Nervous system
- Responsible for processes that underlie
- Movement preparation
- execution
- controll
Central nervous system
- Brain and spinal cord
- sensory information integration, decision making
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- Links the body and the CNS
- Afferent (sensory) // ARRIVES
- Efferent (motor) // EXIT
Sensory receptors
- Exteroceptors
- interceptors
- proprioceptors
Sensory Receptors
Exteroceptors
- External environment
- pressure, pain, temperature, VIBRATION, 5 senses
Sensory Receptors
Interoceptors
- Internal environment
- hunger, nausea, fatigue
Sensory receptors
Proprioreceptors
- Provide information on muscles tension, joint position, equilibrium (inner ear)
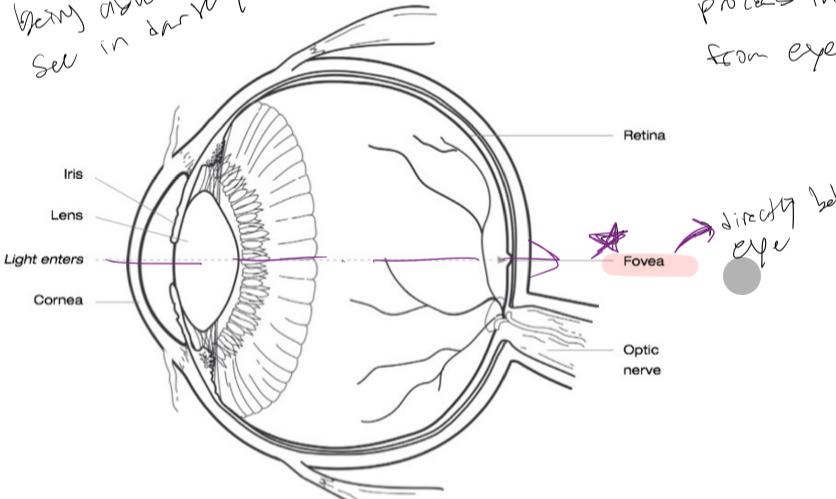
Vision
Sensory receptors
70% are in the eyes (most)
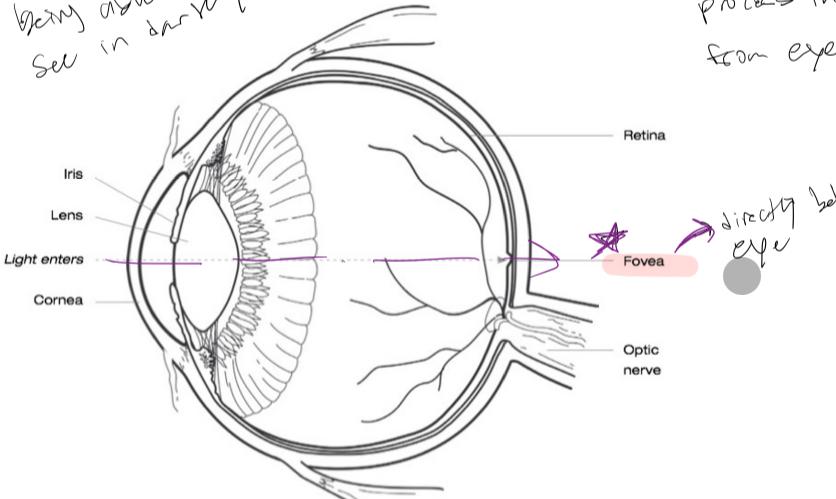
Vision
cerebral cortex
- 40% processes visual information
- EX. Being able to see in the dark
- Fovea: directly behind the eyes
Vision: photoreceptors (pathways)
- Light rays enters eye
- light rays are manipulated + focused on the retina
- an image is formed + converted into
nerve impulses
- photoreceptors: light sensitive cells that converts light rays into nerve impulses
Vision Photoreceptors: 2 types
- Rods
- Cones
Vision photoreceptors
Rods
- Vision in dim light, enables us to see shapes + movements, and discriminate
Vision photoreceptors
Cones
- Operates best in BRIGHT LIGHT (in fovea)
- specilize for color vision and vision acuity (sharpness)
Vision: Optic Chiasm
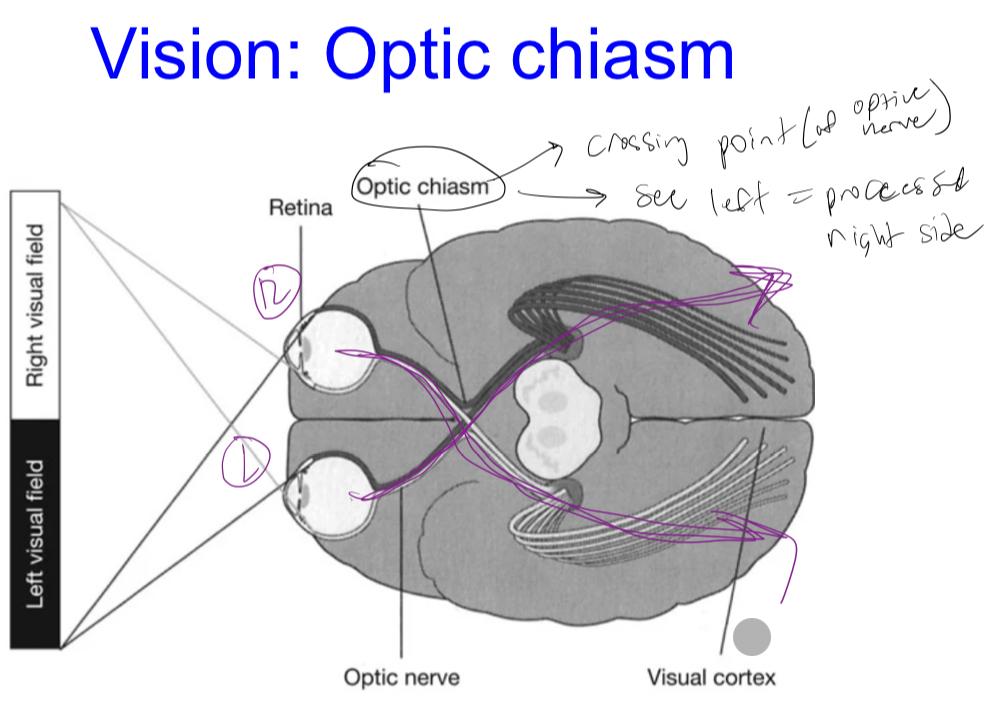
Vision
Focal Vision
- Involves the fovea
- used to focus on objects directly in central region of the visual field
- operatates under voluntary control // EX. Driving to not rear end a car
- ”WHAT IS IT?”
- not good in low light conditions
Vision
Ambient Vision
- Subconsious
- used for spracial localization and orientation (surroundings)
- not effected by light, serves the peripheral and central visual fields
Vision
- Information is processed through both systems simultaneously
- EX. Walk around the room and text someone
Vision and Performance
- eye dominance
- spotting
- visual search
- quiet eye
Vision and Performance
Eye Dominance
- Eye that processes information FASTRER
- Cross-dominant = advantage
Vision and Performance
Spotting
- keeps proper orientation
- reduces dizziness
- used in rotational skill
- EX. dancing, figure-skating
Vision and Performance
Visual search
- scan of environment for regularory cues
- familiarity
- Ex. where's waldo activity
Vision and Performance
Quiet eye
- final fixation on target before movement
- EX. watching the hoop rim before a free throw
vision
- targeting skills
- interceptive skills
- tactical skills
Vision
targeting skills
- propessling an object towards a target
- specific fixation on target is key
Vision
Interceptive skills
- tracking of stimulus // timing of stimulus // limb movement to intercept stimulus
- time to contact
- Tau: size of retina image/rate of change of image
- Typically objects are NOT TRACK to CONNECT
Vision
Tactical skills
- require quick, accurate decision making
Locomotion
- optic flow
- feedflow
Locomotion
Optic flow
- perceived relative motion between objects + observers
- allows for discernment of how QUICKLY objects approach / move away
Locomotion
Feedfoward
- allows info to be sent AHEAD of movement (for preparation)
- details of terrain, object dimensions, etc.
- used to contact and avoid objects`
Visual training programs
- search strategies
- pattern recognition
- anticipation
- decision-making skills
Visual training programs
Visual search strategies
- instructions => FEEDBACK should direct learners' attention
to areas where critical cues occur
- EX. release point of a pitched ball
- design appropriate learning experiences that provides PRACTICE for task-relevant cues
Visual training programs
Pattern recognotion
- d
Visual training programs
Anticipation
- video training where oppoennts actions are studied (TAPE)
Visual training programs
Decision-making skills
- w
Proprioception
- Golgi tendon organs
- muscle spindles
- joint kinesthetic receptors
- vestibular apparatus
Proprioception
Golgi tendon organs
- located at junction of tendon (with muscle)
- detects => muscle tension
- protects => form heavy/great load
- relaxes muscles if load is too great
Proprioception
Muscle spindles
- located @ muscle fibers in muscle belly
- detects => muscle stretch
- protects => from excessive stretching
- responsible for STRETCH REFLEXES
Proprioception
joint kinesthetic receptos
- located in + around synovial joints
- detects => pressure, acceleration. deceleration strain
- determines if => movements too slow, fast, wrong direction
Proprioception
Vestibular Apparatus
- group of receptor organs in INNER EAR
- detects => changes in posture + balance
- provides sensory information on EQUILIBRIUM
Proprioception and Performance
- makes motor control more efficient + flexible
- Goal = movement effects error detection
Proprioception and Performance
Practitioners
- promote development of proper frame of reference
- provide a variety of positions + movements + multiple environments
- stress kinesthetic feedback for optimal learning
Balance and Posture
- info provided by
- vetsibular apparatus, touch, proprioception in feet+ankles
- reestablishing proprioception is key in rehab programs
Balance and Posture
Equlibrium
-
Compensatory adjustments
- Movement w/ perturbation or loss of balance
-
Anticipatory adjustments
- voluntary movement to prevent loss of balance
Spinal Cord
- carries sensory information to the brain, motor information to effectors
- ascending pathways
- descending pathways
Spinal Cord
Ascending Pathways (sensory information)
-
spinothalamic
- pain, temperature, crude touch, deep pressure
-
dorsal column
- proprioception, discriminative touch, light pressure, vibrations
Spinal Cord
Descending Pathways (motor impulse)
-
pyramidal
- skilled VOLUNTARY movements
-
extrapyramidal
- SUBCONSCIOUS movements
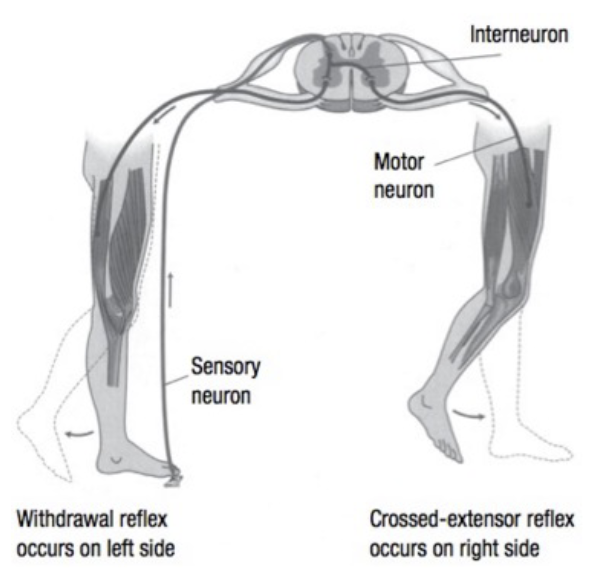
Spinal Reflexes
- reflex arc
- monosynaptic reflex
- polysynaptic reflex
Spinal Reflexes
Reflex arc
- receptor,
- sensory neauron,
- integration
center,
- motor neuron,
- effector
- motor neuron,
- integration
center,
- sensory neauron,
Spinal Reflexes
Monosynaptic reflex
- 1 synapse => 1 motor neuron
- stretch reflex
- very fast b/c 1 synapse connection
Spinal Reflexes
Polysynaptic reflex
- multiple synapses
- sensory => interneurons =. motor neuron
- slower = multiple synapses
Stretch reflex
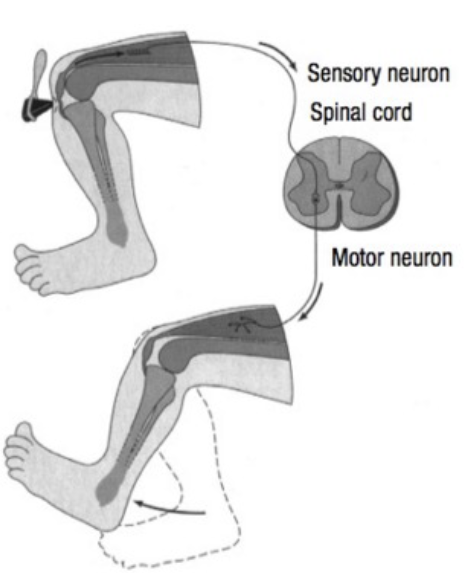
Cossed extensor reflex
Brain
- brainstem
- diencephalon
- cerebrum
- cerebellum
Brain
brain stem + diencephalon
- reflex and relay center
Brain
Cerebrum
- most motor functions
- 2 hemispheres = control opposite sides of body
- higher brain functions
Brain
Cerebellum
- receives input from proprioceptors + visual receptors
- detecting/correcting errors
- coordination center
- maintains posture + balance
cerebral cortex
- sensory areas
- motor areas
- association areas
cerebral cortex
sensory areas
- Primary: cutaneous receptors, proprioceptors
- Secondary: integrates + interprets signals
cerebral cortex
Motor areas
- coordinate, initiate voluntary movement
- Primary motor cortex: precise muscle control
- Premotor cortex: organizes learned coordinated movements (w/ complex muscle sequencing)
cerebral cortex
Association areas
- Prefrontal cortex: emotional + cognitive function, judgements, planning, motivation
Memory Graph
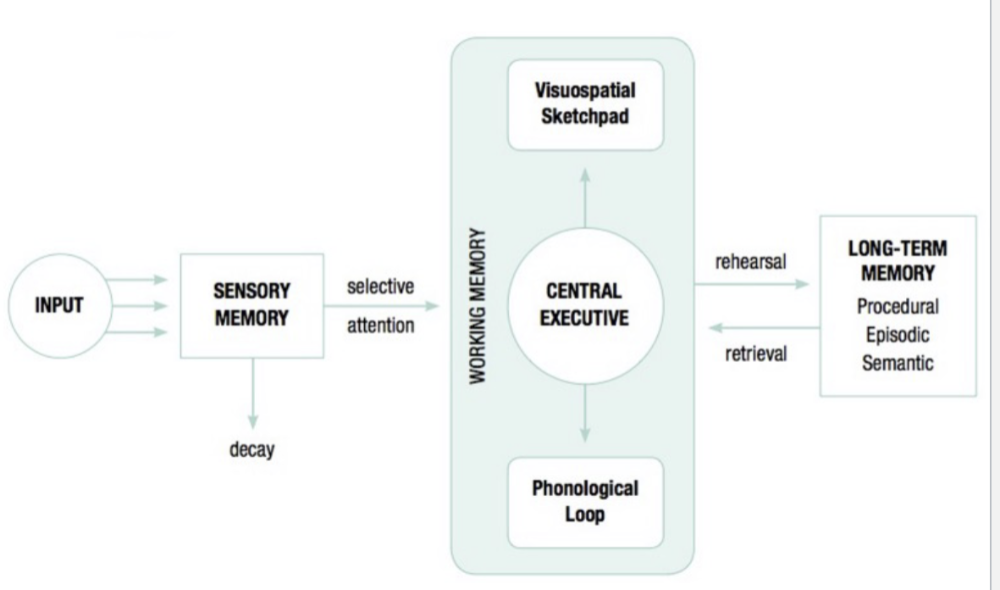
Memory
working memory
- can only hole 7+- 2 information at once
- info gathered for only 20-30seconds
- active processing = longer to transfer to long-term memory
Memory
long term memory
-
Procedural: how to perform skills, actions
- Ex. Riding a bike
-
Declarative: facts or events
- Episodic: personal experiences associated with time (Ex. year you graduated HS)
- Semantic: general knowledge, conceptual knowledge (Ex. how to know what motor is)
Forgetting
Decay Theory
- forgetting = over time memory disappears
Forgetting
Interference Theory
- old skills=> can retain new memory skills
- new memory => can't remember old skills
Practical implications
- Keep instructions, verbal cues, feedback short and simple
- Repeat key learning points
- Provide ample opportunities for physical rehearsal
- Relate skill being learned to previous skills
- Use meaningful verbal labels and analogies to strengthen associations
- “Chunk” several moments together