Changes in state are called phase changes. A phase change is a change from one physical state (gas, liquid, or solid) to another. The amount of energy necessary to melt 1 mole of any solid is called its enthalpy of fusion. The amount of energy necessary to vaporize 1 mole of any substance is called its enthalpy of vaporization.
The enthalpy of vaporization of liquid water is 40.65 kJ/mol. Calculate the energy required to vaporize 12.5 g of liquid water.
- 3.26 kJ
- 508 kJ
- 28.2 kJ
- 58.6 kJ

28.2 kJ
We use specialized vocabulary to describe the properties of solids.
Which statement best defines the term “crystalline” when used to describe a solid?
- A crystalline solid has no long-range order of atoms.
- A crystalline solid has a well-ordered arrangement of atoms.
- Crystalline solids have a high density.
- Crystalline solids have a low density.
A crystalline solid has a well-ordered arrangement of atoms.
Ex.
A crystalline solid has a well-ordered arrangement of atoms . An amorphous solid has no long-range order of atoms. The definition of crystalline does not say anything about the density of the solid.
Intermolecular forces are the interactions between molecules and are generally weaker than bonds within molecules.
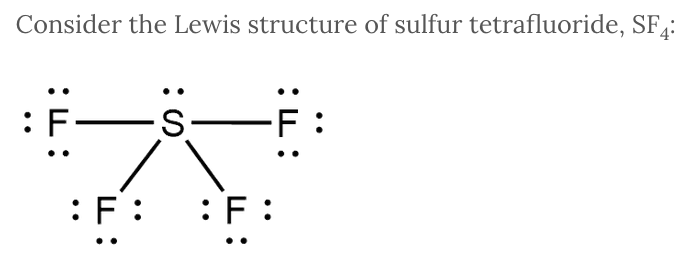
Consider the Lewis structure of sulfur tetrafluoride, SF 4 :
What types of intermolecular forces are found in SF 4 ?
- Dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding
- Dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding
- Dispersion and dipole-dipole forces
- Only dispersion forces
- Only hydrogen bonding
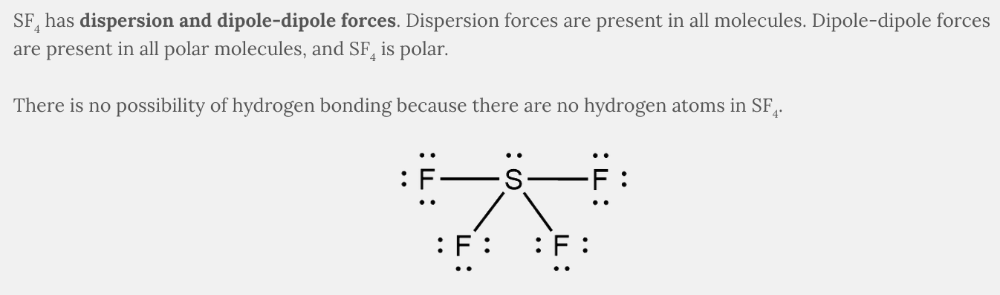
Dispersion and dipole-dipole forces
Intermolecular forces are the interactions between molecules and are generally weaker than bonds within molecules.
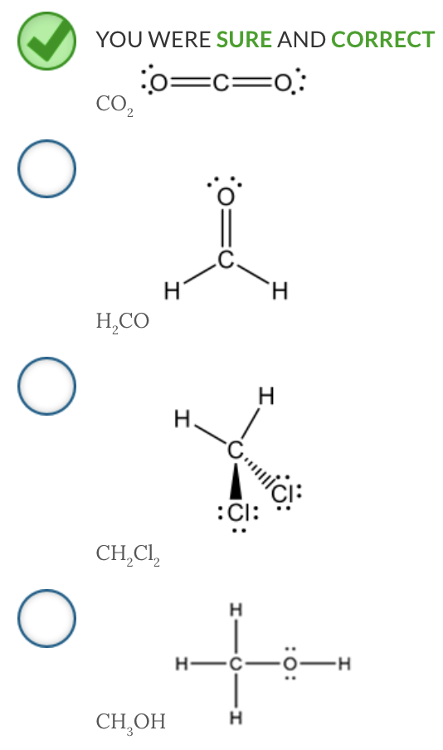
Which molecule has only dispersion forces with like molecules?
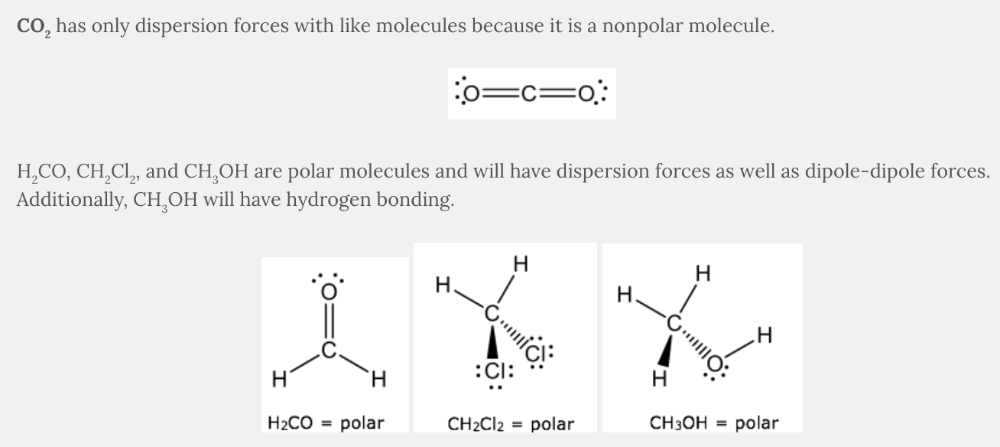
CO2
Intermolecular forces are the interactions between molecules and are generally weaker than bonds within molecules.
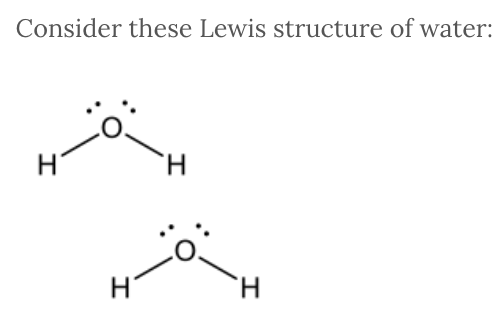
Consider these Lewis structure of water:
____
What type of interaction occurs between hydrogen of water and the oxygen of another water molecule?
- Hydrogen bonding
- Ionic forces
- Dipole-dipole forces
- Dispersion forces
- Ion-dipole forces
Hydrogen bonding
Ex.
The intermolecular force between the hydrogen in water and the oxygen of another water molecule is hydrogen bonding . Hydrogen bonding occurs between a hydrogen attached to a fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen on one molecule and the fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen on another molecule.
Dispersion forces occur between two nonpolar molecules.
Dipole-dipole forces occur between two polar molecules.
Ion-dipole forces occur between an ion and a polar molecule.
Ionic forces occur between two ions of opposite charges.
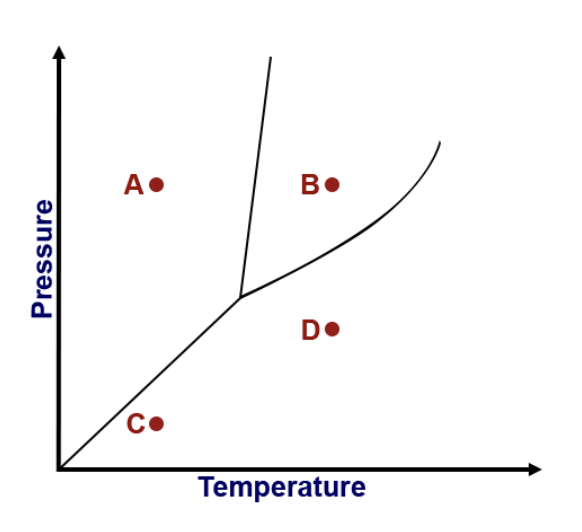
What type of phase change occurs going from A to B on the phase diagram?
- Fusion
- Vaporization
- Condensation
- Sublimation
- Deposition
- Freezing
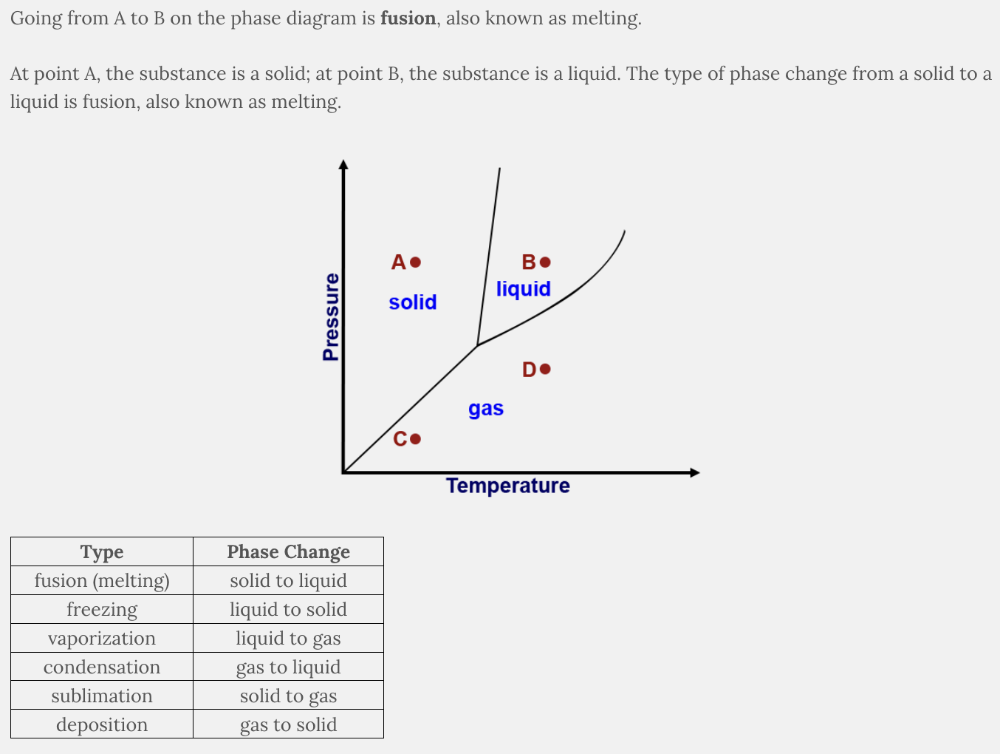
Fusion
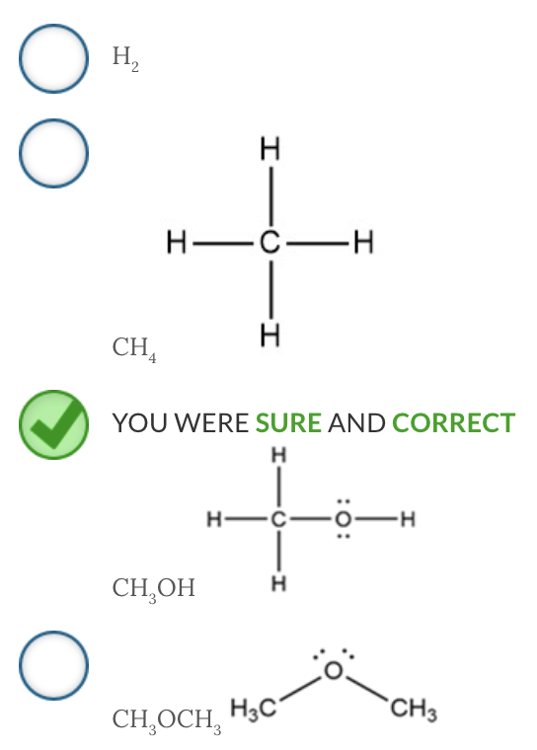
Intermolecular forces are the interactions between molecules and are generally weaker than bonds within molecules.
Which molecule will have hydrogen bonding between like molecules?
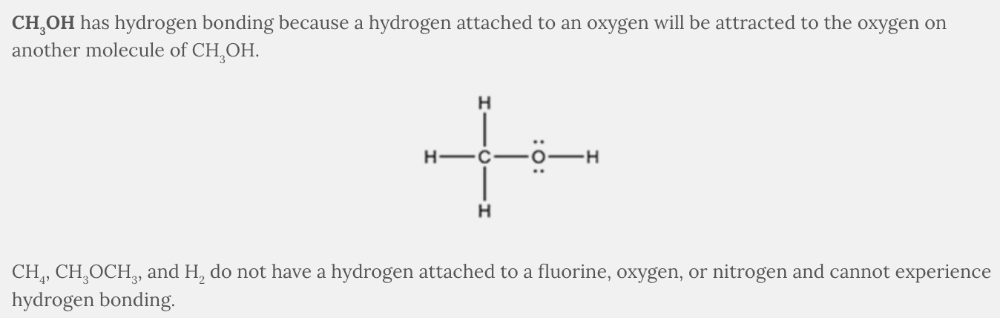
CH 3 OH
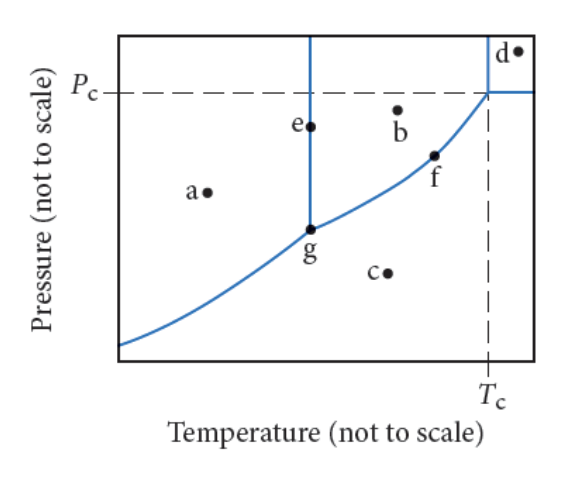
Phase diagrams show the conditions under which each phase of matter exists and the lines indicate the equilibrium between two or more phases.
Identify the point in the diagram where the substance exists as a solid.
- c
- b
- d
- a
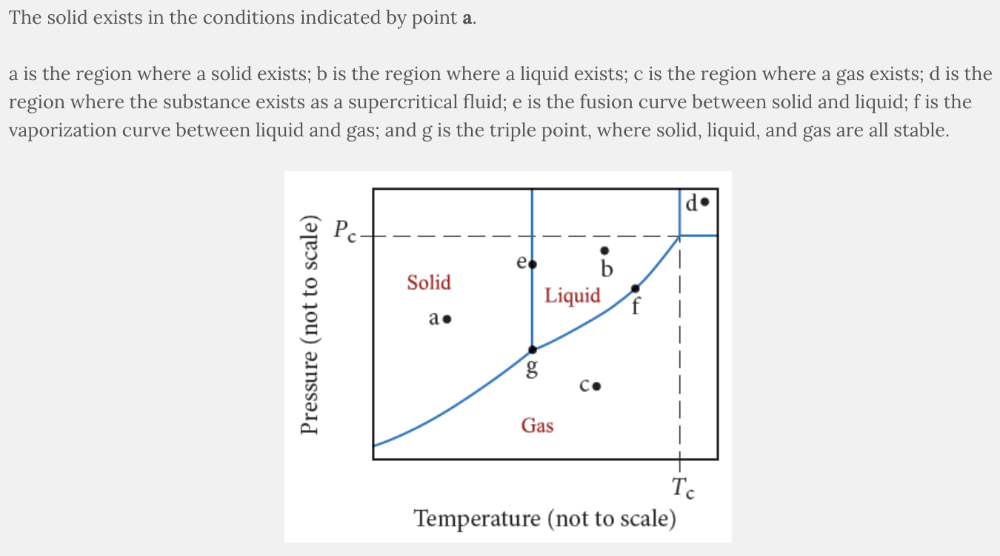
a

How much energy is required to take a 22.0-g sample of liquid water at 25.0 °C to steam at 145.0 °C?
- 2.50 kJ
- 5.50 kJ
- 58.6 kJ
- 55.0 kJ

58.6 kJ
Ex.
The energy required to take a 22.0-g sample of liquid water at 25.0 °C to steam at 145.0 °C is 58.6 kJ .
To find the energy needed for this process, determine the steps included since a substance can either change phase or change temperature but not both at the same time. The heats are calculated using the specific heat (which vary by the phase) and the enthalpies of the phase changes.
What is the triple point?
- The point at which none of the three phases can exist
- The point when the temperature is three times the value of the pressure
- The point when the values of the temperature and pressure are equal to one another
- The point at which all three phases are in equilibrium
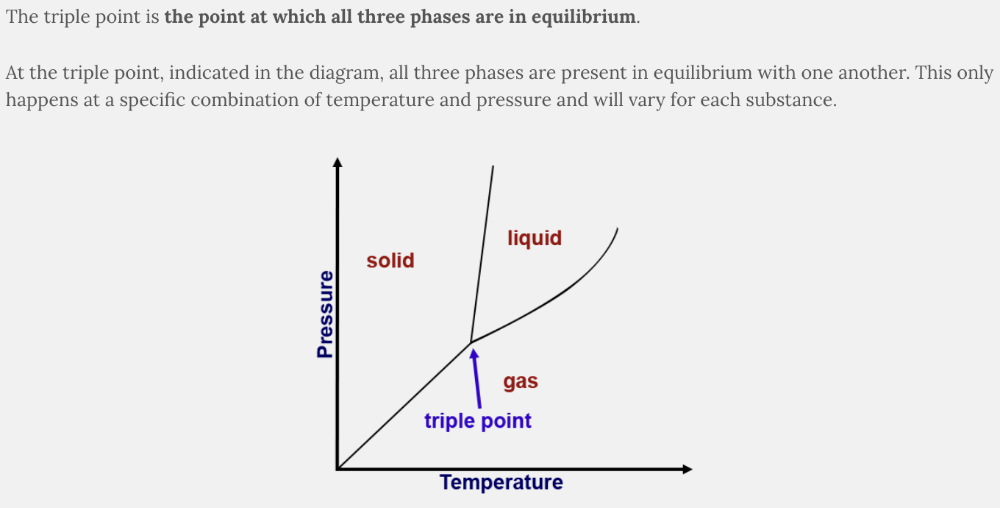
The point at which all three phases are in equilibrium
What phase change is known as vaporization?
- Gas to solid
- Solid to liquid
- Gas to liquid
- Liquid to solid
- Liquid to gas
- Solid to gas
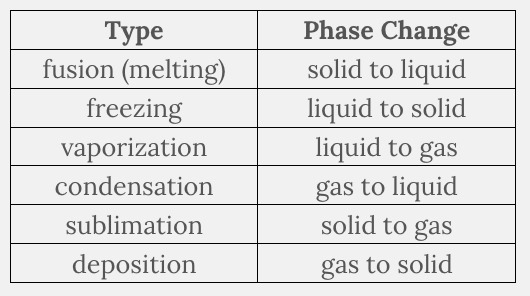
Liquid to gas
Ex.
Vaporization is the phase change from liquid to gas .
What term identifies the phase change from solid to liquid?
- Fusion (melting)
- Condensation
- Sublimation
- Freezing

Fusion (melting)
Ex.
The phase change from solid to liquid is known as fusion (melting) . Freezing is the phase change from liquid to solid. Sublimation is the phase change from solid to gas. Condensation is the phase change from gas to liquid.
How much energy is needed to vaporize 25.0 g of H 2 O at 100 °C, given that ΔH vap of water = 40.7 kJ/mol?
- 11.1 kJ
- 163 kJ
- 29.3 kJ
- 56.5 kJ

56.5 kJ
Select the true statement regarding the enthalpy of phase changes.
- The enthalpy of fusion equals the enthalpy of freezing.
- The enthalpy of vaporization is endothermic.
- The enthalpy of vaporization equals the enthalpy of fusion.
- The enthalpy of vaporization is exothermic.
The enthalpy of vaporization is endothermic.
Ex.
The enthalpy of vaporization is endothermic.
Both the enthalpy of vaporization and fusion are endothermic, whereas the enthalpy of condensation and freezing are exothermic. The enthalpy of vaporization does not equal the enthalpy of fusion.
What is the change in heat when 50.0 g of isopropyl alcohol (C 3 H 8 O) melts, given that ΔH fus of isopropyl alcohol = 5.37 kJ/mol?
- 6.45 kJ
- 5.60 kJ
- 5.37 kJ
- 4.47 kJ

4.47 kJ
The vapor pressure of dichloromethane at 260 K is 71 torr. What is the vapor pressure at 310 K, given that Δ H vap = 31.4 kJ/mol?
- 851 torr
- 1785 torr
- 708 torr
- 737 torr
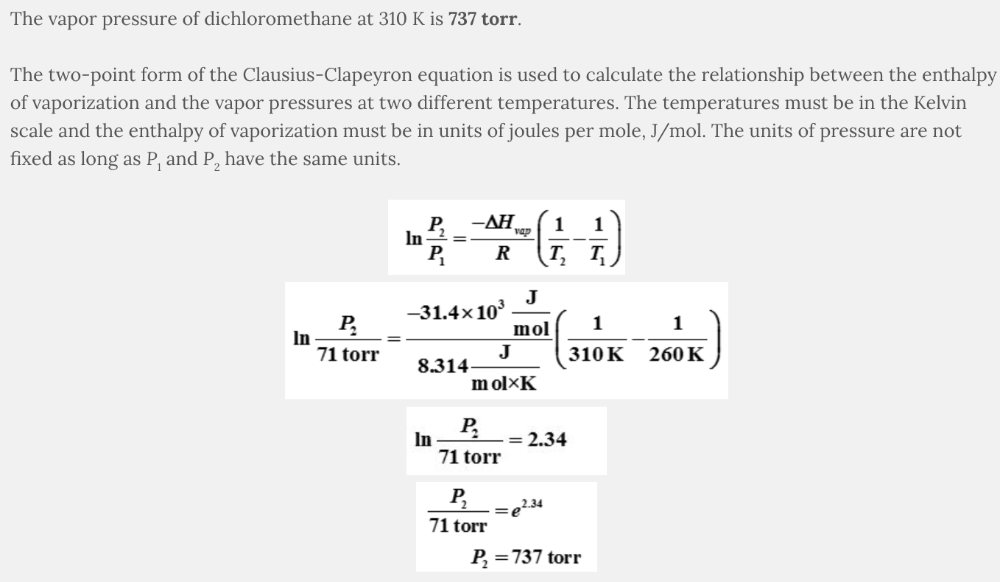
737 torr
We use specialized vocabulary to describe the properties of solids, liquids, and gases.
Select the true statement about the properties of gases.
- Gases have a definite shape and definite volume.
- Gases have an indefinite shape and a definite volume.
- Gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume.
- Gases have a definite shape and an indefinite volume.
Gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume.
Ex.
Gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume. Solids have a definite shape and definite volume. Liquids have an indefinite shape and a definite volume.