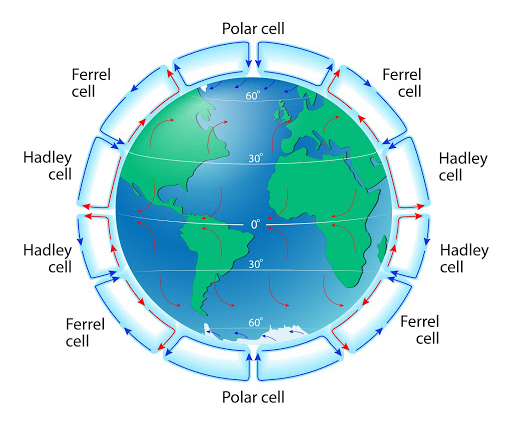
Atmospheric Movement
Global air circulation within the atmosphere held to Earth by gravity and warmed as heat radiated from Earth; influenced by convection of warm, less dense air (rises and spreads out) and cold, dense air (sinks)
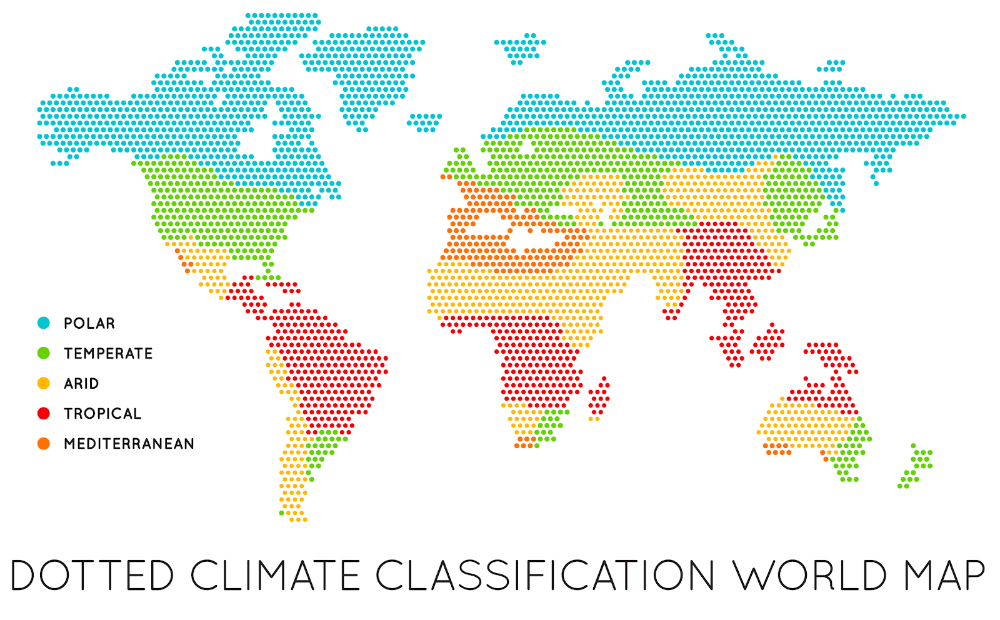
Climate
Average weather patterns for a particular region
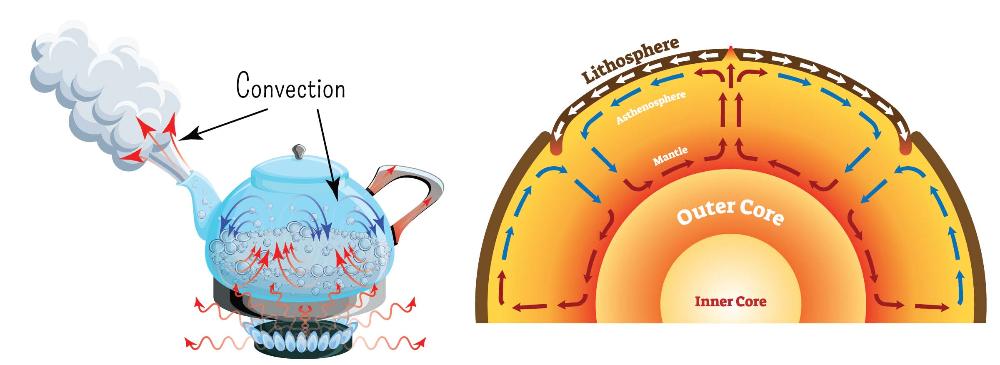
Convection
Heat transfer caused by the rising of hotter, less dense fluids and the falling of cooler, denser fluids.
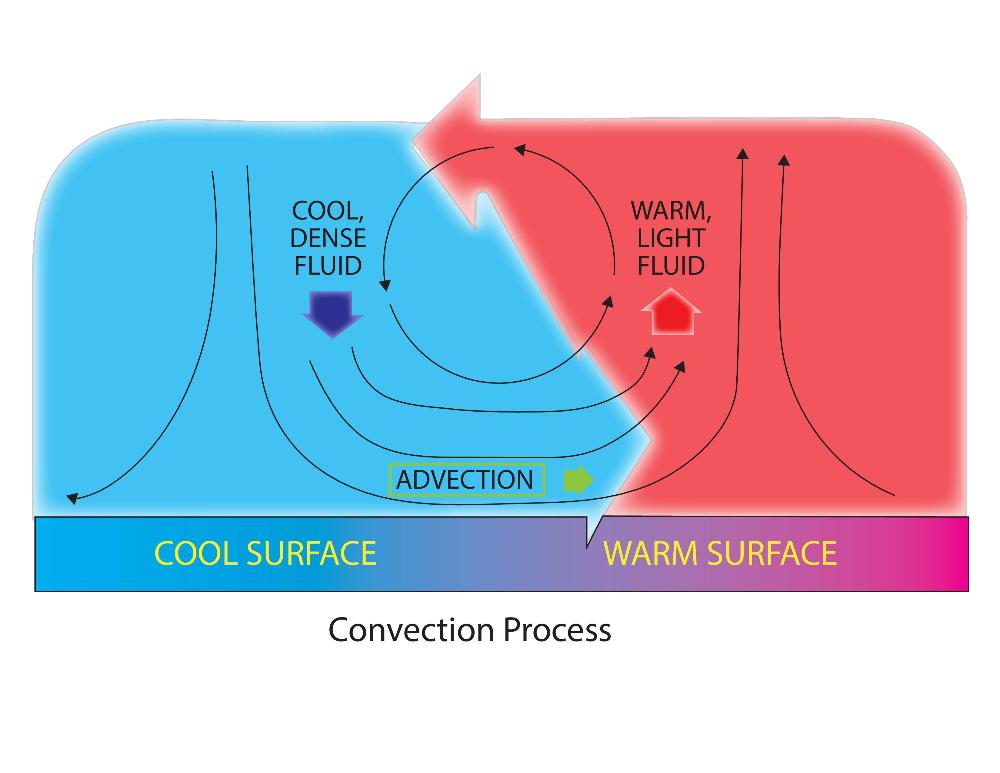
Convection Current
A circular movement of fluids caused by the rising of hotter, less dense fluid and the falling of cooler, denser fluid.
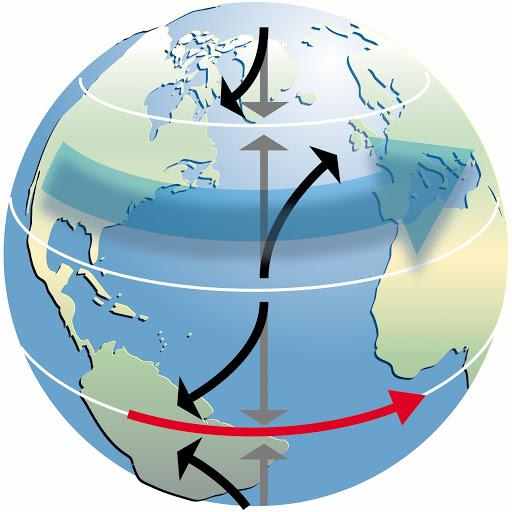
Coriolis Effect
The apparent deflection of moving air, as seen by an observer on Earth, as a result of Earth's rotation.
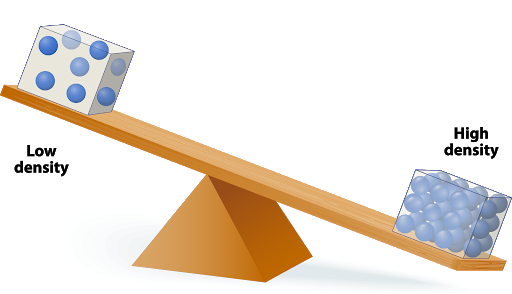
Density
The amount of matter in a given space or volume
Global
Relating to the whole world
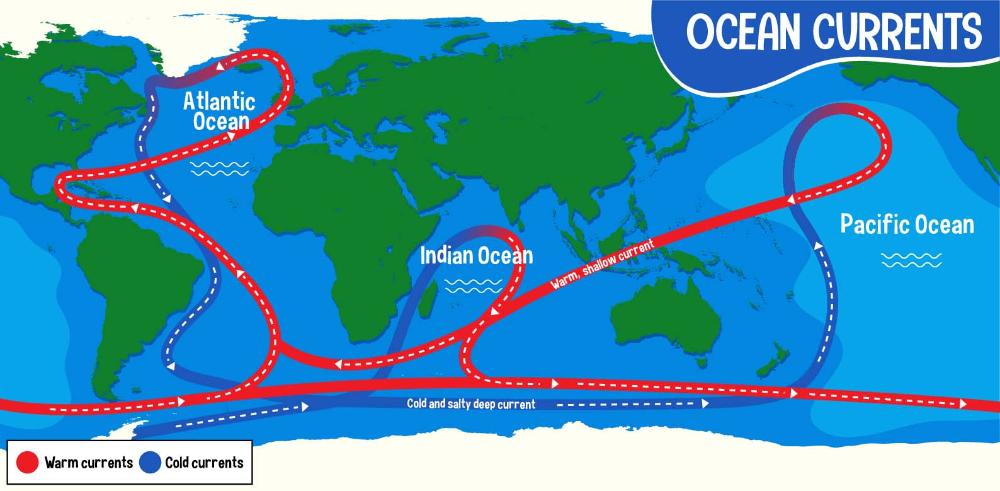
Ocean Currents
Directional movements of ocean water; surface currents result from steady winds over the ocean surface; deep currents result from density variations due to temperature and salinity differences.

Rotation
The spinning of Earth on its axis that causes day and night to occur

Salinity
Saltiness of dissolved salt content of a body of water

Temperature
Average kinetic energy of all the particles in a material; measured by a thermometer in degrees (usually degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit)