What are the 3 stages of cell signaling? Where do they occur?
1. Signal reception (signal is detected) - outside the cell
2. Signal transduction (amplifies signal)- inside the cell
3. Cellular response - (triggers a response) inside the cell (cytoplasm/nucleus)
What are some types of local signaling(direct contact)?
Paracrine and synaptic (when a neurotransmitter is released)
Both occur in animals
What is a type of long distance signaling?
Endocrine (hormonal)
Plasmodesmata occur in what organisms?
Plants
Cell-surface molecules are in what organism?
animal
Gap junctions occur in what organism?
animals
What is reception in cell signaling?
When a signaling molecule binds to a receptor protein causing it to change its shape.
Where are most signal receptors found?
In the plasma membrane proteins or inside the cell
The binding between a signal molecule(ligand) and receptor is what?
very specific
What does GDP do to receptors?
turns them off
What does GTP do to receptors?
turns it on (active)
What are GCPRs?
They are the largest family of receptors and the G stands for guanosine
What are the 3 main cell receptors?
GPCR's, RTK's, and Ion channel receptors
What does a GPCR do?
A receptor that works with a G protein to bind with GTP (similar to ATP)
What does GTP stand for?
guanosine triphosphate
What is a ligand?
It is what binds to signaling molecules
What makes RTK's different different from GPCR's?
They can signal multiple pathways at once
True or false. Ligands bind with RTK's.
True
What does a RTK do?
It speeds up the phosphate transfer process from ATP to another protein(tyrosine kinase)
What do Ion channel receptors do?
Act as a gate and opens/closes when a ligand changes it shape to allow specific ions through.
(Ions like Na and Ca)
What is a intracellular receptor?
Proteins that are found in the cytoplasm or nucleus of target cells.
What does transduction mean in cell signaling?
molecular interactions transmit signals from receptors to relay molecules in a cell
What is protein phosphorylation?
When protein kinases transfer phosphate from ATP to protein
What is protein dephosphorylation?
When protein phosphatases remove phosphates from proteins
What does adenylyl cyclase do?
It is an enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP in response to a extracellular signal.
What is Cyclic AMP (cAMP)?
Small molecules that are produced from ATP and is a second messenger.
What are second messengers?
Small, non protein, water soluble molecules that spread throughout the cell using diffusion. Specifically GPCRs and RTKs)
What are some types of second messengers?
Cyclic AMP (produced from ATP) and calcium ions
Were does the cellular response occur?
In the nucleus or cytoplasm
What happens during apoptosis?
Cells shrink and form lobes, which are eventually shed as membrane fragments
What is programmed cell death?
When infected or damaged cells die and it prevents enzymes from leaking out the dying cell and damaging neighboring cells.
What are the stages of cell division (IPpMAT)? Know the picture
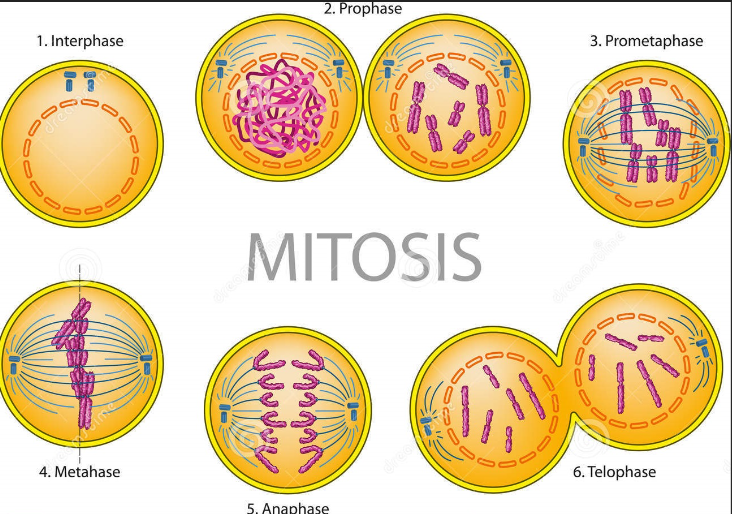
Interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
The continuity of life is based on what?
cell division
What distinguishes living from non living things?
The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind.
What is a genome?
All the DNA in a cell. (2 meters long)
What is chromotin?
They are condensed chromosomes
Somatic vs gametes
Somatic: non reproductive cells that have 46 chromosomes (asexual) - mitosis
Gametes: reproductive cells that have 23 chromosomes (sexual) - meiosis
Where can DNA be found?
the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast
What is chromatin?
Condensed chromosomes
What are sister chromatids?
two identically joined copies of the original chromosomes
What are centromeres?
The waist or the part where the two sister chromatids attach.
What are centrioles?
they are tubular structures that help with cell division and mobility
What are centrosomes?
where the microtubules come from (organizing center)
What are chromatids called when they seperate?
chromosomes
What is mitosis?
the division of genetic material in the nucleus
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm
What are the stages of interphase and explain them?
G1- growth phase
S phase- DNA is replicated, sister chromatids form
G2- second growth phase, protein synthesis
90% of cell cycle happens here
What happens in prophase?
Chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form, nuclear envelope breaks down, centrosomes move to poles
What happens in prometaphase?
Chromosomes continue to condense, kinetochores appear, microtubules attach to kinetochores
What happens during metaphase?
Chromosomes line in the middle, sister chromatids attach to spindle fibers
What happens in anaphase?
Centromeres split in 2, sister chromatids split and are now called chromosomes, spindle fibers begin to elongate.
What happens in telophase/cytokinesis?
nuclear envelop forms, miotic speindle breaks down, 2 identical daughter cells begin to form.
Kinetechore vs non-kinetechore
Kinetochores- "walk" the chromosomes to one pole
Non-kinetochores- elongate the whole cell during anaphase
What is a miotic spindle?
fibers made of microtubules that pull chromosomes to middle of cell
What forms after cell division in animals?
a cleavage furrow
What forms after cell division in plants?
a cell plate
What is a cell cycle control system?
How the cell cycle is directed. It is regulated by internal and external controls
What are checkpoints in the cell cycle control system?
It is where the cell cycle stops until the go-ahead signal is received.
What are the 2 regulatory proteins that are involved in the checkpoints?
Cyclins and Cdks(proteins)
Cdks have to be attached to cyclins to be active
What is MPF (m-phase promoting factor)?
Triggers the cell past the G2 checkpoint and into M-phase
What do growth factors do?
They are released by certain cells to stimulate other cells to divide
Explain how cancer cells grow and divide?
They don't need normal signals or growth factors to grow and divide.
What is binary fusion in bacteria?
When chromones replicate, and the two daughter chromosomes actively move apart, lastly, the plasma membrane pinches inward, dividing the cell into two.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Chromosomes paired in somatic cells
Diploid vs haploid cells
Diploid(2n)- somatic cells that have two types of each chromosome
Haploid(n)- gametes have only on set of chromosomes
How many homologous chromosomes do humans have? How many chromatids?
23 pairs of chromosomes and 92 chromatids
What is a kartotype?
An arrangement of chromsomes
What is the fusion of gametes called?
fertilization
What type of chromosomes do females have?
XX
What type of chromosomes do males have?
XY
What is the life cycle?
The generation to generation of stages in a reproductive history of an organism
What experiences alternation of generations?
plants and some algae
What stages do fungi and protist go through?
They only go through single celled zygote and not multicellular diploid.
True or false. Only diploid cells can undergo meiosis?
True
What are the phases of meiosis?
Meiosis I and meiosis II
Where does crossing over occur in meiosis?
In prophase I.
between non sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes.
Meiosis I
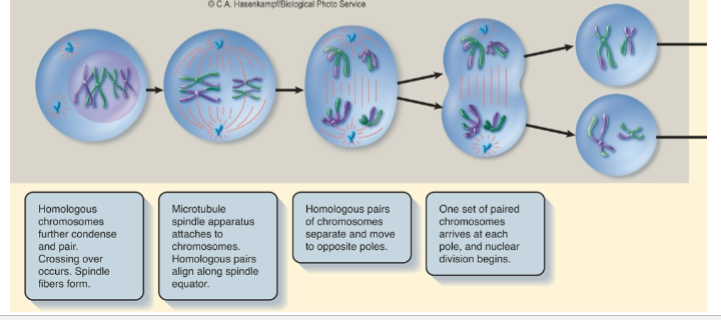
homologous chromosomes separate
Meiosis II
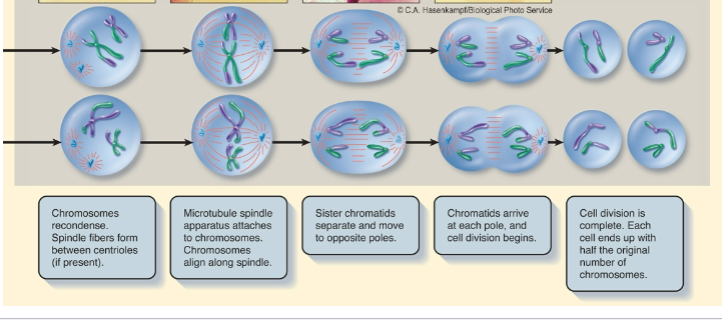
sister chromatids separate
What does meiosis start and end with?
What does mitosis start and end with?
Meiosis- start (1) diploid, end (4) haploid
Mitosis- start diploid, end diploid
What is independent assortment?
the possibility of different combinations of parental chromosomes
What 3 mechanisms contribute to genetic variation?
1. Independent assortment of chromosomes
2. Crossing over
3. random fertilization
What is a character?
A heritable feature that varies among individuals
ex: flower color
What is a trait?
Each variant for a character
ex: purple/yellow
What are the female organs of a flower?
Carpel
What are the male organs of a flower?
Stamen
What did Mendel discover?
The laws of inheritance
What is a dominant trait?
Capital letter - R
overpowers recessive
What is a recessive trait?
lower case letter - r
What was Mendel's first law?
alternative versions of genes (alleles) account for variations in inherited characters
What was Mendel's second law?
for each character (example flower color), an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent
What was Mendel's third law?
if the two alleles at a locus differ, then one (the dominant allele) determines the organism’s appearance, and the other (the recessive allele) has no noticeable effect on appearance
What was Mendel's fourth law?
The law of segregation
the two alleles for a heritable character separate
(segregate)
during gamete formation and end up in different gametes
What is a phenotype?
physical appearance of an organism
What is a genotype?
genetic appearance of an organism
Creating a punnet square is doing what?
testcrossing
Law of independent assortment?
each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation.
Gene's located near each other tend to be inherited together
Know how to do punnet squares and the multiplication product rule
...
What is complete dominance?
When phenotypes of the heterozygote and dominant homozygote are identical
What is incomplete dominance?
confirms that alleles are genes that are discrete and not blendable
What is codominance?
two dominant alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways
What is pleitrophy?
When one gene affects multiple traits.
ex: sickle cell
What is epistatic mean?
A gene at one locus alters the phenotypic expression of a gene at a second locus
What is a polygenic inheritance?
multiple genes affecting one phenotype.
ex: skin color and height in humans
What is pedigree?
a family tree that describes the interrelationships of parents and children across generations. can also be used to make predictions
What are some genetic disorders or dieases?
Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell, dwarfism, and Huntington's disease
What is chromosomal theory of inheritance? And who/what did they work with?
genes are found at specific locations on chromosomes. (Law od inheritance)
Thomas morgan hunt - fruit flies
What is larger X or Y chromosomes?
X are larger while Y are smaller
What are sex linked genes?
A gene that is located on either sex chromosomes.
Y and X linked genes
What is the gene on the Y chromosome called?
SRY - Sex determining region on the Y (Y linked)
Are X or Y genes more related to sex determination?
Y linked genes
What are some disorders that are caused by recessive alleles?
Color blindness (X linked), hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy
True or false. Almost all of the X chromosomes becomes inactive in early embryonic development.
True
What do inactive X chromosomes do and when do they reactivate?
X condenses into a Barr body and is reactivated in cells that give rise to eggs after meiosis.
What are linked genes?
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together
Parental vs recombinant types?
Parental - Offspring with a phenotype matching one of
the
parental phenotypes
Recombinant- Offspring with nonparental phenotypes
What is a genetic map?
an ordered list of the genetic loci along a particular chromosome
What is a linkage map?
a genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies
What is Aneuploidy?
results from the fertilization of gametes in which nondisjunction occurred
What is Polyploidy?
a condition in which an organism has more than two complete sets of chromosomes. (It is common in plants not animals)
What causes human disorders?
Alterations of chromosomal number and structure
What are some examples of alterations of chromosome number?
Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and turner syndrome
How does down syndrome occur?
When there are 3 copies of chromosome 21
How does Klinefelter syndrome occur?
the result of an extra chromosome in a male (XXY)
How does turner syndrome occur?
Produces X0 female chromosomes (sterile)
What is genomic imprinting?
the silencing of certain genes depending on which parent passes them on
How does linkage of genes and crossing over affect inheritance?
Linkage helps keep genes in a chromosome together and crossing over facilitates the separation of genes.
What are transcription factors?
They are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to nearby DNA by target genes.
Why is it important that the nuclear membrane disappears during cell division?
To facilitate spindle fibers and get the mitosis part of cell division started.
What are histones?
They are groups of proteins found in chromatin and are condensed. They are important in the packing of DNA and help regulate genes.
What would be the genotypes of an individuals used in true-breeding?
Homozygous
What will be the genotype of the individual used for a test cross?
It is between an individual with an unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive genotype