11/02
intro to plasmodium, cause of malaria
disease
malaria - disease
plasmodium spp. - microbe that causes the disease
very ancient
TB impacting humans for thousands of years (about 50 thousand)
prok vs. euk
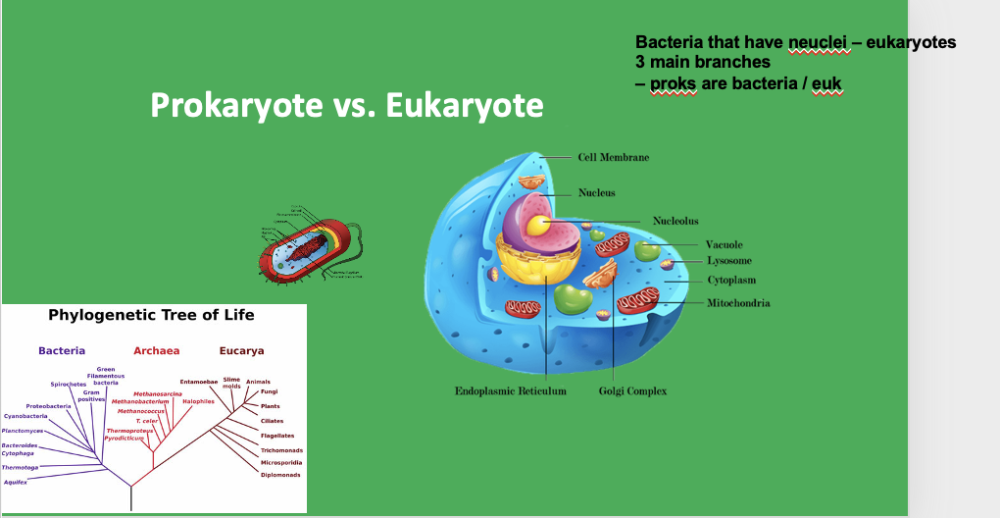
bacteria that have nuclei - eukaryote
3 main branches
virus vs bacterium vs eukaryote
Plasmodium – has 14 chromosomes and 23 million base pairs
~5,300 genes
3 infection sites with plasmodium
RBC
mosquitos
liver
infection in 3 acts
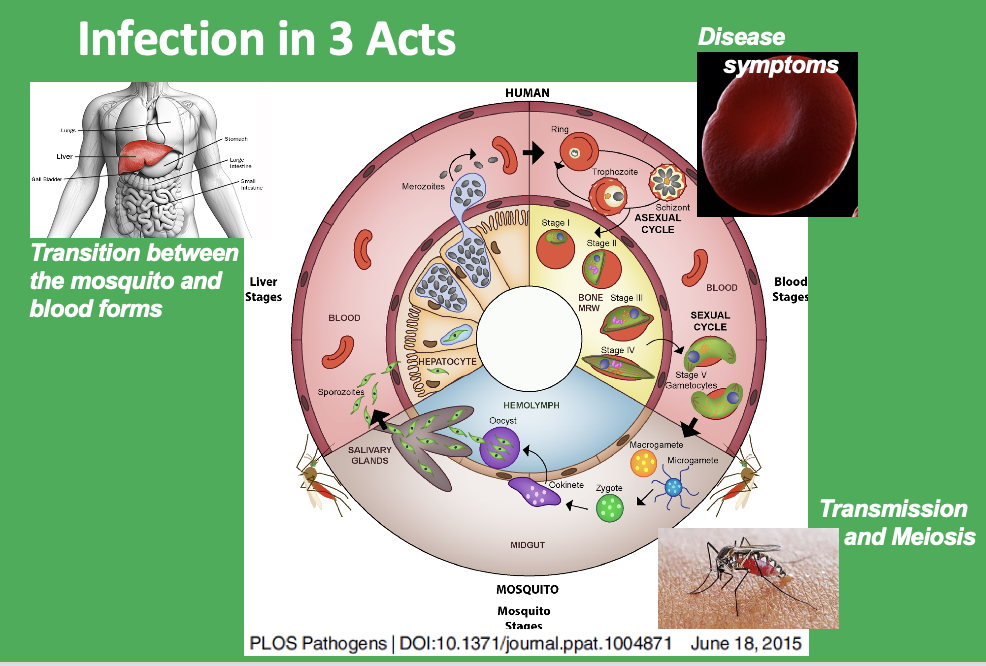
tansition between mosquito and blood form:
Know this figure
This schematic shows almost everything
Merozoites – form that infects RBC – only thing that they do
- once infected, makes more of itself
- infected RBC breaks -> release baby merozoits + infect more RBCs
- once in a while , when merozoite in rbc -> instead of making more -> will go to bone marrow + form 1 of 2 gametocytes
-> gametocytes release back into blood +
- if mosquito take bloodmeal -> pick up gametocyte (must pick up opposite sex ones) -> fertilization process in mosquito make zygotes
-> zygotes in dev into oocyst - gives rise to sporozoite form of plasmodium
- sporozoites emerge from oocyst
- sporozoites -> transfer to another individual when mosquito bites them (SPOROZOITES ARE THE TRANSFER FROM MOSQUITO)
- sporozoites from mosquito travel blood -> (OCCUR EXCLUSIVELY/ONLY IN LIVER CELLS) liver -> infect liver cells (hepatocytes) – where sporozoite grows + change form back into merozoite (IN INFECTED LIVER CELLS)
- what leaves liver cells = MEROZOITES
- merozoites emerging liver cells = complete cycle -> start over -> infect RBC, etc.
KNOW WHAT ALL THE FORMS ARE
(bottom 1/3 of graph is inside the mosquito)
Mosquito – vector
- mosquito also where genetic shuffling occurs
merogony
- (biology) form of asexual reproduction whereby a parasititc protozoan replicates its own nucleus inside its host cells and then induces cell segmentation; schizogony
- (medicine) the development of part of an ovum after damage
merozoite form of plasmodium is VERY small
merogony - means when merozoite infect RBC when get inside
imaging of merozoite
invasion in fixed cells
imaging of merozoite invasion in fixed cells
- purified merozoites were fixed in the process of invasion to visualize invasion events
- they were examines at the point of initial binding to the RBC surface, midway, and after invasion was complete
merozoites invading, growing, and then getting out of the RBC
lyse + release progeny/baby merozoites
see pic
instead of making more merozoites, a merozoite can differentiate into a "sex cell", the gametocyte
stages of P. falciparum
- normal red cell
- trophozoite
- correspond to ring stage trophozoite
- schizonts
- mature macrogametocytes (female)
- mature microgametocytes (male)
Slides of what infected RBCs look like
Don’t need to know stage names
Can dev into either macro or micro gametocyte(male/female)
- instead of making more merozoites, CAN make gamtocytes
- random whether make male or female
plasmodium in the mosquito (anopheles spp.)
gametocytes taking up in blood
release sporozoite by mosquito into individual (about 2 weeks later)
process begin in gut/intestinal tract of mosquito
- if male and female both present - fuse and form zygote ->
- oozyte come out of gut -> make sporozoites -> migrate to salivary gland of mosquito -> transfer when bite next victim
mosquito to hepatocyte: sporozoite
Sporozoites about 20x or more bigger than merozoite
sexual reproduction occurring in plasmodium is EXACTLY the same as in animals and plants
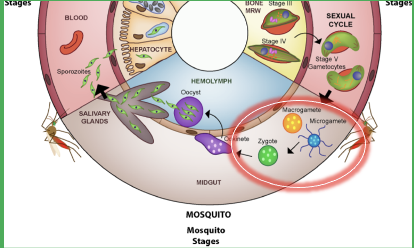
animals: egg (n - halpoid) + sperm (n - haploid) -> zygote (nn - diploid)
plasmodium: macrogamete (n - haploid) + microgamete (n - haploid) -> zygote (nn - diploid)'
Macro gamete – haploid – fuse w/ opposite sex gamete -> zygote = diploid cell
Occurs in circled stage
= MEIOSIS
Oocyst – in tissue of mosquito – diploid
-> Forms sporozoites (haploid)
-> We get infected w/ haploid cells
-> Whole process = meiosis (does a lot of gene shuffling)