In the United States and Canada, bats have become infected by a fungus, Geomyces destructans. Many infected bats have a delicate, white filamentous mat on their muzzles, which is referred to as white-nose syndrome (WNS). The G. destructans mat most likely consists of which of the following structures? A) hyphae B) haustoria C) yeasts D) basidia
A
Which of the following describes a similarity between fungi and arthropods? A) The haploid state is dominant in both groups. B) Both groups are predominantly autotrophs that produce their own food. C) Both groups use chitin for support. D) Both groups have cell walls.
C
Fungi have an extremely high surface-to-volume ratio. What is the advantage of this characteristic to an organism that gets most of its nutrition through absorption? A) The high ratio allows for more material to be acquired from the surroundings and transported through the cell membrane. B) The lower volume prevents the cells from drying out too quickly, which can interfere with absorption. C) This high ratio creates more room inside the cells for additional organelles involved in absorption. D) This high ratio means that fungi have a thick, fleshy structure that allows the fungi to store more of the food it absorbs.
A
What are the filamentous mats formed by most fungi called? A) mycelia B) hyphae C) haustoria D) arbuscles
A
Which of the following experimental designs would allow a researcher to determine the effect of mycorrhizae on plant growth? A) measure and compare the growth of two different plants that both have mycorrhizae associated with their roots B) measure and compare the growth of two different plants, one of which has had antifungal substances added to it and one that has not C) measure and compare the growth of two different plants that do not have mycorrhizae associated with their roots D) measure and compare the growth of two different plants, one of which has had antibiotics have been added to it and one that has not
B
If all fungi in an environment were to suddenly die, then which group of organisms is most likely to benefit, due to the fact that its fungal competitors have been removed? A) flowering plants B) protists C) prokaryotes D) grasses
C
When a mycelium infiltrates a recently killed mouse carcass, which of the following is most likely to appear within the tissues of the mouse soon thereafter? A) fungal haustoria B) fungal enzymes C) increased oxygen levels D) larger bacterial populations
B
A fungal spore germinates, giving rise to a mycelium that grows outward into the soil surrounding the site where the spore originally landed. Which of the following accounts for the outward growth of the mycelium? A) karyogamy B) mycelial flagella C) breezes distributing spores D) cytoplasmic streaming in hyphae
D
When pathogenic fungi are found growing on the roots of grape vines, grape farmers sometimes respond by covering the ground around their vines with plastic sheeting and pumping a gaseous fungicide into the soil. Which of the following results might be a concern for the grape farmers who engage in this practice? A) fungicide might also kill the native yeasts residing on the surfaces of the grapes B) lichens growing on the vines' branches are not harmed C) fungicide might also kill mycorrhizae D) sheeting is transparent so that photosynthesis can continue
C
Which of the following statements describes an adaptive advantage associated with the filamentous nature of fungal mycelia? A) the ability to form haustoria and parasitize other organisms B) the potential to inhabit almost all terrestrial habitats C) the increased probability of contact between different mating types D) an extensive surface area well suited for invasive growth and absorptive nutrition
D
Some fungal species live in plants and can kill herbivores that feed on the plant. What type of relationship does this fungus have with its host? A) parasitic B) mutualistic C) commensal D) predatory
B
Researchers grew two plants of different species (plant 1 and plant 2) and added the same mychorrhizal species to the soil. They then measured the growth of each plant after one month. Plant 1 grew significantly more than plant 2. Which of the following conclusions is most consistent with these results? A) both plants formed mutualistic relationships with the mycorrhizal fungi B) neither of the plants formed mutualistic relationships with the mycorrhizal fungi C) plant 2 formed a mutualistic relationship with the mycorrhizal fungi and plant 1 did not D) plant 1 formed a mutualistic relationship with the mycorrhizal fungi and plant 2 did not
D
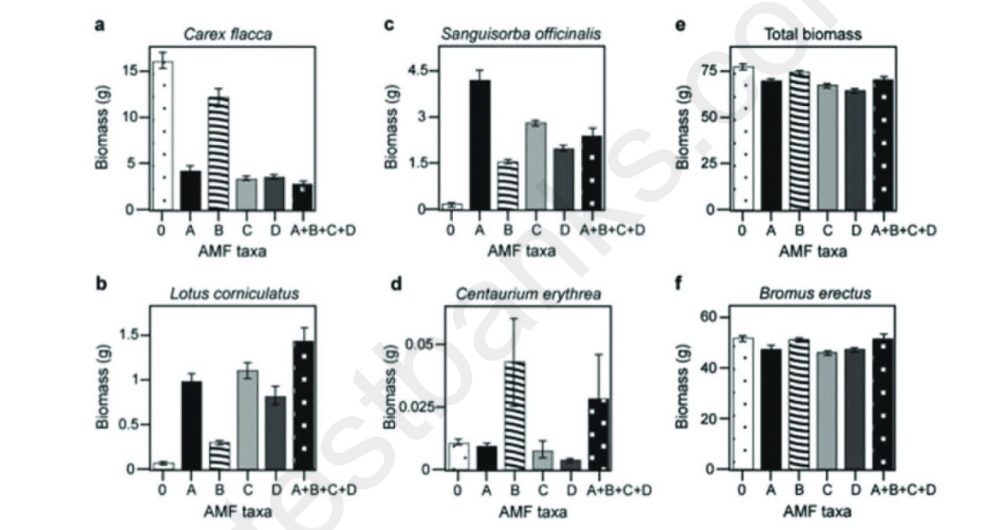
Use the following information to answer the question.
A group of Canadian and Swiss researchers wanted to know if the diversity of arbuscular
mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) was important to the productivity of grasslands. Specifically, they
wanted to know if it mattered which specific AMF species were present, or just that some type of
AMF was present. They grew various plants in combination with one of four AMF species (A,
B, C, and D), no AMF species (O), or all four AMF species together (A + B + C + D); and they
measured plant growth under each set of conditions. All plant species were grown in each plot,
so they always competed with each other with the only difference being which AMF species
were present. The results showing the biomass of five different grass species along with the total
biomass of the combined grass species are shown in the graphs. (M.G.A. van der Heijden et al.,
Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability, and
productivity, Nature 396:69-72 (1998)).
What is the major difference between Bromus erectus (graph f) and the other plant species
(graphs a-d) included in the study?
A) Bromus erectus grows best with a diversity of fungal partners.
B) Bromus erectus is unaffected by AMF diversity.
C) Bromus erectus does not form mycorrhizal associations.
D) Bromus erectus produces very little biomass regardless of AMF.
B

Use the following information to answer the question.
A group of Canadian and Swiss researchers wanted to know if the diversity of arbuscular
mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) was important to the productivity of grasslands. Specifically, they
wanted to know if it mattered which specific AMF species were present, or just that some type of
AMF was present. They grew various plants in combination with one of four AMF species (A,
B, C, and D), no AMF species (O), or all four AMF species together (A + B + C + D); and they
measured plant growth under each set of conditions. All plant species were grown in each plot,
so they always competed with each other with the only difference being which AMF species
were present. The results showing the biomass of five different grass species along with the total
biomass of the combined grass species are shown in the graphs. (M.G.A. van der Heijden et al.,
Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability, and
productivity, Nature 396:69-72 (1998)).
Based on graphs e and f, which is the most well-supported prediction for the effect on total plant
biomass in relation to AMF diversity?
A) Bromus erectus produces the most biomass.
B) Bromus erectus produces the least biomass.
C) Carex flacca produces the most biomass.
D) Centaurium erythrea produces the most biomass.
A
Some companies advertise and sell mycorrhizae to home gardeners and commercial farms, claiming that the presence of mycorrhizae improves plant growth and survival. If the company conducted experiments on plants with and without mycorrhizae, which of the following results would support their claim? A) smaller apple size in plants with mycorrhizae than in plants without mycorrhizae B) increased production of corn ears in plants with mycorrhizae than in plants without mycorrhizae C) increased need for fertilizer in plants with mycorrhizae than in plants without mycorrhizae D) increased mortality in plants with mycorrhizae than in plants without mycorrhizae
B
Some nematode worms consume plant juices from the roots of plants and are economically important agricultural pests. Some fungi are usually decomposers of plant material, but some trap and kill nematodes at times. Arthrobotrys traps and kills nematodes, especially when they lack nitrogen sources. These two facts suggest that farmers could find Arthrobotrys an important tool in combating nematode infestations. Which of the following research questions would make a good starting point for developing such a defense against nematode pests? A) Does nitrogen fertilization of crops affect the likelihood that Arthrobotrys will trap and kill nematodes? B) Do nitrogen-fixing bacteria provide nitrogen to the fungi? C) What is the evolutionarily oldest method of trapping nematodes? D) What mechanisms do nematodes have that could allow them to escape from Arthrobotrys?
A
Which of the following best explains how mycorrhizal fungi are more efficient than plants at acquiring mineral nutrition from the soil? A) Hyphae are 100 to 1,000 times larger than plant roots. B) Hyphae have a smaller surface area-to-volume ratio than do the hairs on a plant root. C) Mycelia are able to grow in the direction of food. D) Fungi secrete extracellular enzymes that can break down large molecules.
D
At which stage of a basidiomycete's life cycle would reproduction be halted if an enzyme that prevented the fusion of hyphae was introduced? A) fertilization B) karyogamy C) plasmogamy D) germination
C
Which of the following statements correctly describes deuteromycetes? A) they represent the phylum in which all the fungal components of lichens are classified B) they are the group of fungi that have, at present, no known sexual stage C) they are the group that includes molds, yeasts, and lichens D) they include the imperfect fungi that lack hyphae
B
For the past several decades, amphibian species worldwide have been in decline. A significant proportion of the decline seems to be due to the spread of the chytrid fungus, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Chytrid sporangia reside within the epidermal cells of infected animals, animals that consequently show areas of sloughed skin. Sexual reproduction has not been observed in B. dendrobatidis. If its morphology and genetics did not identify it as a chytridiomycete, then to which fungal group would B. dendrobatidis be assigned? A) zygomycetes B) glomeromycetes C) basidiomycetes D) deuteromycetes
D
Plasmogamy can directly result in which of the following types of cells? A) cells with a single haploid nucleus or dikaryotic cells B) heterokaryotic cells or dikaryotic cells C) heterokaryotic cells or cells with two diploid nuclei D) dikaryotic cells or cells with two diploid nuclei
B
Which of the following statements correctly describes the daughter cells that result from cytokinesis in budding yeasts? A) similar nucleus and more cytoplasm than the mother cell B) smaller nucleus and less cytoplasm than the mother cell C) larger nucleus and less cytoplasm than the mother cell D) similar nucleus and less cytoplasm than the mother cell
D
In most fungi, karyogamy does not immediately follow plasmogamy. Which conclusion is most consistent with this information? A) It means that sexual reproduction can occur in specialized structures. B) It results in multiple diploid nuclei per cell. C) It allows fungi to reproduce asexually most of the time. D) It results in heterokaryotic or dikaryotic cells.
D
Which of the following describes a reproductive strategy in yeast? A) they pinch off "bud cells" that are smaller than the parent cell B) they pinch off "bud cells" that are larger than the parent cell C) they undergo meiosis, producing two cells of unequal size D) they undergo meiosis, producing two cells of equal size
A
Fungi and plants evolved during the same time period. What combination of environmental and morphological change is similar in the evolution of both fungi and plants? A) presence of "coal forests" and change in mode of nutrition B) periods of drought and presence of filamentous body shape C) predominance in swamps and presence of cellulose in cell walls D) colonization of land and loss of flagellated cells
D
Which of the following describes the evolution of multicellularity in fungi and animals? A) common ancestry B) convergent evolution C) inheritance of acquired traits D) serial endosymbioses
B
Which feature seen in chytrids supports the hypothesis that they diverged early in fungal evolution? A) the absence of chitin within the cell wall B) coenocytic hyphae C) flagellated spores D) parasitic lifestyle
C
Chitin is a long-chain polymer derived from glucose. It strengthens cell walls of fungi and the outer covering (exoskeleton) of arthropods (including crabs, shrimps, and insects). The presence of chitin in these groups is likely the result of which of the following processes? A) secondary endoparasitism B) horizontal gene transfer C) paraphyletic evolution D) convergent evolution
D
Which of the following observations would best support the hypothesis that the ability to form mycorrhizal associations arose very early in plant evolution? A) presence of genes in the earliest fungi that showed an ability to digest cellulose and lignin B) presence of genes for chitin in the oldest flowering plants and oldest fungi C) fossils that show hyphae wrapped around seeds D) formation of mycorrhizae by a flowering plant that expresses a gene from a liverwort
D
Which of the following structures carries out sexual reproduction in ascomycetes? A) basidia B) ascocarps C) zygosporangia D) hyphae
B
It has been hypothesized that fungi and plants have a mutualistic relationship because plants make sugars available for the fungi's use. What is the best evidence in support of this hypothesis? A) Fungi survive better when they are associated with plants. B) Radioactively labeled sugars produced by plants eventually show up in the fungi with which they are associated. C) Fungi associated with plants have the ability to undergo photosynthesis and produce their own sugars, while those not associated with plants do not produce their own sugars. D) Radioactive labeling experiments show that plants pass crucial raw materials to the fungus for manufacturing sugars.
B
You observe the gametes of a fungal species under the microscope and realize that they resemble animal sperm. To which of the following groups does the fungus belong? A) chytrids B) zygomycetes C) basidiomycota D) ascomycota
A
Which of the following structures in an ascomycete is haploid? A) ascospore B) ascocarp C) ascus D) basidium
A
Which answer arranges the following structures in order from largest to smallest, assuming that they all come from the same fungus? A) mycelium, gill, basidiocarp, basidium, basidiospore B) gill, basidiocarp, mycelium, basidium, basidiospore C) gill, basidiocarp, basidiospore, basidium, mycelium D) mycelium, basidiocarp, gill, basidium, basidiospore
D
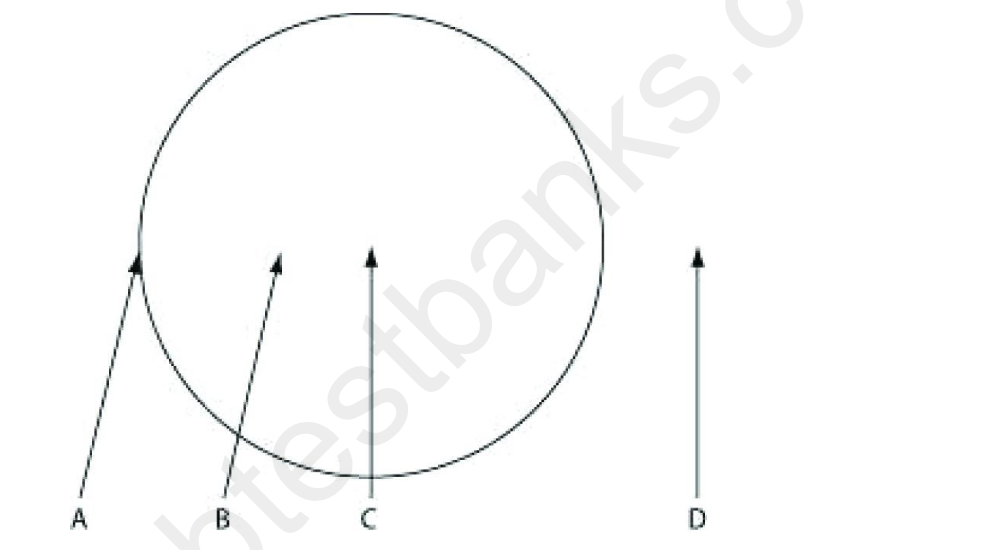
Use the information to answer the following question.
The figure depicts the outline of a large fairy ring that has appeared overnight in an open
meadow, as viewed from above. The fairy ring represents the furthest advance of this mycelium
through the soil. Locations A-D are all 0.5 meters below the soil surface.
Where would you expect to find the oldest portion of this mycelium?
A) location A
B) location B
C) location C
D) location D
C

Use the information to answer the following question.
Which location is nearest to basidiocarps?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
A
Use the following information to answer the question. For the past several decades, amphibian species worldwide have been in decline. A significant proportion of the decline seems to be due to the spread of the chytrid fungus, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Chytrid sporangia reside within the epidermal cells of infected animals, animals that consequently show areas of sloughed skin. The infection cycle typically takes four to five days, at the end of which zoospores are released from sporangia into the environment. Apart from direct amphibian-to-amphibian contact, which of the following is responsible for the movement of zoospores from one free-living amphibian to another? A) wind-blown spores B) flagella C) cilia D) hyphae
B
Use the following information to answer the question. For the past several decades, amphibian species worldwide have been in decline. A significant proportion of the decline seems to be due to the spread of the chytrid fungus, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Chytrid sporangia reside within the epidermal cells of infected animals, animals that consequently show areas of sloughed skin. The infection cycle typically takes four to five days, at the end of which zoospores are released from sporangia into the environment. When adult amphibian skin harbors populations of the bacterium Janthinobacterium lividum, chytrid infection seems to be inhibited. Which of the following is the best experimental design to test whether this inhibition is actually due to the presence of J. lividum? A) Inoculate uninfected amphibians with J. lividum and determine whether the amphibians continue to remain uninfected by chytrids. B) Inoculate infected amphibians with J. lividum and determine whether the amphibians recover from infection by chytrids. C) Take infected amphibians and assign them to two populations. Leave one population alone; inoculate the other with J. lividum. Measure the rate at which infection proceeds in both populations. D) Take infected amphibians and assign them to two populations. Inoculate one population with a high dose of J. lividum; inoculate the other with a low dose of J. lividum. Measure the survival frequency in both populations.
C
Diploid nuclei of the ascomycete Neurospora crassa contain 14 chromosomes. A single diploid cell in an ascus will undergo one round of meiosis, followed in each of the daughter cells by one round of mitosis, producing a total of eight ascospores. How many chromosomes would a single ascospore nucleus of this species contain? A) 7 chromosomes B) 14 chromosomes C) 21 chromosomes D) 28 chromosomes
A
Which of the following characteristics would be most helpful in distinguishing among different species of fungi? A) morphology B) hyphae structure C) DNA sequence D) life cycle
C
Which of the following types of fungi often live in the digestive tracts of sheep and cattle? A) ascomycetes B) mucuromycetes C) chytrids D) basidiomycetes
C
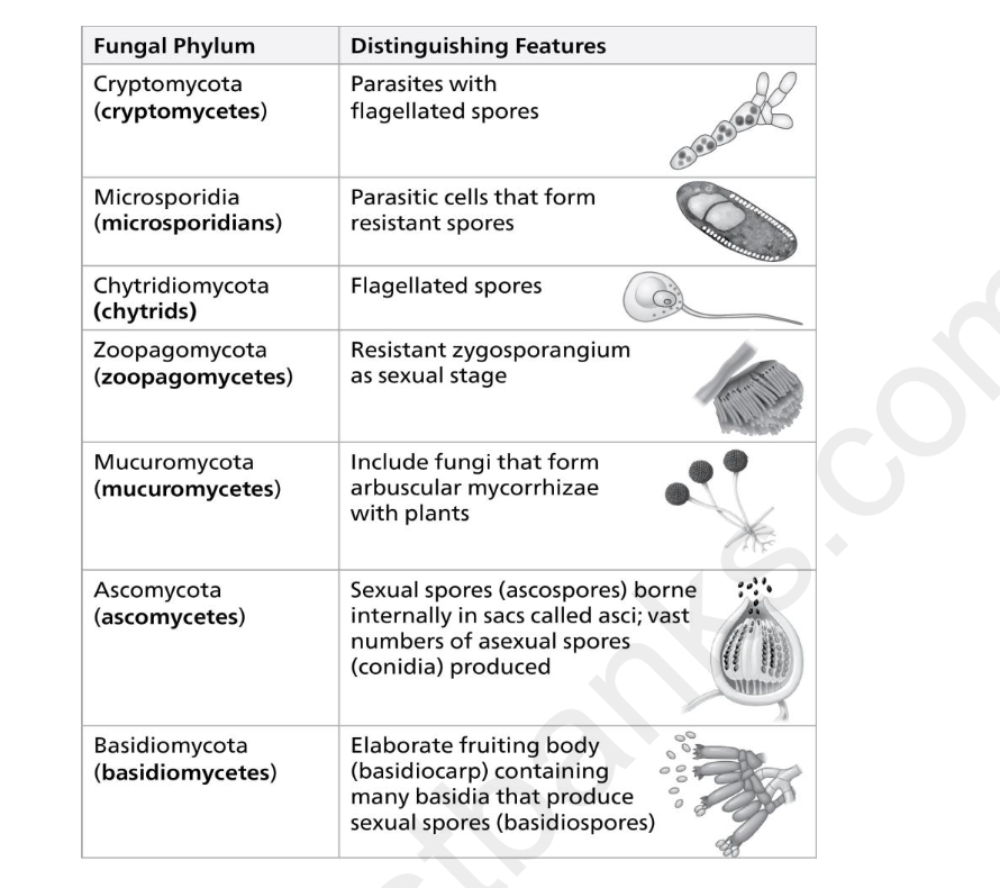
Which of the following statements accurately describes our current understanding of the
phylogeny of fungi as represented in the figure?
A) the zygomycetes are a basal taxon
B) basidiomycetes are more closely related to ascomycetes than they are to zygomycetes
C) basidiomycetes are more closely related to zygomycetes than they are to ascomycetes
D) glomeromycetes are a basal taxon
B

Which of the following statements accurately describes our current understanding of the
phylogeny of fungi as represented in the figure?
A) the chytrids are a basal taxon
B) zygoomycetes are more closely related to ascomycetes than they are to glomeromycetes
C) basidiomycetes are more closely related to zygomycetes than they are to ascomycetes
D) glomeromycetes are a basal taxon
A
In which of the following human mycoses should one expect to find a growth pattern most similar to that of the mycelium that produces a fairy ring? A) skin mycoses B) coccidiomycosis (lung infection) C) systemic (blood-borne) Candida infection D) infection of lymphatic vessels
A
Rose-picker's disease is caused by the yeast Sporothrix schenkii that if introduced into the human body can assume a hyphal morphology and grow along the interiors of lymphatic vessels until they reach a lymph node. Lymph nodes are important for the immune system because many white blood cells (phagocytes and lymphocytes) reside there. Given that a successful infection by S. schenkii damages lymph nodes themselves, which of the following is most probable? A) The hyphae secrete antibiotics, which increases the ability of the infected human to tolerate the fungus. B) The fungal conversion from yeast to hyphal morphology allows such fast growth that the body's defenses are at least temporarily overwhelmed. C) Defensive cells of humans cannot detect foreign cells that are covered with cell walls composed of cellulose. D) Given that most fungal pathogens attack plants, human defenses are simply not adapted to seek out and destroy fungi.
B
Which of the following statements describes the relationship between a fungus and a photosynthetic microorganism in a lichen? A) neither organism derives any benefit from the relationship B) the fungus provides the photosynthetic microorganism a suitable environment for growth C) the fungus fixes nitrogen for the photosynthetic microorganism D) the photosynthetic microorganism helps the fungus retain minerals
B
A billionaire buys a sterile volcanic island that recently emerged from the sea. Seeding the island with which of the following would most likely accelerate the development of conditions that would support plant growth? A) basidiospores B) spores of ectomycorrhizae C) lichens D) yeasts
C
Orchid seeds are tiny, with virtually no endosperm and with miniscule cotyledons. If orchid seeds are deposited in a dark, moist environment, then which of the following represents the most likely means by which fungi might assist in seed germination? A) by transferring some chloroplasts to the embryo in each seed B) by providing the seeds with water and minerals C) by providing the embryos with some of the organic nutrients the fungi have absorbed D) by strengthening the seed coat that surrounds each seed
C
Which of the following best describes the physical relationship of the partners involved in lichens? A) Fungal cells are enclosed within algal cells. B) Lichen cells are enclosed within fungal cells. C) Photosynthetic cells are surrounded by fungal hyphae. D) Fungi grow on rocks and trees and are covered by algae.
C
Mycorrhizae are often found associated with the roots of vascular plants. Where are fungal endophytes typically found in vascular plants? A) leaf mesophyll B) stem apical meristems C) root apical meristems D) xylem
A
Fungi interact with many organisms in mutualistic ways. Which of the following involves a fungus that is mutualistic with another organism? A) a fungus and a protozoan that live together as a lichen B) a fungus that is raised by ants on leaves that the ants collect from trees and shrubs C) a fungus that lives inside plant roots and produces toxins that kill neighboring plants D) a fungus that produces penicillin that is used by humans to kill infectious bacteria
B
Fungi produce many compounds that humans use medicinally. Which of the following statements best describes the evolution of these compounds in fungi? A) Humans used artificial selection to develop fungi that produced specific compounds. B) The presence of the compounds in the fungi were accidentally produced and have no function. C) The compounds probably provide a benefit to the fungi. D) The compounds are produced as a result of sexual reproduction and recombination.
C
Truffles are the fruiting bodies of certain fungi whose mycelium grows below ground. The truffle is also underground and can be detected by many mammals, which eat the truffle and expel the spores with their feces. Which of the following statements is likely accurate with respect to this interaction? A) The truffle spores are probably wind dispersed. B) Truffles produce an odor that mammals can detect and find attractive. C) Truffles probably produce toxins that can harm the mammals that eat them. D) Truffle fruiting bodies are important in decomposition of wood.
B
If you wanted to use fungi to improve the environment, which of the following research goals would make the most sense? A) Discover the lignin-digesting enzymes of fungi, and use them to digest plant tissues left over from food-crop residues to reduce landfill waste. B) Discover the enzymes that the fungal partner in lichens uses to break down rock so that large rock expanses can be turned into agricultural lands. C) Discover the enzymes that fungi use to break down plant matter and use them to increase decomposition rates in order to slow global warming. D) Develop a strain of fungus that produces enzymes that absorb oxygen and will help slow global warming.
A
All fungi are ________. A) symbiotic B) heterotrophic C) flagellated D) decomposers
B
Which of the following cells or structures are associated with asexual reproduction in fungi? A) ascospores B) basidiospores C) zygosporangia D) conidiophores
D
The closest relatives of fungi are thought to be the ________. A) animals B) vascular plants C) mosses D) slime molds
A
The most important adaptive advantage associated with the filamentous nature of fungal mycelia is ________. A) the ability to form haustoria and parasitize other organisms B) the potential to inhabit almost all terrestrial habitats C) the increased chance of contact between mating types D) an extensive surface area well suited for invasive growth and absorptive nutrition
D