What is spectrophotometry?
It is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through a sample solution.
What is chromatography in simple words?
is a process for separating components of a mixture. To get the process started, the mixture is dissolved in a substance called the mobile phase, which carries it through a second substance called the stationary phase.
What is a chromatogram?
is the trace generated by the detector signal and requires a carefully controlled flow rate of the carrier gas (mobile phase) and a carefully controlled temperature of the column (stationary phase) to yield repeatable results.
What are the 4 types of chromatography?
- gas chromatography
- high-performance liquid chromatography
- thin-layer chromatography
- paper chromatography
Paper Chromatography
compound spotted directly on cellulose paper
Method of paper Chromatography
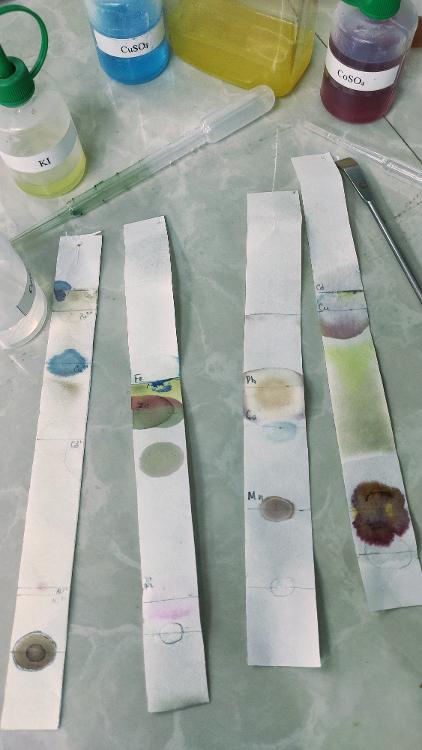

separating a mixture of different colors. The liquid soaks through the paper and carries the mixture with it. Some substances are carried faster than others so the substances are separated along the paper
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
-rapid check of reactions or mixtures
-is a method for separating non-volatile mixtures.
-the experiment is carried out on a sheet of glass, plastic, or aluminum foil that has been lightly covered in an adsorbent substance. Typically, silica gel, cellulose, or aluminum oxide are the materials used.
What are the 3 main types of liquid chromatography?
1. thin layer chromatography
2. paper chromatography
3.
column chromatography
what is liquid chromatography or LC?
chromatographic technique in which the mobile phase is a liquid
What is the mobile phase and the stationary phase of liquid chromatography?
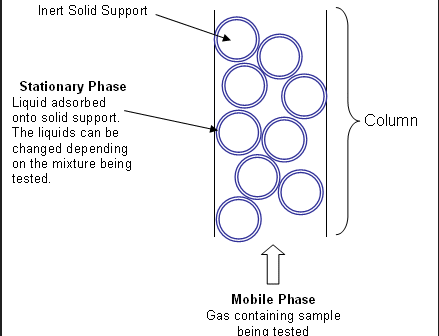
The mobile phase is a solution (such methanol, acetone, acetonitrile, water,… ) which transport our components to column (stationary phase)
What are hydrates?
substances that contain water in the form of H2O molecules.
What are anhydrous?
substances that contain no water
what is a hygroscopic material?
a substance that has the ability to adsorb and absorb moisture or water from the surrounding environment
what is a desiccant material?
drying agents
Beer-Lambert law formula
Au X (Cs/As) = Cu
Au = absorbance of unknown
Cu = concentration of unknown
As = absorbance of standard
A = absorbance
This formula is applied to assays that exhibit linear relationships between changes in absorbance with changes in concentration to calculate the concentration of the unknown sample.
what is the beer-lambert law?
states that there is a linear relationship between the concentration and the absorbance of the solution, which enables the concentration of a solution to be calculated by measuring its absorbance.
what is an anticoagulant?
commonly added to collection tubes either to maintain blood in the fluid state for hematological testing or to obtain suitable plasma for coagulation and clinical chemistry analyses.
what is a class A fire?
involve ordinary combustible materials, such as cloth, wood, paper, rubber, and many plastics.
what is a class B fire?
fires are ones where flammable liquids and/or gases are involved. They are the fuel source in the fire triangle (fuel, heat, oxygen + chemical reaction).
what is a class C fire?
fires involve electrical equipment, such as appliances, wiring, circuit breakers and outlets.
The mean is considered the________?
the average
The median is considered the_______?
the middle
the mode is considered the_____?
the most common number that appears in your set of data.
the total allowable error is
is a pre-determined number that can be tolerated without invalidating the clinical usefulness of the analytic result.
Which of the following lamps provides a continuous spectrum of radiant energy in the visible, near IR, and near UV regions of the spectrum?
Tungsten-filament
Which of the following isolates light within a narrow region of the spectrum?
Monochromator
A monochromator is a ____________
device for selecting a narrow band of wavelengths from a continuous spectrum.
Which of the following is not descriptive of a photomultiplier
tube?
A. Emits electrons proportionally to initial light
absorbed
B. Must be shielded from stray light
C. Cannot be
used with a chopper
D. Amplifies the initial signal received
C. Cannot be used with a chopper
What is a photomultiplier tube?
are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum
Which of the following is false about a photomultiplier tube?
A. Converts radiant energy (light) to electrical energy
(current)
B. Amplifies the current significantly
C. Has a
very rapid response time
D. Is composed of an iron plate and a
layer of selenium
D. Is composed of an iron plate and a layer of selenium
Which type of photodetector employs a linear arrangement that allows
it to respond to a specific wavelength resulting in complete
UV/visible spectrum analysis?
A. Photomultiplier
tube
B. Phototube
C. Barrier layer cell
D. Photodiode array
D. Photodiode array
what is a photodiode?
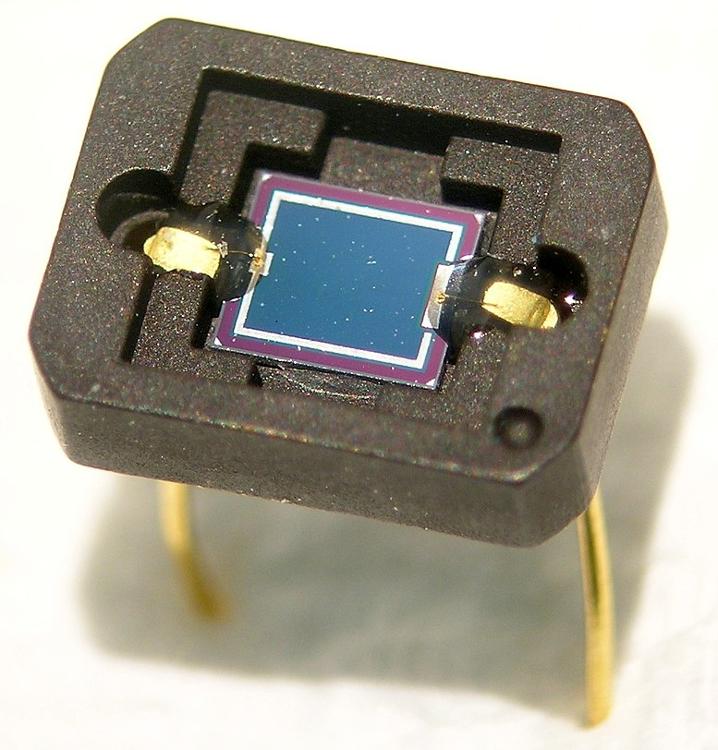
it is a form of light sensor that converts light energy into electrical energy (voltage or current)
When performing spectrophotometer quality assurance checks, what is
the holmium oxide glass filter used to assess?
A.
Linearity
B. Stray light
C. Absorbance accuracy
D.
Wavelength accuracy
D. Wavelength accuracy
In spectrophotometric analysis, what is the purpose of the reagent
blank?
A. Correct for interfering chromogens
B.
Correct for lipemia
C. Correct for protein
D. Correct for
color contribution of the reagents
D. Correct for color contribution of the reagents
In regard to bichromatic analysis, which of the following is
false?
A. Absorbance is measured at the spectral
absorbance peak for a blank
and the sample using the same
wavelength.
B. Eliminates background interferences
C.
Sample concentration determined from difference in two measured
absorbances
D. Functions as a reference blank for each sample
A. Absorbance is measured at the spectral absorbance peak for a blank and the sample using the same wavelength.
The bandpass of a spectrophotometer is 10 nm. If an instalment is set
at 540 nm, the wavelengths that are permitted to impinge on the sample
will be within what wavelength range?
A. 530-540
nm
B. 530-550 nm
C. 535-545 nm
D. 540-550 nm
C. 535-545 nm
540 ± 5 nm (10-nm bandpass) will be equivalent to a wavelength range of 535-545 nm.
Which of the following formulas is an expression of the Beer-Lambert
law that is routinely applied to spectrophotometric analysis?
A. Au X (Cs/As) = Cu
B. Cu X (Cs/As)= Au
C. As X
(Cs/Cu) = Au
D. A = 2 - log %T
A. Au X (Cs/As) = Cu
In spectrophotometry, which of the following is a mathematical
expression of the relationship between absorbance and
transmittance?
A. A = abc
B. Au/Cu = As/Cs
C. A
= 2 - log %T
D. A = log %T
C. A = 2 - log %T
Which of the following is not a problem inherent in
turbidimetry?
A. Variation in particle size of
samples
B. Variation in particle size of standards
C. Rate
of aggregation or settling of particles
D. Need to maintain a
constant and specific temperature
D. Need to maintain a constant and specific temperature
Turbidimetry is the ___________________
measurement of the amount of light blocked by particulate matter in passing through a turbid solution.
Which of the following may be associated with reflectance
spectrophotometry as it relates to the dry reagent slide
technique?
A. Light projected to the slide at 180-degree
angle
B. Dye concentration directly proportional to
reflectance
C. Unabsorbed, reflected light detected by
photodetector
D. Reflectance values are linearly proportional to
transmission values
C. Unabsorbed, reflected light detected by photodetector
Fluorometers are designed so that the path of the exciting light is
at a right angle to the path of the emitted light. What is the purpose
of this design?
A. Prevent loss of emitted light
B.
Prevent loss of the excitation light
C. Focus emitted and
excitation light upon the detector
D. Prevent excitation light
from reaching the detector
D. Prevent excitation light from reaching the detector
Because the right-angle configuration does not prevent loss of the exciting or the emitted light.
Which of the following represents a primary advantage of performing
fluorometric over absorption spectroscopic methods of analysis?
A. Increased specificity and increased sensitivity
B.
Increased specificity and decreased sensitivity
C. Purity of
reagents used not as critical
D. Ease of performing assays
A. Increased specificity and increased sensitivity
Which of the following may be associated with fluorescence
polarization?
A. Plane-polarized light is used for sample
excitation.
B. Small molecular complexes show a greater amount
of polarization.
C. It is a heterogeneous technique employed in
fluorophore-ligand immunoassays.
D. Polarized light detected is
directly proportional to concentration of ligand in sample.
A. Plane-polarized light is used for sample excitation.
Which of the following may be associated with bioluminescence?
A. Light emission produced due to enzymatic oxidation of a
substrate
B. Less sensitive than direct fluorescent
assays
C. Electron excitation caused by radiant energy
D.
Employs a radioactive label
A. Light emission produced due to enzymatic oxidation of a substrate
Nephelometry is based on the measurement of light that is
A. Absorbed by particles in suspension
B. Scattered by
particles in suspension
C. Produced by fluorescence
D.
Produced by excitation of ground-state atoms
B. Scattered by particles in suspension
Which of the following instruments is used in the clinical laboratory
or in
reference laboratories to detect beta and gamma
emissions?
A. Fluorometer
B. Nephelometer
C.
Scintillation counter
D. Spectrophotometer
C. Scintillation counter
Which of the following best describes chemiluminescence?
A. Electron excitation caused by radiant energy
B.
Enzymatic oxidation of a substrate produces light emission
C.
Chemical energy excites electrons that emit light upon return to
ground state
D. Employs a fluorescent label that produces light
C. Chemical energy excites electrons that emit light upon return to ground state
In assaying an analyte with a single-beam atomic absorption
spectrophotometer, what is the instrument actually measuring?
A. Intensity of light emitted by the analyte on its return to
the ground state
B. Intensity of light that the analyte absorbs
from the hollow-cathode lamp
C. Intensity of light that the
analyte absorbs from the flame
D. Intensity of the beam from the
hollowcathode lamp after it has passed through the analyte-containing flame
D. Intensity of the beam from the hollowcathode lamp after it has passed through the analyte-containing flame
What is the function of the flame in atomic absorption
spectroscopy?
A. Absorb the energy emitted from the metal
analyte in returning to ground state
B. Supply the thermal
energy needed to excite the metal analyte
C. Bring the metal
analyte to its ground state
D. Supply the light that is absorbed
by the metal analyte
C. Bring the metal analyte to its ground state
Most atomic absorption spectrophotometers incorporate a beam chopper
and a tuned amplifier. The purpose of these components is to avoid
errors that would be caused by
A. Variations in flame
temperature
B. Deterioration of the hollow-cathode lamp
C.
Stray light from the hollow-cathode lamp
D. Measurement of light
emitted by the analyte
D. Measurement of light emitted by the analyte
In potentiometry, which of the following is considered the standard
electrode?
A. Hydrogen electrode
B. Calcium
electrode
C. Potassium electrode
D. Copper electrode
A. Hydrogen electrode
In an electrolytic cell, which of the following is the half-cell
where reduction takes place?
A. Anode
B.
Cathode
C. Combination electrode
D. Electrode response
B. Cathode
Mercury covered by a layer of mercurous chloride in contact with
saturated potassium chloride solution is a description of which of the
following types of electrodes?
A. Sodium
B.
Calomel
C. Calcium
D. Silver/silver chloride
B. Calomel
When a pH-sensitive glass electrode is not actively in use, in what
type of solution should it be kept?
A. Tap water
B.
Physiologic saline solution
C. The medium recommended by the
manufacturer
D. A buffer solution of alkaline pH
C. The medium recommended by the manufacturer
When measuring K+ with an ion-selective electrode by means of a
liquid ionexchange membrane, what antibiotic will be incorporated into
the membrane?
A. Monactin
B. Nonactin
C.
Streptomycin
D. Valinomycin
D. Valinomycin
What are the principles of operation for a chloride analyzer that
generates silver ions as part of its reaction mechanism?
A. Potentiometry and amperometry
B. Amperometry and
polarography
C. Coulometry and potentiometry
D. Amperometry
and coulometry
D. Amperometry and coulometry
When quantifying glucose using an amperometric glucose electrode
system, which of the following is not a component of the system?
A. Product oxidation produces a current
B. Hydrogen
peroxide formed
C. Hexokinase reacts with glucose
D.
Platinum electrode
C. Hexokinase reacts with glucose
To calibrate the pH electrode in a pH/ blood gas analyzer, it is
necessary that
A. The barometric pressure be known and
used for adjustments
B. Calibrating gases of known high and low
concentrations be used
C. The calibration be performed at room
temperature
D. Two buffer solutions of known pH be used
D. Two buffer solutions of known pH be used
The measurement of CO2 in blood by means of a PCO2 electrode is
dependent on the
A. Passage of H+ ions through the
membrane that separates the sample and the electrode
B. Change
in pH because of increased carbonic acid in the electrolyte
surrounding the electrodes
C. Movement of bicarbonate across the
membrane that separates the sample and the electrode
D. Linear
relationship between PCO2 in the sample and measured pH
B. Change in pH because of increased carbonic acid in the electrolyte surrounding the electrodes
The measurement of oxygen in blood by means of a PO2 electrode
involves which of the following?
A. Wheatstone bridge
arrangement of resistive elements sensitive to oxygen
concentration
B. Direct relationship between amount of oxygen in
the sample and amount of current flowing in the measuring
system
C. Change in current resulting from an increase of free
silver ions in solution
D. Glass electrode sensitive to H+ ion
B. Direct relationship between amount of oxygen in the sample and amount of current flowing in the measuring system
Which of the following blood gas parameters are measured directly by
the blood gasanalyzer electrochemically as opposed to being calculated
by the instrument?
A. pH, HCO-3, total CO2
B. PCO2,
HCO-3, PO2
C. pH, PCO2, PO2
D. PO2, HCO-3, total CO2
C. pH, PCO2, PO2
Which formula correctly describes the relationship between absorbance
and %T ?
A. A = 2 - log %T
B. A = log 1/T
C. A
= -log T
D. All of these options
D. All of these options
Which of the following techniques is more commonly used to measure
vitamins?
A. High-performance liquid
chromatography
B. Spectrophotometry
C. Nephelometry
D. Microbiological
A. High-performance liquid chromatography
In the United States, most cases of scurvy occur in children between
the ages of 7 months to 2 years. Scurvy is a disease caused by a
deficiency in which of the following?
A. Vitamin
A
B. Vitamin C
C. Vitamin D
D. Vitamin K
B. Vitamin C
Vitamins A, D, E, and K are classified as __________?
fat-soluble vitamins.
Vitamin C are classified as ____________?
water-soluble vitamins and as such are not lipid compounds.
The term "lipid" encompasses a wide variety of compounds
characterized as being insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar
solvents. Which of the following vitamins is not classified as fat
soluble?
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin C
C. Vitamin
D
D. Vitamin E
B. Vitamin C
Measuring which of the following compounds is useful in the
diagnosis
of steatorrhea?
A. Vitamin B12
B.
Vitamin C
C. Carotenoids
D. Folic acid
C. Carotenoids
What is steatorrhea?
it is an increase of fat excretion in the stools. Another term for it is called fat malabsorption.
Carotenoids are __________?
a group of fat-soluble compounds that are precursors of vitamin A (retinol). They are not synthesized in humans, and their absorption depends on intestinal fat absorption. Therefore, the serum carotene level is sometimes used as a simple screening test for steatorrhea.
Which of the following is another name for vitamin B12?
A. Retinol
B. Pyridoxine
C. Cyanocobalamin
D. Riboflavin
C. Cyanocobalamin
Which of the following is not associated with vitamin B12?
A. Insoluble in water
B. Intrinsic factor
C. Schilling
test
D. Pernicious anemia
A. Insoluble in water
Vitamin B12 is a _____________?
water-soluble vitamin.
Which of the following tissues is important in vitamin D
metabolism?
A. Skin
B. Spleen
C.
Pancreas
D. Thyroid
A. Skin
A deficiency in which of the following leads to increased clotting
time and may result in hemorrhagic disease in infancy?
A.
Riboflavin
B. Pyridoxine
C. Tocopherols
D. Menaquinone
D. Menaquinone
Menaquinone is __________?
Vitamin K₂
Tocopherols is _________?
Vitamin E
Pyridoxine is ___________?
Vitamin B-6
Riboflavin is ___________ ?
Vitamin B2
In absorption spectrophotometry:
A. Absorbance is
directly proportional to
transmittance
B. Percent
transmittance is directly proportional to concentration
C.
Percent transmittance is directly proportional to the light path
length
D. Absorbance is directly proportional to concentration
A. Absorbance is directly proportional to
transmittance
Which wavelength would be absorbed strongly by a red-colored
solution?
A. 450 nm
B. 585 nm
C. 600 nm
D.
650 nm
A. 450 nm
a solution that looks red in color would probably absorb most strongly in the wavelength range ____________?
400–600nm
A green-colored solution would show highest transmittance at:
A. 475 nm
B. 525 nm
C. 585 nm
D. 620 nm
B. 525 nm
SITUATION: A technologist is performing an enzyme assay at 340 nm
using a visible-range spectrophotometer. After setting the wavelength
and adjusting the readout to zero %T with the light path blocked, a
cuvette with deionized water is inserted. With the light path fully
open and the 100%T control at maximum, the instrument readout will not
rise above 90%T. What is the most appropriate first course of
action?
A. Replace the source lamp
B. Insert a wider
cuvette into the light path
C. Measure the voltage across the
lamp terminals
D. Replace the instrument fuse
A. Replace the source lamp
Which monochromator specification is required in order to measure the
true absorbance of a compound having a natural absorption bandwidth of
30 nm?
A. 50-nm bandpass
B. 25-nm bandpass
C.
15-nm bandpass
D. 5-nm bandpass
D. 5-nm bandpass
Because the narrower the bandpass, the greater the photometric resolution.
Which photodetector is most sensitive to low levels of light?
A. Barrier layer cell
B. Photodiode
C. Diode
array
D. Photomultiplier tube
D. Photomultiplier tube
How does photomultiplier tube work?
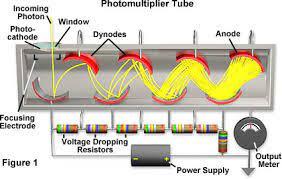
The photomultiplier tube uses dynodes of increasing
voltage to
amplify the current produced by the photosensitive cathode. It is
10,000 times as sensitive as a barrier layer cell, which has no
amplification. A photomultiplier tube requires a DC-regulated lamp
because it responds to light fluctuations caused by the AC cycle
Which condition is a common cause of stray light?
A.
Unstable source lamp voltage
B. Improper wavelength
calibration
C. Dispersion from second-order spectra
D.
Misaligned source lamp
C. Dispersion from second-order spectra
Which type of filter is best for measuring stray light?
A. Wratten
B. Didymium
C. Sharp cutoff
D. Neutral density
C. Sharp cutoff
Which of the following materials is best suited for verifying the
wavelength calibration of a spectrophotometer?
A. Neutral
density filters
B. Potassium dichromate solutions traceable to
the National Bureau of Standards reference
C. Wratten
filters
D. Holmium oxide glass
D. Holmium oxide glass
The half-band width of a monochromator is defined by:
A.
The range of wavelengths passed at 50% maximum transmittance
B.
One-half the lowest wavelength of optical purity
C. The
wavelength of peak transmittance
D. One-half the wavelength of
peak absorbance
A. The range of wavelengths passed at 50% maximum transmittance
The reagent blank corrects for absorbance caused by:
A.
The color of reagents
B. Sample turbidity
C. Bilirubin and
hemolysis
D. All of these options
A. The color of reagents
Which instrument requires a highly regulated DC power supply?
A. A spectrophotometer with a barrier layer cell
B. A
colorimeter with multilayer interference filters
C. A
spectrophotometer with a photomultiplier tube
D. A densitometer
with a photodiode detector
C. A spectrophotometer with a photomultiplier tube
What happens If the PH of blood decreases from 7.4 to 7.1?
[H+] is doubled
When the measure of an [k] acid strength increase so does __________?
[H+ ]hydrated hydronium ion
What happens If the blood increases from 7.4 to 7.7?
[H+] is halved
What does a blood pH of 7.4 correspond to in nM?
40 nM [H+]. This is the mean of the normal range (44 to 36 nM)
What is the normal pH of blood's range?
7.36 to 7.44
What is the condition called when the pH of blood rises above 7.44 ([H+] < 36 nM)?
alkalemia
What is the condition called when the pH decreases below 7.36 ([H+] > 44 nM)?
acidemia
What does the suffix -emia mean?
blood; usually to an abnormal concentration in blood.
Over the pH range of 7.20 to 7.50 what is the change in nM [H+] for every change in 0.01 pH unit?
1 nm [H+] in the opposite direction.
Which of the following technique measures light scattered and has a following light source placed at 90 degrees from the incident light?
A. Chemiluminescence
B. Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
C. Nephelometry
D. Turbidity
C. Nephelometry
Nephelometry is ___________?
a technique that measures light scattered by particular in suspension with a detector at an angle to the incident light (often 45 or 90 degrees)
Which of the following may be associated with reflectance spectrophotometry as it relates to the drying reagent slide technique?
A. Light projected to the slide at 180- degree angle
B. Dye concentration directly proportional to reflectance
C. Unabsorbed, reflected light detected by photodetector
D. Reflectance values are linearly proportional to transmission value
C. Unabsorbed, reflected light detected by photodetector
What indicator electrode uses a membrane made of dioxides the combine with result in an ion exchange with the analytes of interest in a patent sample?
A. Glass
B. Liquid
C. Silver-silver chloride
D. Calomel
A. Glass
An example of glass electrode is the PH electrode.
Which of the following method allows for the separation for the separation of charged particles based on their rates of migration in an electric field?
A. Rheopheresis
B. Electrophoresis
C. Electroendosmosis
D. Ion Exchange
B. Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is ____________?
method of separating charged particles by their rates of migration in an electric field.
Electroendosmosis is ____________?
the movement of water and the contents within through a porous material when under the influence of an electric charge
Which of the following techniques is based on electro-osmotic
flow?
A. Capillary electrophoresis
B. Zone
electrophoresis
C. Iontophoresis
D. Isoelectric focusing
A. Capillary electrophoresis
In isoelectric focusing electrophoresis, am-pholytes create a pH gradient where:
The higher pH gradient is toward the cathode
In serum protein electrophoresis, when a buffer solution of pH 8.6 is
used, which of the following characterizes the proteins?
A. Exhibit net negative charge
B. Exhibit net positive
charge
C. Exhibit charge neutrality
D. Migrate toward the cathode
A. Exhibit net negative charge
At the alkaline pH, the serum proteins have a net negative charge. Therefore the negatively charged serum proteins migrate toward the anode.
What is an anode?
the positively charged electrode
What is cathode?
the negatively charged electrode
Which of the following characteristics will a protein have at its
isoelectric point?
A. Net negative charge
B. Net
positive charge
C. Net zero charge
D. Mobility
C. Net zero charge
The isoelectric point (pI) of a protein refers ___________?
to the pH at which the number of positive charges on the protein molecules equals the number of negative charges, causing the protein to have a net charge of zero.
What dye may be used for staining protein bands following
electrophoresis?
A. Fat red 7B
B. Sudan
blackB
C. Ponceau S
D. Oil redO
C. Ponceau S
When electrophoresis is performed, holes appear in the staining
pattern, giving the stained protein band a doughnut-like appearance.
What is the probable cause of this problem?
A. Protein
denatured and will not stainproperly
B. Ionic strength of the
buffer was toohigh
C. Protein reached its isoelectric pointand
precipitated out
D. Protein concentration was too high
D. Protein concentration was too high
What is the purpose of using ampholytesin isoelectric focusing?
A. Maintain the polyacrylamide gel ina solid state
B.
Maintain the protein sample ina charged state
C. Maintain the pH
of the buffersolution
D. Establish a pH gradient in the gel
D. Establish a pH gradient in the gel
Which of the following is an electrophoretic technique employing a ph
gradient that separates molecules with similar isoelectric
points?
A. Zone electrophoresis
B. High-resolution
electrophoresis
C. Isoelectric focusing
D. Immunoelectrophoresis
C. Isoelectric focusing
Given the following information on a particular compound that has
been visualized by means of thin-layer chromatography, calculate the
Rf of the compound.
Distance from origin to spot center =
48mm
Distance from spot center to solvent front = 93
mm
Distance from origin to solvent front = 141mm
A.
0.29
B. 0.34
C. 0.52
D. 0.66
B. 0.34
=origin to spot center/origin to solvent front
=48/141=.34
To achieve the best levels of sensitivity and specificity, to what
type of detector system could a gas chromatograph be coupled?
A. UV spectrophotometer
B. Bichromatic
spectrophotometer
C. Mass spectrometer
D. Fluorescence detector
C. Mass spectrometer
Which of the following instruments has a sample-introduction system,
solvent delivery system, column, and detector as components?
A. Atomic absorption spectrometer
B. Mass
spectrometer
C. High-performance liquid chromatograph
D. Nephelometer
C. High-performance liquid chromatograph
Which type of elution technique may be used in high-performance
liquid chromatography?
A. Amphoteric
B.
Isoelectric
C. Gradient
D. Ion exchange
C. Gradient
Which of the following statements best describes discrete
analysis?
A. Each sample-reagent mixture is handled
separately in its own reaction vessel.
B. Samples are analyzed
in a flowing stream of reagent.
C. Analyzer must be dedicated to
measurement of only one analyte.
D. It does not have random
access capability.
A. Each sample-reagent mixture is handled separately in its own reaction vessel.
Which of the following chromatography systems may be described as
having a stationary phase that is liquid absorbed on particles packed
in a column and a liquid moving phase that is pumped through a
column?
A. Thin-layer
B. High-performance
liquid
C. Ion-exchange
D. Gas-liquid
B. High-performance liquid
Which of the following chromatography systems is characterized by a stationary phase of silica gel on a piece of glass and a moving phase of liquid?
A. Thin-layer
B. Ion-exchange
C. Gas-liquid
D. Partition
A. Thin-layer
Which of the following does not apply to gas-liquid
chromatography?
A. Separation depends on volatility of
the sample.
B. Separation depends on the sample's solubility in
the liquid layer of the stationary phase.
C. Stationary phase is
a liquid layer adsorbed on the column packing.
D. Mobile phase
is a liquid pumped through the column.
D. Mobile phase is a liquid pumped through the column.
Ion-exchange chromatography separates solutes in a sample based on
the
A. Solubility of the solutes
B. Sign and
magnitude of the ionic charge
C. Adsorption ability of the
solutes
D. Molecular size
B. Sign and magnitude of the ionic charge
Which parameter is used in mass spectrometry to identify a
compound?
A. Ion mass-to-charge ratio
B. Molecular
size
C. Absorption spectrum
D. Retention time
A. Ion mass-to-charge ratio
What is the x-mass on the mass spectrum?
A. Mass
B. Mass/energy
C. Mass/charge
D. Charge
C. Mass/charge
A mass spectrum is an __________?
Intensity vs. mass/ charge ration plot representing an analysis.
Which chromatography system is commonly used in conjunction with mass
spectrometry?
A. High-performance liquid
B.
Ion-exchange
C. Partition
D. Gas-liquid
D. Gas-liquid
Which of the following may be a sampling source of error for an
automated instrument?
A. Short sample
B. Air bubble
in bottom of sample cup
C. Fibrin clot in sample probe
D.
All the above
D. All the above
Checking instrument calibration,temperature accuracy, and electronic
parameters are part of
A. Preventive maintenance
B.
Quality control
C. Function verification
D. Precision verification
C. Function verification
For which of the following laboratory instalments should preventive
maintenance procedures be performed and recorded?
A.
Analytical balance
B. Centrifuge
C. Chemistry
analyzer
D. All the above
D. All the above
Which hemoglobin may be differentiated from other hemoglobins on the
basis of its resistance to denature in alkaline solution?
A. A1
B. A2
C. C
D. F
D. F
In the Clark electrode, for every molecule of oxygen reduced at the cathode, how many electrons of current flow?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
C. 4
With each molecule of oxygen that is reduced at the cathode, it causes four electrons of the current flow
When performing electrophoresis at pH 8.6, which hemoglobin molecule
migrates the fastest on cellulose acetate toward the anode?
A. A1
B. A2
C. F
D. S
A. A1
Hemoglobin A migrates the fasts toward anode, followed by hemoglobin F and S. Then A2 and C.
When using EMIT, the enzyme is coupled to
A.
Antibody
B. Antigen
C. Substrate
D. Coenzyme
B. Antigen
Which of the following is not associated with the enzyme-multiplied
immunoassaytechnique (EMIT)?
A. Is a homogeneous enzyme
immunoassay
B. Determines antigen concentration
C. Employs
a labeled reactant
D. Enzyme reacts with drug in serum sample
D. Enzyme reacts with drug in serum sample
Which of the following stimulates the production of singlet oxygen at
the surface of the sensitizer particle in a luminescent oxygen
channeling immunoassay?
A. Radiant energy
B. Heat
energy
C. Enzymatic reaction
D. Fluorescent irradiation
A. Radiant energy
Singlet oxygen reacting with a precursor chemiluminescent compound to
form a decay product whose light energizes a fluorophore best
describes
A. Fluorescent polarization immunoassay
B.
Enzyme-multiplied immunoassay technique
C.
Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay
D. Luminescent oxygen
channeling immunoassay
D. Luminescent oxygen channeling immunoassay
pre-analytical variables in lab testing include:
specimen acceptability
which of the following is NOT a potential source of post-analytical errors?
labeling the specimen at the nurse's station
a pre-analytical error can be introduced by:
vigorously shaking the blood tube to prevent clotting
the most important diagnosis and therapeutic mgmt decision tool used to interpret test results is:
reference intervals
a CC (clean-catch) urine is submitted to the lab for routine UA/Culture. the routine UA is done first, and 3 hours later, the specimen is sent to micro for culture. the specimen should:
rejected for time delay
Urine samples should be examined within 1 hour of voiding because:
bacterial contamination will cause alkalinization of the urine
a urine comes to the lab 7 hours after it is collected. it is acceptable for culture only if the specimen has been stored:
at 4-7C
which of the following statements about analytical errors is true?
analytical errors are not obvious to providers
the first procedure to be followed if the blood gas instrument is out of control for all parameters is:
recalibrate and repeat controls
upon completion of a run of cholesterol tests, the tech recognizes that the controls are not within the 2 standard deviations confidence range. what is the appropriate course of action?
run new set of controls and repeat specimens
Using a common labeling system for hazardous material identification
such as HMIS or NFPA 704, the top red quadrant represents which
hazard?
a reactivity
b special reactivity
c
health
d flammability
flammability