Intro of shoulder complex
- 4 articulations (sternum, clavicle, ribs, scapula, and humerus
- Has high amounts of mobility = low stability
- Almost no single muscle works in isolation; all work in teams = produce coordinated movement (synergies)
Osteology: BONES
- sternum
- clavicle
- scapula
- (proximal) humerus
Sternum
- Features:
- manubrium
- clavicular facets
- costal facets
- jugular notch
Clavicle (posterior/back view)
- shaft
- sternal end
- costal facet
- costal tuberosity
- acromial end
- acromial facet
- conoid tubercle
- trapezoid line
Both shoulders view (with angles)
- 20 degrees = clavicle
- 30-40 degrees = scapular plane
- 30 degrees = humeral head retroversion to mid-lateral axis at the elbow
Glenoid Fossa
- space between scapula and humerus head
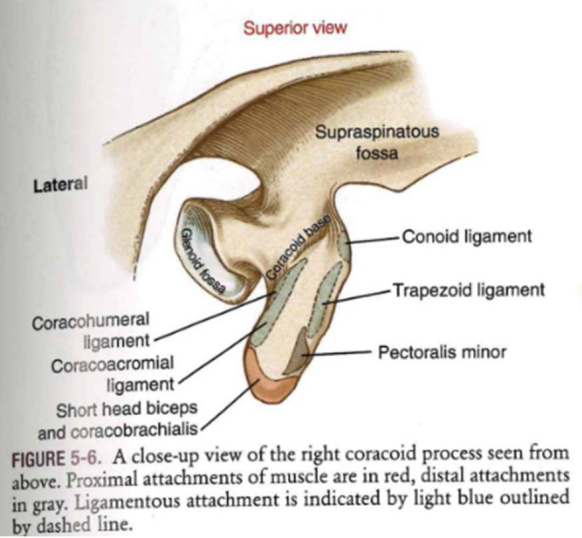
Coracoid Process w/ scapula
- attachment points for muscles and ligaments
- projects out sharply like crows beak
coracoid process (superior view)
Proximal to humerus
Proximal-to-mid Humerus: Retroversion
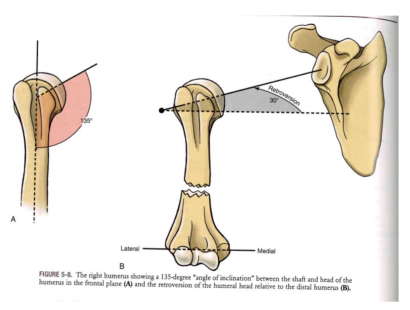
Clinical Application: Retroversion
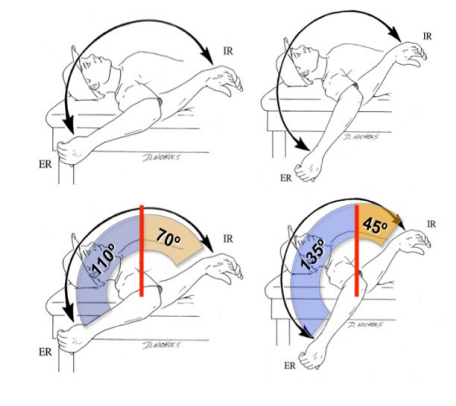
Loss of IR in pitching arm is okay, as long as Total ROM is equal bil
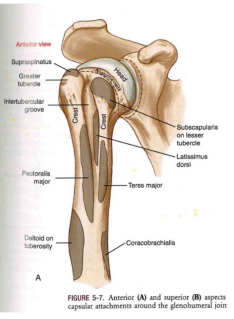
Proxima-to-humerus: With muscles
The major sandwich

Antrology
- the study of anatomy, function, dysfunction and treatment of
joints and articulations => JOINT SURFACES
- Sternoclavicular, arcomioclavicular, glenohumeral, scapulothoracic (physiologic)
- ROLL-SLIDE MECHANICS
Scapulothoracic Movements: Different types
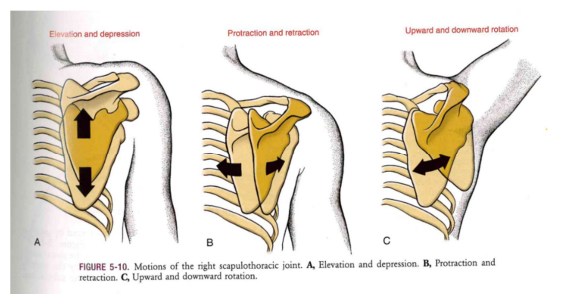
- Elevation and depression
- Protraction and retraction
- upward and downward rotation
Scapualr movements: key things to know
- multiple joints working together = ST movements
- Goal: keep humeral head in as much contact with the glenoid as possible!!
Scapular joint
- ONLY attachment of shoulder complex to axial skeleton = very robust
- LARGE ROM
- How?
- extensive connective tissue
- saddle joint
#Sternoclavicular joints (anterior of capsule and ligament section)
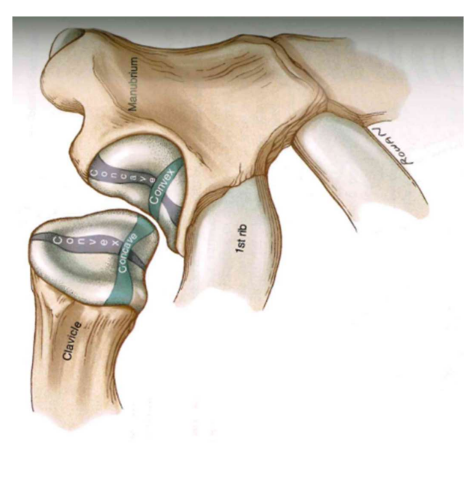
SC osteokinematics
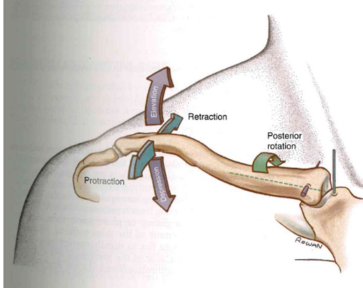
- elevation+depression
- protraction+retraction
- posterior clavicular rotation
SC arthrokinematics
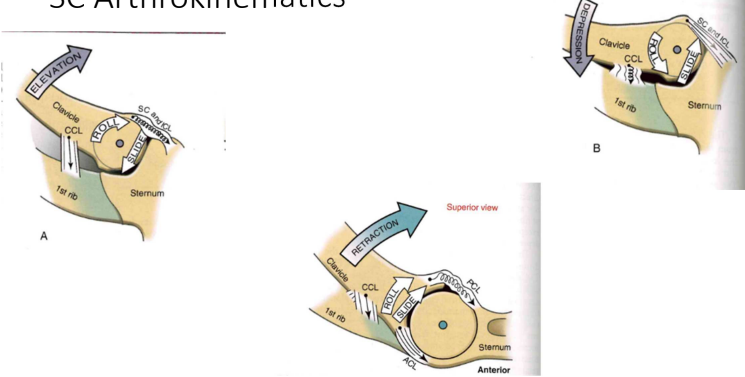
- Elevation (Roll Up // Slide down) = convex+concave
- Depression (Roll down // slide up) = convex+concave
- Retraction (Roll and Slide Up)
Acromioclavical joint: what behavior?
- A gliding or plane joint
- NO role-slide arthrokinematics
AC Joint Osteokinematics
- NO ROLL-SLIDE mechanics
- Rotation
- UP/DOWN and Internal/External
Scapulothoracic "joint" kinematics
- Posterior view
- elevation (SC joint)
- downward rotation (AC joint)
- Superior view
- protraction (SC joint)
- internal rotation (AC joint)
Acromioclavicular Joint
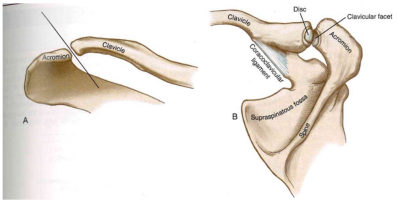
A gliding or a plane joint => NO roll-slide arthrokinematics
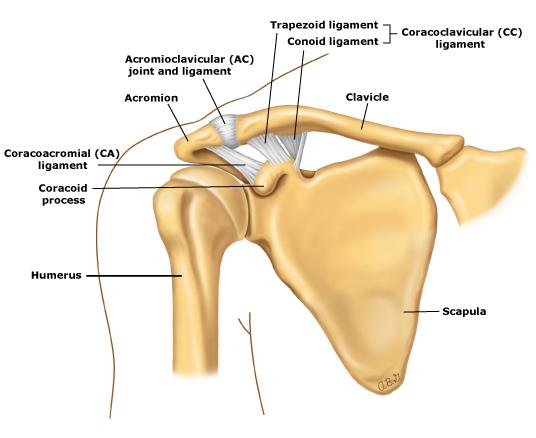
Acromioclavicular joint with ligaments
AC Joint Osteokinematics
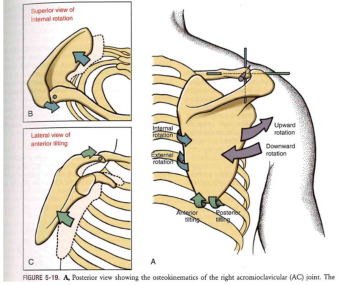
- NO ROLL SLIDE
- Upward/Downward rotation
- Internal/External rotation
- Anterior/Posterior tilting
Scapulothoracic “joint” kinematics: Protraction (hunch shoulders)
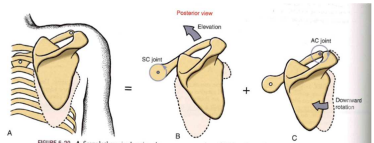
- Protraction(SC joint) + internal rotation (AC joint)
Scapulothoracic “joint” kinematics: Upward rotation (raise shoulders)
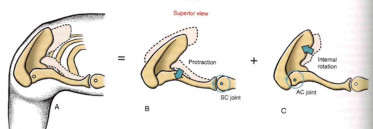
- elevation (SC joint) + downward rotation (AC joint)
#Scapulothoracic “joint” kinematics: Elevation (raise arm up)
- upward elevation (SC joint) + upward rotation (AC joint)
Glenohumeral Joint
- Glenohumeral (GH) + ST = large AROM
- glenoid is
directed anterolaterally in the plane of the scapula and with upward
inclination
- => to keep humerus in as much contact as possible
#Glenohumeral Joint: Fibrous capsule
- GHJ is surrounded by a fibrous capsule
- volume of capsule = 2x the side of the humeral head( Axillary pouch =large ROM)
- fibrous capsule is thin, = reinforced by thicker
external ligaments
- stability of the GHJ is not from passive structures = from active ones (muscles)
Additional Stability from Muscles & Labrum
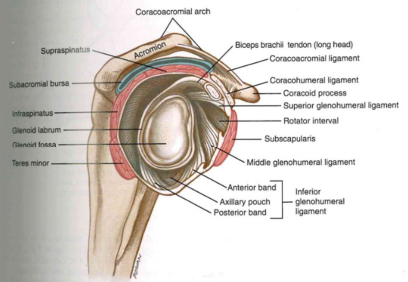
Anterior view of arm
#GH Joint stability (slight incline)
- slight incline of glenoid "locks" the joint
- passive tension of superior capsular structure (CSC) to combat gravity (G) and yield compression force (CF)
GH Osteokinematics
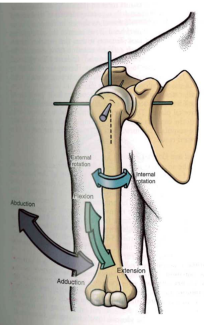
- EXT/FLX
- I.Rotation + Ex. Rotation
- Abbduction+Adduction
GH Arthrokinematics: Flexion/Extension
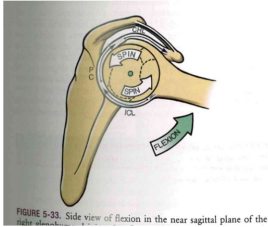
- SPIN + UP FLEXION
GH Arthrokinematics: Abduction
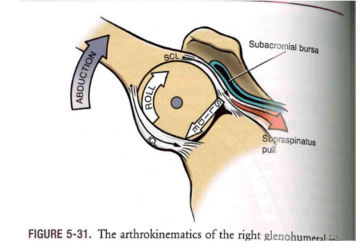
- UP ROLL + DOWN SLIDE + UP Abduction
- convex on concave
GH Arthrokinematics: ER/IR
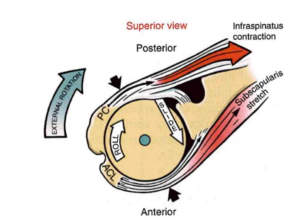
- ROLL UP + SLIDE DOWN + EXTERNAL ROTATION UP
- convex on concave
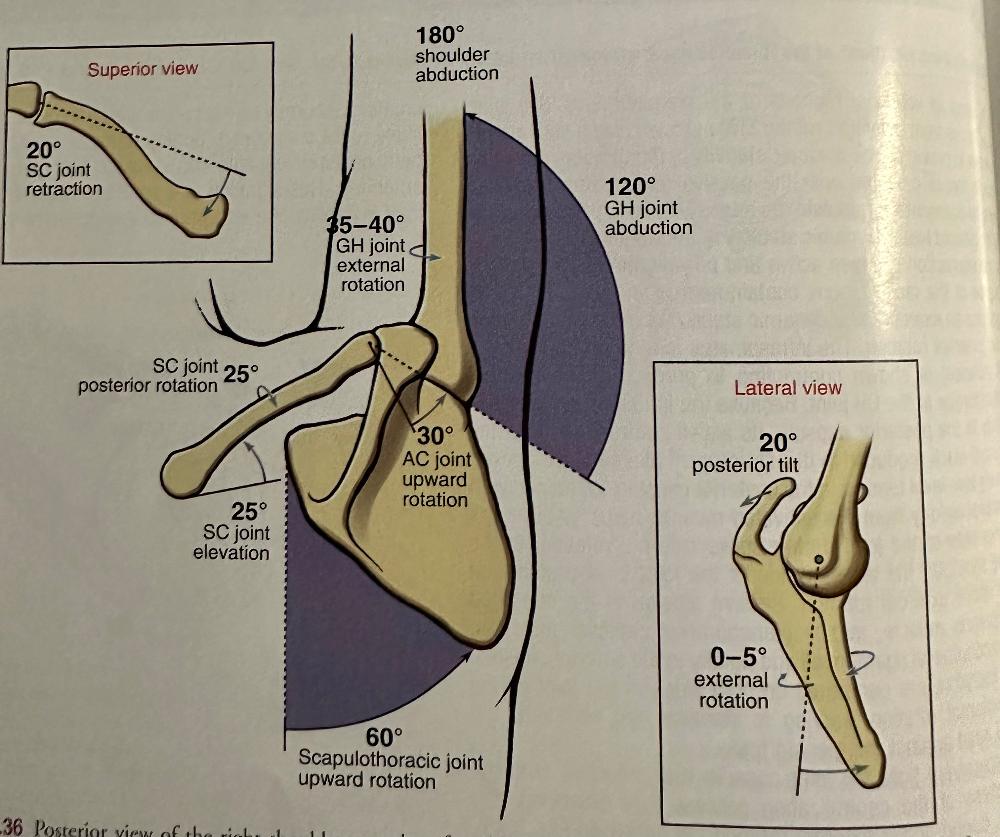
The Six Kinematic Principles 1
- scapulohumeral rhythm = active simultaneous of 180 degrees
- HOW: simultaneous 120 degrees of glenohumeral (GH) joint abduction
- HOW: 60 degrees scapulothoracic upward rotation
The Six Kinematic Principles 2
- 60 degrees of upward rotation of scapula during full shoulder
abduction
- simultaneous
The Six Kinematic Principles 3
- the clavicle retracts at the sternoclavicular joint(SC) during shoulder abduction
The Six Kinematic Principles 4
scapular posteriorly tilts & externally rotates (@full shoulder abduction)
The Six Kinematic Principles 5
clavicle posteriorly rotates around OWN axis @shoulder abduction
The Six Kinematic Principles 6
GH joint externally rotates during shoulder abduction
The Six Kinematic Principles: picture
why is the clavicle curvy?
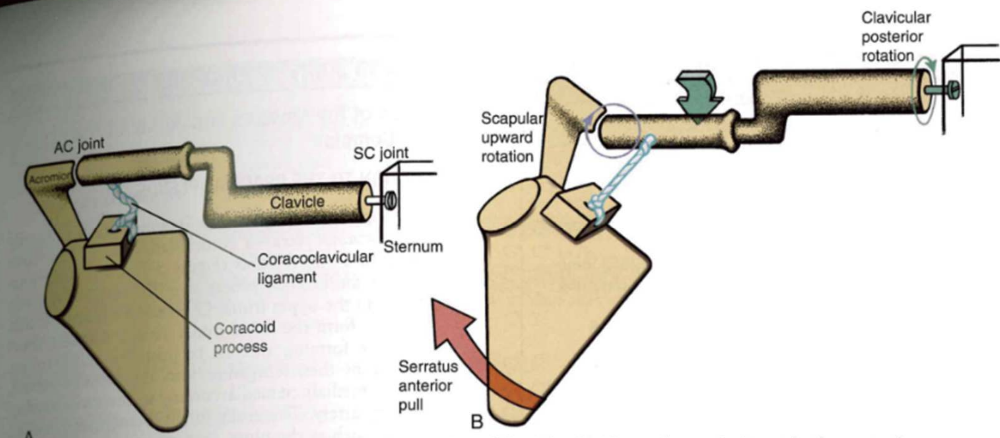
- AC joint party location
- serratus muscle pulls up =
coracoclavicular ligament is pulled tight
- creates tension + rotates clavicle posteriorly (back) => allows AC joint to full upward rotation
- serratus muscle pulls up =
coracoclavicular ligament is pulled tight
Muscles of the Shoulder Complex: categories
- proximal stabilizers
- distal mobilizers
ST Joint: Elevators Muscles
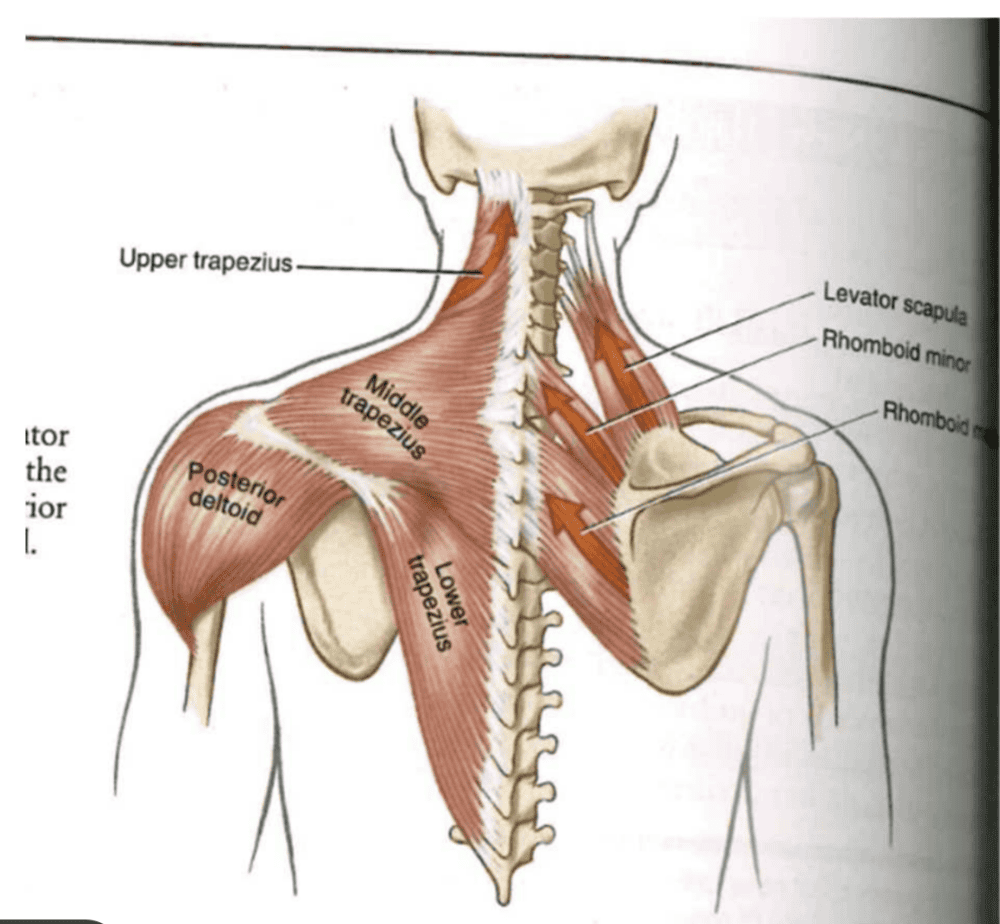
- Muscle:
- upper trapezius
- levator scapulae
- rhomboids (lesser extent)
- keeps shoulder gridle elevated + upward inclination of glenoid = MORE COMPRESSION FORCE
ST: Depressor Muscles
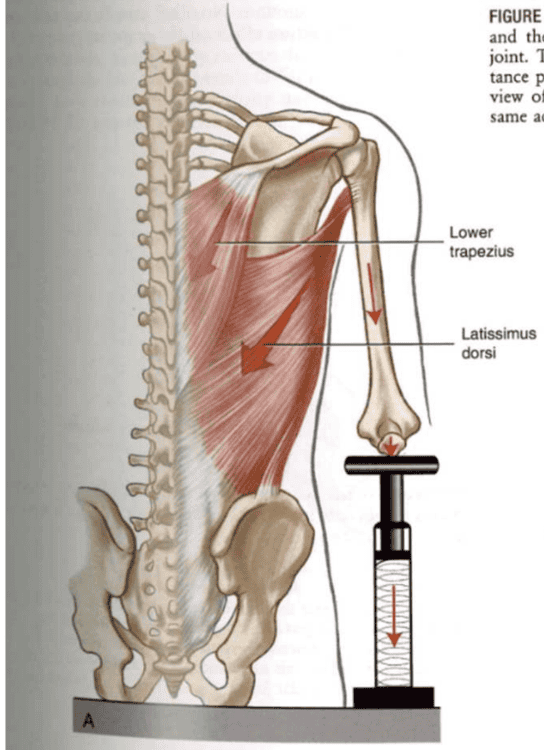
- Lower Trapezius
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Pec minor
- Subclavius (lesser extent)
When scapular depression is “blocked”
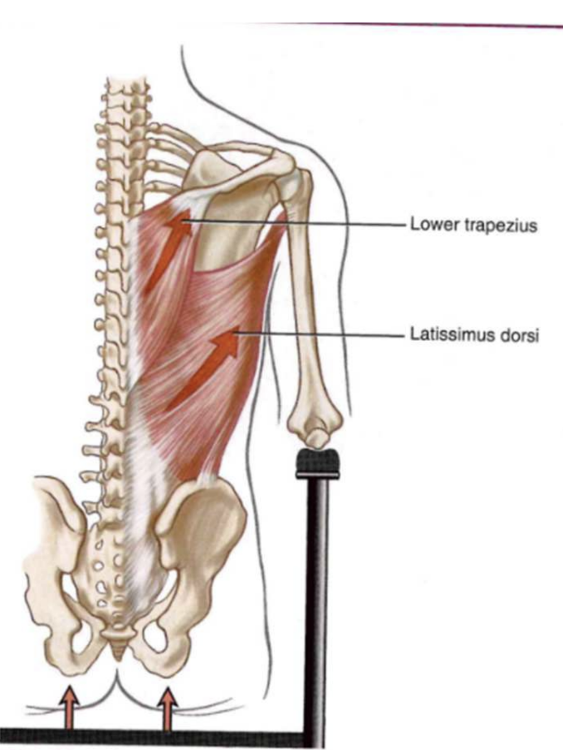
- force from the depressor msucels raise the thorax RELATIVE to fixed scapula and ulna
- lower traps+lats elevate up => pelvic trunk segment moves to fixed scapula arm segment
ST: Protraction
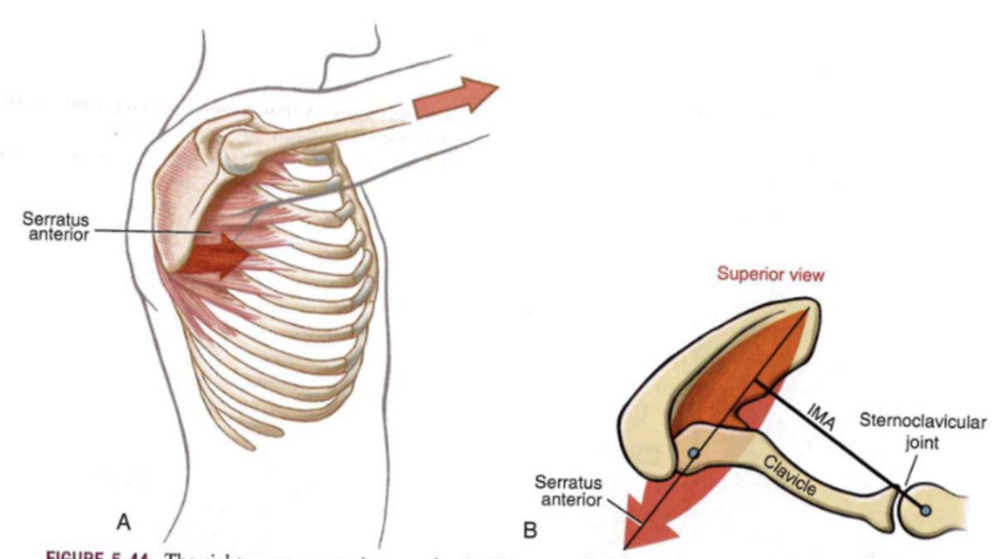
- muscle
- serratus anterior
ST: Retractors
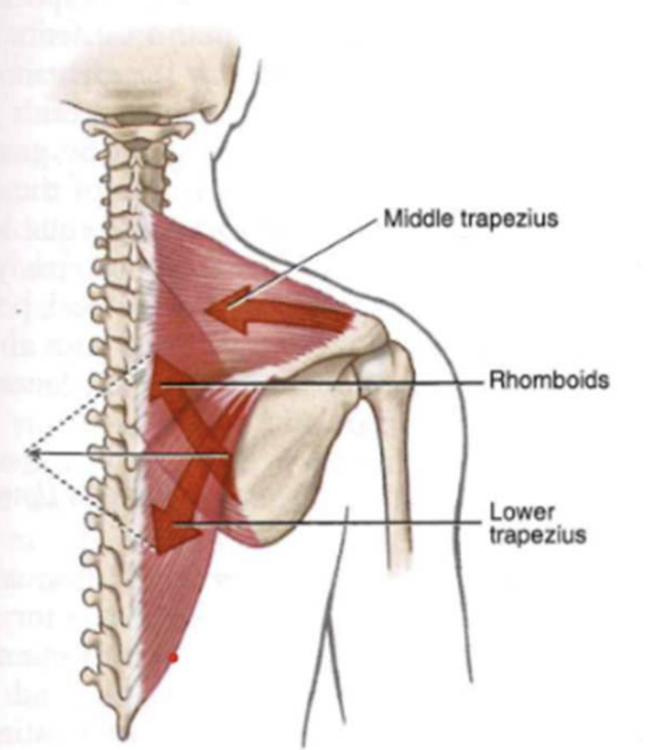
- Muscles:
- Middle Trapezius
- Rhomboids
- Lower trap
Upper Extremity: Elevation
- “Elevation” of the UE requires:
- Elevation of the GH joint
- Upward rotation of the ST joint
- Dynamic stability/control of arthrokinematics of the GHJ (via the rotator cuff)
GH Joint: Elevators muscles
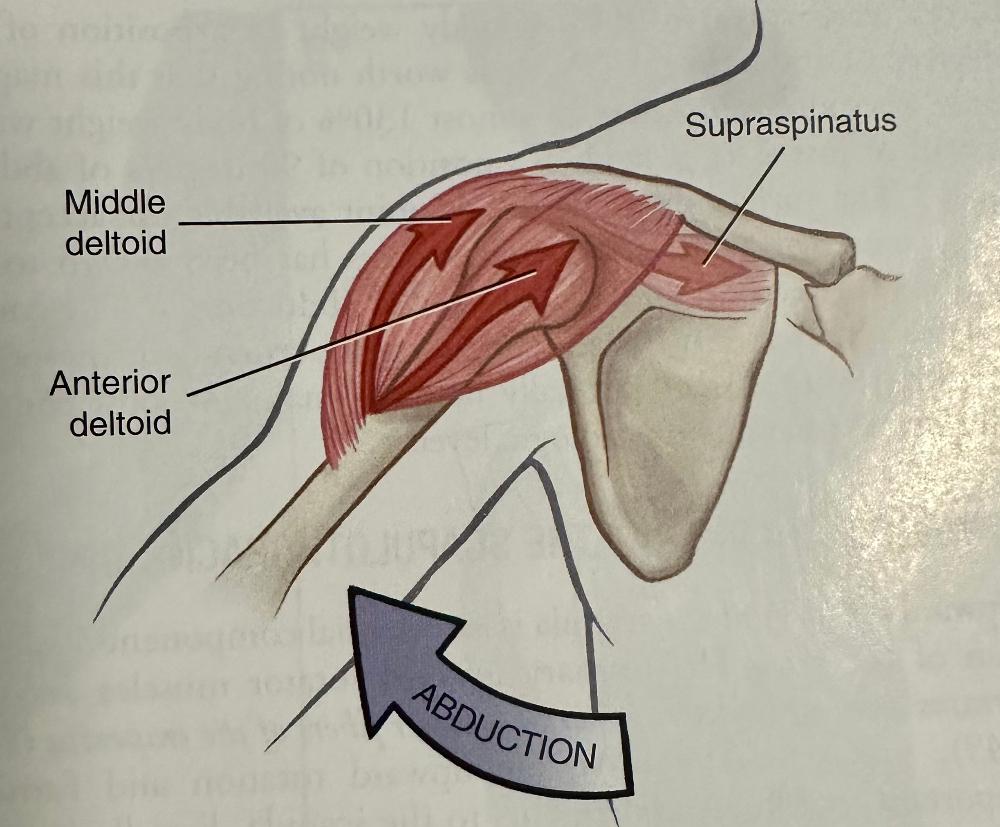
GH Joint: Elevators muscles
ABDUCTION
- Anterior Deltoid
- Middle Deltoid
- Supraspinatus
GH Joint: Elevators muscles
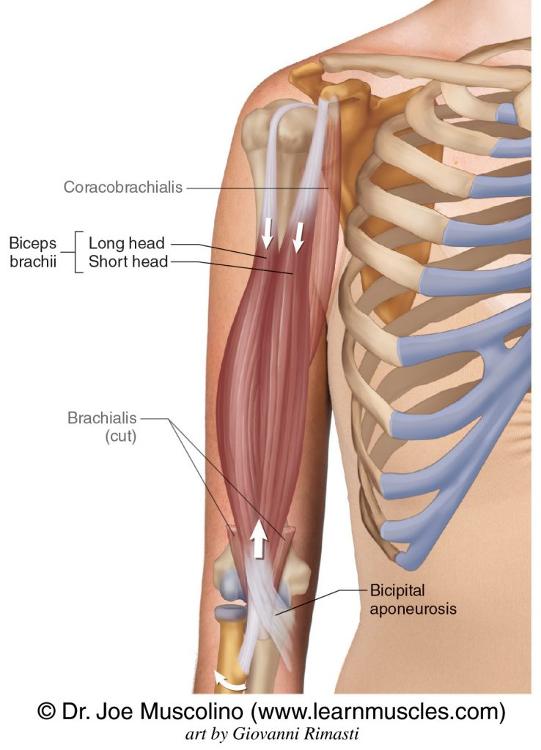
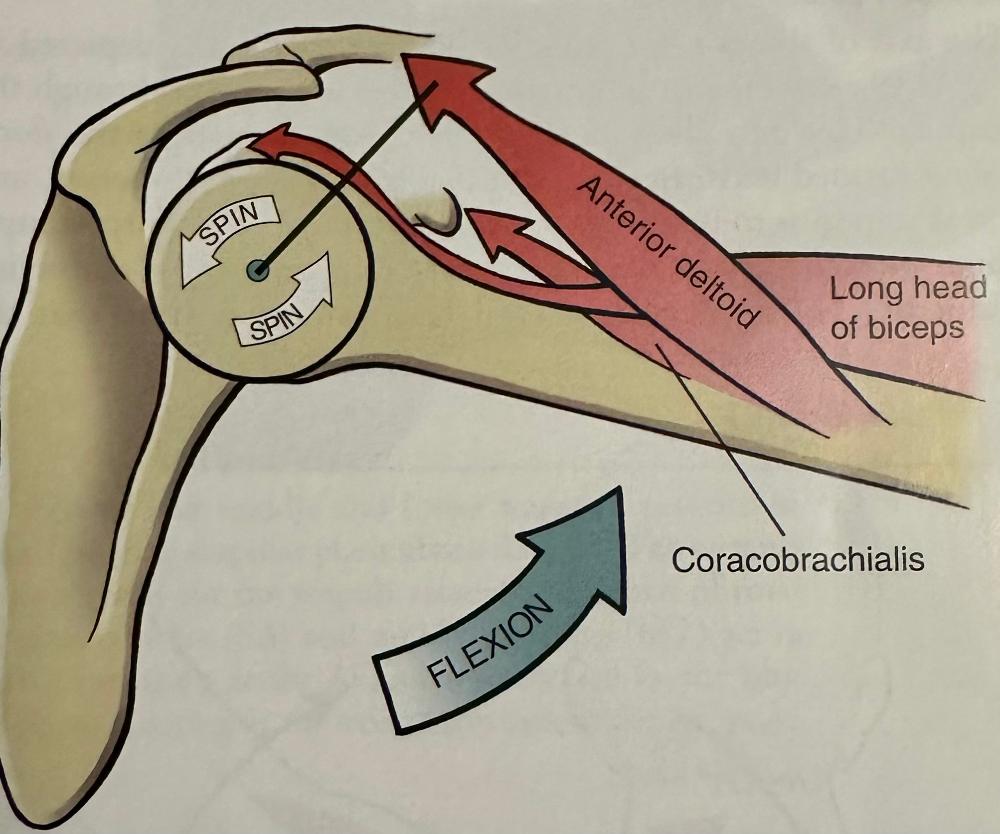
FLEXION
- Anterior deltoid
- Coracobrachialis
- Long head of biceps brachii
Glenohumeral joints muscles flexion
biceps flexion GHJ
ST: Upward rotators & synergy!
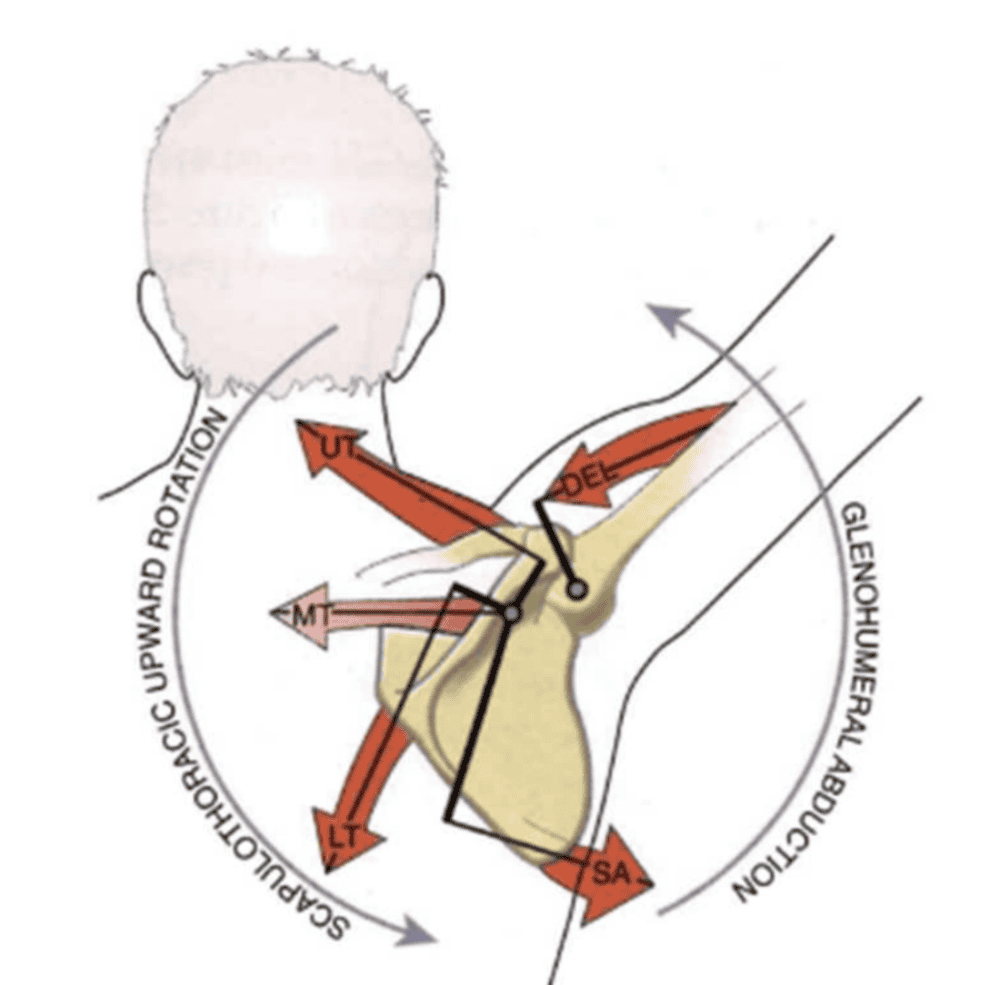
- Muscles:
- Serratus anterior
- Upper Trapezius
- Lower Trapezius
GH and rotator cuff
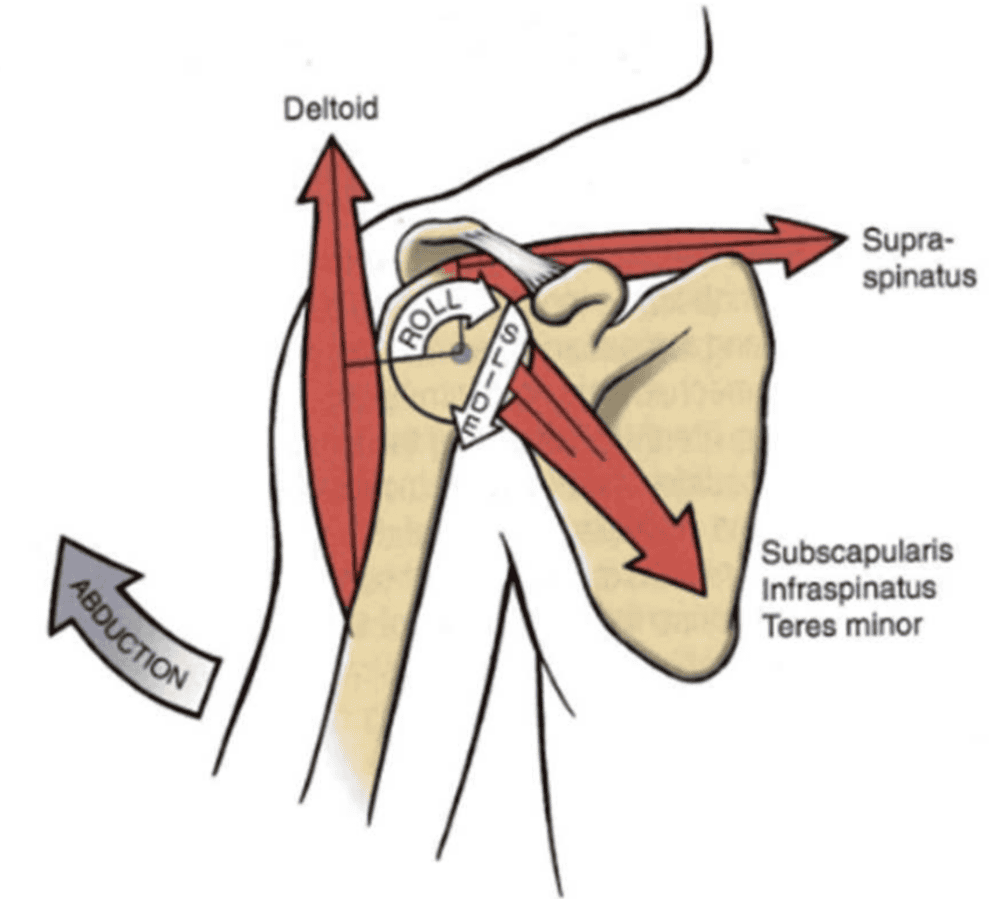
- GH is loose = high mobility
- rotator cuff controls motion of the humeral head
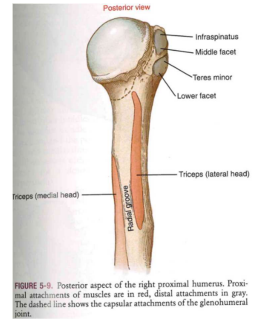
The Rotator Cuff muscles
- Supraspinatus
- Subscapularis
- Infraspinatus
- Teres Minor
Shoulder: Adduction & Extension
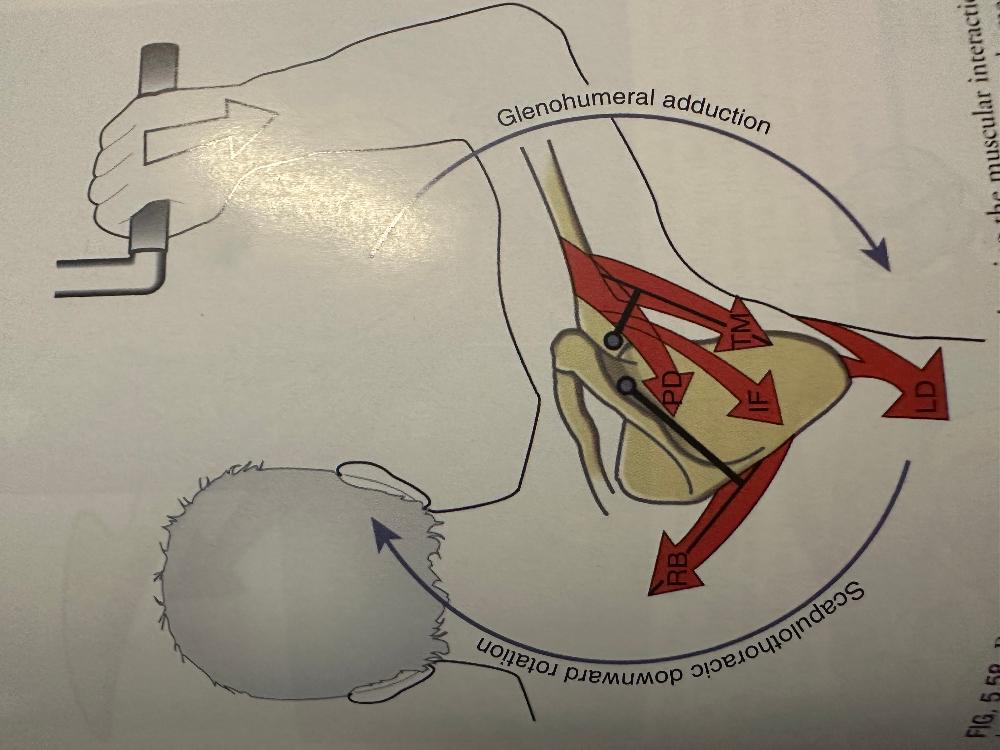
- (sternocostal portion) Pectoralis major*
- Latissimus dorsi*
- Teres major*
- Posterior deltoid
- Long head of triceps brachii
Shoulder: IR (internal rotation)
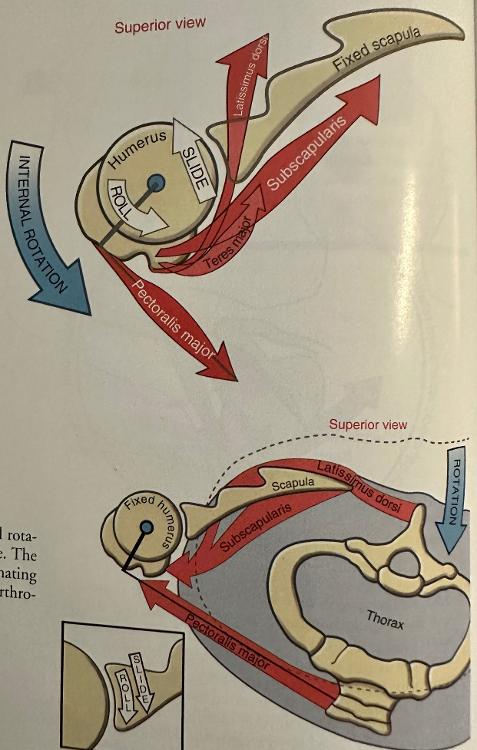
- MORE MUSCLE MASS THAN ER
- SALT P
- Subscapularis
- Anterior deltoid
- Latissimus dorsi
- Teres Major
- Pectoralis Major
Shoulder: ER (external rotation)
- Infraspinatus
- Teres Minor
- Posterior Deltoid
Muscle for scapula thoracic protraction
Serratus anterior