Muscle functions
- postural stability
- torque production for mvt (create + transmit)
- Protection (back muscles = internal organs)
- Fine mvt of head and neck (gaze)
Muscle general structure
- cross at multiple joints (spine muscles)
- vary in
different
- length
- shape
- fiber direction
- cross-sectional area
- leverage
Muscle organization
- Trunk
- posterior, anterolateral, additional muscles
- craniovical region
"strength"
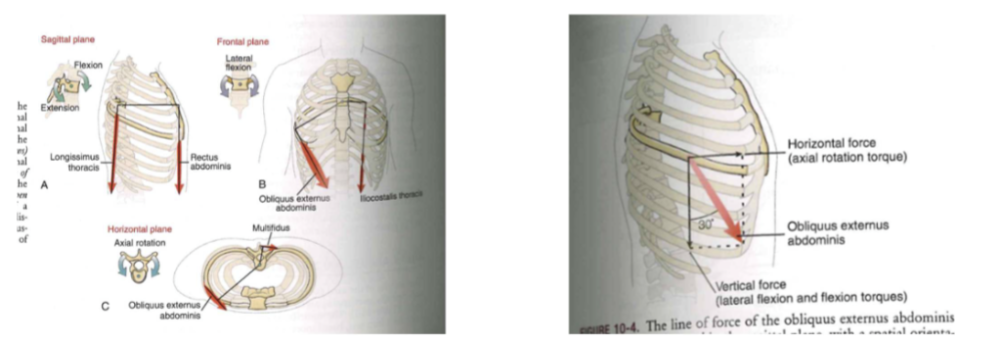
- produce force at torques/summation of torque + angles (mostly
at spine)
- force * moment arm (=> moment arm)
- ability to produce a lot of force
- 80 degree of force (verticle) = hulling you up
Special considerations

- muscles on both sides/sets activated
- sagittal plane = flexion + extension
- muscle one activated
- sagittal plane + multiplane (axial rotation or frontal plane motion)
Muscles of posterior trunk: SUPERFICIAL
- Traps, lats, rhomboids, levator scap, serratus anterior
(shoulder + arm stuff)
- Bilateral -> extension
- Unilateral -> lateral flexion & sidebending
Muscles of posterior trunk: INTERMEDIATE
(ventilation & proprioception)
- low cross-sectional + body imaging/space
- Serratus posterior superior
- Serratus posterior inferior
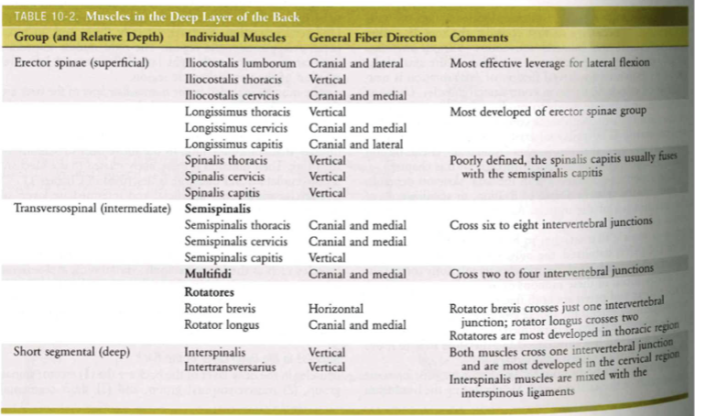
Muscles of posterior trunk: DEEP
- WHAT MOVES YOU AROUND
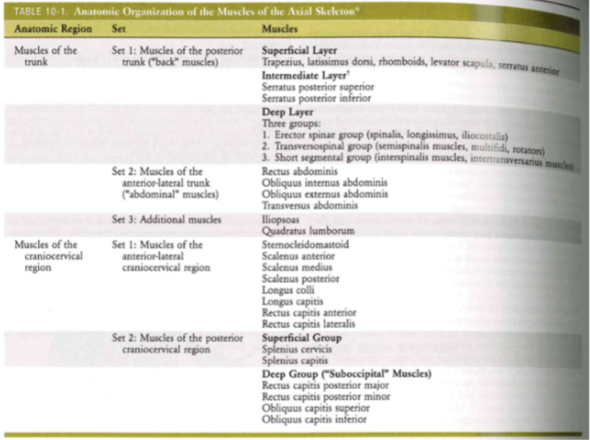
- Erector spinae group
- Transversospinal group
- Short segmental group
Transversospinal group + short segmental
Muscles of trunk and craniocervical region
Erector Spinae group
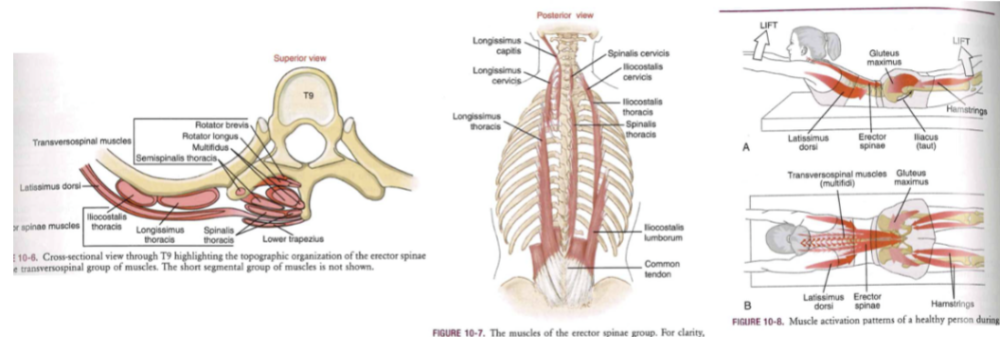
- turn on both sides = pure extension
- turn on one side = rotation/sideband (unilaterally) + extension
- BIG MOVEMENTS (DL)
- Main move extension
Transversospinal group
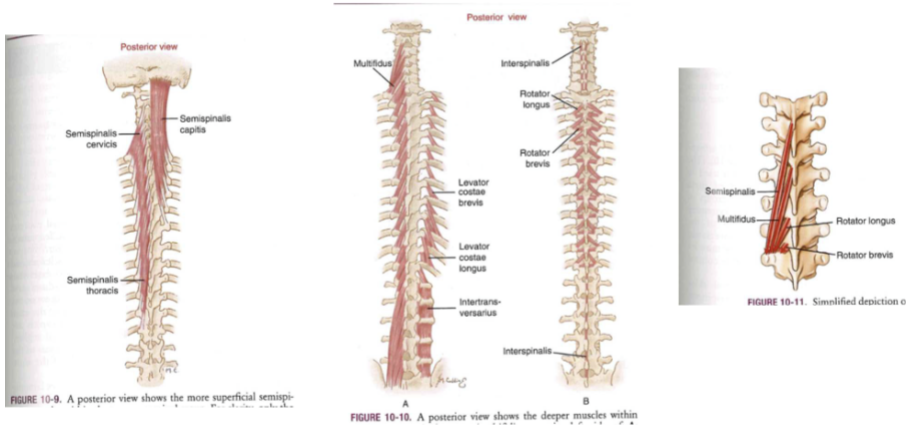
- semispinalis (semi. thoracic/cervicis/captits) -> multifid -> rotatores (brevia/longus)
- low cross-sectional + many levels + lost strength
- fine motor mvts
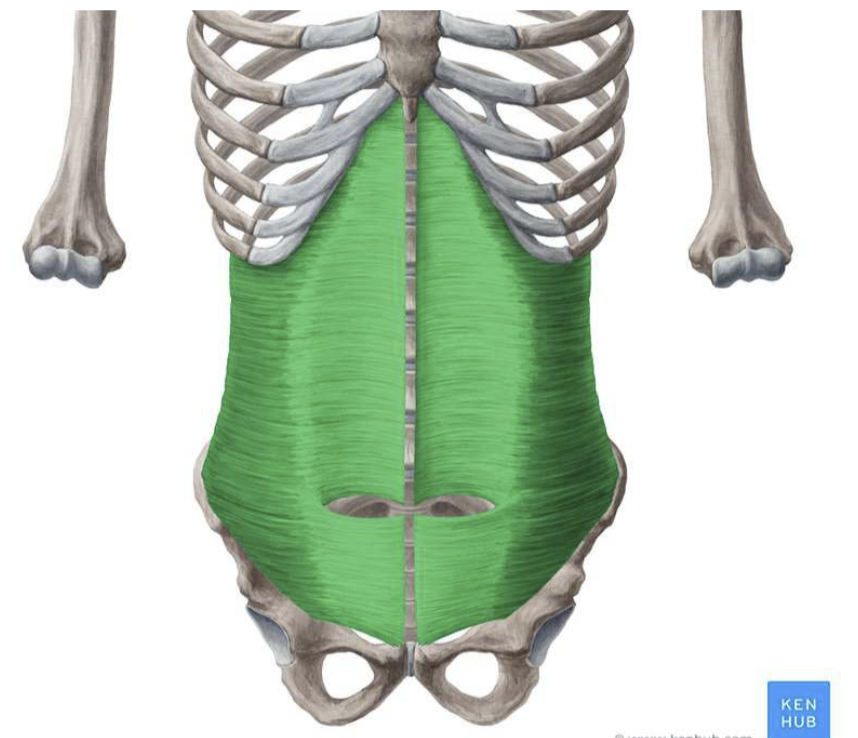
Muscles of the anterolateral trunk (abs): function
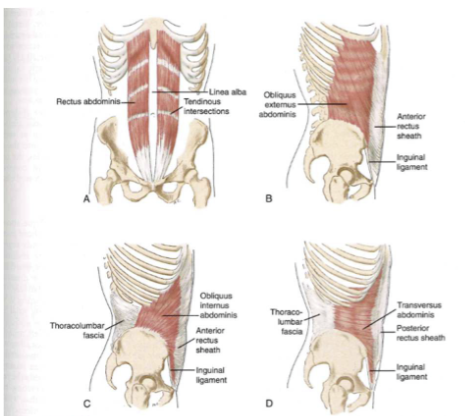
- obliquus internus abdominis
- protective work of ab organs
- high intrabdominal + thoracic pressure
Muscles of the anterolateral trunk (abs) [specific]
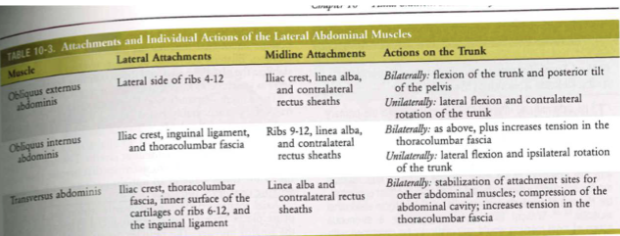
- obliquus externus abdominis
- obliquus internus abdominis
- transverse abdominis
Short Segmental
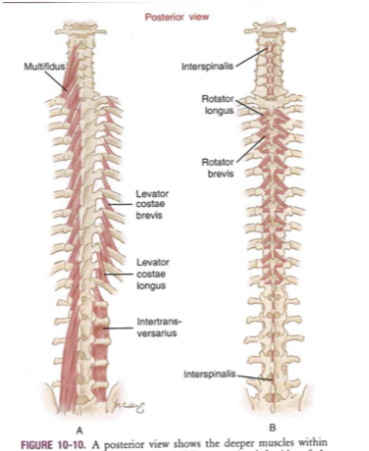
- no force generation + lots of muscle spindle
- tracks muscle length = proprioception
- supervisor muscles
Muscles of the anterolateral trunk (abs) [errector abdominous movement]
- both sides on(bilateral errector ab): trunk flexion
- 1 side on: flexion + lateral
Muscles of the anterolateral trunk (abs): external + internal oblique
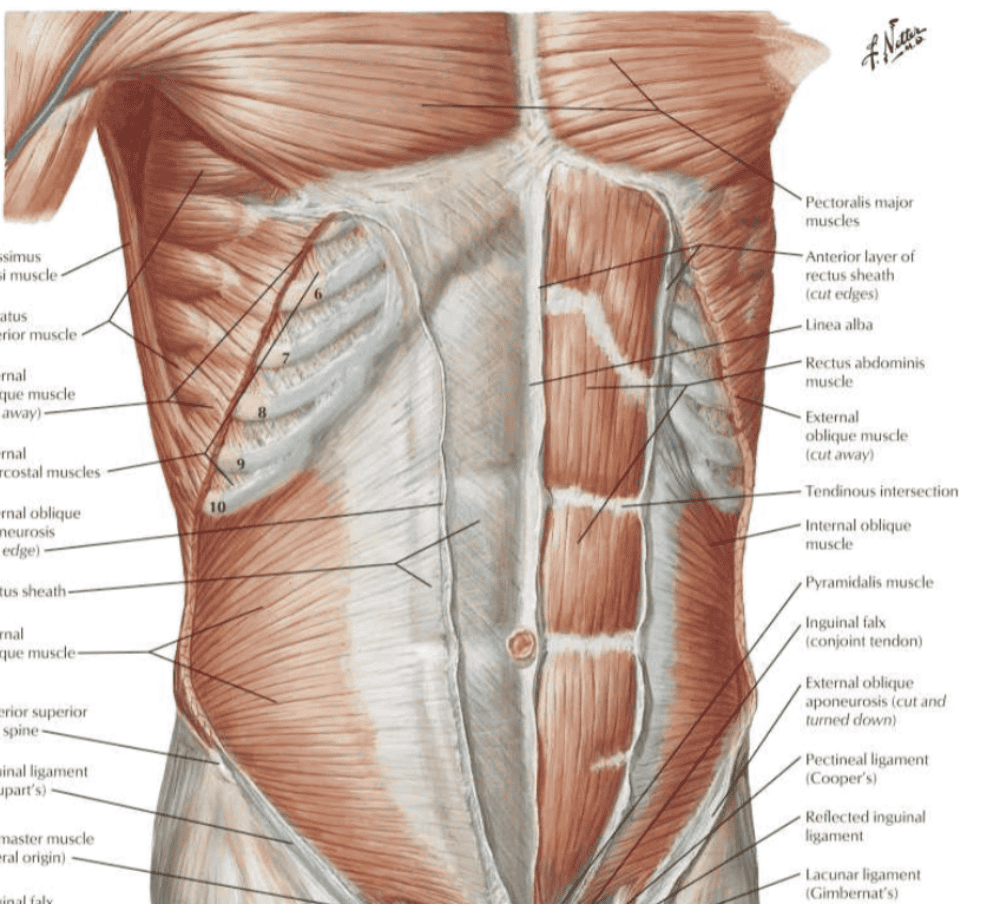
- longest moment arm (rotation)
- large cross-sectional area (x2 of errectus abdominous)
- Turn left: right external obli on
- Turn right: right internal obliq on
- PSOAS = middle (does everything/depend on starting position)
Research Paper
- transverse abdominal work = helps create pressure, prevent distention/sweeting of guts (Olympic weight belt)
- external
load application (dumbbell + barbel) = highest core application
- EMG activation (on)
Superman vs. Deadlift: So which one creates more torque??

- not same activity
- superman increases use of deep
muscles
- more accessible, more better prescribed, low-load
- deadlift: bracing, depends on what muscles (erectus spinous)
Extension Torque > Flexion Torque
- Flexor-to-extensor torque (isometrically) is .45-.77
- Trunk flexors: greater leverage
- extensors: greater mass & better vertical orientation
Additional muscles: Iliopsoas & Quadratus Lumborum
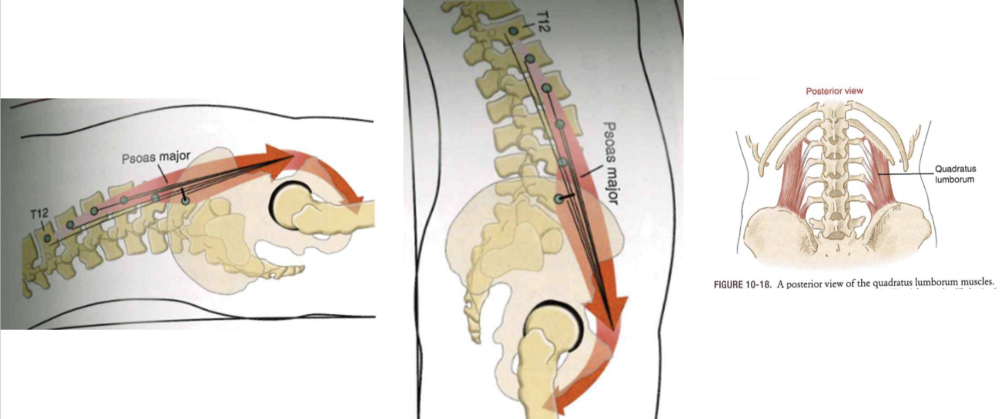
- Iliopsoas: hip flexor with femur-on-pelvis (hang leg raise) or pelvis-on-femur (sit-ups), lateral flexion, vertical stabilizer (trunk)
- Quadratus Lumborum: dynamic control of pelvis, extensor of lumbar (bilaterally), flexor of LR (unilaterally)
Muscle interactions division
- Intrinsic stabilizer
- extrinsic stabilizer
Muscle interactions: Intrinsic stabilizer
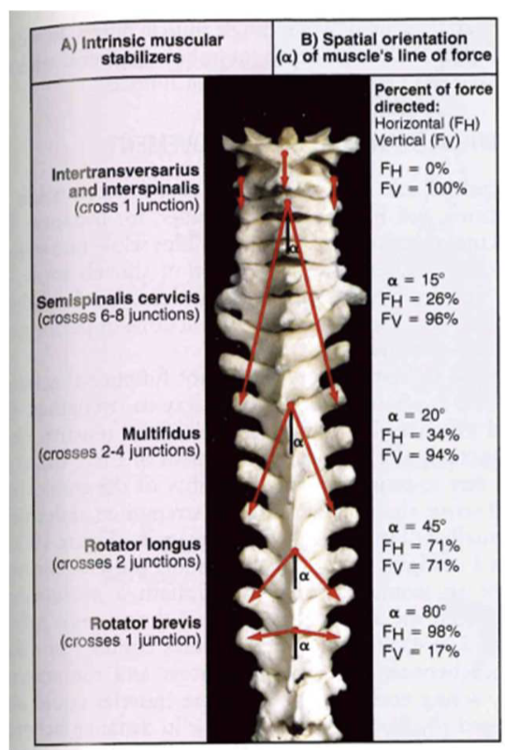
- Transversospinals // short segmentals
- oriented completely verticle (telephone pole)
- stabilization, compression, no sliding
- prevent bowstringing (with big mvt) = generate stabilization (fine coordination)
Muscle interactions: extrinsic stabilizer
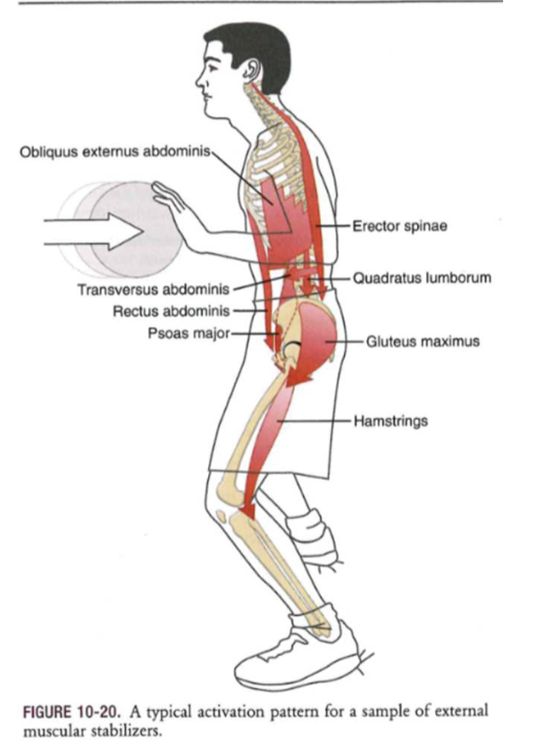
- Anterolateral (abs) // Erector Spinae // QL // Ilioposas // Hip muscles
- prevent bowstringing (with big mvt) = generate stabilization (deep muscles)
Sit ups
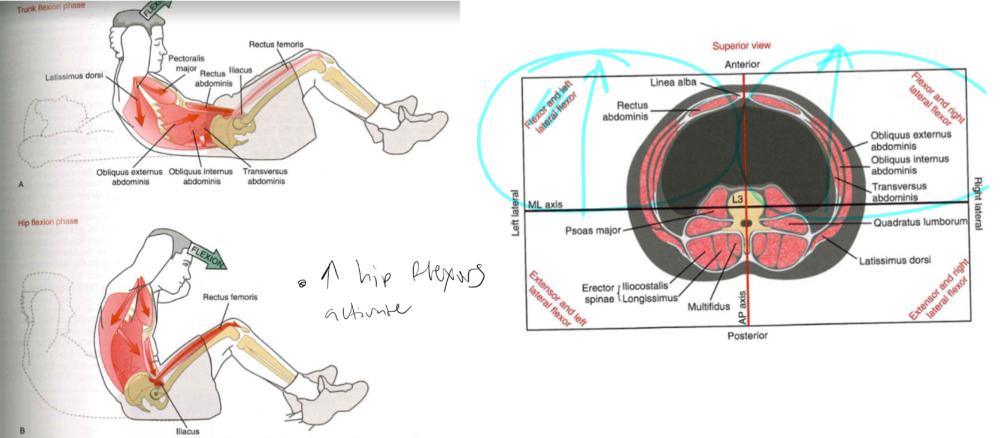
- causes hip flexor activation
- erectors abdominus/lats/pec/oblique/rectus+transverse abdominus/
- max flexion torque: turn all muscles north of spine
- max extension torque: turn all south of spine
sumo deadlift + squat
- hip extension + lumbar extension (knees/calf/back/legs)
- start position
- don't need flexors on = bracing automatic/trainned = ???
Cervical spine head (AT NEUTRAL)
- potential movement = depend on starting position
- not a lot of plantar movements
- more extensor + flexor
Sternocleuidomastoid
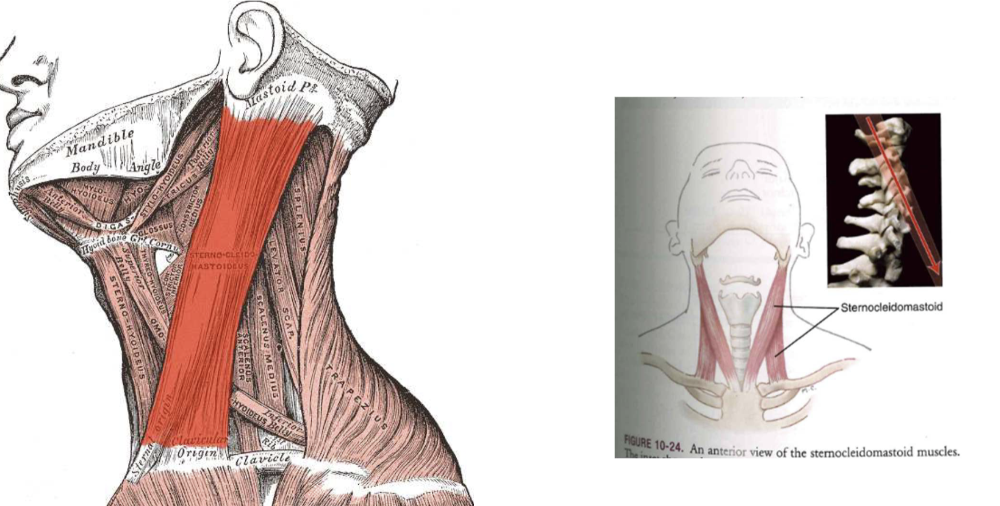
- neutral vs extensor start
- extension
- unilateral + contralateral axial rotator (flex+extend)
Scalene muscles
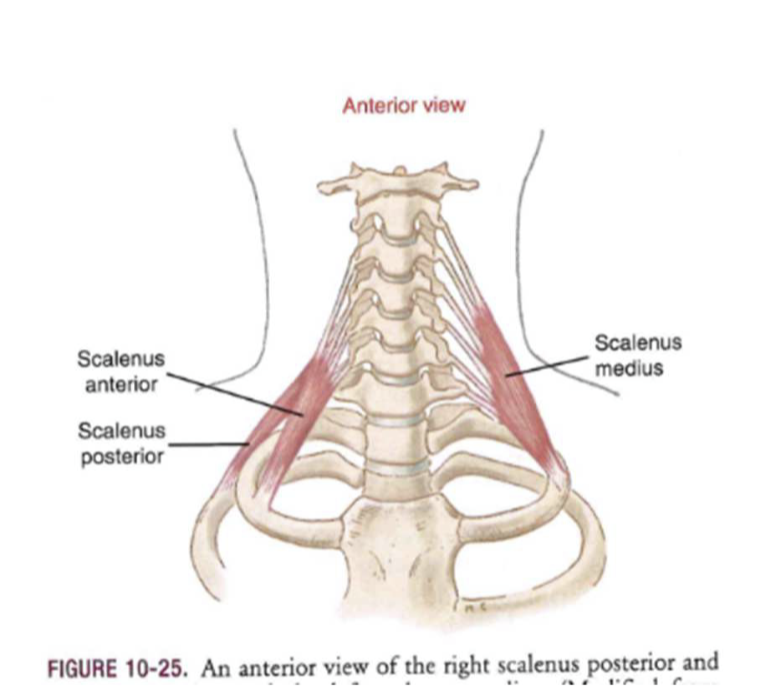
- unilateral flexor
- both sides on: help with ventilation, raise thoracic spine up (COPD patients)
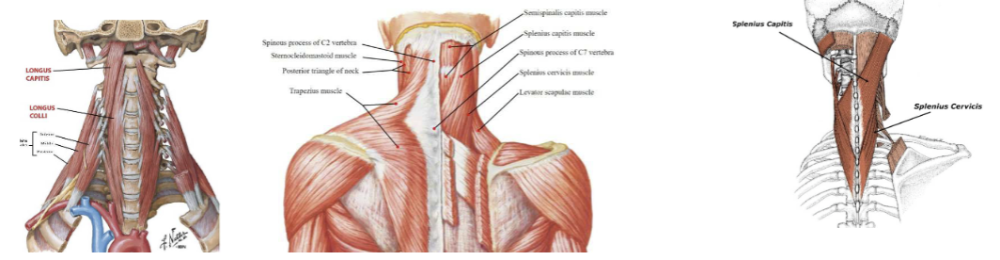
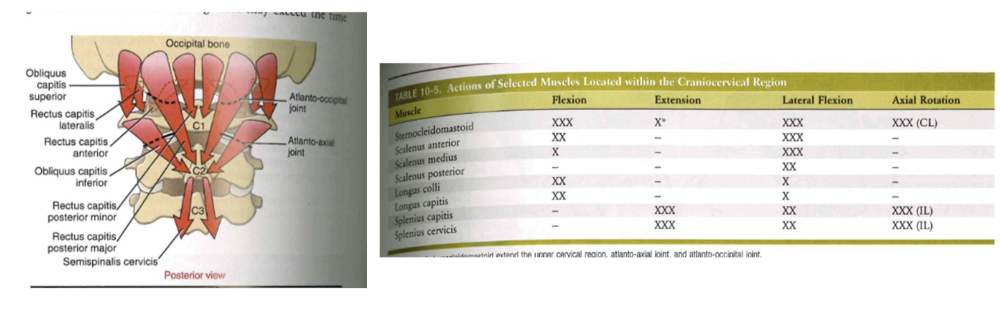
Deep muscles (right longus capitis, right rectus capitis anterior, right rectus capitis lateralis, left longus colli)
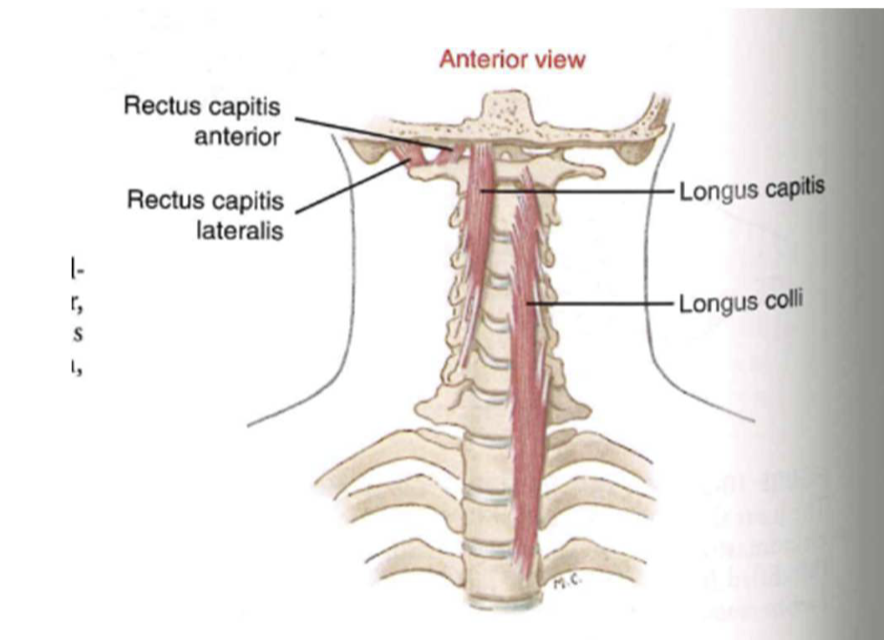
- dynamic anterior longitudinal ligament
- helps with flexion
large mover muscles (neck/head)
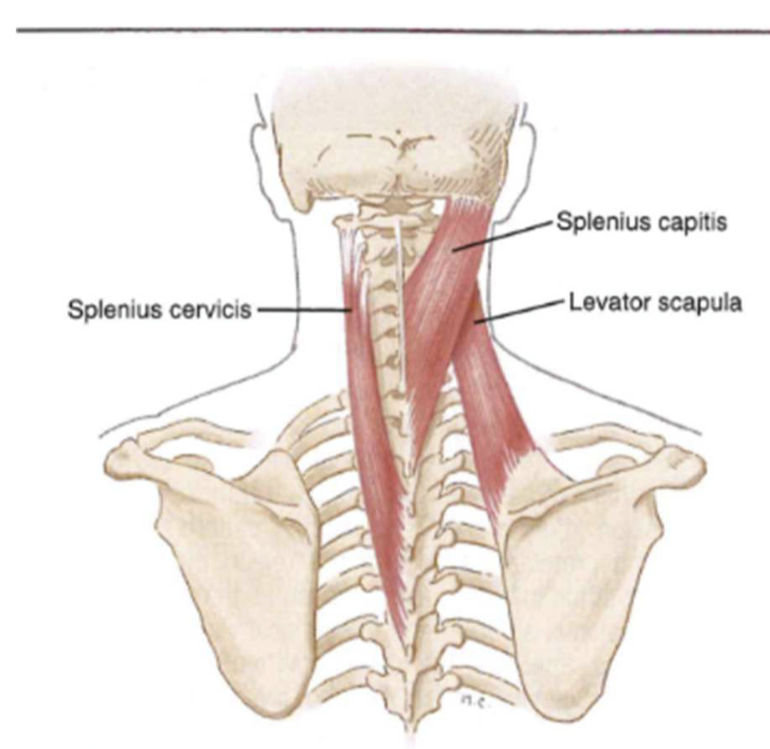
- multi-level movers
- splenius captitis: rotation + side bend
- splenius cervicis: side bend + ecternal + rotation
- levator spinae: side bend
small/single mover muscles (neck/head)
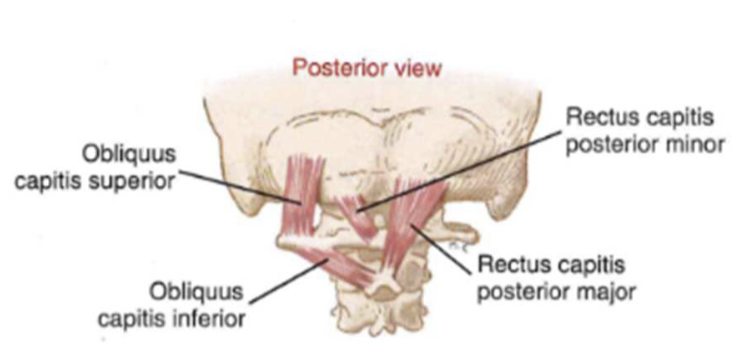
- precise control of occipital and axial joints
- provide neural feedback on position + rate of head movement (balance, equilibrium, eye-head coordination)
Cervical interactions
eye / fine movement / neck muscles
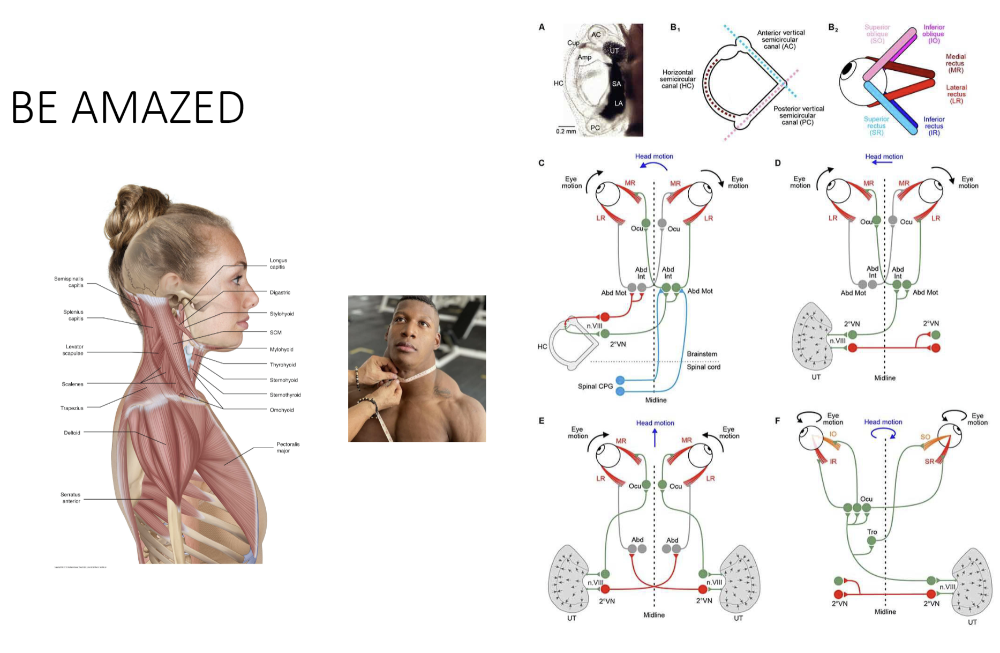
- allows the head to stay on the neck after car accident/collision
- vestibule system + neck muscles = control
gaze
- sends signals to each other
- balance, equilibrium, eye-head coordination