Which of the following detects light during de-etiolation (greening) of a tomato plant? A) carotenoids B) xanthophylls C) phytochromes D) auxins
C
Which of the following plant parts elongate in response to etiolation during seedling germination? I) Roots II) Hypocotyl III) Internodes IV) Leaves A) I and II B) II and III C) I, II, and III D) I, II, III, and IV
B
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events that takes place during the plant responses to internal and external signals? A) transduction, reception, and response B) reception and transduction C) reception, transduction, and response D) reception and response
C
Four physiological events that occur during de-etiolation (greening) of plants are listed below. I) detection of light signal II) activation of phytochrome III) activation of specific protein kinase1 IV) formation of de-etiolation response protein Which of the following lists these events in the correct order? A) I, III, II, and IV B) I, II, III, and IV C) IV, III, II and I D) II, I, IV and III
B
Which of the following is an evolutionary adaptation for a plant growing in darkness? A) evolution of accessory photosynthetic pigments B) rapid root elongation C) production of unexpanded leaves D) formation of thick, stubby stems
C
Which of the following can be involved in the mechanism of plant hormone function? I) altering the expression of genes II) modifying the permeability of the plasma membrane III) modifying the structure of the nuclear envelope A) I and II B) I and III C) II and III D) I, II and III
A
Which of the following describes a difference between hormonal regulation in plants compared to animals? A) There are no dedicated hormone-producing organs in plants as there are in animals. B) There is no long-distance transport of hormones in plants as there is in animals. C) Only animal hormone concentrations are developmentally regulated. D) Only animal hormones respond to either external or internal stimuli.
A
Auxins frequently interact with other plant hormones to cause a particular process. Which of the following processes is attributed ONLY to auxin? A) apical dominance B) fruit development C) phototropism D) xylem differentiation
C
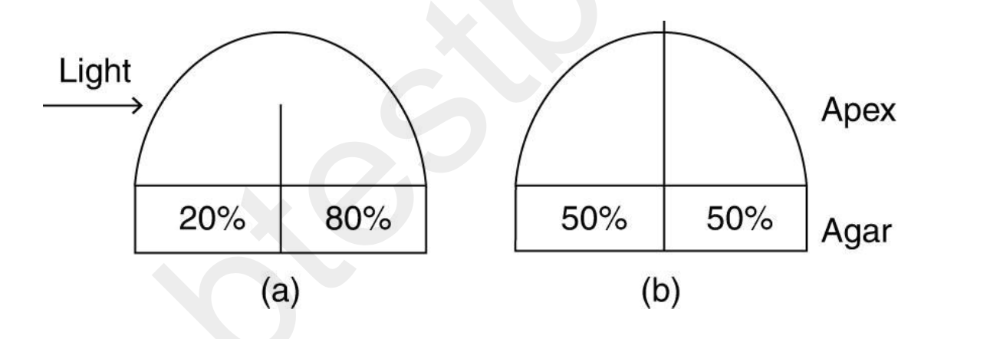
In an experiment investigating phototropism, pieces of shoot apices were applied to small
blocks of agar with light shining from one side only. The apices were either partly or completely
divided in two with a barrier that also divided the blocks. The figure summarizes the results of
the experiment. Numbers indicate the percent of auxin moving from the apex into the agar
segment below it.
Which of the following hypotheses is best supported by the data?
A) light destroys auxin
B) auxin diffuses through the plant apoplast
C) auxin is synthesized on the shaded side of the apex
D) auxin can move away from light
D
What are the primary sites of auxin (IAA) production in plants? A) shoot apical meristem and young leaves B) roots C) seeds D) ripening fruits
A
What are the sites of highest ethylene production in plants? A) shoot apical meristem and young leaves B) roots C) seeds D) ripening fruits
D
Which of the following hormones primarily function(s) to regulate plant cell division? A) auxin (IAA) B) ethylene C) gibberellins D) cytokinins
D
Which one of the following hormones stimulate(s) rapid stem elongation (straight growth) and pollen tube growth? A) auxin (IAA) B) ethylene C) gibberellins D) cytokinins
C
Unlike animal hormones, plant hormones can have multiple functions depending on which of the following factors? I) site of action II) concentration III) developmental stage IV) chronological age A) I, II, III, and IV B) I, II, and III C) I and II D) II
B
Which of the following plant responses requires integration of auxin, cytokinin, and strigolactone? A) cell elongation B) fruit development C) cell division D) apical dominance
D
The following steps occur during a plant's response to drought stress. I) ABA accumulates in the leaves II) stomata close III) transpiration decreases IV) guard cell potassium channels open Which of the following places the steps in the correct sequence to represent the acquisition of drought tolerance in the plant? A) I, II, III, and IV B) I, IV, II, and III C) II, I, III, and IV D) IV, I, II, and III
B
Which of the following statements best summarizes the acid growth hypothesis in an actively growing shoot? A) Auxin stimulates proton pumps in the tonoplast to pump hydrogen ions out of the vacuole and allow water to enter. B) Auxin-activated proton pumps lower the pH of the cell wall, which breaks hydrogen bonds and makes the walls more flexible. C) Auxins and gibberellins together act as a lubricant to allow cellulose microfibrils to slide past each other. D) Auxins activate aquaporins that increase turgor pressure in the cells forcing them to expand.
B
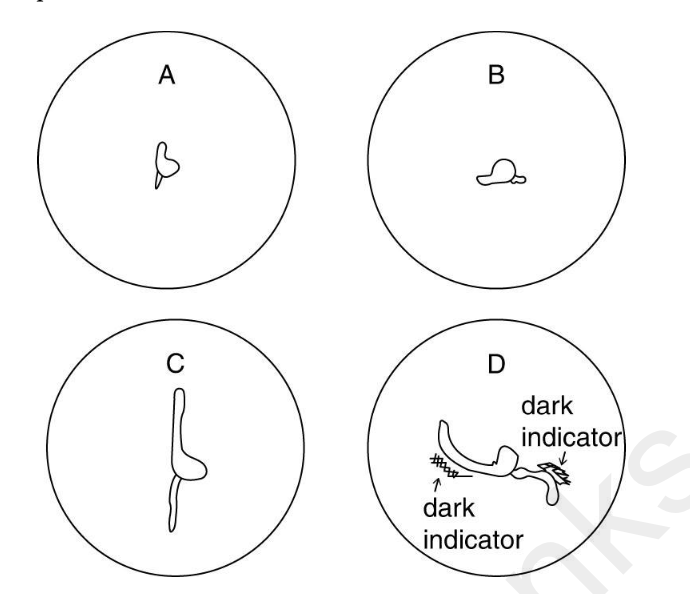
Corn seeds were germinated on two petri dishes of agar containing a colored pH indicator.
The dishes were placed on edge with the seedling oriented either vertically (A) or horizontally
(B). After 24-hours growth, the plates appeared as in C and D. Dark areas in D indicate lower
pH.
Which of the following statements is supported using the data?
A) During gravitropism, the concentration of auxin is higher on the topside of a coleoptile and
the bottom side of a root.
B) During gravitropism, the pH is higher on the topside of the coleoptile and the bottom side of
the root.
C) The higher the concentration of auxin in a tissue, the lower will be the pH around that tissue.
D) Phototropism affects only stems causing them to bend up; gravitropism affects only roots
causing them to bend down
B
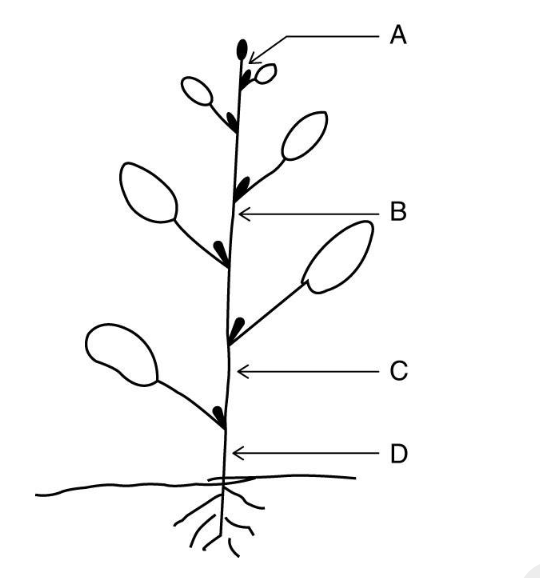
You want to alter the shape of a growing plant, causing it to bend by applying auxin to one
side of the stem. Application at which of the following positions, A, B, C, or D would produce
the greatest bending?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
A
You have a small tree in your yard that is the height that you want it, but does not have as many branches as you want. Which of the following pruning strategies will trigger increased branching? A) Cut off the leaves at the ends of several branches. B) Cut off the tips of the main shoots. C) Cut off lower branches. D) Cut off the leaves at the base of most of the branches.
B
Cytokinins, produced primarily in roots, travel by which of the following structures to influence branching in a recently topped tree (tree whose upper branches have been trimmed off)? A) symplastic B) vascular cambium C) phloem D) xylem
D
Which of the following illustrates a commercial application of cytokinins? A) shippers spraying on fruit to delay ripening while in transit to stores B) grocers spraying on fruit before sale to enhance taste C) florists dipping the ends of cut flower stems to keep leaves and flowers fresh longer D) farmers spraying on flowers to enhance pollination
C
If a farmer wanted less tightly packed clusters of grapes, he would most likely spray the immature bunches with which of the following hormones? A) auxin B) gibberellins C) cytokinins D) abscisic acid
B
Which hormone prevents seeds from germinating until conditions are favorable for the growth of the plant? A) Ethylene B) Zeaxanthin C) Gibberellin D) Abscisic acid
D
A population of plants experienced several years of severe drought. Most of the plants died due to lack of water, but a few individuals survived. The surviving plants probably produced higher levels of which of the following hormones? A) auxin B) gibberellin C) cytokinin D) abscisic acid
D
If you were shipping green bananas to a supermarket thousands of miles away, removing which of the following chemicals from the plants' environment will best prevent premature fruit ripening? A) carbon dioxide B) cytokinins C) ethylene D) auxin
C
In the fall, the leaves of some trees change color. This happens because chlorophyll breaks down and the accessory pigments become visible. What hormone triggers this response in plants? A) phototropin B) abscisic acid C) cytokinin D) ethylene
D
Which type of mutant is most likely to produce a bushier phenotype? A) auxin overproducer B) strigolactone overproducer C) cytokinin underproducer D) strigolactone underproducer
D
Vines in tropical rain forests must grow toward large trees before being able to climb toward the sun. Which of the following responses would promote vine growth towards a tree? A) negative thigmotropism B) negative phototropism C) positive gravitropism D) positive phototropism
B
Charles Darwin and his son Francis did a series of experiments to test their hypothesis that the tips of grass coleoptiles sense the direction of light. In the first experiment, coleoptiles with their tips cut off did not bend toward light, but intact coleoptiles did. Why was it necessary to follow this experiment with another experiment where only the tips of treated coleoptiles were covered with opaque foil? A) More than one repetition of an experiment is needed to test a hypothesis. B) Only correct hypotheses can be proven by experiments. C) An alternative explanation for the first experiment could be that cutting off the tips injured the plants, so they could not respond. D) Coleoptiles actually bend below the tip, so the tip is needed to know where the bending begins.
C
An individual plant was discovered that could not grow towards light. After some research, it was determined that the reason was a defective gene that did not allow for the level of cell elongation necessary for a phototropic response. This mutation greatly reduces the fitness of the individual plant. Which of the following best explains the reduction in fitness in the mutant plant? A) The plant was too short to attract insects for pollination. B) The plant could not adjust to directional light, which reduced photosynthetic activity and therefore energy available for reproduction. C) Because the plant grew much taller and straighter, resources that could be used for reproduction were used for growth. D) The loss of a phototropic response meant that the plant's seeds could not germinate, so reproduction would be unsuccessful.
B
Upon exposure to blue light, plants not only begin to grow toward the light, but redistribute the chloroplasts to the sunny side of each cell. Which of the following best explains the adaptive advantage of moving chloroplasts to the sunny side of each cell? A) It maximizes light absorption by the chloroplasts for photosynthesis. B) It increases production of phototropic hormones. C) It maximizes heat absorption by the chloroplasts for cellular respiration. D) It increases adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production during the light-independent reactions.
A
Mammalian eyes sense light because the photoreceptor cells have molecules called opsins that change structure when exposed to light. Which of the following plant molecules is most analogous to mammalian opsins in their light-sensing ability? A) auxin B) expansin C) phytochrome D) cytokinin
C
Seed packets give a recommended planting depth for the enclosed seeds. Which of the following is the most likely reason some seeds are to be covered with only a thin layer of soil after planting? A) Seedlings from these seeds do not have an etiolation response. B) Light is required to germinate these seeds. C) A higher temperature is required to promote germination of these seeds. D) These seeds are very sensitive to waterlogging.
B
Suppose a plant had a photosynthetic pigment that absorbed far-red wavelengths of light. In which of the following environments is the plant most likely to thrive? A) on the surface of a lake B) on the forest floor, beneath a canopy of taller plants C) on the ocean floor, in very deep waters D) on mountaintops, closer to the sun
B
Which of the following mechanisms is most directly responsible for controlling circadian rhythms in plants? A) periodic oscillations of light and dark B) periodic oscillations of gene transcription C) a free-running period of 24-hours D) changes in temperature that correlate with light and dark
B
Which of the following colors of visible light induces phototrophic curvature in coleoptiles most effectively? A) red B) blue C) violet D) orange
B
Phytochrome plays a critical role in germination of some seeds. Which of these colors of light maximizes germination in these seeds? A) red B) blue C) violet D) orange
A
Many plants flower in response to day-length cues. Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship between day length and flowering? A) The longer the day, the faster a long-day plant will flower. B) Long-day plants usually flower in the fall. C) Long-day plants flower in direct response to long days. D) Short-day plants flower in direct response to long nights.
D
Plants often use changes in day length (photoperiod) to trigger events such as dormancy and flowering. Which of the following best explains why day-neutral plants are more common in the tropics than in temperate zones? A) In the tropics there is little photoperiodic change during the year. B) Warm temperature in the tropics denatures phytochrome pigments. C) The biological clock runs faster in the warm tropics. D) Precipitation change is more predictable than photoperiodic change during the year.
A
A gardener in Canada wants to surprise his mother on her birthday and make her favorite hibiscus bush flower in May instead of at the end of June. The bush is growing in the greenhouse. Which of the following treatments is most likely to make the hibiscus bush flower early? A) increase the temperature in the greenhouse in March or April B) turn on the greenhouse lights before dawn in March or April C) turn on a far-red light during the night in March or April D) leave blue lights on in the greenhouse all winter long
B
A plant scientist was hired by a greenhouse operator to devise a way to force iris plants to bloom in the short days of winter. Iris normally blooms as a long-day (short-night) plant. Which of the following treatments has the best chance of creating iris blooms in winter? A) artificially increase the period of darkness in the greenhouse B) increase the temperature to more closely follow summer temperatures C) alternate 4 hours of darkness with 4 hours of light repeatedly over each 24-hour period D) interrupt the long winter nights with a brief period of light
D
Which of the following environmental factors can be sensed by plants? I) gravity II) pathogens III) wind IV) light A) only I and III B) only I, II, and IV C) only II, III, and IV D) I, II, III, and IV
D
Shoots can be characterized as which of the following? A) positive for phototropism and negative for gravitropism B) neutral for phototropism and positive for gravitropism C) negative for phototropism and positive for gravitropism D) positive for phototropism and neutral for gravitropism
A
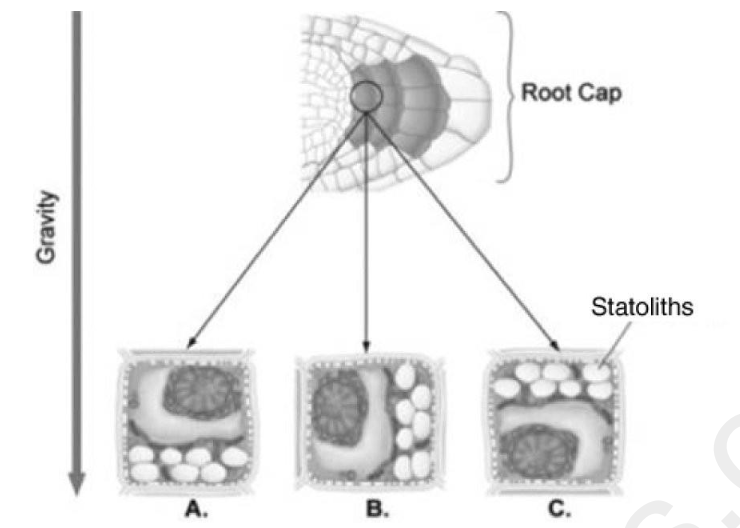
45) Use the figure to answer the following question.
Suppose you laid a seedling on its side so that the root was parallel to the ground as shown in the
figure. Several hours after the change in position, in which labeled position(s), A, B, or C in the
figure, are statoliths most likely to be located?
A) A only
B) B only
C) C only
D) A and C
A
Which of the following is involved in the rapid leaf movements resulting from a response to touch (thigmotropism)? A) potassium channels B) nervous tissue C) cytokinin transport D) stress proteins
A
Which of the following is an adaptation that allows woody species to survive freezing temperatures? A) emptying water from the vacuoles to prevent freezing B) decreasing the numbers of phospholipids in cell membranes C) increasing the proportion of saturated fatty acids in phospholipids D) increasing cytoplasmic levels of specific solute concentrations, such as sugars
D
Most scientists agree that climate change is underway; thus, it is important to know how plants respond to heat stress. Which of the following would be a useful line of inquiry to try and improve plant response and survival to heat stress? A) the production of heat-stable carbohydrates B) increased production of heat-shock proteins C) the opening of stomata to increase evaporational heat loss D) protoplast fusion experiments with xerophytic plants
B
You are out working in your garden, and you notice that one of your favorite flowering plants has black, dead spots on the leaves. Which of the following is most likely responsible for the symptoms you observe? A) PAMP-triggered response B) hypersensitive response C) systemic acquired resistance D) chlorotic nutrient deficiency
B
Which of the following terms describes a generalized defense response in organs that are distant a site of infection? A) hyperactive response B) systemic acquired resistance C) pleiotropy D) hypertonicity
B
A particular type of virus carries a gene for salicylate hydroxylase, an enzyme that breaks down salicylic acid. Which of the following responses is most likely? A) The virus will be more virulent because systemic acquired resistance will be blocked. B) The virus will be less virulent because the hypersensitive response will no longer function. C) The host will be more susceptible because the hypersensitive response will no longer function. D) There will be no difference in virulence because salicylic acid affects only fungal pathogens.
A
Which event during the evolution of land plants favored the synthesis of secondary compounds? A) the greenhouse effect throughout the Devonian period B) the reverse-greenhouse effect during the Carboniferous period C) the association of the roots of land plants with mycorrhizal fungi D) the rise of herbivory by animals
D
Which of the following must occur for a plant to initiate chemical responses to herbivory, before it is directly affected by herbivores? A) a plant must be old enough to have already flowered at least once B) volatile "signal" compounds must be perceived from already attacked plants C) gene-for-gene intraspecific recognition must occur between the plant and the herbivore D) phytoalexins must be released by the herbivore
B
The hormone that helps plants respond to drought is ________. A) auxin B) abscisic acid C) cytokinin D) ethylene
B
Auxin enhances cell elongation in all of these ways except ________. A) increased uptake of solutes B) gene activation C) acid-induced denaturation of cell wall proteins D) cell wall loosening
C
Charles and Francis Darwin discovered that ________. A) auxin is responsible for phototropic curvature B) red light is most effective in shoot phototropism C) light destroys auxin D) light is perceived by the tips of coleoptiles
D
How may a plant respond to severe heat stress? A) by reorienting leaves to increase evaporative cooling B) by creating air tubes for ventilation C) by producing heat-shock proteins, which may protect the plant's proteins from denaturing D) by increasing the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes, reducing their fluidity
C
The signaling molecule for flowering might be released earlier than usual in a long-day plant exposed to flashes of ________. A) far-red light during the night B) red light during the night C) red light followed by far-red light during the night D) far-red light during the day
B
If a long-day plant has a critical night length of 9 hours, which 24-hour cycle would prevent flowering? A) 16 hours light/8 hours dark B) 14 hours light/10 hours dark C) 4 hours light/8 hours dark/4 hours light/8 hours dark D) 8 hours light/8 hours dark/light flash/8 hours dark
B
A plant mutant that shows normal gravitropic bending but does not store starch in its plastids would require a reevaluation of the role of ________ in gravitropism. A) auxin B) calcium C) statoliths D) differential growth
C