forearm
any hole in a bone
fossa
shallow depression in bone
tubercle
rough raised surface of bone
tuberosity
large rough raised surface of bone
trochanter bone
prominent feature found only on femur
canal bone
deep hole through a thick piece pf bone
spine bone
sharp bone projecting from bone
line bone
slightly raised elevation on bone
ridge bone
higher raised elevation of bone
fissure bone
hole or crack on bone
condyle bone
rounded surface involved articulation of two bone
facet bone
flat surface of bone involve a joint
axial skeleton
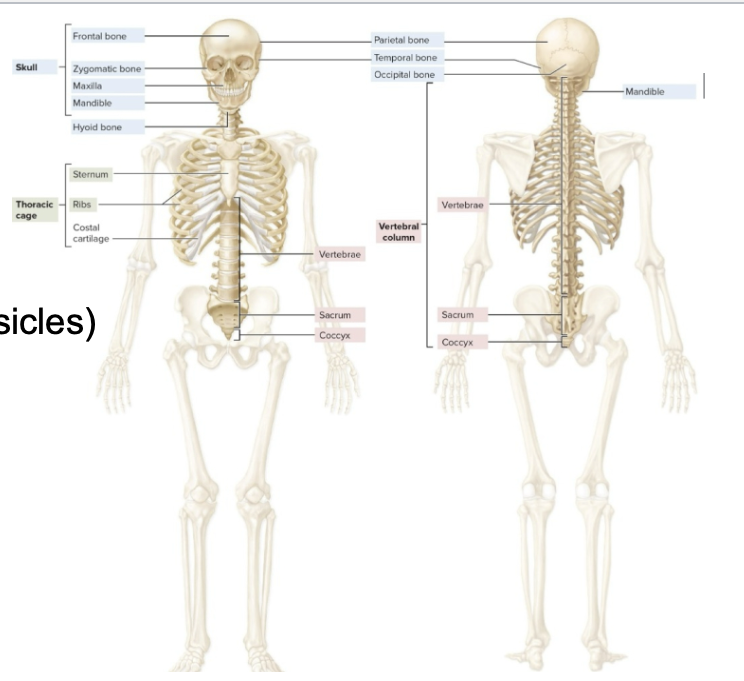
skull
hyoid bone
auditory bones
vertebral column (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx)
thorax (sternum, ribs)
skull is composed of :
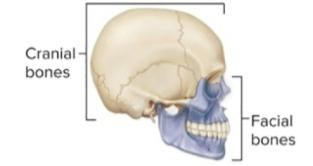
cranial and facial bones
cranial bones
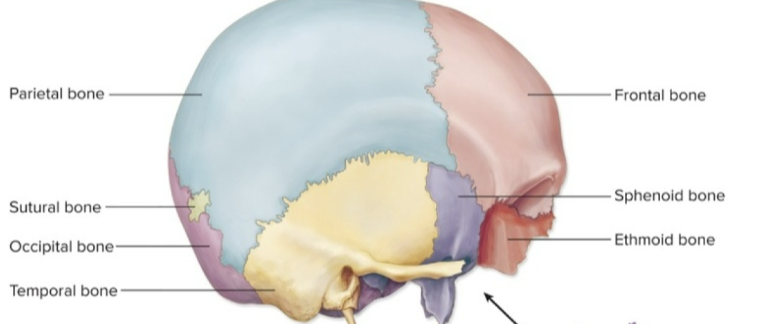
8 bones surround the brain
unpaired cranial bones
ethmoid, frontal, occipital, and sphenoid bones
paired cranial bones
parietal and temporal bones
facial bones
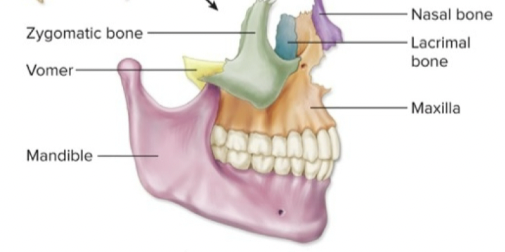
14 bones that form the face and no brain contact
unpaired facial bones
vomer and mandible bones
paired facial bones
maxillae, nasal, lacrimal, zygomatic,
palatine, and inferior
nasal conchae bones
sutures
immovable joints btw skull bones
goes away with aging , commonly small
coronal suture
junction btw frontal and parietal bones
lambdoid suture
junction btw occipital and parietal bones
sagittal suture
junction btw parietal bones
squamous suture
junction btw temporal and parietal bones
2 movable bones in the skull
ossicles and mandible
the cranial fossae
depression in a bone
The floor of the cranial cavity contains three cranial fossae (floors)
• Anterior cranial fossa (frontal lobes)
• Middle cranial fossa
(temporal lobes)
• Posterior cranial fossa (cerebellum)
the bones of the orbit (eye socket)
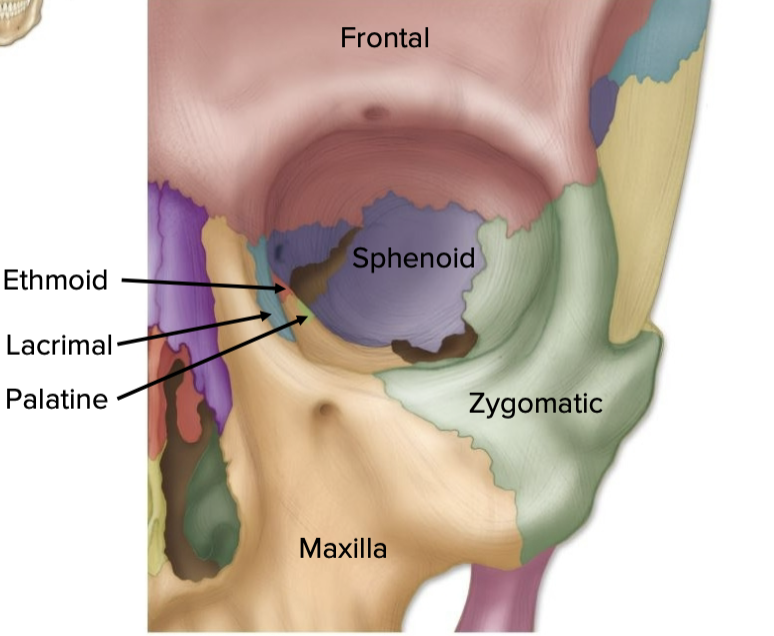
• Frontal
• Lacrimal
• Ethmoid
• Sphenoid
•
Maxilla
• Zygomatic
• Palatine
nasal cavity
partially cartilage
passage for air during breathing
bones of nasal cavity
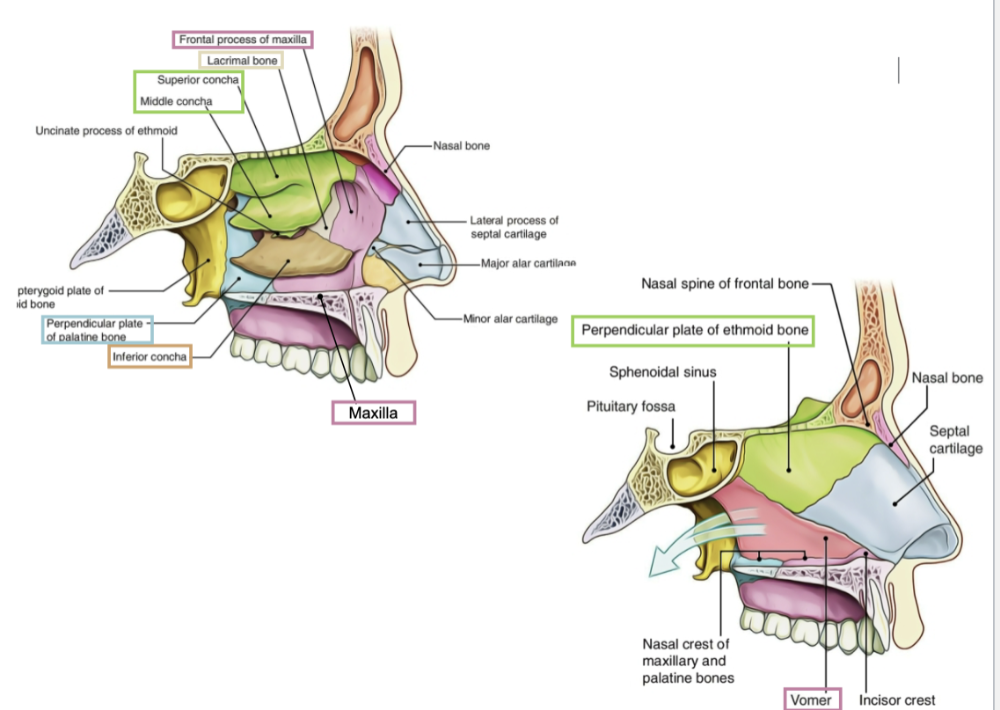
• Maxilla
• Ethmoid
• Lacrimal
• Palatine
•
Vomer
• Inferior Nasal Conchae
Paranasal Sinuses
Air-filled spaces in skull bones around nasal cavity
oral cavity:
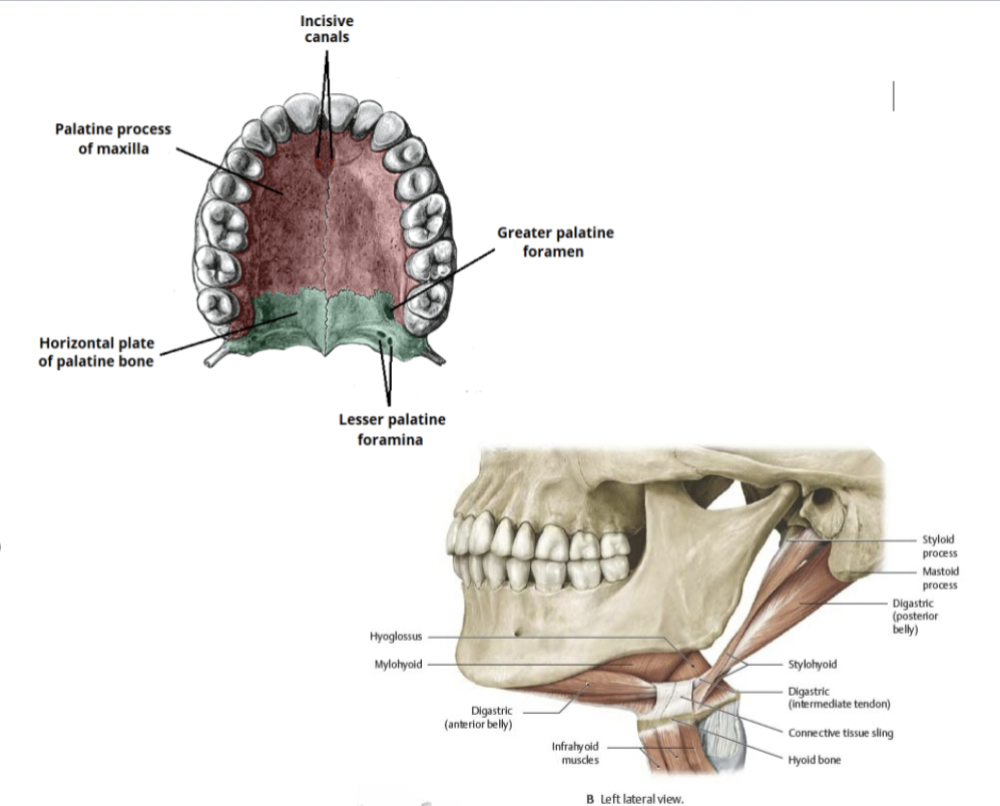
mouth
• Maxillae
• Palatine
• Teeth
• Mandible
• Hyoid bone
frontal bone:
form the forehead and the root of the orbit
Frontal sinuses
parietal bones
four sided bones
forms roof and sides of the cranium
parietal is Connected to other bones with various
sutures:
1. Coronal suture
2. Lambdoid suture
3. Sagittal
suture
4. Squamous suture
occipital bone
Forms back of the head and the majority of the
base of the
cranium
• Foramen magnum - spinal cord vertebral +spinal arteries
occipital condyles -Articulate with the 1st cervical vertebrae
temporal bones
Form the inferior lateral portion of the
cranium
• Also
forms a portion of the cranial floor
key features of the temporal bones
1. Zygomatic Process
2. Styloid process
3. Mastoid
process
4. External Auditory Meatus
5. Internal Auditory
Meatus
6. Carotid Canal
7. Jugular Foramen
sphenoid bone
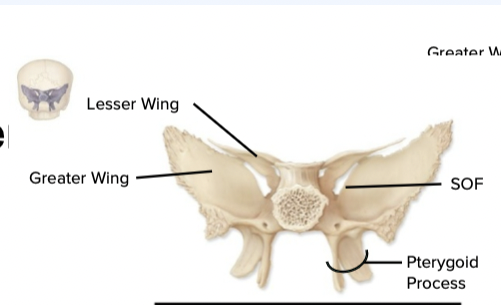
butterfly shaped , mid base of skull , houses pituitary glands
Attachment for muscles of
mastication
ethmoid bones
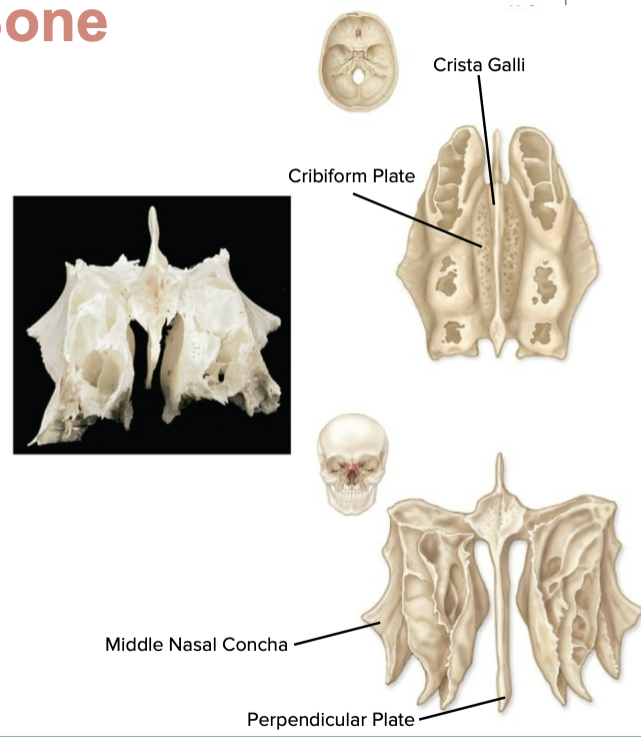
delicate bone btw the orbits
perpendicular plate
superior nasal septum
cribriform plate
• Anterior floor of cranium and roof of nasal cavity
• Contains
olfactory foramina
• CN I
• Superior projection: crista
galli
• Attachment for falx cerebri
bones of the face
1. nasal bone - near the nose
2. palatine bone - roof of mouth
3. inferior nasal conchae - covered with mucosa - filters air
4. vomer - triangle floor of the nasal cavity
5. lacrimal bones - smallest bone of face gathers tears
6. zygomatic bones - check bones -Attachment of muscles of mastication and facial expression
7. maxilla - upper jaw
8. mandible - lower jawbone largest
parts of the mandible bone
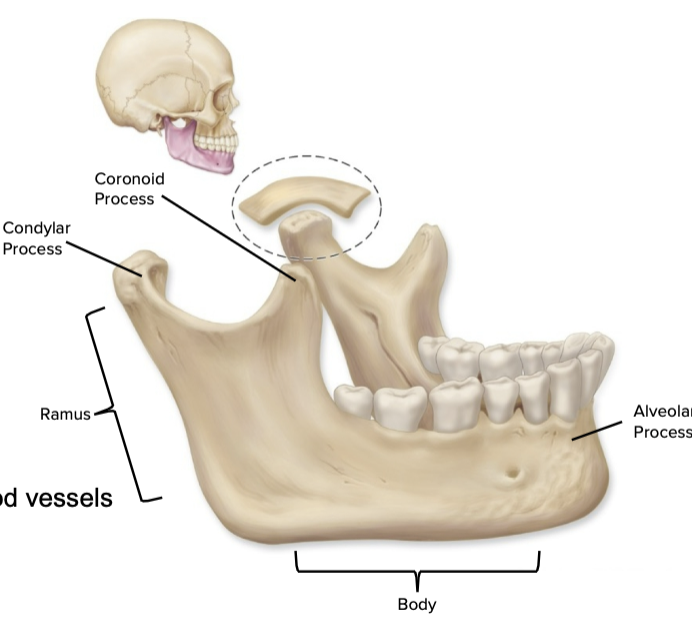
body- mental foramen
rami- mandibular foramen
Condylar process
Coronoid process
the ossicles
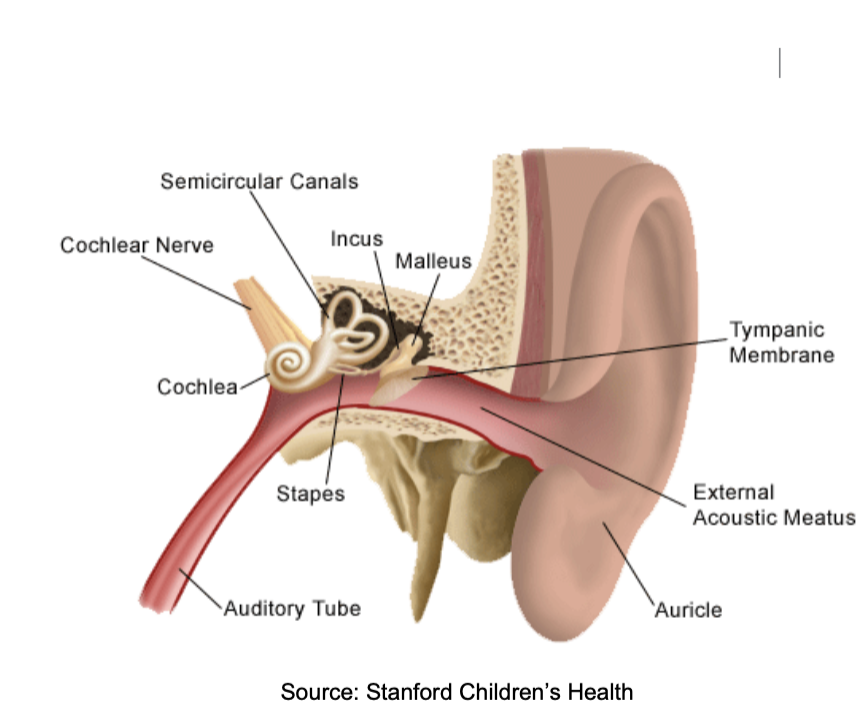
• Bones of the middle ear
• Malleus, Incus, Stapes
• Found
within the temporal bone
• Transmit and amplify
vibrations
from tympanic membrane (ear
drum) to cochlea
(inner ear)
the hyoid bone
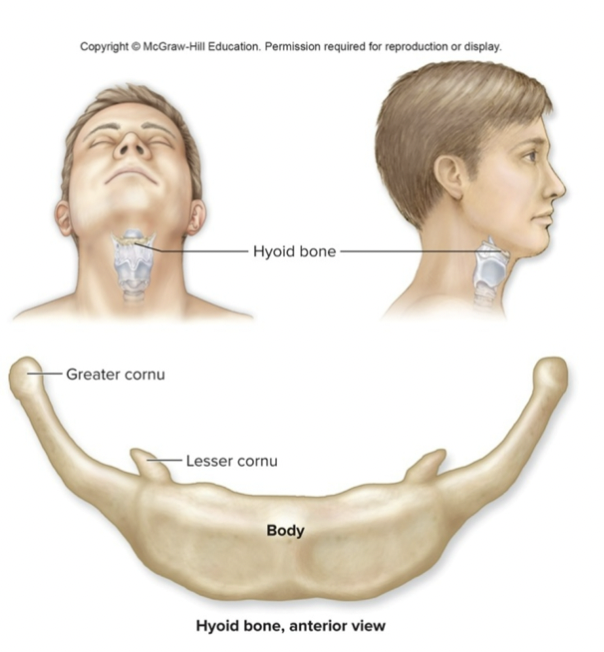
small u shaped inferior to mandible
not connected to other bones
supports the mouth and neck muscles
the vertebral column
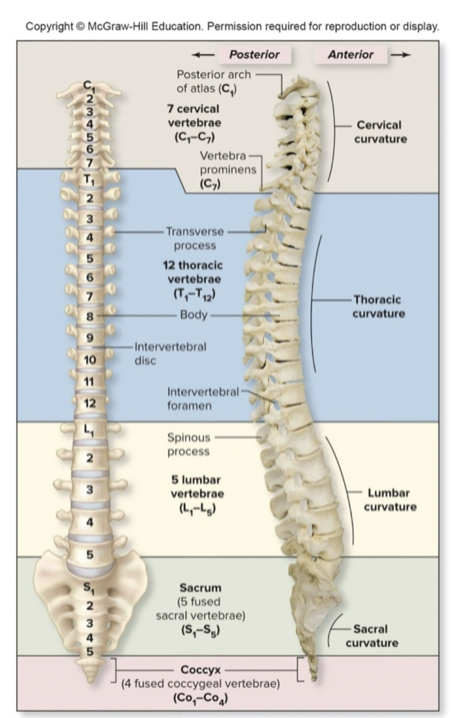
• 26 vertebra
• Cervical 7
• Thoracic 12
• Lumbar 5
• Sacrum 1
(fused)
• Coccyx 1 (fused)
• Intervertebral discs
• 25% of height of column
• Avascular
• Two
parts
• Annulus fibrosus: fibrocartilage (in a ring around the
outside)
• Nucleus pulposus: soft, mucoid substance (center)
function of the vertebral column
• Encloses and protects spine (nervous tissue)
• Supports
head
• Attachment point for ribs, pelvis, and muscles of the
back, upper
and lower limbs
• Balance and shock absorption
structure of the vertebral column
Functions to maintain balance while upright, absorb shocks, protection from fracture
Convex (secondary curves)
• Cervical
• Lumbar
•
Concave (primary curves)
• Thoracic
• Sacral
Kyphosis: “Hunchback
• Increase in thoracic curve
• Seen in the elderly due to
degeneration of
intervertebral discs
Lordosis “Swayback”
• Increase in lumbar curve
• Due to increased weight of
abdomen
• Common in pregnancy
Scoliosis
• Lateral bending
• Often in thoracic region
• May be congenital
Herniated Discs
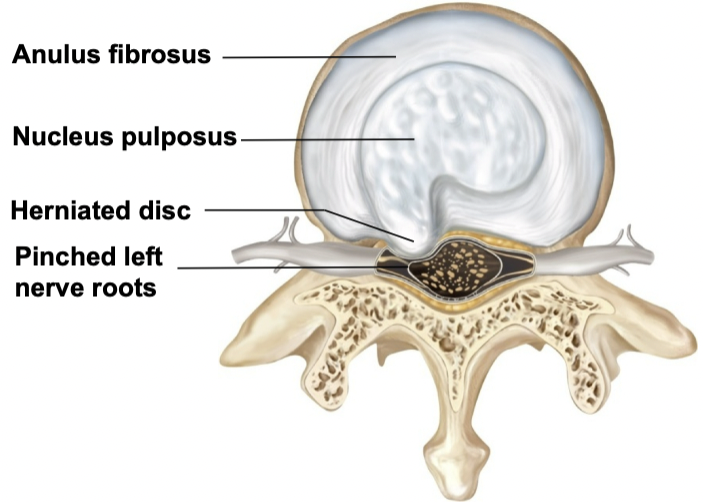
Often seen in the lumbar region of the vertebral
column
•
Annulus fibrosis can be weakened and rupture
• Leads to
protrusion of the nucleus
pulposus→herniated disc
• May
press on spinal nerves, resulting in pain
A “Typical” Vertebra
Processes
• Transverse (2)
• Spinous (1)
• Superior
articular (2)
• Inferior articular (2)
• Vertebral
foramen/canal
• Intervertebral foramen
cervical
• Flatter and smaller
• Smaller bodies and larger vertebral
canals
• Additional hole (transverse foramen) for
vertebral
artery (blood supply to brain)
thoracic
• Larger than cervical, smaller than lumbar
• Additional facets
lumbar
Largest of vertebrae with smallest vertebral canal
C1 atlas
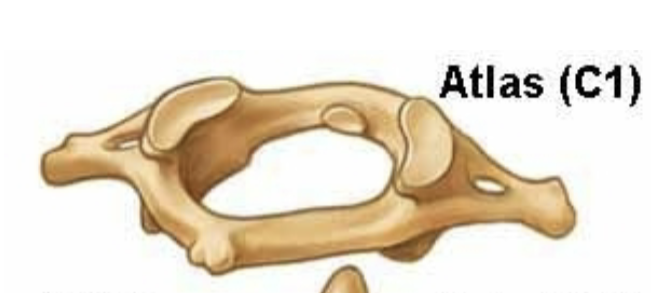
• Ring of bone
• No vertebral body or spinous process
•
Articulates with occipital condyles to make atlanto-
occipital
joint
• Allows to nod head “yes”
C2 axis
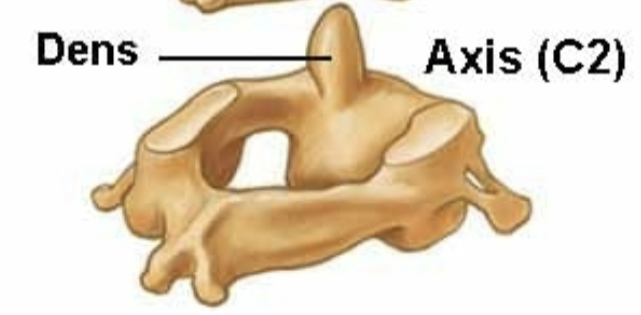
• Dens: process which atlas rotates around
• Allows to shake
head “no”
• Atlanto-axial joint
sacrum
• Fusion of five vertebrae
• Foundation for pelvic girdle
•
Sacral canal
coccyx
Termination of vertebral column
• 3-5 fused vertebrae
•
Fusion complete between 20-30 years old
• “Vestigial Tail”
thoracic cage
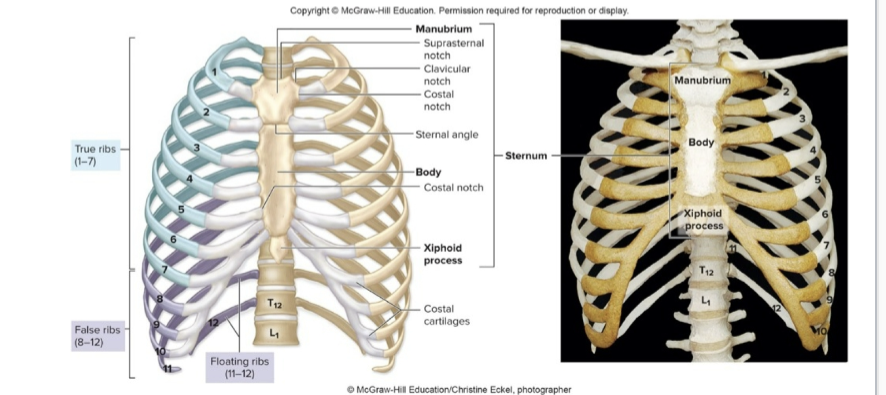
Bony frame around chest composed of:
• Thoracic vertebrae
posteriorly
• Ribs laterally
• Sternum anteriorly
•
Protects heart, lungs, trachea, esophagus, and other thoracic organ
12 pairs of ribs
Articulate posteriorly with thoracic
vertebrae
true ribs
Ribs 1-7
• Connect to sternum via cartilage
false ribs
Ribs 8-10
• Connect via shared cartilage
floating ribs
Ribs 11-12
• Do not join sternum at al
sternum
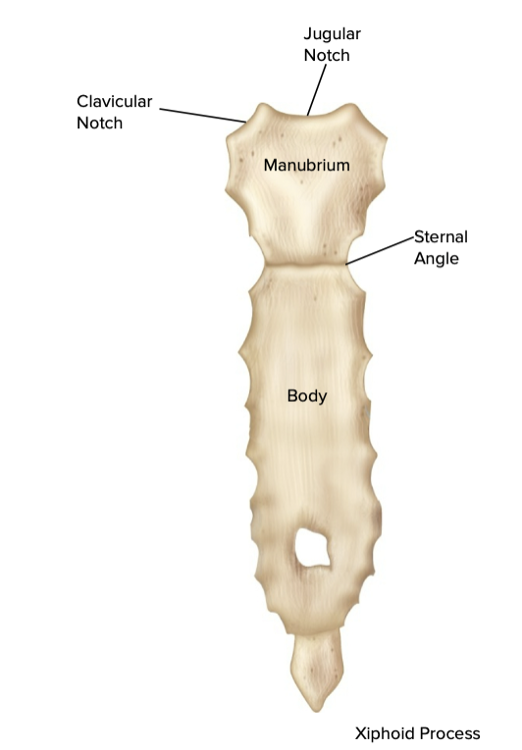
The “breastbone” in anterior midline
• Three parts
•
Manubrium
• Attachment of clavicle & first ribs
•
Body
• Attachment of ribs 2 to 10
• Xiphoid process
•
Sharp point of bone
• Attachment for some anterior abdominal muscles