The density of ethanol is 0.789 g/mL. What is the density in units of kg/m 3 ?
- 789 kg/m3
- 1.27 kg/m3
- 0.0789 kg/m3
- 0.237 kg/m3

789 kg/m 3
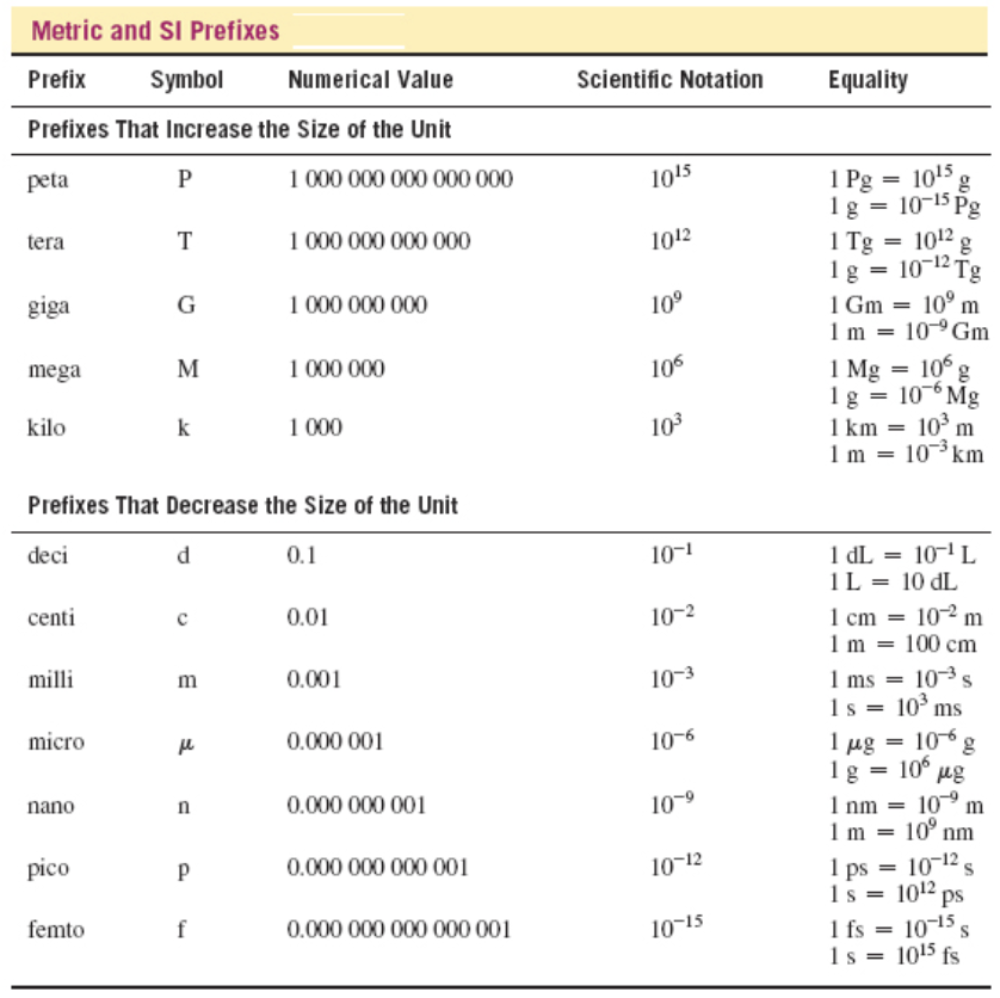
Which of the following equalities can be used to indicate the number of nanoliters (nL) in one liter (L)?
- 1 nL = 1 × 106 L or 1 × 10-6 nL = 1 L
- 1 nL = 1 × 109 L or 1 × 10-9 nL = 1 L
- 1 nL = 1 × 10-6 L or 1 × 106 nL = 1 L
- 1 nL = 1 × 10-9 L or 1 × 109 nL = 1 L
1 nL = 1 × 10 -9 L or 1 × 10 9 nL = 1 L
Ex.
Nanoliters has the prefix nano, which has a numerical value of .000000001 or 1 × 10 -9 . Based on this information, the correct equalities that indicate the number of nanoliters in a liter are the following:
1 nL = 1 × 10 -9 L or 1 × 10 9 nL = 1 L
The other sets of equalities have the wrong magnitudes and do not correctly indicate the size of a nanoliter relative to a liter.
Complete the relationship. __________ mg = __________ µg.
- 1000; 100
- 100; 1000
- 1; 1000
- 1000; 1
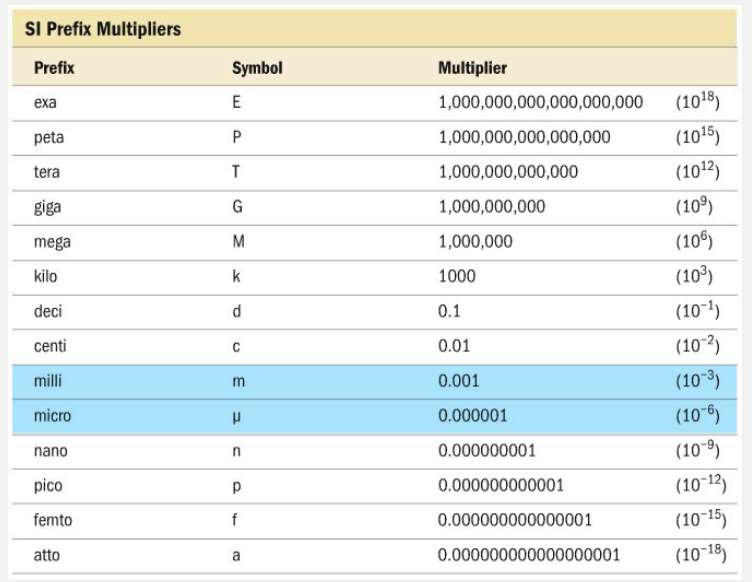
1; 1000
Ex.
A correct relationship between milligrams (mg) and micrograms (µg) is 1 mg = 1000 µg because they differ by three orders of magnitude, with micrograms being smaller than milligrams.
The density of ice is 0.93 g/cm 3 . What is the volume, in cm 3 , of a block of ice whose mass is 5.00 kg? Remember to select an answer with the correct number of significant figures.
- 5.4 × 103 cm3
- 4.3 × 103 cm3
- 4.7 × 103 cm3
- 1.9 × 103 cm3

5.4 × 10 3 cm 3
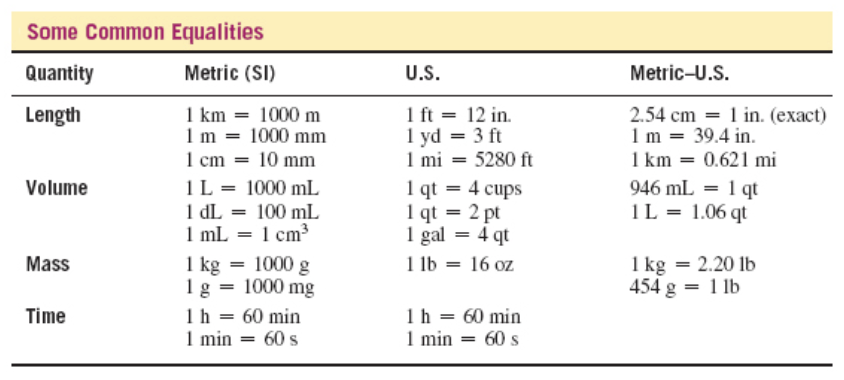
Using the table of equalities, calculate the seconds in one day.
- 86,400 s
- 34,560 s
- 3,600 s
- 2,073,600 s

86,400 s
Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space. Matter exists in three different states: solids, liquids, and gases. Because solids, liquids, and gases all have a well-defined mass, the differences in the state of matter can be determined by their shape and their volume.
Which of the following descriptions describes the gas state?
- Matter in this state has a definite volume, and the shape is determined by the container.
- The shape and volume are determined by the container.
- Matter in this state has a definite shape and definite volume.
The shape and volume are determined by the container.
Ex.
The shape and volume are determined by the container for the gas state.
In a gas, the particles are far apart and move randomly, and at high speeds, throughout the space they occupy. Due to this, a gas fills the entire volume of the container.
Solids have a definite shape and definite volume, whereas liquids have a definite volume but the shape is determined by the container.
Perform the following calculation and give the answer with the correct number of decimal places.
196.395 mg – 3.21 mg
- 193.2 mg
- 193.19 mg
- 193.185 mg
- 193 mg
193.19 mg
Ex.
196. 395 mg – 3. 21 mg = 193.185 mg = 193. 19 mg
In subtraction, the final answer has the same number of decimal places as the measurement having the fewest decimal places. The first measured number, 196.395 mg, has three decimal places and the second measured number, 3.21 mg, has two decimal places. Therefore, the answer should have two decimal places. When you subtract the two numbers, you have 193.185 mg. Because you need the answer with two decimal places, you round off. Because the first digit dropped (5 in this case) is 5 or greater, the last retained digit is increased by 1 to give 193.19 mg.
Mixtures involve two or more substances that are physically mixed or intermingled. However, these substances are not chemically bonded together. Therefore, the mixed substances can be present in any ratio.
There are two types of mixtures: homogeneous and heterogeneous. A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition, whereas a heterogeneous mixture does not have a uniform composition. Because of this, homogeneous mixtures look identical throughout the mixture to our eyes, as we cannot physically see the presence of more than one substance due to the uniformity. In terms of heterogeneous mixtures, we are able to see a physical boundary between different substances within the mixture, indicating the presence of more than one substance.
Which of the following is an example of a homogenous mixture?
- Raisin bran cereal
- Cranberry juice
- Iced tea, with ice cubes
- Chocolate chip cookies
Cranberry juice
Ex.
Cranberry juice is the only homogenous mixture listed, as it has a uniform composition and, as a result, looks identical throughout the mixture.
All of the other substances are heterogeneous mixtures, as they do not have a uniform composition, resulting in physical boundaries between different substances within the mixture.
Which one of the following correctly pairs the prefix with its abbreviation?
- Micro-, m
- Mega-, m
- Giga-, g
- Peta-, P
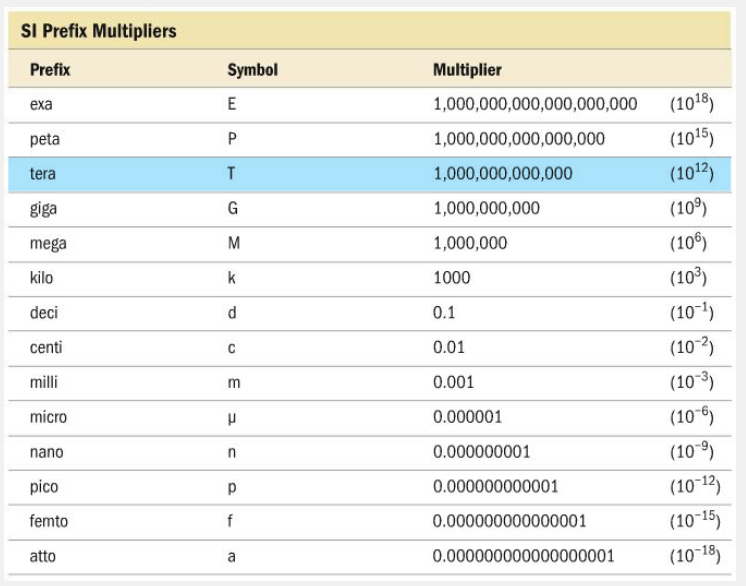
Peta-, P
Ex.
Peta-, P,T correctly pairs the prefix with its abbreviation. The abbreviation for peta- is P. The abbreviation for micro- is µ, while m is the abbreviation for milli-. The abbreviations for giga- and mega- are G and M, respectively. While the letter given in the answer choices is the same, they must be capitalized to be the correct abbreviation.
What is the multiplier for the prefix atto-?
- 1.0 × 10-9
- 1.0 × 10-15
- 1.0 × 10-18
- 1.0 × 10-12
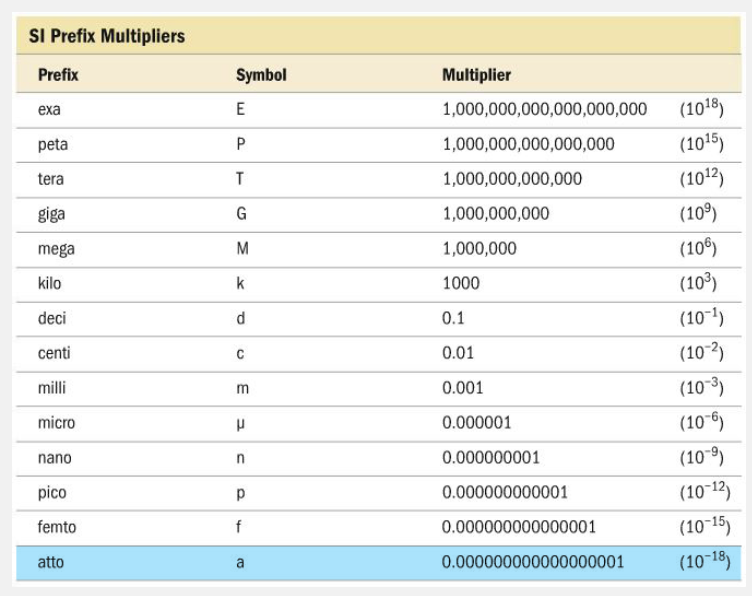
1.0 × 10 -18
Ex.
The multiplier for atto- is 1.0 × 10 -18 . The other multipliers are for nano- (1.0 × 10 -9 ), pico- (1.0 × 10 -1 2 ), and femto- (1.0 × 10 -15 ).
Calculate the density of an object, if the mass is 34.8 g and the volume is 6.2 mL.
density = mass / volume
Remember to select an answer with the correct number of significant figures.
- 5.6 g
- 0.18 g/mL
- 5.6 g/mL
- 0.18 mL

5.6 g/mL
Chemistry involves two basic types of changes: physical and chemical. Associated with these changes are physical properties and chemical properties.
Physical properties are characteristics used to describe the appearance of a substance. This includes observations like the state, color, size, and shape of matter.
Chemical properties are characteristics used to describe the chemical behavior of a substance. This includes observations like reactivity, as well as the inability to react.
Which of the following describes a physical property of copper metal?
- Copper does not react with water.
- Copper slowly oxidizes to form a green patina, like that on the Statue of Liberty.
- At high temperatures, copper forms a black copper oxide.
- Copper metal is ductile. It can be pulled into thin wires.
Copper metal is ductile. It can be pulled into thin wires.
Ex.
Copper metal is ductile. It can be pulled into thin wires. This is an example of a physical property, as the copper is simply undergoing a change in shape.
All of the other examples are descriptions of copper’s reactivity, which are chemical properties.
A cube of copper, which has a density of 8.96 g/cm 3 , has an edge length of 2.50 cm. What is the mass of the sample?
- 22.4 g
- 140. g
- 112 g
- 67.2 g

140. g
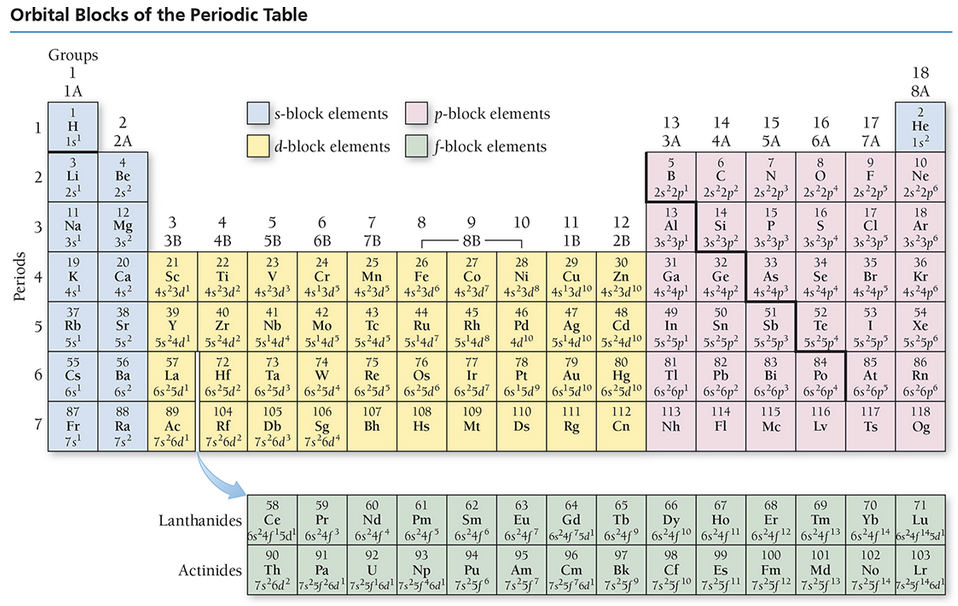
A compound is a form of matter that contains two or more different elements bonded together in a fixed ratio. Because a compound contains only elements bonded in a fixed ratio, it is a pure substance. For instance, water is a compound as it always consists of the elements hydrogen and oxygen. More specifically, water contains two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
Which of the following is an example of a compound?
- Barium, Ba
- Silver, Ag
- Ammonia, NH3
- Aluminum, Al
Ammonia, NH 3
Ex.
Ammonia, NH 3, is the only compound listed, as it comprises two different elements bonded together in a fixed ratio. More specifically, ammonia consists of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms bonded together.
All of the other substances are elements, as they consist of only one type of matter and can be found on the periodic table
Chemistry involves two basic types of changes: physical and chemical.
Physical changes are changes that do not require a change in the chemical identity of a substance. They often involve changes in the state of matter or the creation or separation of a mixture.
Chemical changes are changes that involve a change in the chemical identity of a substance. In other words, a new chemical or substance is created through a chemical change. A chemical change is also thought of as a chemical reaction.
Which of the following is a physical change?
- Photosynthesis in a plant
- Yeast causing dough to rise
- Fruit ripening
- Grinding peppercorns into pepper flakes
Grinding peppercorns into pepper flakes
Ex.
Grinding peppercorns into pepper flakes is an example of a physical change as the peppercorns are being physically altered but there is no change in the chemical identity.
All of the remaining examples are chemical changes as they involve a change in the chemical identity of the original substance due to a chemical reaction.
Perform the following calculation and give the answer with the correct number of significant figures.
32.5 × 0.019
- 0.62
- 0.618
- 0.6
- 0.6175
0.62
Ex.
32.5 × 0.0 19 = 0.6175 = 0.62
3SF 2SF 2SF
In multiplication or division, the final answer is given so it has the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the fewest significant figures. The first number, 32.5, contains three significant figures, and the second number, 0.019, contains two significant figures. The answer should be given with two significant figures. When you multiply the two numbers, you have 0.6175. The last two digits, 75, are dropped. Because the first digit dropped (7, in this case) is 5 or greater, the last retained digit is increased by 1 to give 0.62.
Round 0.003437 L to three significant figures.
- 344 L
- 0.00344 L
- 0.003 L
- 0.0034 L
- 0.00343 L
0.00344 L
Ex.
To round 0.003437 L to three significant figures, drop the last digit, 7. Because the first digit dropped (7 in this case) is 5 or greater, the last retained digit is increased by 1 to give 0.00344 L .
Remember that zeros are not significant if they are at the beginning of a decimal number, so 0.003 L has only one significant figure.
The answer 344 L does have the correct number of significant figures; however, this number is greater than 1 and the original number, 0.003437 L, is a number much less than 1.
There are two types of pure substances: elements and compounds.
An element is the simplest form of matter that retains its own unique properties, which are different from all other elements. The Periodic Table of the Elements lists all of the known elements in the universe.
A compound is a form of matter that contains two or more different elements, bonded together in a fixed ratio. For instance, water is a compound as it always consists of the elements hydrogen and oxygen. More specifically, water contains two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
There are two types of impure substances or mixtures: homogeneous and heterogeneous.
Mixtures involve two or more substances that are physically mixed or intermingled. However, these substances are not chemically bonded together. Therefore, the substances can be present in any ratio.
A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition, whereas a heterogeneous mixture does not have a uniform composition.
Is chicken noodle soup an element, a compound, a homogeneous mixture, or a heterogeneous mixture?
- Homogeneous mixture
- Heterogeneous mixture
- Compound
- Element
Heterogeneous mixture
Ex.
Chicken noodle soup is a heterogeneous mixture as it contains several different substances, and it does not have a uniform composition. As a result, you can clearly identify the noodles in the soup.
Chicken noodle soup cannot be a homogenous mixture, as it does not contain a uniform composition.
Chicken noodle soup cannot be an element or a compound, as they are pure substances, and chicken noodle soup is an impure substance.

Using the table of equalities, calculate the number of kilograms (kg) in 15.8 pounds (lb). Remember to select an answer with the correct number of significant figures.
- 7.18 kilograms
- 34.8 kilograms
- 15.8 kilograms
- 2.20 kilograms

7.18 kilograms
A helium balloon has a volume of 0.503 cubic feet. What is the volume of the balloon in units of cubic centimeters?
- 15.3 cm3
- 1.42 × 104 cm3
- 6.53 × 103 cm3
- 46.0 cm3

1.42 × 10 4 cm 3
Chemistry involves two basic types of changes: physical and chemical.
Physical changes are changes that do not require a change in the chemical identity of a substance. They often involve changes in the state of matter or the creation or separation of a mixture.
Chemical changes are changes that involve a change in the chemical identity of a substance. In other words, a new chemical or substance is created through a chemical change. A chemical change is also thought of as a chemical reaction.
Which of the following is a chemical change?
- A piece of iron is molded into a nail.
- Hair is cut.
- Butter melts in a pan.
- Meat spoils when it is not refrigerated.
Meat spoils when it is not refrigerated.
Ex.
Meat spoils when it is not refrigerated. This is an example of a chemical change, as microorganisms grow and breakdown the meat. Both the growth of microorganisms and the breakdown of meat are chemical reactions, which are also considered to be chemical changes.
All of the remaining examples are physical changes as they do not involve a change in the chemical identity of the original substance. In other words, the chemical identity of the substance remains the same.
How many significant figures are there in the measured quantity 0.0304 L?
- Two significant figures
- Three significant figures
- Five significant figures
- Four significant figures
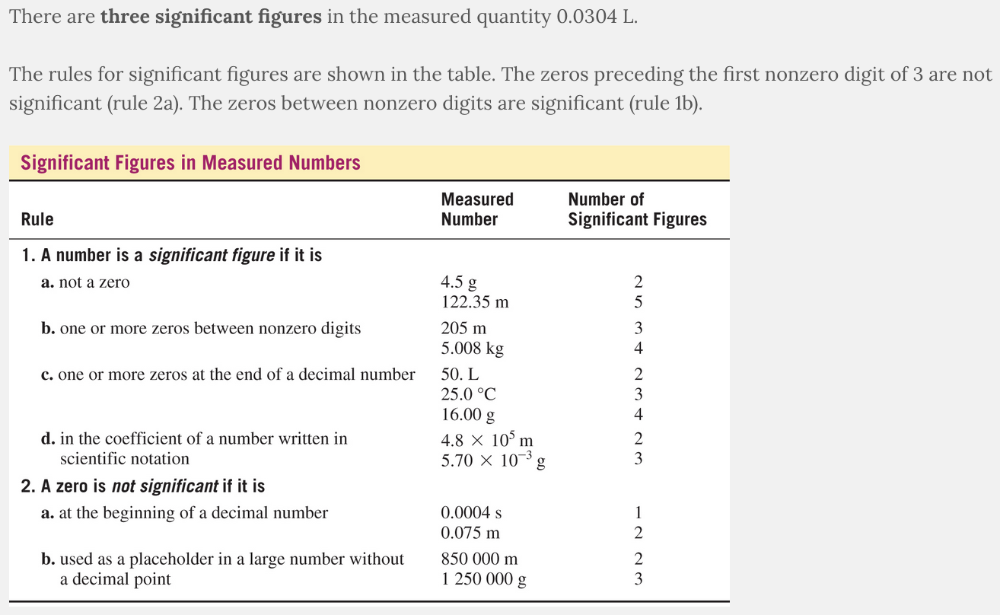
Three significant figures

Using the table of equalities, select the correct conversion factors that indicate the number of grams (g) in one pound (lb).
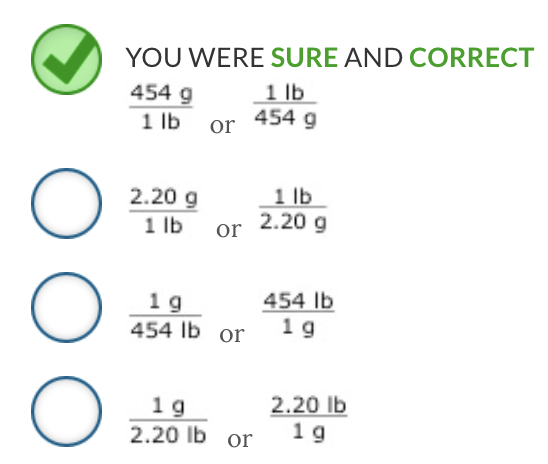
Ex.
According to the table of equalities, 454 g = 1 lb ; therefore, the correct conversion factors are:
454 g / 1 lb or 1 lb / 454 g
A car is travelling 35 miles per hour. How fast is it going when measured in meters per minute?
- 7.7 × 102 m/min
- 3.6 × 102 m/min
- 34 m/min
- 9.4 × 102 m/min

9.4 × 10 2 m/min

Select the correct conversion factors based on the information in the following statement:
One gallon of milk costs $3.50
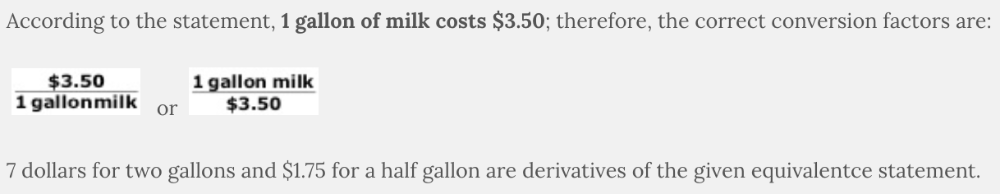
Which unit represents a value that is one order of magnitude larger than a decimeter?
- Millimeter
- Meter
- Centimeter
- Decameter

Meter
Rank the following in order of increasing size (smallest to largest).
- 1 millimeter, 1 decimeter, 1 picometer, 1 nanometer
- 1 picometer, 1 nanometer, 1 millimeter, 1 decimeter
- 1 decimeter, 1 picometer, 1 nanometer, 1 millimeter
- 1 nanometer, 1 decimeter, 1 picometer, 1 millimeter

1 picometer, 1 nanometer, 1 millimeter, 1 decimeter
Which pair correctly matches the symbol for a prefix with its multiplier?
- k, 1.0 × 106
- n, 1.0 × 109
- G, 1.0 × 109
- c, 100
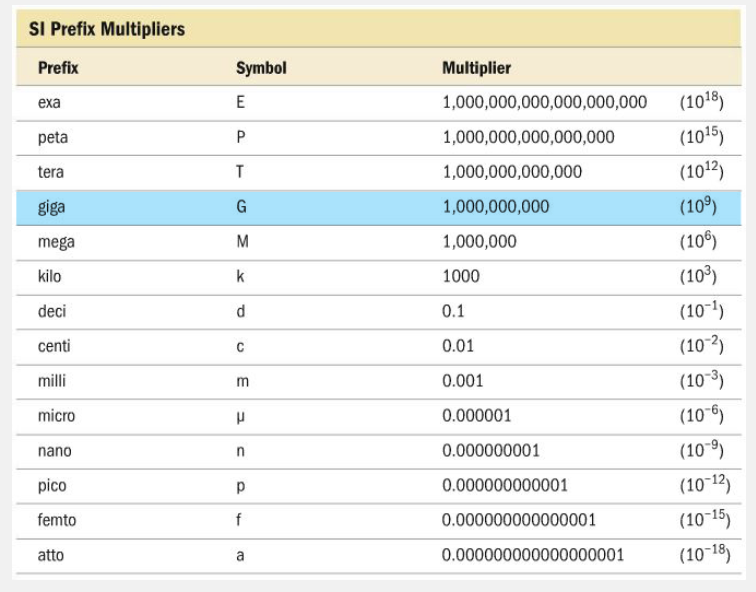
G, 1.0 × 10 9
Ex.
G, 1.0 × 10 9 correctly matches the symbol for a prefix with its multiplier.
The prefix giga- is abbreviated G and has 1.0 × 10 9 as its multiplier. Nano- (n), centi- (c), and kilo- (k) have multipliers of 1.0 × 10 - 9 , 0.01, and 1000, respectively.
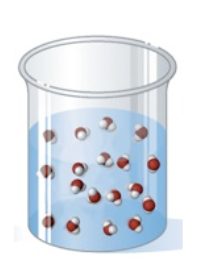
Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space. Matter exists in three different states: solids, liquids, and gases. Because solids, liquids, and gases all have a well-defined mass, the differences in the state of matter can be determined by their shape and their volume.
On the micro-level, or the atomic level, the particles in the three states of matter are also arranged differently, which helps to contribute to their unique properties.
In the solid state, the particles are well organized and very close together. This results in the solid state having a fixed shape and fixed volume.
In the liquid state, the particles move slowly, move in random directions, and are close together, due to their attractions. This results in the liquid state having a well-defined volume but taking on the shape of the container.
In the gas state, the particles move quickly and in random directions. As a result, the particles are far apart and fill the container. Therefore, the volume and shape of a gas are determined by the container.
The figure given below depicts one of the three states of matter on the micro-level. Which state of matter is shown?
- Liquid
- Solid
- Gas
Liquid
Ex.
The image depicts the liquid state, as the liquid takes the shape of the container and has a well-defined volume. In addition, the particles are randomly organized but relatively close to one another, as can be seen on the micro-level.
Chemistry involves two basic types of changes: physical and chemical. Associated with these changes are physical properties and chemical properties.
Physical properties are characteristics used to describe the appearance of a substance. This includes observations like the state, color, size, and shape of matter.
Chemical properties are characteristics used to describe the chemical behavior of a substance. This includes observations like reactivity, as well as the inability to react.
Which of the following describes a chemical property of water?
- Water is liquid at room temperature.
- Water boils at 100 °C.
- Water is a colorless liquid.
- Water reacts violently with sodium metal.
Water reacts violently with sodium metal.
Ex.
Water reacts violently with sodium metal. This is an example of a chemical property that demonstrates the chemical reactivity, or behavior, of water.
All of the other examples are descriptions of water’s appearance and physical traits, which are physical properties.
Complete the relationship. 1 millimeter = __________ meter.
- 1000
- 0.001
- 100
- 0.01
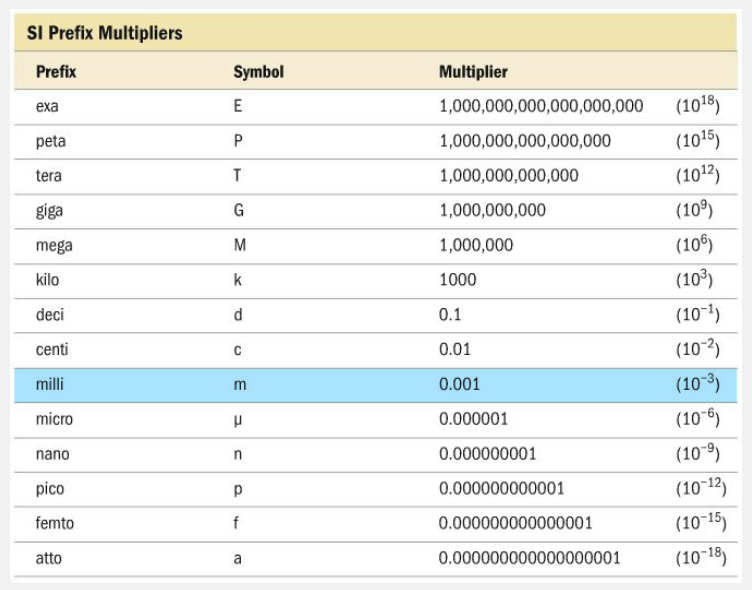
0.001
Ex.
1 millimeter = 0.001 meter.
The prefix milli- indicates 1/1000 (0.001) of a meter, so 1 millimeter is equal to 0.001 meters.