How big are cells generally?
0.1-0.5 micrometer
Are prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells bigger?
Eukaryotic becuase they contain more organelles than prokaryotic cells
Why does Cell growth is limited?
Becuase volume of cells increase way more compared to surface area eventhough more surface area means more area for food absorption but it still isn't sufficient for the volume you need to feed
What is Cell theory?
- All organisms are made up of cell(s)
- All existing cells are produced by other living cells
- Cell is the basic unit of life
What is the bacteria cell wall made of?
Sugars and Amino acids
What is the function of the Capsule of prokaryotic cells?
To make the prokaryotic cell able attach to its environmental surfaces
What is the role of pilis in prokaryotic cells?
To transform genetic materials during conjugation(sexual reproduction of bacteria)
What does the word eukaryotic mean?
True nucleus
What does the word organelle mean?
Little organ
What is the function of Cholesterol in plastmatic membrane of cells?
To regulate fluidity in between the phospholipid bilayer, to not let the two layers get so close to each other when its cold snd vice versa
What is the Fluid-moasic model?

A model to explain the structure of the plasmatic membrane of the cell, that is consist of fluid(cholesterol) +moasic(phospholipids, proteins and Carbohydrates)(moasic simply are an art made from small stones)
What is the funcion of Protones in Nerve cells?
To transform impulses
Name the types of proteins in the plasmatic membrane of cells based on their function.
- Transport
- Enzyme
- Attachment
- Recognition
- Receptor
- Intercellular junction
Explain the function of transport proteins?
Transporting things either by:
- Channels(pores)
- Carriers
What do channel proteins(pores) transport?
Lipids(like triglycerides[which is one of the components of ATP]), insoluble substances, ions(like K+,Na+ and Cl- just like how nerve cells use to transport pulses)
What do receptor proteins do?
They bind to hormones to initiate biochemical reactions
What do Attachment proteins do?
Support the cytoskeleton to hold the shape and structure of the cell
What do recognition proteins do?
For cells to recognise each other, just like how red blood cells recognise each other
Name examples of recognition proteins?
Glycoproteins, although they aren't proteins but Glycolipids
What do intercellular junction proteins do?
Provide space between cells wether its:
- Gap junctions
- Tight junctions
To allow substance transform and enough space so if one cell is infected it'll stay away from the other cells
What are microvilli?
Finger like structures made of folding the plasmatic membrane
What is the use of Microvilli?
They increase the surface area of cells so that they have more places to absorb substances from
What is celiac disease?

Its when the microvilli of the small intestine get flattened so they can't absorb the gluten proteins in bread
Where are microvilli found?
Small intestine
What is the function of Carbohydrates in the plasmatic cell membrane?
They decorate proteins(to make glycoproteins) and lipids(to make glycolipids) so that cells can recognise each other
What is the function of Plasmatic membrane?
- Protect
- Keep homeostasis
- Semi-permable membrane
- Keep the shape of cells
- Barrier between the cell and its environment
What are the types of passive transport?
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
What is diffusion?
Transporting of substances from high concentration to low concentration to achieve homeostasis
What is osmosis?
Is what you call diffusion but only for water
What substances are transported by diffusion?
- Gases
- Water
- Lipids(steriod hormones)
- Lipid soluble molecules(hydrocarbon, alcohols and some vitamins)
What is Tonicity?
the ability of a solution to change cell volumes by changing their water content
What are the types of tonicity?
- Isotonic
- Hypotonic(lower water in material)
- Hypertonic(higher water in material)
What are the types of Active Transport?
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
What are the types of Endocytosis?
- Phagocytosis
- Pinocytosis
What is Phagocytosis?
Know also as cell eating, which is when cells dissolve bacteria in them
What is the importance of active transport?
- Bring molecules(ions, amino acids, glucose, nucleotides)
- Get rid of molecules(like urine in kidneys)
- Maintain homeostasis
- Control pH
What is the function of Vesicles?
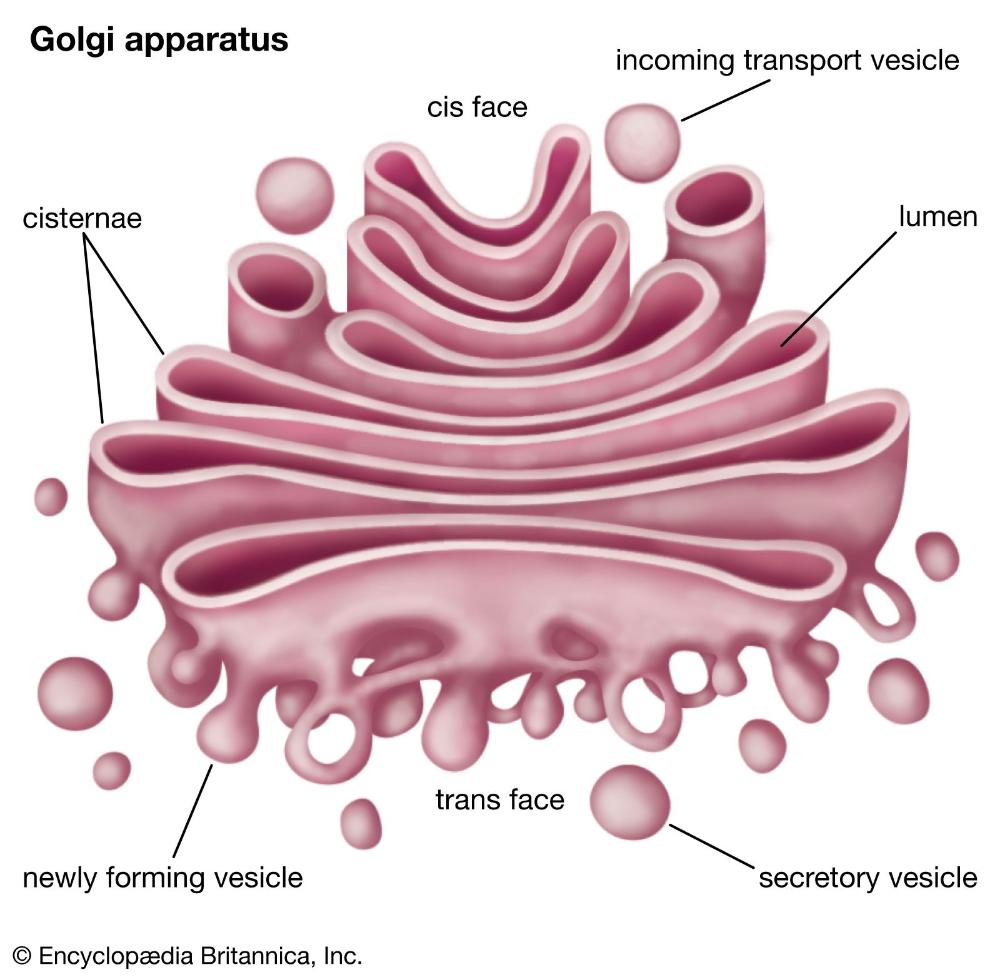
Created by the golgi apparatus to Bulk transport macromolecules in and out of cells including:
- Proteins
- Polysaccharides
- Polynucleotides
- Whole cells
- Hormones
- Waste
- Mucus
- Neurotransmitters
What do Macrophages do?
They are part of the immune system, that dissolve bacteria and old red blood cells in them
What is Pinocytosis?
Also called cell drinking, which is when cells absorb liquid and/or small molecules dissolved in liquid, just like the intestine, kidneys and plant roots