sensation
senses collect info from environment and convert it to signals that travel through the brain
perception
the process by which the brain organizes and interprets sensory input
tranduction
transforms stimulus energy into electrochemical energy of neural impulses for all the senses except for smell
bottom- up processing
taking sensory information and assembling it until an object is formed in minds
top- down processing
processing and perceiving new information you encounter with things you already know
psychophysics
studies how physical energy affects our psychological experiences
sensory adaptaion
the diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
absolute threshhold
the smallest level of stimulus that can be detected at least half of the time
signal detection theory
predicts that the intensity of stimuli and state of the person affects whether or not they are able to detect the stimuli
subliminal sensation
stimuli that are under your absolute threshold for conscious awareness
difference threshold
minimum difference person can detect between 2 stimuli half the time
webers law
2 stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage to be perceived different
selective attention
when we focus on one particular stimuli in our environment and ignore the rest
inattentional blindness
when our focus is directed at one stimulus, leaving us blind to other stimuli
change blindness
when a stimulus undergoes a change without being noticed by its observer due to visual interruptions
pupil
the adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
iris
a colored muscle that dilates or constricts in response to light intensity or inner emotions
lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images in the retina
retina
light- sensitive inner surface of the eye which contains the receptor rods and cones and neurons
rods
receptor cells in the retina responsible for detecting light in general
cones
receptor cells that are responsible for color vision and visual adaptation to changes in light
fovea
the retinas central area of focus, where most cones are clustered around
optic nerve
the nerve that carries visual information to the brain
blind spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye and there are no receptors
bipolar cells
the main interneurons, providing the main pathway between the photoreceptors of the eye to ganglion cells
ganglion cells
retinal cells that are responsible for carrying the visual stimuli to the brain
feature detectors
neurons located in the visual cortex that respond to specific features of stimulus
parallel processing
the ability of the brain to process things such as color, motion, shape, etc. simultaneously
young- helmholtz trichromatic theory
theory that your retina contains 3 types of receptor cells that can process three colors (green, blue, and red)
opponent- process theory
theory that opposing retinal processes (red- green, yellow- blue, and white- black) enable color vision
wavelenegth
distance of wave of light from peak to peak, which determines the color of the wave
hue
dimension of color that is determined by the wavelength of the light
amplitude
height of each peak in a wavelength, which determines the brightness of the light
afterimage
continuation of visual sensation even after the stimulus is removed
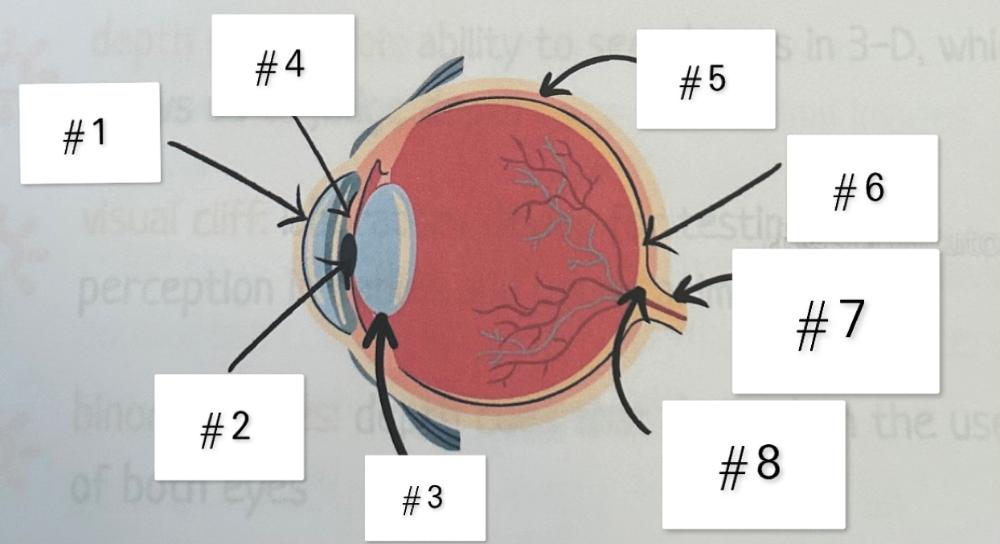
#1
cornea

#2
pupil

#3
lens

#4
iris

#5
retina

#6
fovea

#7
optic nerve

#8
blind spot
gestalt
organized whole; we tend to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes
figure- ground
organization of visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings
grouping
perceptual tendency to organise stimuli into coherent groups
depth pereception
ability to see objects in 3-D, which allows us to judge depth
visual cliff
laboratory device for testing depth perception in babies and young animals
binocular cues
depth cues that depend on the use of both eyes
retinal disparity
binocular cue for perceiving depth (greater disparity means closer object)
monocular cues
depth cues such as interposition and linear perspective, not dependent on use of both eyes
phi phonomenon
illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and odd in quick succession
perceptual constancy
perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change
color constancy
perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color even if changing illumination alters the wavelength reflected by object
perceptual adaptation
ability to adjust to an artificially displaced or even inverted visual field
audition
biological process by which our ears process sound waves
amplitude
how loud sound is, measured on a scale of decibels (dB)
frequency
number of wavelengths in a sound wave every second
pitch
wavelength of sound wave (high or low) determined by the frequency of the wave
outer ear
portion of ear that can be seen with inspection (pinna, ear canal, and ear drum)
pinna
visible part of ear that directs sound waves into the ear canal
ear canal
canal that guides sound waves down it to the eardrum
ear drum
also known as the tympanic membrane, which vibrates when the sound waves hit it
middle ear
chamber between the eardrum and the cochlea containing the hammer, anvil and stirrup
ossicles
the hammer, anvil, and stirrup are known as ossicles, they are responsible for transferring the vibrations from the eardrum to the cochlea
inner ear
innermost part of the ear (cochlea, semicircular canals, basilar membrane, and vestibular sacs)
cochlea
a fluid- filled tube responsible for triggering nerve impulses from sound waves
semicircular canals
fluid- filled tubes are responsible for helping you maintain your balance
basilar membrane
membrane of cochlea that moves due to the fluid, causing action potential
organ of corti
located in the basilar membrane and responsible for changing vibrations into neural impulses
vestibular sacs
sensory cells responsible for maintaining balance
sensorineural hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea receptor cells or auditory nerves
conduction hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea
cochlear implant
device for converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulation the auditory nerve
place theory
theory that links pitch we hear with the place that the cochlea is stimulated
frequency theory
theory that rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of tone
perceptual set
set of mental tendencies to perceive one thing and not another
extra sensory perception (ESP)
controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input
parappsychology
study of paranormal phenomena (ex: ESP or psychokinesis)
gate- control theory
theory that spinal cord contains "gate" that blocks or sends pain signals
nociceptor
sensory receptor for painful stimuli, which act as predictors of harm
kinesthesia
system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
vestibular sense
sense of body movement and position including the sense of balance
sensory interaction
principle that one sense may influence another (ex: smell and taste)
embodied cognition
influence of bodily sensations, gestures, etc. on cognitive preferences/ judgements