1
General Adaption Syndrome
- Initially one becomes alarmed by a stressor that activates the hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system
- Alarm stage
- Adaption stages
- Exhaustion stages
2
Alarm Stage
- (1) the alarm stage or reaction, in which the central nervous system (CNS) is aroused and the body's defenses are mobilized
-
Stressor triggers the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA)
axis
- Activates the sympathetic nervous system (SNS)
3
Adaption Stage
Resistance (adaptation) stage
- resistance or adaptation, during which mobilization contributes to “fight or flight”
- Begins with the actions of
adrenal hormones
- Cortisol, epinephrine, and norepinephrine
4
Exhaustion Stage
-
Exhaustion stage (allostatic overload)
Occurs only if stress continues and adaptation is not successful - stage of exhaustion, where continuous stress causes the progressive breakdown of compensatory mechanisms (acquired adaptations) and homeostasis
- Exhaustion marks the
onset of certain diseases (diseases of adaptation)
- if
stress continues and adaptation is not successful, can cause
impairment of the immune response, heart failure, and kidney
failure,
leading to death.
- if
stress continues and adaptation is not successful, can cause
impairment of the immune response, heart failure, and kidney
failure,
5
Reactive, Anticipatory, and Conditional Response
Reactive response
- Involves psychologic stressors
Anticipatory response
- Anticipates a disruption in homeostasis "anticipate something bad", react to a predator or experience-dependent memory programs
- occurs when physiologic responses develop in anticipation of disruption of the optimal steady-state, also known as homeostasis
Conditional response
- Associates a stimulus with danger
- May cause posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or phobias
6
Concepts of Stress
- Is initiated by the central nervous system and the endocrine system
- Stressor can be a perceived or real threat
7
Effects of Stress: Sympathetic Nervous System
- Epinephrine and norepinephrine released
- Which binds to adrenergic receptors on various cells
Causing:
- Blood pressure elevation
- Heart rate and cardiac contractility increase
- Pupil dilation
- Reduction of blood flow to skin, guts, and kidneys
8
Cortisol: the Stress Hormone
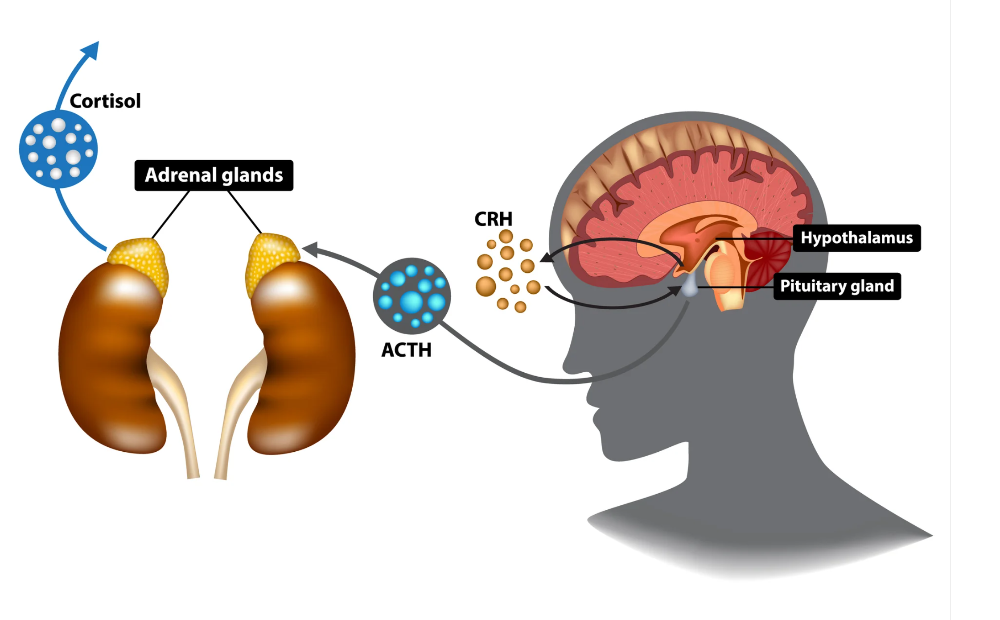
- Hypothalamus
- secretes Corticotropin Releasing Factor (CRF)
- secretes Corticotropin Releasing Factor (CRF)
- Anterior pituitary
- secretes adrenocorticoid hormone (ACTH)
- Adrenal
Cortex
- secretes glucocorticoid: Cortisol
- Contributes to the development of metabolic syndrome and the pathogenesis of obesity
- Development of diabetes is secondary to cortisol-induced obesity
- Chronic cortisol excess induces lipogenesis in the abdomen, trunk, and face, resulting in central obesity
- Alters glucose, fat, and protein metabolism
- Increases blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis.
- Suppresses inflammatory and immune responses
9
Cortisol in the Immune System
- Systemic responses to stress may cause a decrease in innate immunity and enhance adaptive immunity
- Local responses to stress, under certain conditions, can induce proinflammatory activities
- Many immune-related conditions and diseases are associated with stress
- Stress and negative emotions increase levels of proinflammatory cytokines, providing a possible link among stress, immune function, and disease