion, excretion, reproduction C) nutrient source for sperm D) vaginal mucus gland
B
Where do female insects like honeybee queens store sperm? A) nests B) abdominal tract C) uterus D) spermatheca
D
Where do animals using external fertilization reproduce? A) sand dune B) polar ice sheet C) shallow lake D) tallgrass prairie
C
Advantage of internal fertilization? A) less energy invested B) better survival of offspring C) faster population growth D) more genetic diversity
B
Why do green anacondas use internal fertilization? A) live on dry land B) hunt in water C) live in tropics D) produce many offspring
A
Organisms that reproduce asexually don't use what? A) in water B) on land C) internal fertilization D) pheromones
D
Why is induced egg-laying advantageous for male flies? A) Less sperm needed B) More eggs fertilized C) Higher chance his sperm is used D) Less energy spent
C
What female structure is analogous to vas deferens? A) urethra B) oviduct C) uterus D) vagina
B
Order sperm pass during ejaculation: A) epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra B) urethra, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct C) seminiferous tubules, vas deferens, epididymis, urethra D) epididymis, ejaculatory duct, urethra, vas deferens
A
Progesterone receptor mutation would likely result in: A) No secondary sex traits B) Uterus can't support pregnancy C) Enlarged uterine endometrium D) No mammary gland development
B
Which structure/product pair is correct? A) hypothalamus–FSH B) anterior pituitary–LH C) corpus luteum–inhibin D) Sertoli cells–progesterone
B
Similarity in spermatogenesis and oogenesis? A) Start at puberty B) Produce 4 haploid cells C) From germ cells D) Diploid gametes formed
C
Similarity between sperm and ovum after meiosis? A) same chromosomes B) same size C) both have flagella D) produced from puberty to death
A
Which structures are made of erectile tissue? A) penis and clitoris B) vas deferens and oviduct C) testes and ovaries D) prostate and ovaries
A
Where is sperm produced? A) prostate gland B) vas deferens C) seminiferous tubules D) epididymis
C
Effect of removing seminal vesicles? A) no sperm produced B) sperm can't exit body C) semen volume reduced D) testes migrate inward
C
Effect of raising scrotum temperature by 2°C? A) less gonadal hormone production B) impaired spermatogenesis C) faster spermatogenesis D) more semen volume
B
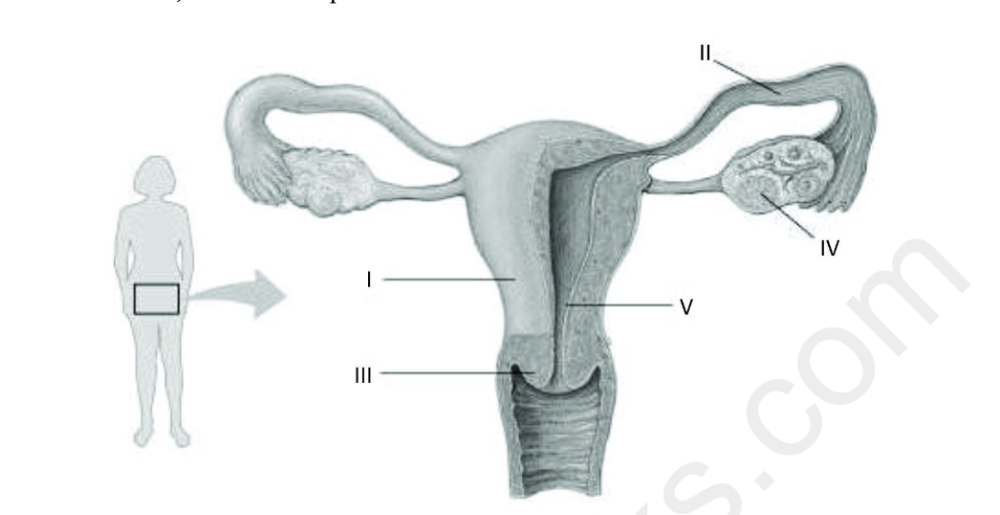
Refer to the following figure, which diagrams the reproductive anatomy of the human female, to answer the question.
In the figure, which letter identifies a structure that is ciliated?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B

Refer to the following figure, which diagrams the reproductive anatomy of the human
female, to answer the question.
In the figure, which letter identifies the site of implantation in a normal human pregnancy?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A
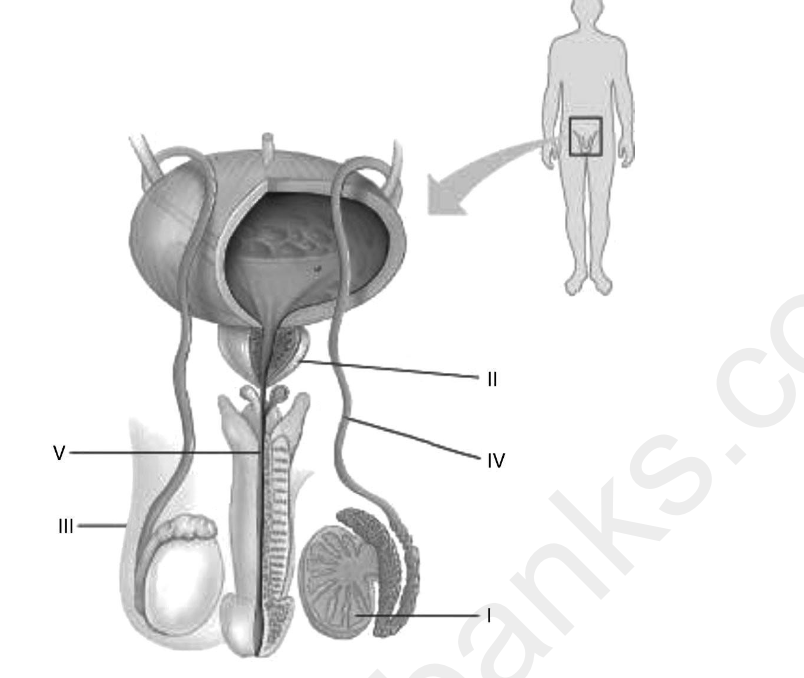
Refer to the following figure, which diagrams the reproductive anatomy of the human male,
to answer the question.
In the figure, which letter identifies an accessory gland that releases its product directly into the
urethra?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
B

Refer to the following figure, which diagrams the reproductive anatomy of the human male,
to answer the question.
In the figure, which letter identifies a paired structure that transports sperm during an
ejaculation?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D
For which of the following is the number the same in spermatogenesis and oogenesis in animals? A) the age at which a male or female begins to produce mature gametes B) the number of functional gametes produced by one cell undergoing meiosis in spermatogenesis or oogenesis C) the number of meiotic divisions required to produce each gamete D) the number of eggs and sperm involved in producing one embryo
C
Which statement about human reproduction is correct? A) Spermatogonia and oogonia are haploid cells. B) In humans, spermatogenesis and oogenesis both function best at normal, core body temperatures. C) A human oocyte only completes meiosis II after fertilization. D) The earliest stages of spermatogenesis occur closest to the lumen of the seminiferous tubules.
C
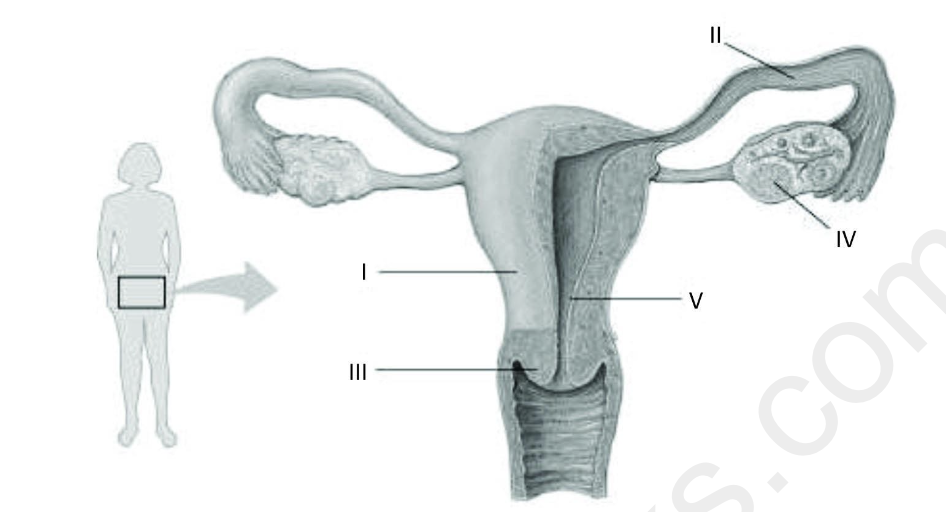
Refer to the following figure, which diagrams the reproductive anatomy of the human
female, to answer the question.
In the figure, which letter identifies the corpus luteum?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
D
Which of the following best describes a change to the female reproductive system that occurs in menopause? A) the ovaries lose their responsiveness to FSH and LH B) the production of gonadotropin hormones by the anterior pituitary gland declines C) the endometrium is reduced and eventually lost D) no more primary oocytes exist in the ovaries
A
Which hormone would you inject to induce ovulation in a female orangutan right away? A) estradiol (estrogen) B) progesterone C) luteinizing hormone D) follicle-stimulating hormone
C
Which hormone would you inject a few days before the male visit to induce ovulation when he arrives? A) estradiol B) progesterone C) luteinizing hormone D) follicle-stimulating hormone
A
What is the most likely immediate result of injecting estradiol into a female mammal? A) follicle will decrease in size B) ovulation will occur C) endometrium will decrease in thickness D) LH production will increase
D
Labor contractions can be increased by a synthetic drug mimicking: A) inhibin B) luteinizing hormone C) oxytocin D) prolactin
C
Which molecule in the urine indicates that a woman is pregnant? A) progesterone B) estrogen C) follicle-stimulating hormone D) human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
D
Which are permanent contraceptive methods that block gametes from meeting? A) the male condom and female condom B) the male condom and oral contraceptives C) vasectomy and tubal ligation D) the diaphragm and subcutaneous progesterone implant
C
What is the result of a vasectomy? A) elimination of spermatogenesis B) elimination of testosterone synthesis C) prevention of ejaculation D) prevention of sperm from entering the male urethra
D
What is the function of the positive feedback loop during labor? A) promotes the development of a new follicle B) ensures continued contractions until labor is complete C) inhibits the release of prostaglandins D) decreases the number of oxytocin receptors in the uterus
B
Which hormone could a doctor use to induce labor? A) progesterone B) luteinizing hormone C) follicle-stimulating hormone D) oxytocin
D
Why would an ectopic pregnancy in the oviduct not be successful? A) The baby would be sideways B) hCG can't be produced in the oviduct C) The oviduct can't support the fetus D) Hormones can't reach the fetus
C
Which can still occur after intercourse if the female had a tubal ligation? A) Sperm can reach the oviduct B) Sperm can fertilize an oocyte C) An embryo can implant in the uterus D) An oocyte can enter the uterus
B
Which of the following characterizes parthenogenesis? A) An individual may change its sex during its lifetime. B) Specialized groups of cells grow into new individuals. C) An organism is first a male and then a female. D) An egg develops without being fertilized.
D
In male mammals, excretory and reproductive systems share ________. A) the vas deferens B) the urethra C) the seminal vesicle D) the prostate
B
Which of the following is not properly paired? A) seminiferous tubule–cervix B) vas deferens–oviduct C) testosterone–estradiol D) scrotum–labia majora
A
Peaks of LH and FSH production occur during ________. A) the menstrual flow phase of the uterine cycle B) the beginning of the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle C) the period just before ovulation D) the secretory phase of the uterine cycle
C
During human gestation, rudiments of all organs develop ________. A) in the first trimester B) in the second trimester C) in the third trimester D) during the blastocyst stage
A
Which of the following is a true statement? A) All mammals have menstrual cycles. B) The endometrial lining is shed in menstrual cycles but reabsorbed in estrous cycles. C) Estrous cycles are more frequent than menstrual cycles. D) Ovulation occurs before the endometrium thickens in estrous cycles.
B
For which of the following is the number the same in human males and females? A) interruptions in meiotic divisions B) functional gametes produced by meiosis C) meiotic divisions required to produce each gamete D) different cell types produced by meiosis
C
Which statement about human reproduction is false? A) Fertilization occurs in the oviduct. B) Spermatogenesis and oogenesis require different temperatures. C) An oocyte completes meiosis after a sperm penetrates it. D) The earliest stages of spermatogenesis occur closest to the lumen of the seminiferous tubules.
D
Which of the following are contraceptive methods that block sperm from entering the uterus? A) the diaphragm and spermicide B) vasectomy and hormonal implant C) the IUD and oral contraceptives D) the male condom and female condom
D
What happens to the endometrium if an embryo does not implant? A) It becomes thicker. B) It remains in place until the next ovulation. C) It is reabsorbed. D) It is shed from the body.
D
Which of the following statements about gametogenesis is true? A) Oogenesis in humans produces four equal gametes. B) Spermatogenesis begins before birth. C) Only oogenesis involves unequal cytoplasmic division. D) Spermatogenesis does not involve meiosis.
C
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating the growth of ovarian follicles? A) LH B) FSH C) progesterone D) estradiol
B
For which of the following is the number the same in spermatogenesis and oogenesis in animals? A) the age at which a male or female begins to produce mature gametes B) the number of functional gametes produced by one cell undergoing meiosis C) the number of meiotic divisions required to produce each gamete D) the number of eggs and sperm involved in producing one embryo
C