____________ is the most import source of energy
Glucose
Is glucose highly soluble?
Yes
__________are the main constitution of body fat in humans and other vertebrates
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are stored in the _______
adipose tissue
Dietary starch & glycogen are broken down initially by
Salivary amylase- maltose & intermediary dextrin's
What is maltose, lactose, sucrose converted into?
monosaccharides
Glucose is the substrate that form ?
glycogen
Glycolysis is
Oxidation of glucose to pyruvate. Anaerobic: Pyruvate is converted into lactate
Purpose of carbohydrates
provide energy through oxidation supply carbon for the synthesis of cell components stored chemical energy and form structure
aldehyde group
A chemical group consisting of a carbon double bonded to oxygen and single bonded to hydrogen (must be at end of chain)
ketone group
A chemical group consisting of a carbon double bonded to oxygen (must be in middle of chain)
another term for ketoses and aldoses
capable of being a reducing
sugar by?
Transferring electrons to another substance
kyrol carbon
Carbon that is bound to 4 different molecules
Penultimate
2nd to last carbon which determines the D& L configuration
anomeric carbon
the new chiral center formed in ring closure; it was the carbon containing the carbonyl in the straight-chain form
Glycogen is mostly stored in
muscle tissue and
liver: stores for whole body
What does insulin do?
it decreases blood glucose
What do the hormones glucagon, epinephrine, GH, cortisol do in the blood stream?
they increase blood glucose levels
Fasting state:
blood glucose low -> HIGH glucagon -> glycogenolysis + gluconeogenesis
Fed state
blood glucose is high -> HIGH insulin -> glycogenesis + glycolysis
glucagon promotes ___________
phosphorylation of glycogen synthase and phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase.
glycogenesis needed:
insulin promotes DEphosphorylation of glycogen synthase and
DEphosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase
=> Insulin
can only posstively regulate
glycogen phosphorylase:
rate limiting enzymes of glycogenolysis
Active: phosphorylated /
inactive: DEphosphorylated
The endocrine pancreatic known as
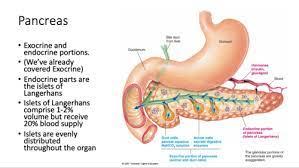
- " the islet of langerhas"
hormones produced by cells of the islet of pancreatic alpha-
glucagon, ghrelin
hormones produced by cells of the islet of beta-
insulin, proinsulin,C peptide, amylin
hormones produced by cells of the islet of gamma-
somatostatin
hormones produced by cells of the islet of epsilon-
ghrelin
hormones produced by cells of the islet of F-
pancreatic polypetide
Communication between cell to cell
cells within the islet communication gap junction
Neural communication:
Cholinergic stimulation increases insulin secretion. . Adrenergic will can either increase and decreases insulin . Or inhibitor effect can decrease insulin
Exocrine pancreases
secretase digestive enzymes helps with digestion and prevents malnourishment.
In 1889 Makowski demonstrated that removing the pancreases from the pancreases from the dogs caused ____________
a syndrome resembling T1D.
the four major organs that play roles in fuel metabolism are:
liver
adipose tissue
muscle
brain
The integration of energy metabolism is controlled by:
insulin and glucagon, with the catecholamines: epinephrine & norepinephrine as supporters
Insulin secretion is closely coordinated with the release of
glucagon by pancreatic α cells.
Hormones that control the integration of energy metabolism
1)Insuln
2)Glucagon
Levels in a normal healthy human
-->Plasma glucose is maintained in a range of **120-140
mg/dl
--> Fatty Acids are maintained at a level ABOVE
In the abscence of nutreitnt absorption from the GI Tract
1)Glucosee is supplied primarily by the LIVEr
2)Fatty Acids are
primarily from the adipose tissue
Lipogenesis
-->Is promoted by **low insulin**
Glucagon like peptide 1(GLP-1 or Incretin)
-->Will bind to its receptor on beta cells & will stimulate increased release of PREPROINSULIN
Why glucose is not a primary energy fuel in liver
saves glucose for other tissues. prefers to use a-keto acids and FAs
will metabolize some glucose only after a meal (i.e. when [glucose] high)
Insulin
- released under fed conditions
a. lowers blood glucose by promoting synthesis of glycogen, stimulating glycolysis, and inhibiting gluconeogenesis
when is glucagon
- released from pancreas under starved conditions (glucose deficiency)
Glucagon can be stimulated by
epinephrine
when is glucagon elevated
elevates blood glucose by promoting breakdown of glycogen in liver and inhibiting glycogen synthesis
Type I
little or no insulin production.
i. Often due to a viral
infection in youth - Antibodies to that virus cross react and destroy
beta cells of the pancreas
Type II
strongly associated with obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, and insulin resistance
During anaerobic conditions, Pyruvate must be converted to__________
lactate in order to free an NADH into NAD+ to continue anaerobic glycosis due to lack of O2
Insulin, a key regulatory protein for glucose levels in the body, has a precursor known as _________
proinsulin
The precursor proinsulin is larger than insulin and mainly differs from insulin by the presence of the ____________
C-peptide, which prevents the substance from being degraded immediately in the body.
Normal fasting glucose levels ___________
60-80 mg/dL
Normal glucose levels 2 hours after a meal ___________
100-150
Normal insulin levels 2 hours after a meal ___________
3-8 U/mL
Normal glucose levels
72-80
hyperglycemias glucose levels
>125
hypoglycemia glucose levels
< 30-45
Beta cells are the only site of ____________
insulin synthesis in mammals
location of cell types
Insulin-expressing b-cells are often in the core of the islet while glucagon-expressing a-cells are in the periphery
Insulin inhibits ____________
glucagon and SST release
what is secreted into the blood by the b cell?
When the beta cell is appropriately stimulated, insulin is secreted from the cell by exocytosis and diffuses into islet capillary blood. C peptide is also secreted into blood, but has no known biological activity.
influences of beta cells?
glucose, ACh, GIP/GLP-1, NA noradrenaline- which inhibits
GLYCOGENOLYSIS
breakdown of glycogen to glucose,e.g. stimulated by glucagon or adrenaline
GLUCONEOGENESIS
formation of glucose from non- carbohydrate precursors (amino acid, glycerol, lactate)
The insulin mRNA is translated as a single chain precursor called _____________
preproinsulin
what do c peptides do?
is a sign that your body is producing insulin. A low level (or no C-peptide) indicates that your pancreas is producing little or no insulin
glycogenesis
glucose converted to glycogen
During a brief fast __________
glycogen and glucose goes up and glucogenesis is synthesized into glucose
During a prolonged fast ____________
gluconeogenesis is the sole source of energy
As insulin binds to α-chain the receptors undergo a ____________
conformation change leading to ATP binding
alpha chains are
entirely extracellular and house insulin binding domains
beta chains
penetrate through plasma membrane
What does GLUT 4 do?
is an insulin-regulated glucose transporter that is responsible for insulin-regulated glucose uptake into fat and muscle cells.
effects of glucose on the liver
The liver both stores and manufactures glucose depending upon the body’s need. The need to store or release glucose is primarily signaled by the hormones insulin and glucagon.
During a meal, your liver will ____________
store sugar, or glucose, as glycogen for a later time when your body needs it.
Which of the following occurs following absorption of
glucose?
A. Glucose is stored as fat in skeletal muscle.
B.
Glucose is stored as glycogen in adipose tissue.
C. Glucose is
converted to fat in the liver.
D. Glucose is used to make energy
by only the brain.
E. Glucose is converted to amino acids in the muscles.
C. Glucose is converted to fat in the liver.
During the absorptive state of metabolism,
A. Liver glycogen is
broken down to glucose, which is released into the blood.
B.
Glycogen in muscle cells is broken down to glucose, which is used for
energy.
C. Lipoprotein lipase breaks down triacylglycerols in
adipose tissue capillaries.
D. Fatty acids and glycerol are
released from adipose tissue.
E. Lactate and pyruvate secretion
into the bloodstream by the muscles increases.
C. Lipoprotein lipase breaks down triacylglycerols in adipose tissue capillaries.
Which of the following tissues is most dependent upon a constant
blood supply of glucose?
A. liver
B. brain
C.
adipose
D. skeletal muscle
E. cardiac muscle
B. brain
Gluconeogenesis is stimulated by decreased levels of:
A.
epinephrine.
B. insulin.
C. glucocorticoids.
D. growth
hormone.
E. glucagon.
B. insulin.
Which event occurs during exercise but NOT during fasting?
A.
increased breakdown of triglycerides
B. increased
glycogenolysis
C. increased glucose uptake by muscle
D.
increased fatty acid oxidation
E. increased cortisol secretion
C. increased glucose uptake by muscle
Which is a symptom of untreated type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes
mellitus?
A. low plasma ketones
B. increased blood
volume
C. decreased respiration
D. hyperglycemia
E.
increased plasma insulin
D. hyperglycemia
In subjects with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus,
which of these occurs?
A. Pancreatic beta cell responses to
increased plasma glucose concentration are normal.
B. Target
tissues respond poorly to insulin.
C. Hypoglycemia is typically
the first symptom.
D. Severe ketoacidosis is common.
B. Target tissues respond poorly to insulin.
Which factor, when increased, increases metabolic rate to the
greatest extent?
A. skeletal muscle activity
B. mental
activity
C. dietary caloric intake
D. environmental
temperature
E. blood glucose levels
A. skeletal muscle activity
A person who is hypothyroid would be expected to:
A. have an
increased basal metabolic rate.
B. have reduced tolerance for
cold temperatures.
C. lose body weight.
D. be restless and
irritable.
E. have symptoms similar to over-activation of the
sympathetic nervous system.
B. have reduced tolerance for cold temperatures.
The subjective feeling of hunger is stimulated when:
A. plasma
insulin concentration increases.
B. plasma ghrelin concentration
decreases.
C. plasma leptin concentration decreases.
D.
plasma glucose concentration increases.
E. body temperature increases.
C. plasma leptin concentration decreases.
Most of the triglycerides absorbed as chylomicrons are ultimately stored as fat in the adipose tissue.
TRUE
During the absorptive state, there is net synthesis of fat, glycogen, and protein, but this process is reversed during the postabsorptive state.
TRUE
Most of the energy used by the body during fasting is provided by gluconeogenesis.
FALSE
The major energy sources for non-nervous tissue during the postabsorptive period are fatty acids and ketones.
TRUE
Metabolic acidosis caused by excessive blood levels of ketones is one of the harmful consequences of untreated type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes.
TRUE
Which correctly describes an action of the hormone insulin?
A.
It increases the uptake and utilization of glucose by muscle and
adipose tissue cells.
B. It is required for the uptake and
utilization of glucose by nervous tissue.
C. It decreases the
uptake of amino acids by muscle cells.
D. It stimulates the
breakdown of glycogen in the liver.
E. It inhibits the action of
lipoprotein lipase in the capillaries of adipose tissue.
A. It increases the uptake and utilization of glucose by muscle and adipose tissue cells.
Glucagon secretion is stimulated by:
hypoglycemia and high plasma epinephrine concentration.
The major metabolic effects of glucagon include:
A. stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver.
Which of the following is a major metabolic effect of glucagon?
increased glycogenolysis in liver
For type II diabetes as ________
body weight increases furtherer so does the degree of insulin resistance
Type II diabetes makes __________
90% of the diabetes rate in America
Which of the following is NOT a symptom that is associated with
untreated type 1
diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent diabetes
mellitus)?
A. hypoglycemia
B. metabolic acidosis
C.
dehydration
D. glucosuria (glucose in urine)
E. increased lipolysis
A. hypoglycemia
Glucagon secretion is stimulated by:
A. hypoglycemia and
parasympathetic nerve firing.
B. hyperglycemia and a high
concentration of epinephrine.
C. high plasma epinephrine and high
plasma incretin concentrations.
D. hypoglycemia and high plasma
epinephrine concentration.
E. hyperglycemia and high plasma
incretin concentration.
D. hypoglycemia and high plasma epinephrine concentration.
How long does it take to diagnose adult hypoglycemia?
By 72-hr fast in the hospital. The sample (glucose, insulin, proinsulin and c peptide) is drawn every 6 hours.
Testing for glucose
- Plasma is used routinely, not whole blood (must be refrigerated and spun down within 20-30 minutes)
- WB is unstable at room temperature because on-going cellular usage of glucose
Hexokinase method
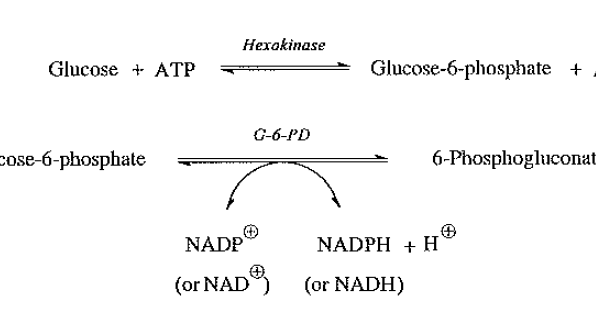
dominant laboratory method of measuring glucose
Plasma glucose in newborns
Reference ranges fasting (between feeding)
-term infants: 30-60
mg/dL
- preemies: 20-60 mg/dL
Plasma glucose in adults
Sample fasting
:74-106 mg/dL
Plasma glucose in children
: 60-100 mg/dL
Glucose oxidase (GO) method
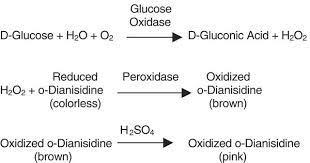
-method incorporated into qualitative urine dipstick methods ('true' glucose method)
-no other sugars will react other than b-D-glucose
-Color rxn: Trinder reaction (measures peroxide)
Glucose monitoring is the measuring _________
the capillary blood
During fasting, ketones produced by the liver:
A. are a waste
product of amino acid metabolism that the kidneys must
excrete.
B. can be used by the brain as an energy source.
C.
are a by-product of anaerobic metabolism.
D. are converted to
fatty acids and released into the blood.
E. are used to
synthesize glucose by gluconeogenesis.
B. can be used by the brain as an energy source.
The major energy sources for non-nervous tissue during the postabsorptive period are fatty acids and ketones.
TRUE
During anaerobic conditions, Pyruvate must be converted to ________________
lactate in order to free an NADH into NAD+ to continue anaerobic
Glycated HbA1c-
represent integrated glucose levels over the preceding 6 to 8 weeks
HbA1c is recommended to be used __________
to help monitor DM glycemic control some methods- problem with variants
hba1c
The A1C test—also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c test—is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months.
hba1c can used to diagnosis __________
prediabetics and diabetes
fructosamine
is a measure of non-enzymatic glycation of circulating proteins including albumin, globulins, and lipoproteins, has evolved to be a reasonable alternative to HbA1c measurement in situations where HbA1c is not reliable
The fructosamine test shows the average level of glucose in the blood over a period of _____________
two to three weeks, while the hemoglobin A1c test shows that average for the past two to three months.
urine albumins typically is a indicator of __________
renal damage
Microalbuminuria
is defined as urinary albumin excretion of more than 300 mg/G
clinical definition of increased UAE
concentration is(30 to 300 mg/24 hr)
Normal albumin levels are
less than 30 mg/g