Where is the articulation?
between femoral head and acetabulum
Deep hip sockets =
stability
large muscles =
large torques to generate ambulation/movement
Osteology: Innominate
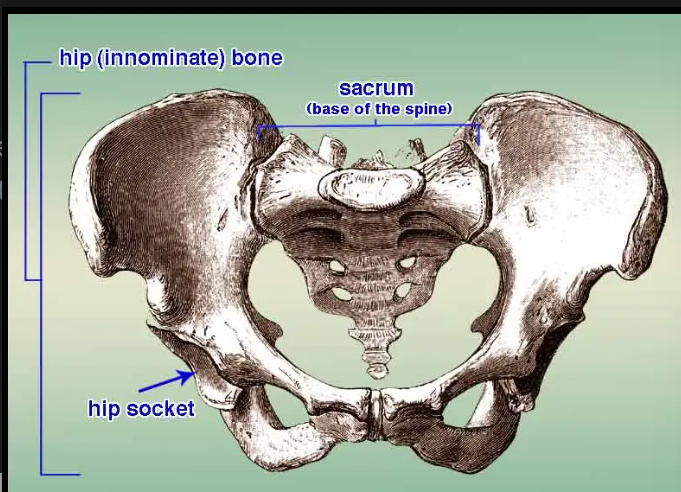
- union of 3 bones: ilium, pubis, ischium
Osteology: Illium
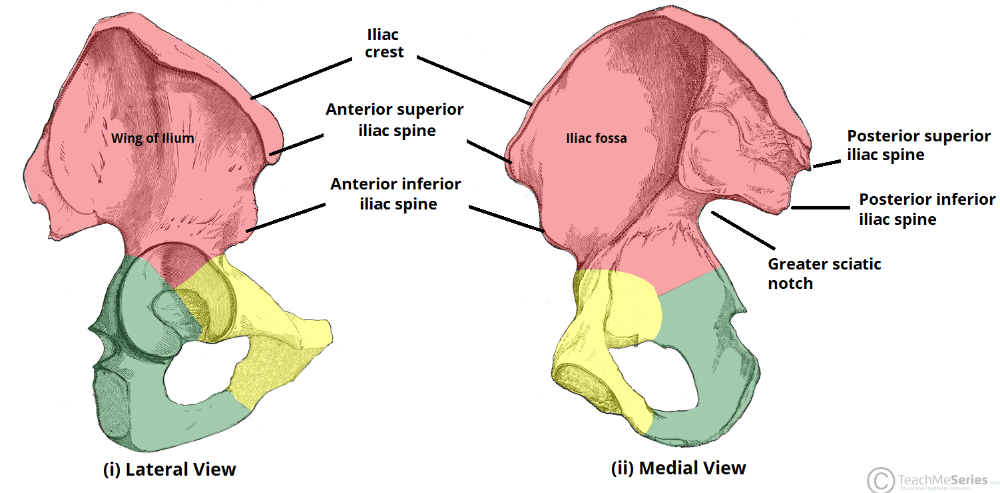
-
3 noticeable features:
- iliac fossa (iliac muscle attachment)
- articular surface (articulate w/ sacrum @sacroliac joint)
- iliac tuberosity (sacroiliac ligament attachment)
Osteology: Pubis
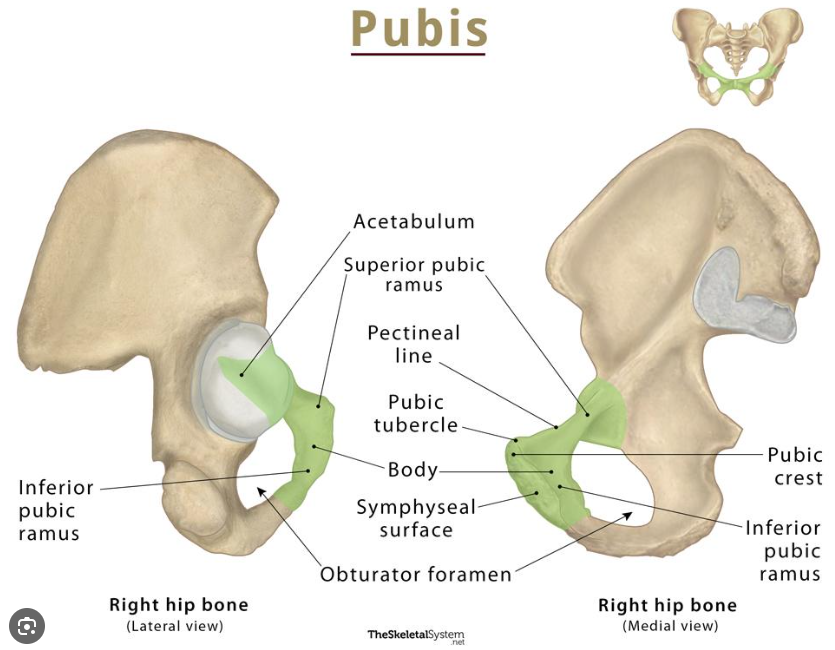
- pubic crest (upper part+attach with rectus abdominus muscle))
- pubic tubercle (inguinal ligament attachment)
- inferior pubic ramus (body to ischium junction)
- pubic symphysis joint+disk (midline of 2 pubic bones)
- interpubic disc (p. symp joint bounding)
PSA
zz
Osteology: Ischium
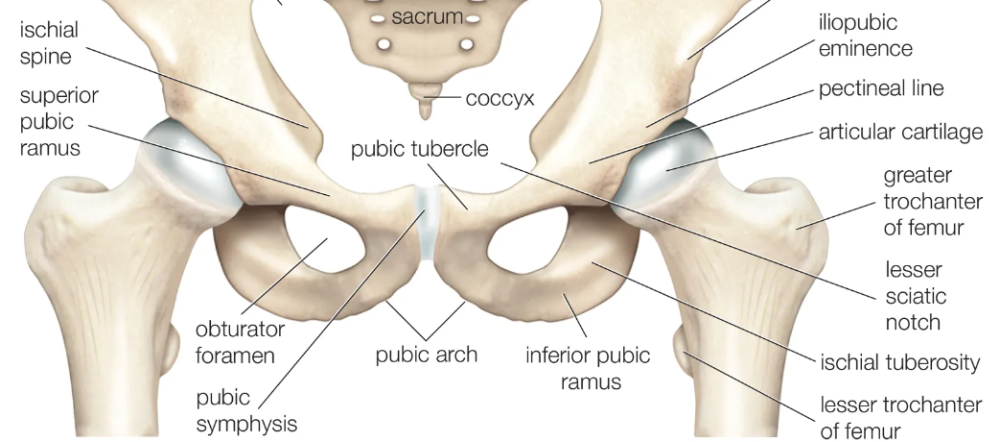
- very stable // force transmission // giant pressure, fitting ring
- ischial spine (BEHIND + ischium + below greater SN)
- lesser sciatic notch (below spine)
- lesser sciatic foramen (sacrospinous + sacrotuberous ligament)
- ischial tuberosity (attachment for hamstrings/adductor magnus)
- ischial ramus
Osteology: Acetabulum
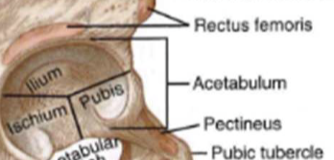
- deep, circular socket (ilium + ischium= 75%, pubis = 25%)(little vinegar cup)
osteology femur
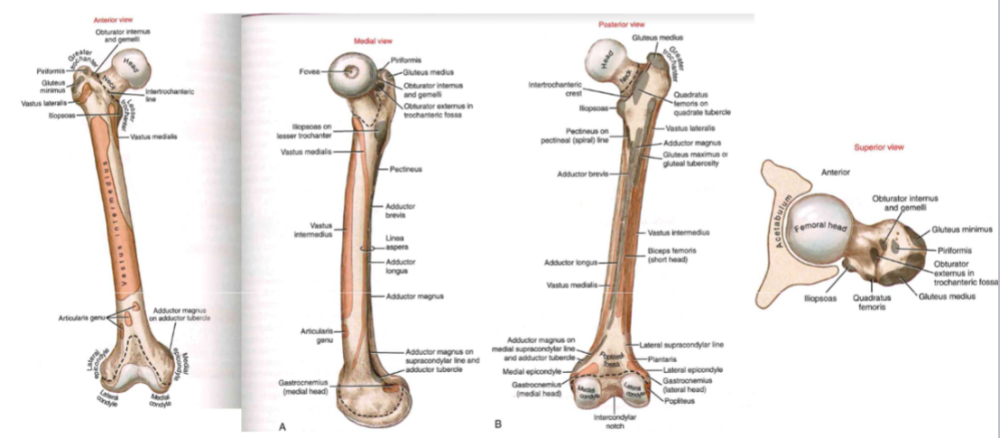
- longest + strongest bone in body
- force travels up the head //allowing for a deep socket cover
- angle = where ground reaction goes
-
shaft = bowing with body weight,
- compressed (along post, shaft)
- tension (along ant. shaft)
- lesser trochanter: post-medial direction, distal attachment for iliopsoas muscle (hip flexor+vertical stabilizer)
Osteology: Proximal Femur, angle of
inclination
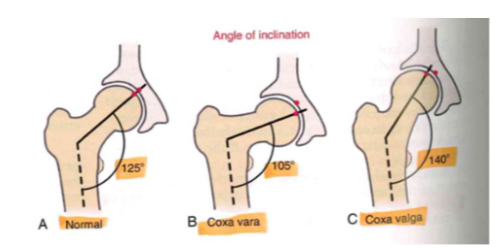
- normal (125 degrees)
-
coxa vara (105 degrees)
- bowing in legs
-
coxa valga (140 degrees)
- bowing in legs
- in childhood from crawling
Osteology: Proximal Femur, femoral
torsion (EXCESSIVE)
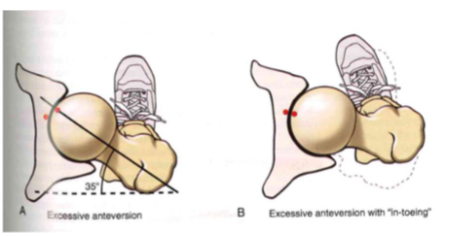
- EX. ant: in kids // 35 degrees
- pigeon walking
- femur tilt forward (affects hips) // "in-toeing" improves joint congruity
Osteology: Proximal Femur, femoral
torsion (3 versions)
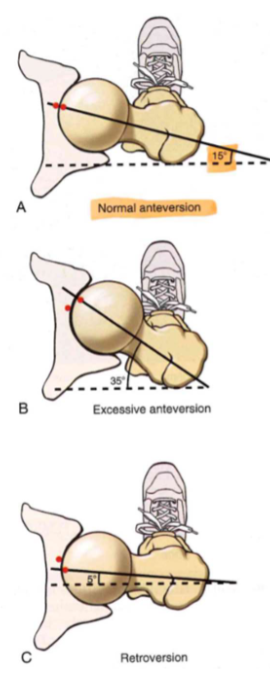
- normal ant (15 degrees_)
- excessive ant (35 degrees)
- retroversion (15 degrees)
Osteology: Proximal Femur, internal structure
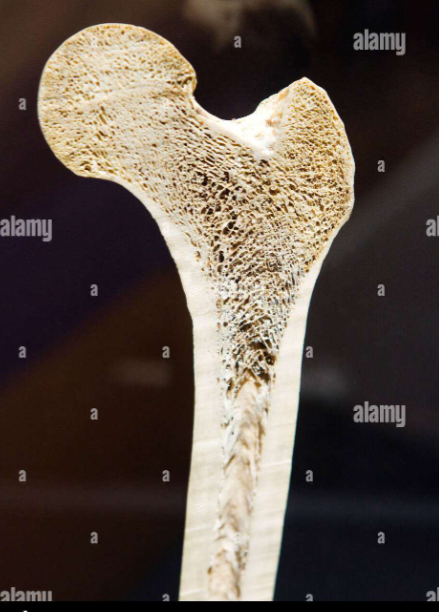
- boney anatomy: resist/counterforce
- tension+compression+shear tension => VERY DYNAMIC SYSTEM
- compact + TROCHLEAR bone: thick sides resist tension + shear
Arthrology: Femoral Head
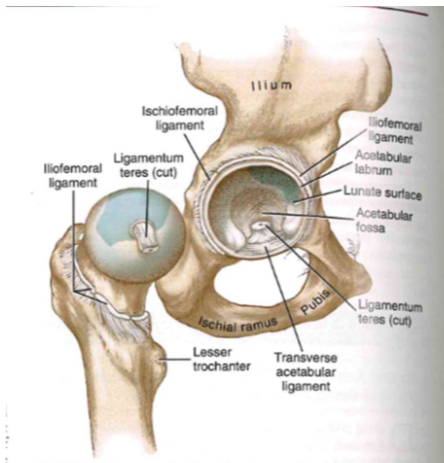
- 2/3 of a perfect sphere
- increased blood flow in children
- ligament teres (ligament to head of femur)
- fovea: prominent pit
Arthrology: Acetabulum
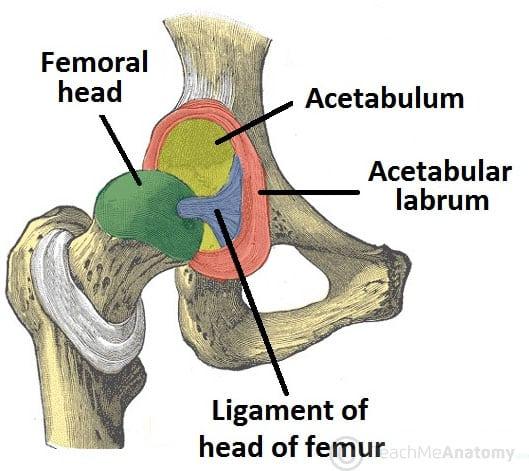
- horseshoe shape represents THICKNESS
- top = more cartilage (x3.5 more thicker)
- bottom = less cartilage
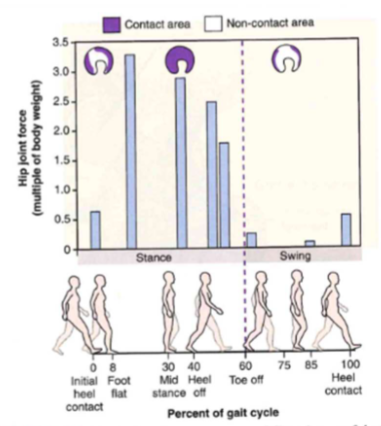
GRAPH: Hip estimate walk
Arthrology: Acetabular labrum

- deep in socket (additional labrum) = adds 30% of depth
- very hard to dislocate hips = strong vacuum mechanism (negative pressure), grips femoral head in socket
- poorly vascularized: slow healing
Arthrology: Acetabular alignment, center-
edge angle
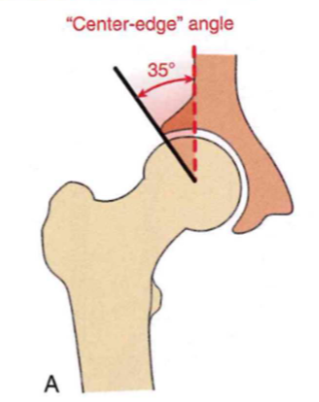
-
central edge angle = 35 degrees
- how much acetabulum covers the femoral head, good for stable + mobility
- LOW (<35 degrees) = less acetabulum cover, 50% less joint pressure, premature degeneration/osteoarthritis
- HIGH (>35 degrees) = more ACT. cover+stable, lead to impingement/injury, can't sit down
Arthrology: Acetabular anteversion angle
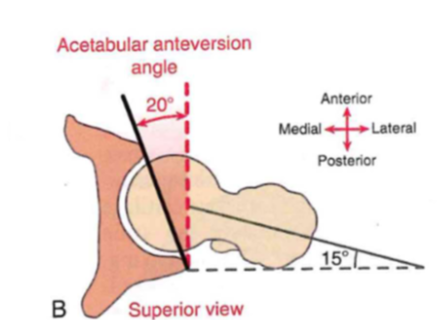
- angle = 20 degrees
- anterior to posterior coverage
- back cover = deeper (squat
Arthrology: Capsule & ligaments
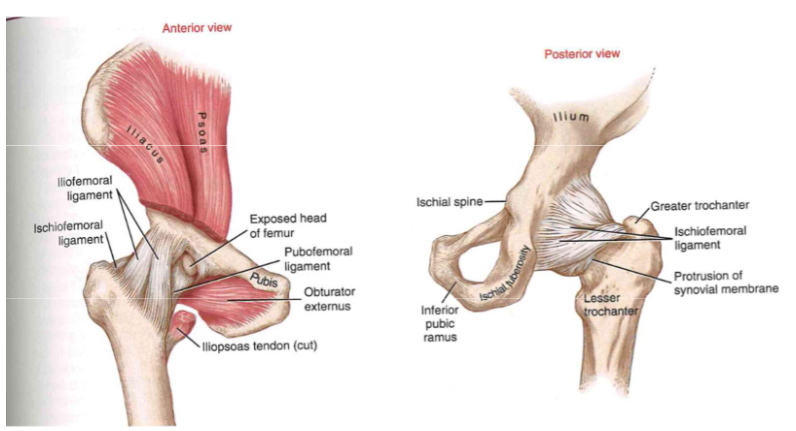
- nature's duct tape (giant ball of leather)
- lots of stuff = had to dislocate
Arthrology: Capsule & ligaments (TABLE)
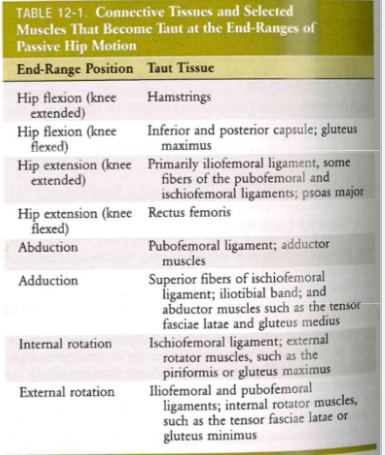
- end range position + taut tissue
- hip flexion (knee extended) => hamstring
Arthrology: Closed-packed position
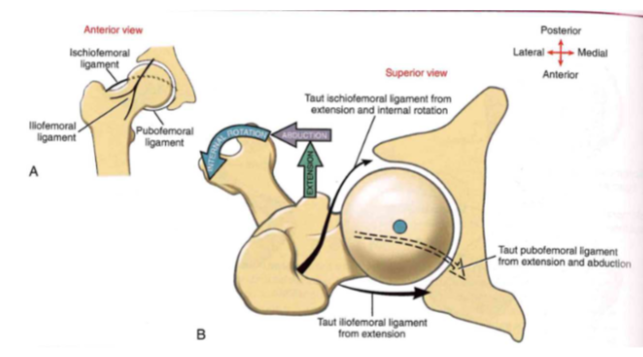
- most stable passive position
-
taut structures: ischiofemoral ligament,
iliofemoral ligament, pubofemoral ligament
- ischiofemoral ligament: extension + internal rotation
- iliofemoral ligament: extension
- pubofemoral ligament: extension and abduction
Osteokinematics: femoral-on-pelvic or pelvic-on-femoral
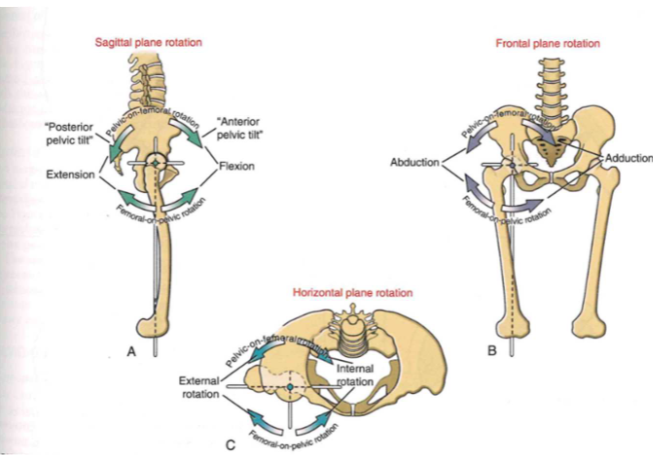
-
extension + flexion
- (TOP = P.on.F)(BOT= F.on.P)
-
abduction + adduction
- (TOP = P.on.F)(BOT= F.on.P)
-
ext. rotation + ir. rotation
- (BACK = P.on.F)(FRONT = F.on.P)
Osteokinematics: femoral-on-pelvic or pelvic-on-femoral (SAGITAL PLANE)
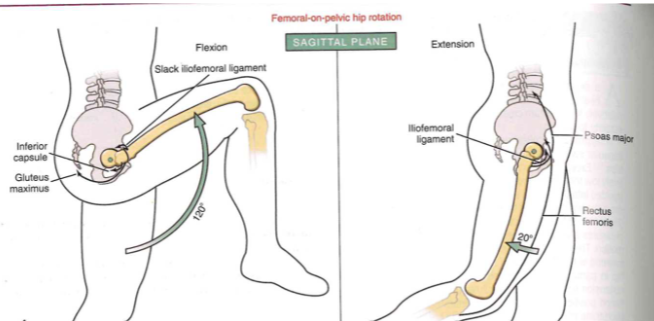
- femoral on pelvic hip rotation
- leg up (120 degrees)
- leg back (20 degrees)
Osteokinematics: femoral-on-pelvic or pelvic-on-femoral (FRONTAL PLANE)
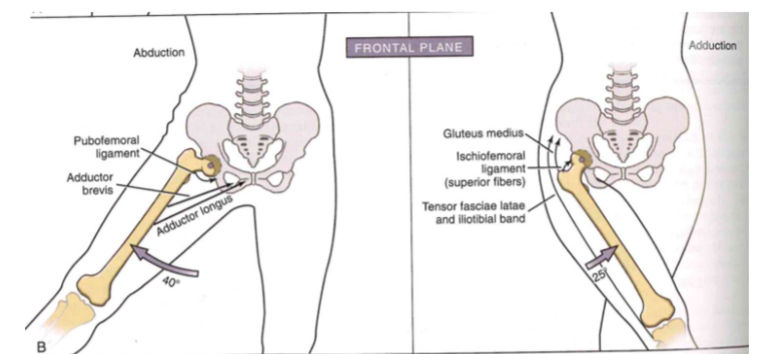
- abduction // leg out to side (40 degrees)
- adduction // leg in (25 degrees)
Osteokinematics: femoral-on-pelvic or pelvic-on-femoral (HORIZONTAL PLANE)
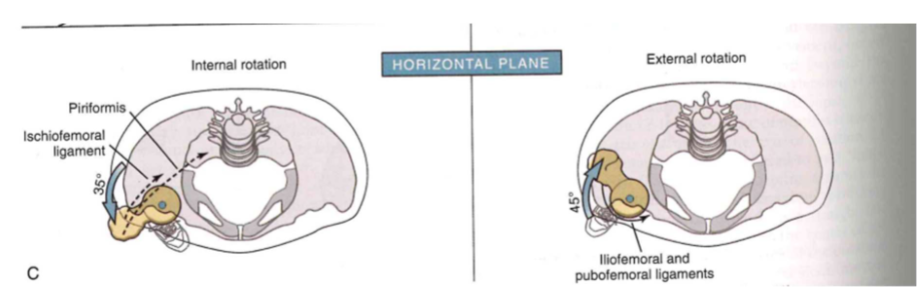
-
internal rotation // foot in (35 degrees)
- piriformis // ischiofemoral ligament
-
external rot // foot out (45 degrees)
- pubofemoral + lliofemoral ligament
Osteokinematics: femoral-on-pelvic or pelvic-on-femoral (SAGITAL PLANE)
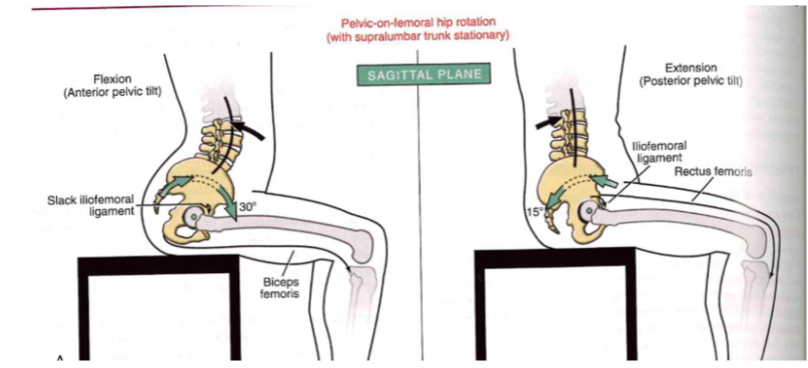
- pelvic on femoral hip rotation
-
flexion (ant. pelvic tilt) // straighten back
- slack iliofemoral ligament (30 degrees) + biceps femoris
-
extension (post. pelvic tilt)
- lliofemoral ligament (15 degrees) + rectus femoris
Osteokinematics: femoral-on-pelvic or pelvic-on-femoral (FRONTAL PLANE)
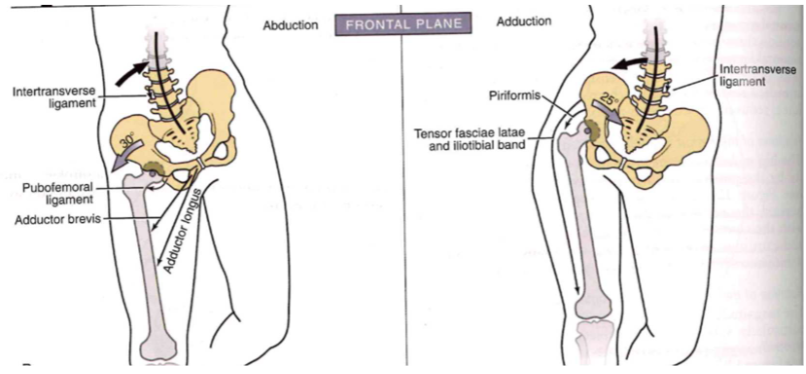
-
abduction // leg weight shift out (30 degrees)
- intertransverse ligament (in), pubofemoral lig (out), adductor brevis (out) // adductor longus (out + down)
-
adduction // leg weight shift in(25 degrees)
- intertransverse ligament (out+down), piriformis (out+down),tensor fasciae latae + iliotibial band(out + down)
Osteokinematics: femoral-on-pelvic or pelvic-on-femoral (HORTIZONTAL PLANE)
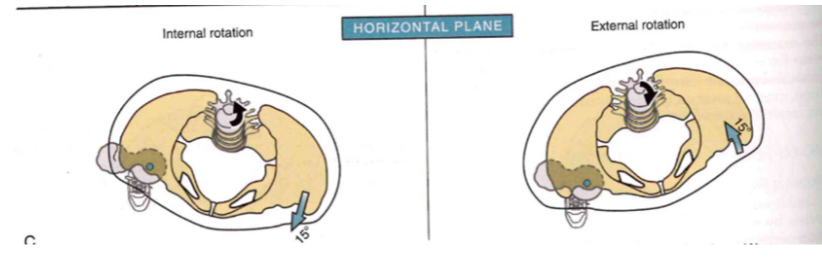
- internal rotation // lean forward (15 degrees)
- external rot // lean backward (15 degrees)
Osteokinematics: Lumbopelvic rhythym
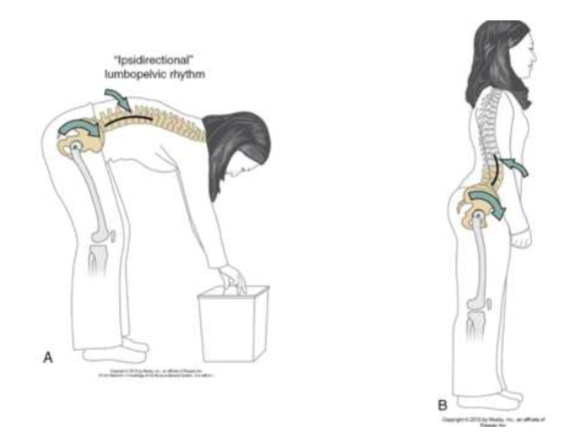
-
"ipsidirectional" // bend forward //
flexion
- TOGETHER = lumbar spine + pelvis rotate
-
"contradirectional" // bend back //
extension
- OPPOSITE= lumbar spine (back) + pelvis rotate (forward)
Arthrokinematics: the same as the shoulder! (less motion!)
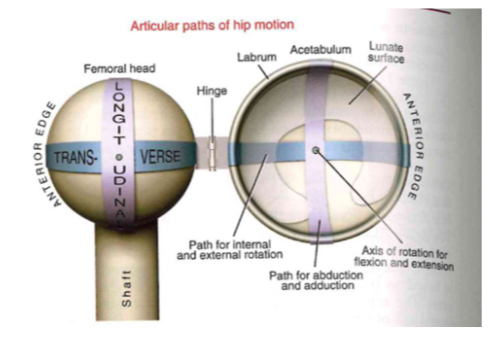
- HINGE JOINT
- longitude: abduction and adduction
- transverse: internal + external rotation
- axis of rotation: flexion and extension
(GH Arthrokinematics): Flexion
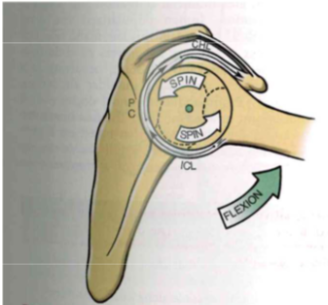
- spin foward + spin back
(GH Arthrokinematics): Abduction
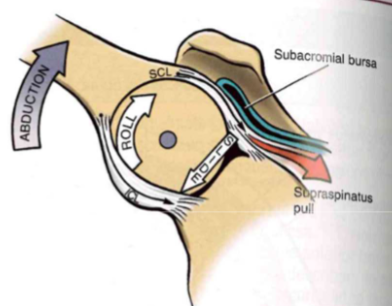
- roll up + slide down
(GH Arthrokinematics): external rotation
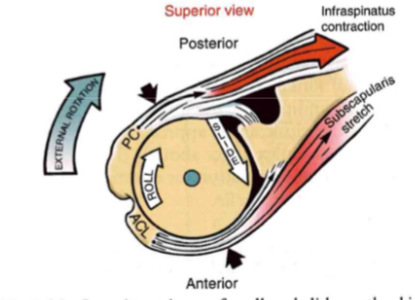
- roll up + slide down
Muscular Function (??)
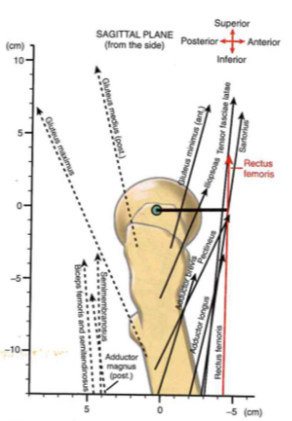
- rectus femoris: straight up (superior)
- illiosas: small mnt arm, UP force b/c beefy
- glute max: UP force // LOW mnt arm
- groups work together: line of pull go across+in front/overlap
- NO force vector force => just angle pull
- mnt arm changes w/ mvt
Muscular function (Table)
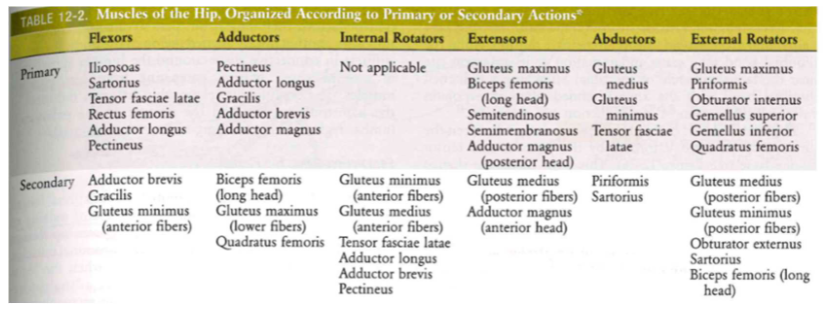
- primary vs. secondary muscles
Muscular function: hip flexors (muscles)
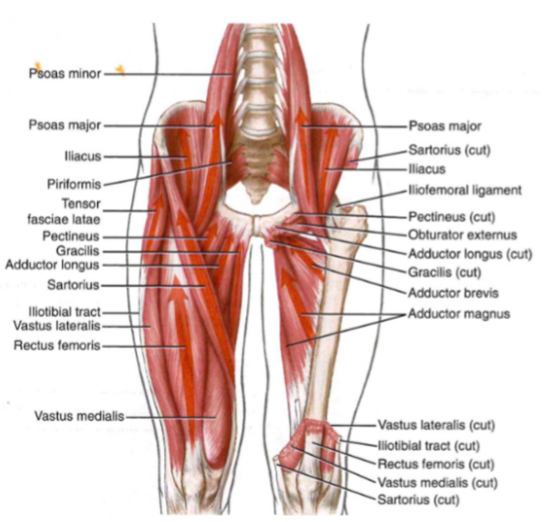
- illiosoas: most potent
- sartorius: hacky sack mvt // external rot
Muscular function: hip flexors, synergies
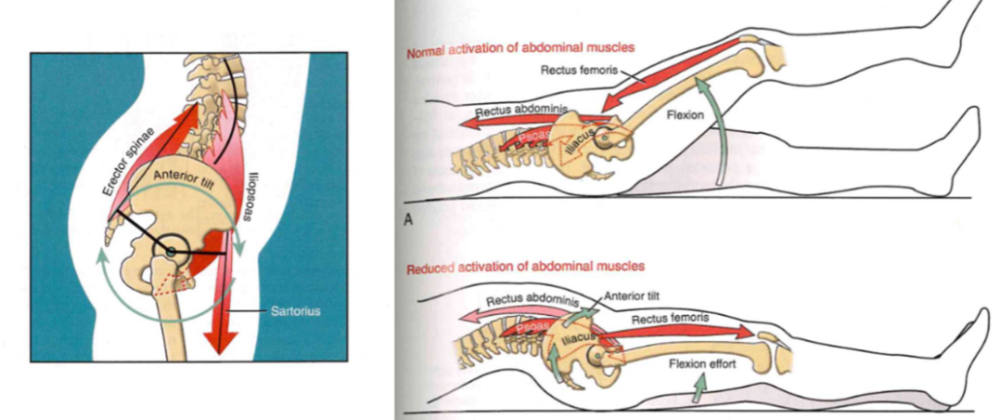
- turn on tilt muscles + muscles that keep body foward
- rectus femoris: keeps body stable
Muscle function: hip adductors graph (??)
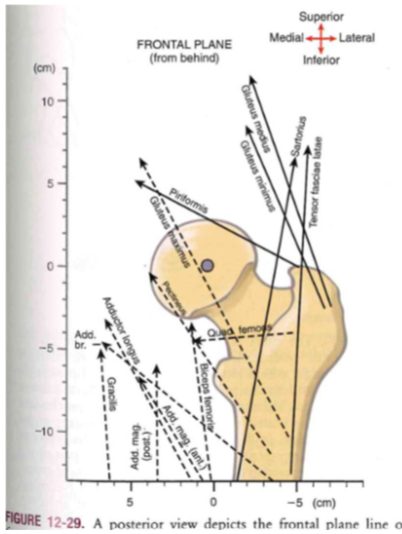
- lateral: looking at back side // abduction
- medial: looking at front side// adduction
Muscle function: hip adductors (angle mvt and bones)
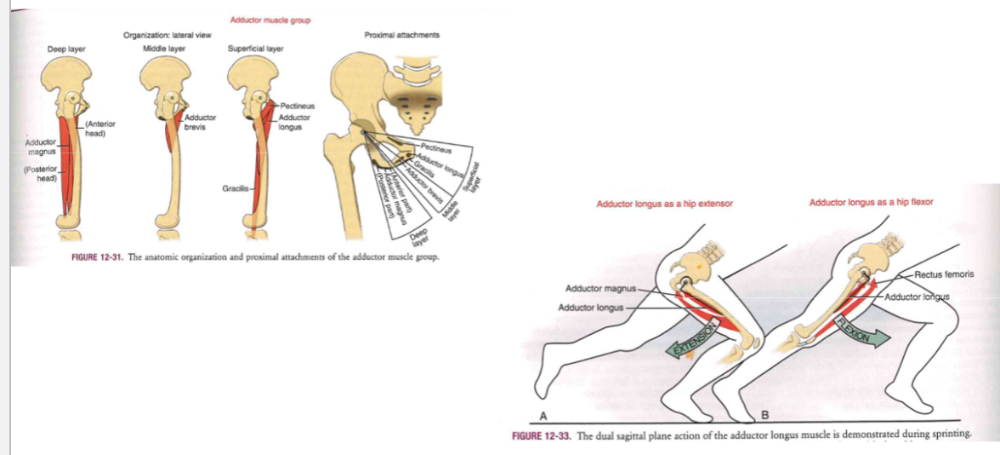
-
Producing force in 3 planes
- deep layer (anterior head // adductor magnus // posterior head)
- middle layer (adductor brevis)
- superficial layer (pectineus // adductor longus // gracillis)
-
Adduction longus + hip extension
- adductor magnus + longus
-
adduction longus as hip flexor\
- adductor longus + rectus femoris
Muscle function: hip internal rotation
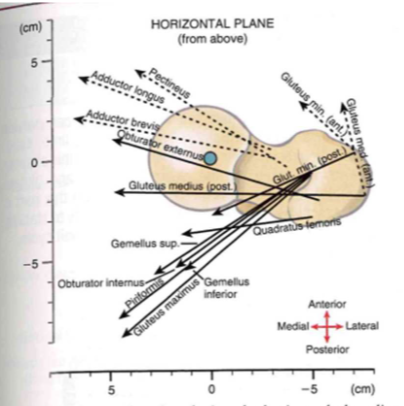
- In the anatomic position, there are NO primary IRs
- external factors = ABOVE axis
Muscle function: hip internal rotation (PRISIFORM) (???)
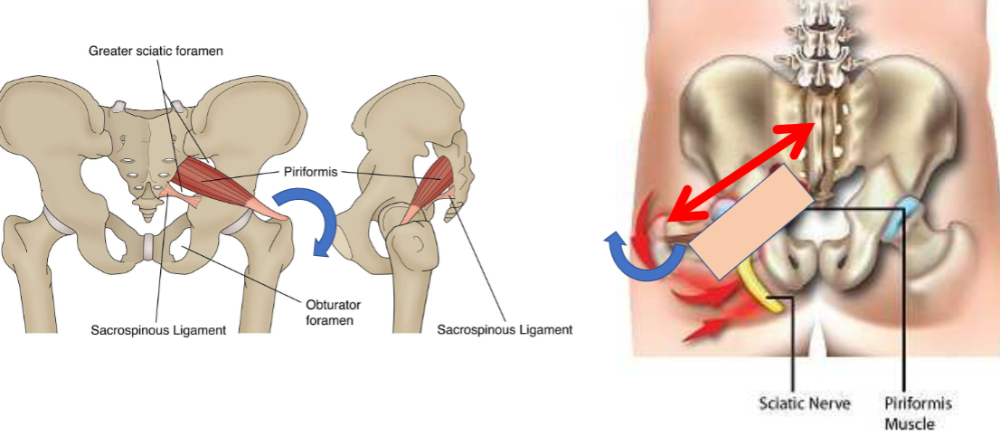
- (PRISIFORM)
Muscle function: hip extensors(Muscle) (???)
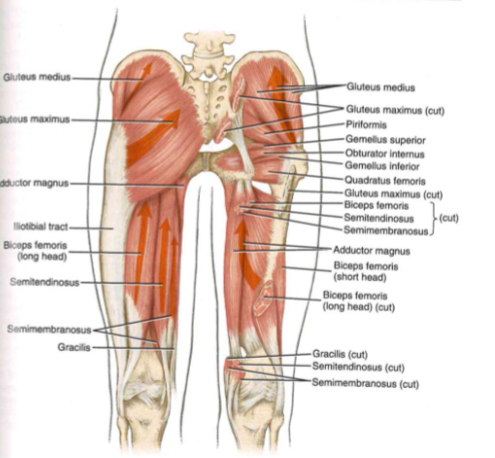
Muscle function: hip extensors, synergies
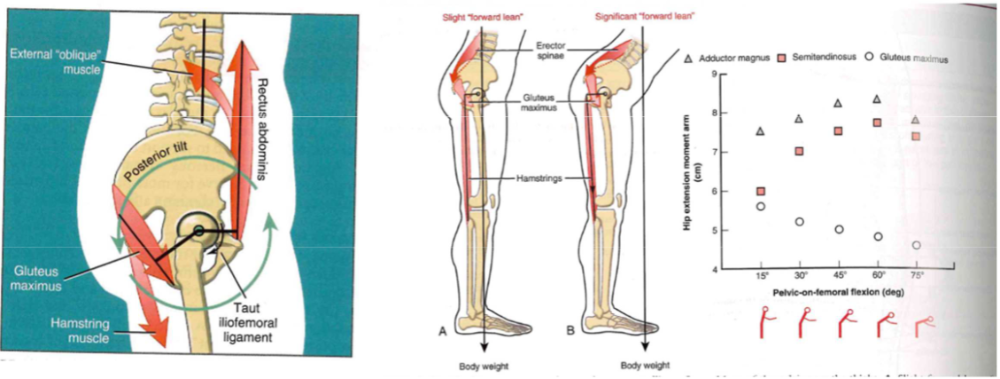
-
lunge w/ foward lean
- glute prominent
-
lunge w/ back lean
- hamstreing prominent
- SLDL vs. DL
- Posterior chain: all muscles work together // contribution just changes
Hiking/climbing up muscle movement
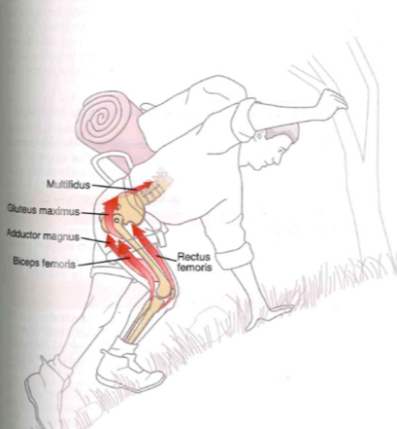
- jump box squat
- high demand: hip, knee, ankle, low back extensors,
Muscle function: hip abductor muscles
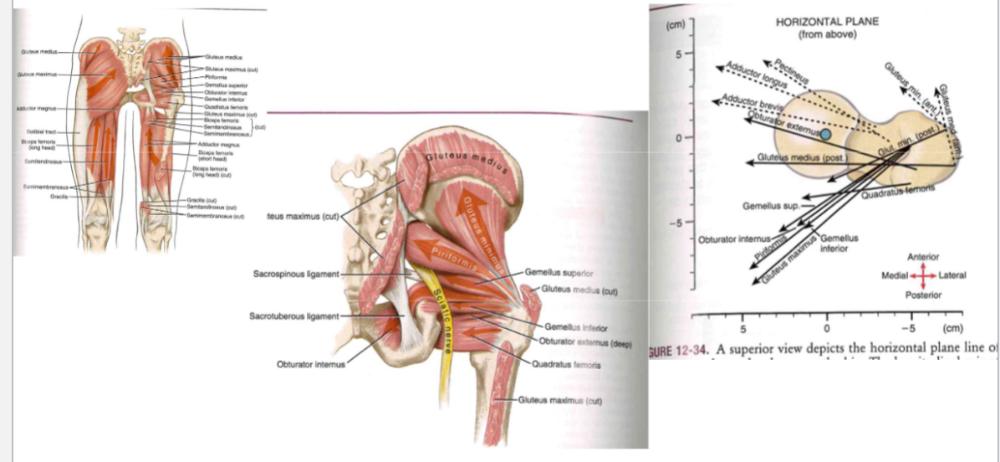
-
glute medius
- 60% of cross-section of all muscles
- internal + external rot
- no one muscle
directly through point (GRAPH)
- must have synergy for pure adduction
Muscle function: hip abductor muscles (torque)
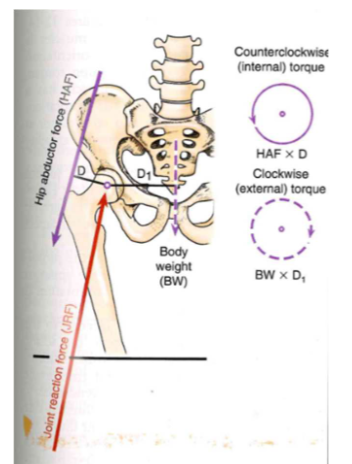
-
counterclockwise: internal torque
- HAF * D // hip abductor force * moment arm
-
clockwise: external torque
- BW * D1 // body weight * external moment arm
Muscle function: hip abductor muscles (normal vs. Trendelenburg sign)
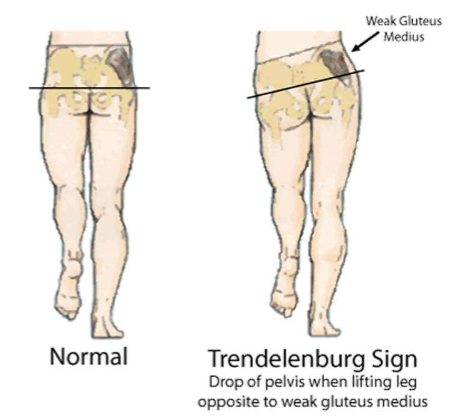
- old people walk = weak glutes
- not use abductors = weak walk
- NORMAL: need to work at 20% of capacity
- T. Sign: lost of 80% of full function
Muscle function: hip external rotators
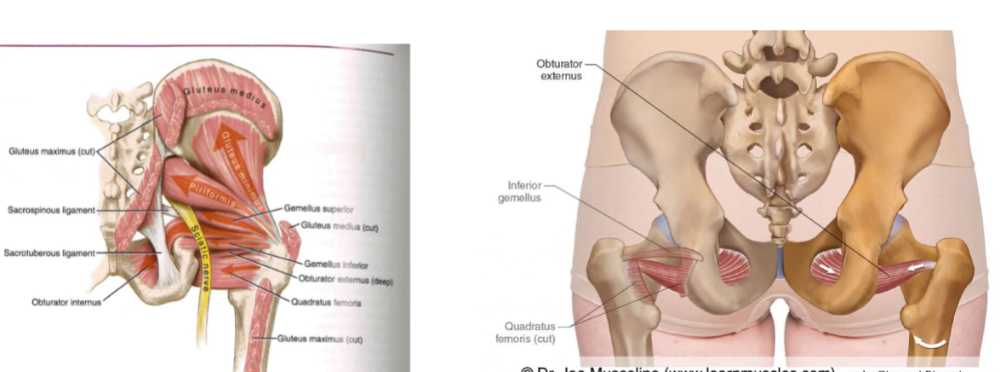
- compress the articular surfaces of the hip joint
-
muscles
- piriformis. // gemellus superior and inferior // obturator internus and externus // quadratus femoris // gluteus maximus
Obturator internus muscle (Hip.ER)
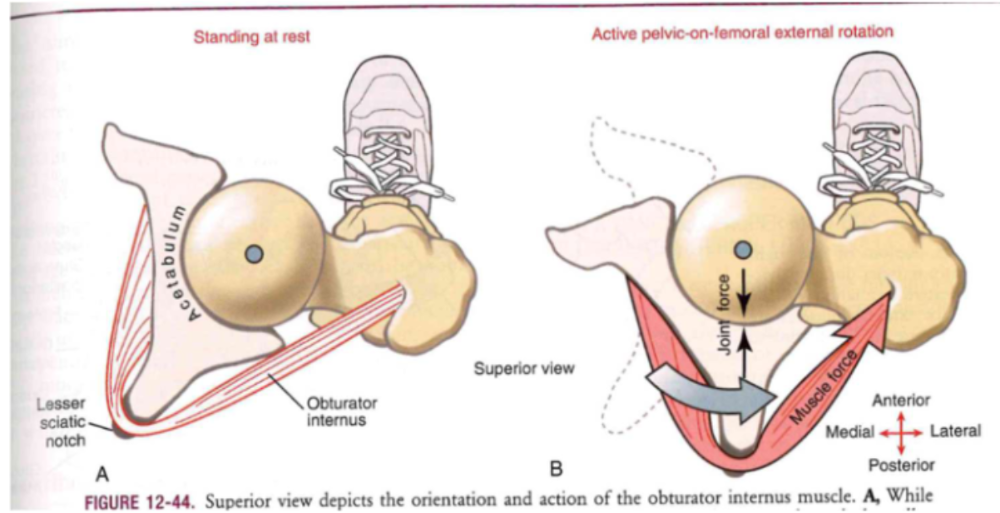
- at rest: 130 degree deflection (pulley through lesser sciatic notch)
- compression force (@joint): muscle contraction
Twisting head and torso mvt (Hip.ER)
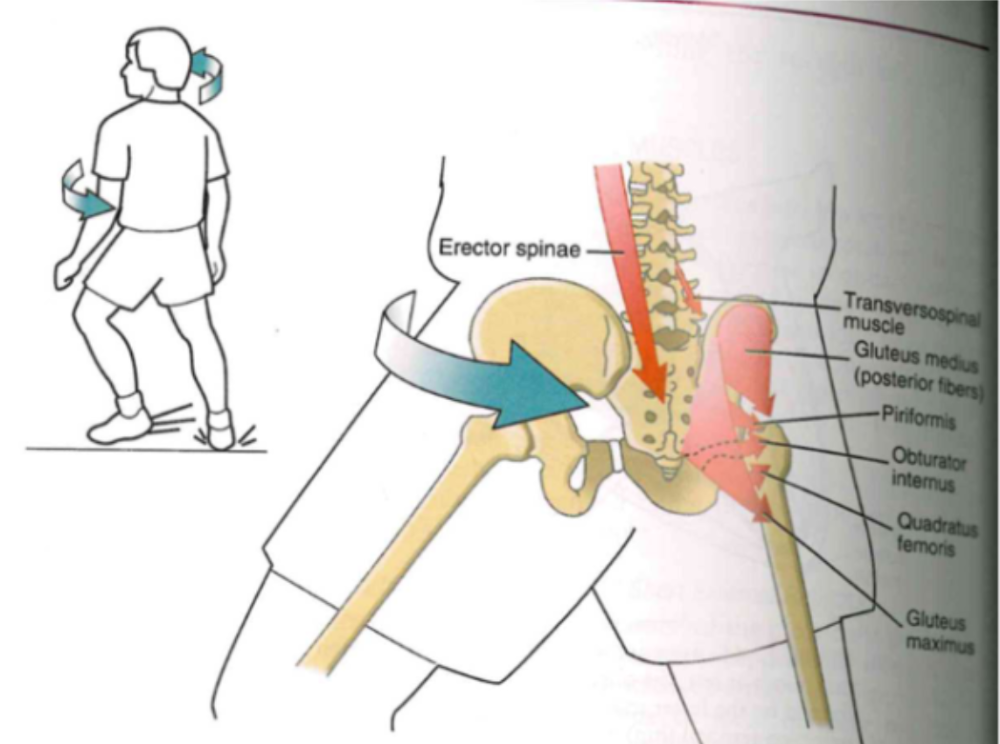
- right external rotator msucles @ pelvis-on-femoral ext. rot of right hip
- back muscles: rot. lower left trunk
MAXIMUM torque
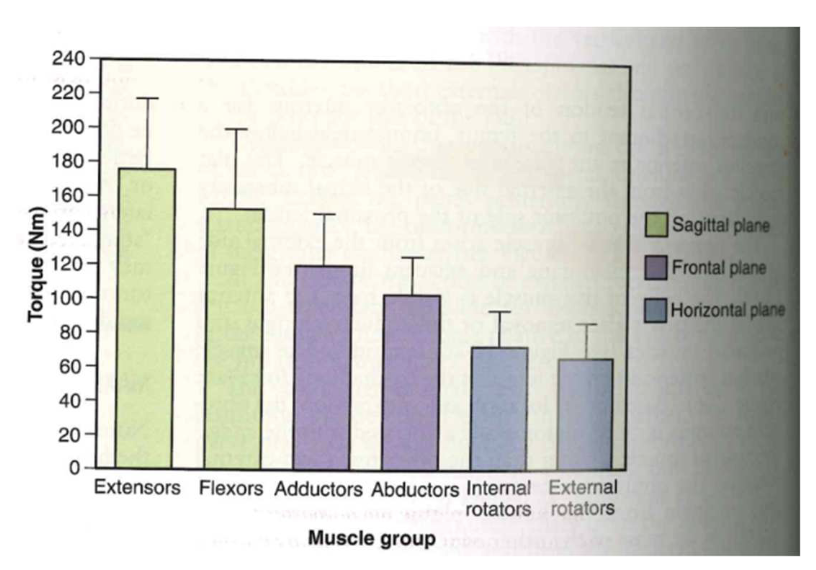
-
extensor: most torque @ sagittal plane
- good + moving foward (straight line spread) (UP torque)(LOW speed/NOT fast)
- Flexors @ sagittal plane: counters extensors (isometric)
- adductors @ frontal plane: help with flex+ ext
- abductors: keeps pelvis level
- internal +external rot: not too forceful / horizontal stuff
How does hip adductor help with hip flexion and extension
Pass in front and behind medial lateral axis
Bones of the Inominate
...