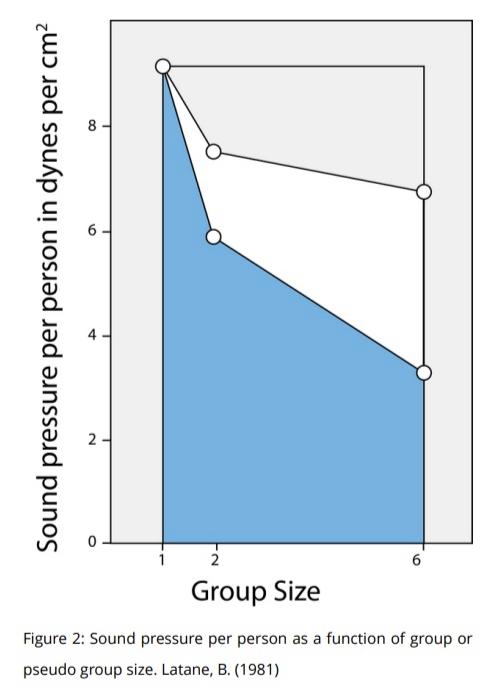
Social pressure
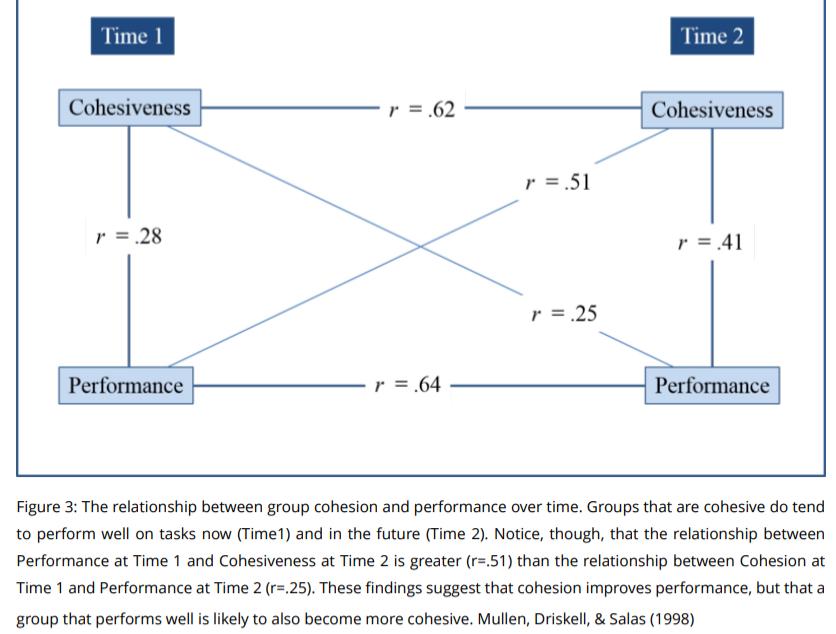
Group cohesion and performance
Collective self-esteem
Feelings of self-worth that are base on evaluation of relationships with others and membership in social groups
Common knowledge effect
- The tendency for groups to spend more time discussing information that all members know (shared information)
- less time examining information that only a few members know (unshared).
Group cohesion
- The solidarity or unity of a group resulting from the development of strong and mutual interpersonal bonds among members and group-level forces that unify the group
- EX. shared commitment to group goals.
Group polarization
- The tendency for members of a deliberating group to move to a more extreme position,
- direction of the shift determined by the majority or average of the members’ predeliberation preferences.
Group think
A set of negative group-level processes, including illusions of
invulnerability, self-censorship, and pressures to conform, that occur
when highly cohesive groups seek concurrence when
making a decision.
Ostracism
- Excluding one or more individuals from a group by reducing or eliminating contact with the person, usually by ignoring, shunning, or explicitly banishing them
Shared mental model
Knowledge, expectations, conceptualizations, and other cognitive
representations that members of a group have in common pertaining to
the group and its members, tasks,
procedures, and resources.
Social comparison
The process of contrasting one’s personal qualities and outcomes, including beliefs, attitudes, values, abilities, accomplishments, and experiences, to those of other people
Social facilitation
Improvement in task performance that occurs when people work in the presence of other people.
Social identity theory
- A theoretical analysis of group processes and intergroup relations that assumes groups influence their members’ self-concepts and self-esteem
- particularly when individuals categorize themselves as group members and identify with the group.
Social loafing
The reduction of individual effort exerted when people work in groups compared with when they work alone.
Sociometer model
A conceptual analysis of self-evaluation processes that theorizes self-esteem functions to psychologically monitor of one’s degree of inclusion and exclusion in social groups
teamwork
The process by which members of the team combine their knowledge, skills, abilities, and other resources through a coordinated series of actions to produce an outcome.
Early attachment and adult intimacy

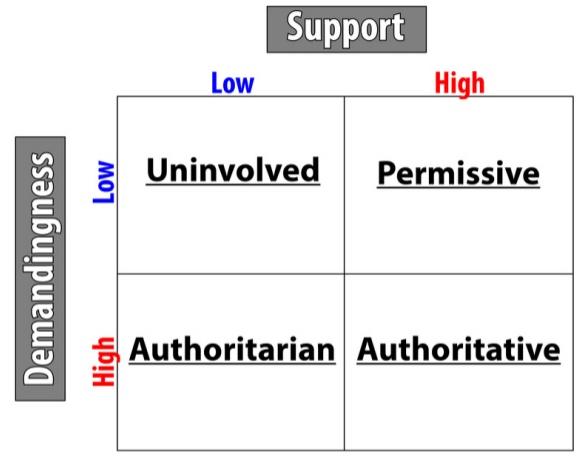
Four parenting styles
Divorce factors

Adoption
To take in and raise a child of other parents legally as one’s own.
Age in place
The trend toward making accommodations to ensure that aging people can stay in their homes and live independently.
Anxious avoidant
Attachment style that involves suppressing one’s own feelings and desires, and a difficulty depending on others.
Anxious-resistant
Attachment style that is self-critical, insecure, and fearful of rejection
Attachment theory
Theory that describes the enduring patterns of relationships from birth to death.
Authoritarian parenting
Parenting style that is high is demandingness and low in support
Blended family
A family consisting of an adult couple and their children from previous relationships.
Boomerang generation
Term used to describe young adults, primarily between the ages of 25 and 34, who return home after previously living on their own.
Child abuse
Injury, death, or emotional harm to a child caused by a parent or caregiver, either intentionally or unintentionally.
Child free
Term used to describe people who purposefully choose not to have children.
Childless
Term used to describe people who would like to have children but are unable to conceive.
Cohabitation
Arrangement where two unmarried adults live together
Coherence
Within attachment theory, the gaining of insight into and reconciling one’s childhood experiences
Elder abuse
Any form of mistreatment that results in harm to an elderly person, often caused by his/her adult child.
Empty Nest
Feelings of sadness and loneliness that parents may feel when their adult children leave the home for the first time
Engagement
Formal agreement to get married.
Family of orientation
The family one is born into.
Family of procreation
The family one creates, usually through marriage.
Family systems theory
Theory that says a person cannot be understood on their own, but as a member of a unit.
Foster care
- Care provided by alternative families to children whose families of orientation cannot adequately care for them
- often arranged through the government or a social service agency
Heterogamy
Partnering with someone who is unlike you in a meaningful way.
Homogamy
Partnering with someone who is like you in a meaningful way.
Intimate partner violence
Physical, sexual, or psychological abuse inflicted by a partner.
Joint family
- A family comprised of at least three generations living together.
- often include many members of the extended family.
Learned helplessness
The belief, as someone who is abused, that one has no control over his or her situation.
Marriage market
- The process through which prospective spouses compare assets and liabilities of available partners
- choose the best available mate.
Modern family
A family based on commitment, caring, and close emotional ties.
Multigenerational homes
Homes with more than one adult generation.
Neglect
Failure to care for someone properly.
Nuclear families
A core family unit comprised of only the parents and children.
Permissive parenting
Parenting that is low in demandingness and high in support.
Physical abuse
The use of intentional physical force to cause harm.
Psychological abuse
Aggressive behavior intended to control a partner
Sandwich generation
Generation of people responsible for taking care of their own children as well as their aging parents.
Second shift
- Term used to describe the unpaid work a parent,
- usually a mother, does in the home in terms of housekeeping and childrearing.
Secure attachments
- Attachment style
- being comfortable with depending on your partner
- having your partner depend on you
Sexual abuse
The act of forcing a partner to take part in a sex act against his or her will.
Single parent family
An individual parent raising a child or children
Stepfamily
A family formed, after divorce or widowhood, through remarriage.
Traditional family
Two or more people related by blood, marriage, and—occasionally-- by adoption
Two-parent family
A family consisting of two parents—typical both of the biological parents-- and their children
Uninvolved parenting
Parenting that is low in demandingness and low in support.
Working models
An understanding of how relationships operate; viewing oneself as
worthy of love and others
as trustworthy