How are impression materials manipulated to shape like cakes?
Putting them in 60C water after shaping them
How could you fix the distortion due to reliefe of internal stress?
By putting the impression in water immediately after removal
How much is Coefficient of thermal expansion?
0.3% generally
How much is Fusion temperature?
43.5C
How much is glass temperature?
39C
How much should you wait to prevent dimensional distortion?
1h
How to fix the coefficient of thermal expansion error?
1-passing the impression over flame to soften it then obtaining the second impression to lower the shrinkage
2-spraying cold water on the tray before putting it with the impression in the mouth to harden the tray while the impression stays soft
What affects viscosity?
1-temperature =1/viscosity
2-prrssure = viscosity
3-nature of the substance
4-time = viscosity
What are hardness tests?
Brinell hardness number (BHN)
Vickers hardness number (VHN)
Knoop hardness (KHN)
Rockwell hardness
Shore A hardness test
What are precautions in using impression materials?
1-long immersion in water, makes the material lose low weight parts of it that cannot be distinguished
2-overheating, makes the material sticky and hard to handle
3-Excessive wetting, messes the flow of material
What are some examples of elastomeric impressions?

Polysulfide
Polyether
Addition silicones
Condensation silicones
What are some examples of irreversible hydrocolloid?
Alginate
What are some examples of Reversible hydrocolloid?
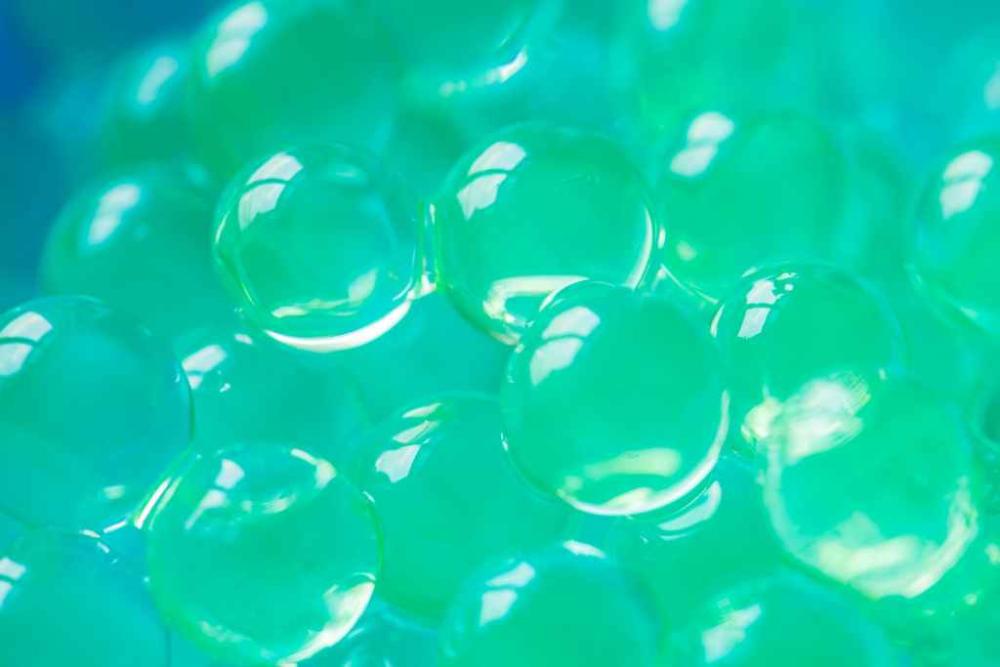

Agar
What are some examples of rigid Irreversible impressions
Zoe impression paste, impression plaster
What are some examples of thermoplastic impression material?
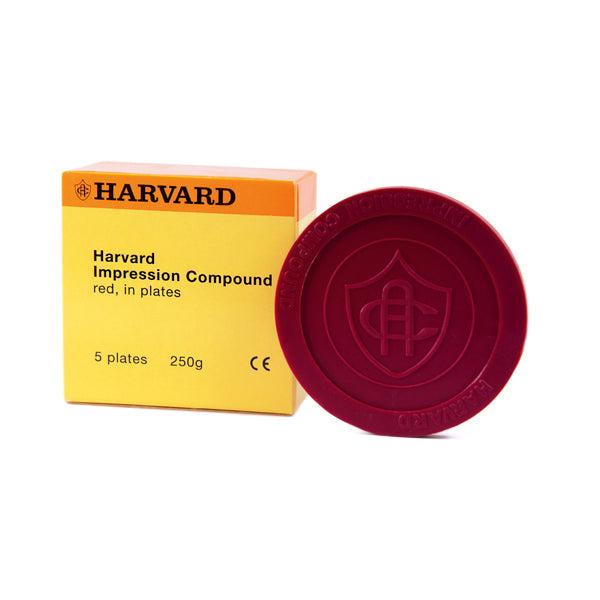

Impression compound
What are some examples of thermoset impression material?
Zinc oxide eugenol
What are some material properties?
1-thermal conductivity
2-coefficient of thermal expansion
3-Flow
4-glass transition temperature
5-fussion temperature
6-surface detail reproduction
7-Dimensional Stability
What are the advantages of using impression compound
1-cheap
2-reusable, you can also modify it after use for more accurate impression
3-doesn't cause irritation for patients
What are the applications of Type I impression compound?
-primary impression
-for making impressions on individual tooth
-for border moulding(manipulation of the border of the impression by the outside tissue in order to catch those information as well
-to check for over cutting or deep cutting in the inner portions of the teeth
What are the applications of Type II impression compound?
To make tray
What are the disadvantages of using impression compound?
1-cant record accurate details
2-uncomfortable for the patient becuase it comprises the tissue since they apply pressure on it
3-Distortion
4-Difficult to remove from undercuts(deep cuts in the inside portion of the teeth)
5-doesnt have a pleasant taste
What are the usefulness of trays?
1-to carry the impressions
2-hold the material close to the teeth
3-avoid breaking during removal
4-prevent bending of the impression
What degree is thermoplastic compounds generally warm?
45C
What does impression plaster mainly made of?
Calcium sulphate hemihydrate that truns into Calcium sulfate dihydrate after reaction with water
What factors produce significant internal stress in the impression material?
1-high thermal expansion
2-low thermal conductivity
3-high heat change between material and environment
What is a 'wash' in Dental material?
A thin layer placed on top of an impression material to record endentulous(inside teeth) impressions
What is adsorption?
The sticking of a material to the surface of another material but not going in it
What is an example of high fusion compound
Tray compound
What is an example of Low fusion compound
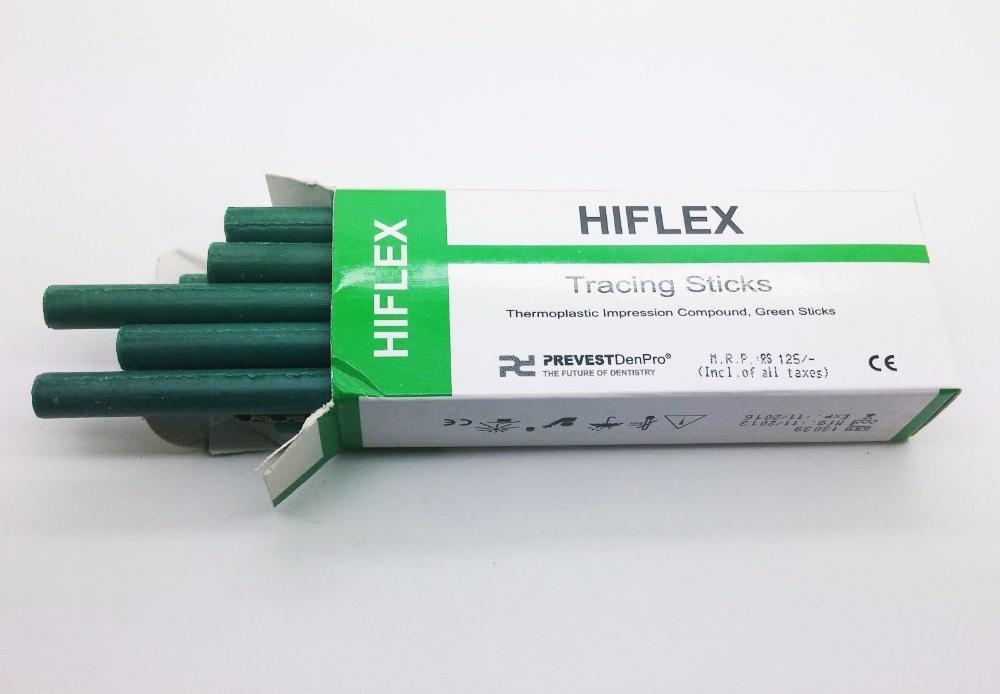

Green stick compound
What is an example of medium fusion compound
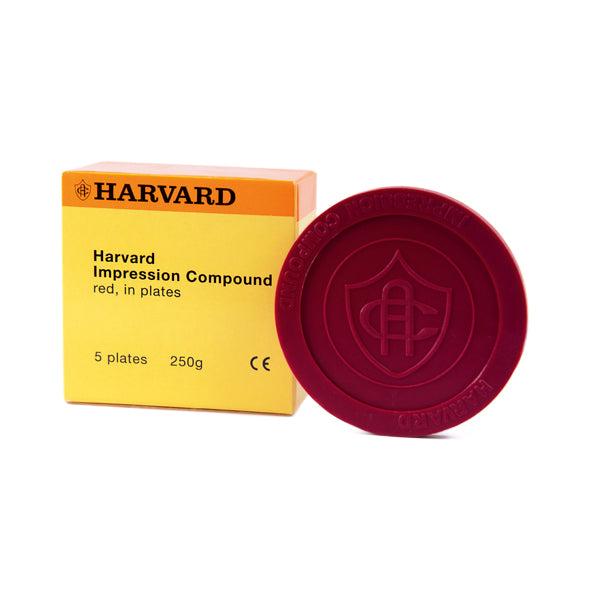

Impression compound
What is an example of reversible rigid impressions?
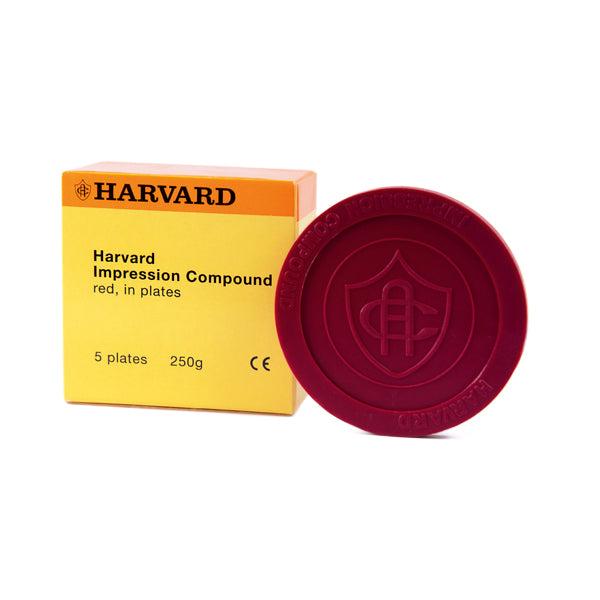

Impression compound
What is fusion temperature?
The temperature where the material turns plastic
What is galvanism?
Its the current produced between two dissimilar materials
What is glass temperature?
The temperature that the material losses its hardness or brittleness
What is hardness?
The resistance of an ability to be penetrated
What is impression plaster used for?
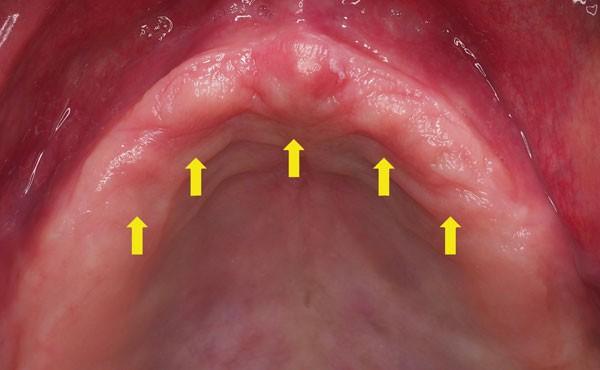
For people who have flappy ridge
What is shear stress?
Its a stress paralell to each other but not on the same line
What is sorption?
Adsorption with absorbtion but not knowing the sequence in which they will happen
What is surface wetting?
The ability of an adhesive material to wet and adherand(the material which the adhesive is stuck to)
What is the advantages of using a cast model?
1-to make his diagnosis and treatment plan
2-to apply his
treatment plan and appliances on
3-to educate the
patient
4-to show before and after treatment
5-save time
What is the bitting force of an individual with Fixed Bridges?
40% of an individual bite force
What is the bitting force of an individual with removable Bridges?
15% of the original bite force
What is the composition of Impression compound

Resin, like wax
-filler, like Talc stone and soap stone
-lubricant
What is the contact angle?
The way we measure how well adhesive materials can stick to an adherand
What is the difference between Brittleness, Ductility and Mellability?
Brittleness: is the ability to fracture near the proportional limit, without showing any deformations like glass
Ductility: the resistance of a material to permanent deformation to tensile load
Mellability: the ability to be spread thin into sheets without breaking
What is the difference between Resilience and Toughness
Resilience: resistance of material for permanent deformation, the region of elasticity before turning plastic
Toughness: resistance of materials for fracture, region of the graph before fracture
What is the difference between Ultimate Strength/stress and Fracture strength/stress
Fracture strength: the stress at the point of Fracture
Ultimate Strength: the stress at the point before Fracture happens, the highest point in the stress and strain curve
What is the difference between wear and erosian?
Wear: resistance of a material surface to be torn apart by friction
Erosion: resistance of a material surface to be torn apart by chemical reactions like acid attack
What is the differnece between Primary and final impressions
1-Primary:
-made by dentist or dental assistance
-used to make custom trays, appliances, not so accurate models meant for diagnoses
-for before and after treatment records
2-final:
-made only by dentist
-used to make reproduction of teeth or implants
What is the most anti expansion material used on impression plaster
Potassium sulphate
What is the most viscose impression material?
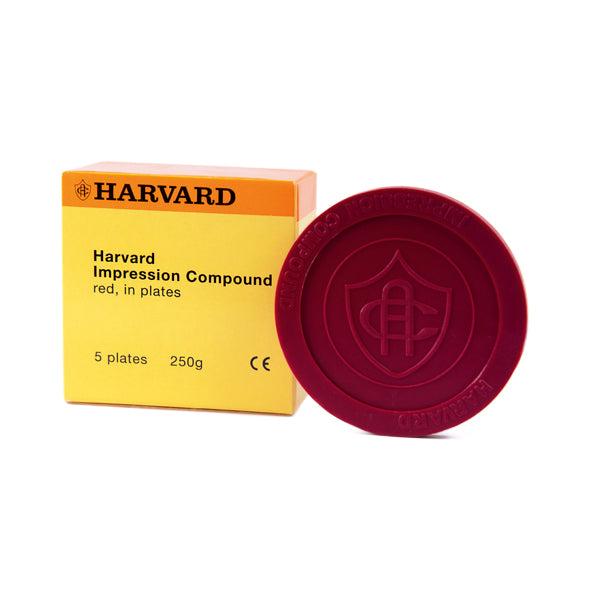

Impression compound
What is Yield strength?
Its 0.1-0.2% offset in the stress-strain curve thats the limit point between the elastic and plastic region
When do thermoplastic materials set?
When they get in the mouth becuase they are cooled to 37C
Why do they put impression plaster in air tight container
To prevent it from sucking the moisture air which results in longer setting