Explain step 1
We start with a glucose molecule and use the enzyme hexokinase (adds/removes a phosphate group) to make glucose-6-phosphate. 1 ATP is used
Explain step 2 (isomerization)
Phosphoglucoisomerase changes the shape of glucose 6 phosphate into fructose 6 phosphate
Explain step 3 (commitment)
Phosphofructokinase adds a phosphate to
fructose-6-phosphate to make fructose-1,6-
diphosphate. 1
ATP is used
Explain step 4 (split step)
Adolase: cuts fructose-1,6-diphosphate in half
to get two
similar pieces. GAP(G3P) and DHAP is produced.
Explain step 5 (conversion/doubling)
Triose phosphate isomerase: changes the shape of
DHAP
to be identical with GAP or G3P. Everything happens twice now
Explain step 6 (oxidation)
G3P or GAP dehydrogenase: removes a hydrogen from EACH GAP and adds it to NAD+ to make NADH and adds a phosphate (from the cytosol) to GAP to make 1,3 biphosphoglycerate. (NADH (2) is made from NAD+)
Explain step 7 (debt settling)
Phosphoglycerokinase: transfers a phosphate from 1,3
biphosphoglycerate to ADP to make ATP. ATP (2) is made
Explain step 8 (shuffle)
Phosphoglyceromutase: shifts the phosphate groups around.
Explain step 9
Enolase: removes a molecule of water from 2-phosphoglycerate. water (2) is made.
Explain step 10 (payday)
Pyruvate kinase: transfers a phosphate from PEP to
ADP to
make ATP. 2 ATP are made
What are the total outputs of glycosis?
2 pyruvates, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH
What are the steps of cellular respiration
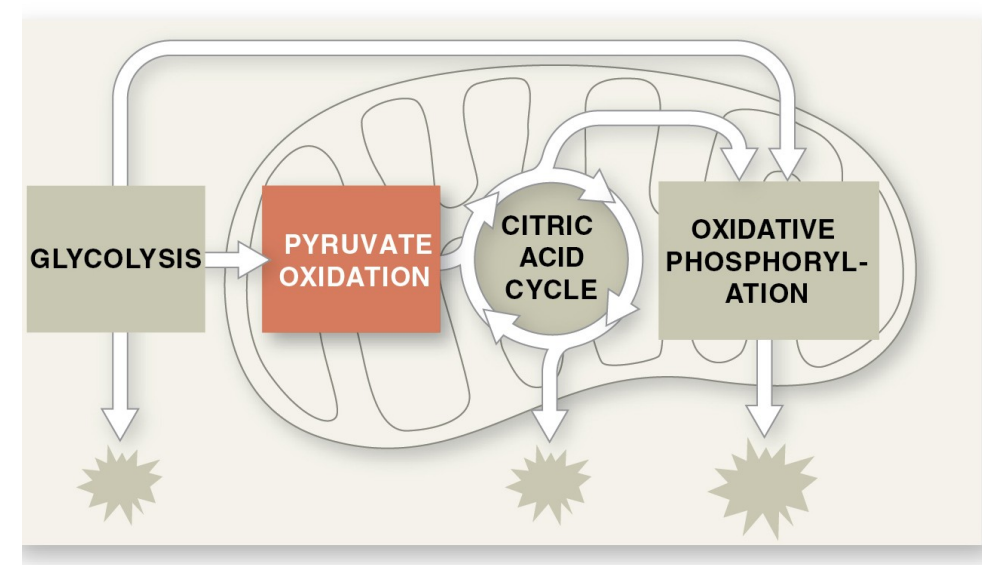
1. glycosis
2. pyruvate oxidation
3. citric acid cycle
4. Oxidative phosphorylation
What is oxidation of Pyruvate
Pyruvate (a 3 carbon compound) is converted to
acetyl coenzyme
A (a.k.a. acetyl CoA—a 2 carbon
compound) before entering the
citric acid cycle
Describe the steps of Oxidation of Pyruvate
1. oxidation of pyruvate’s carboxyl group
2. Reduction of NAD+ to NADH
3. Combination of the remaining two-carbon fragment
with
coenzyme A (CoA) to form acetyl CoA
True or false. 2 Acetyl CoA are produced from 1 glucose molecule
True
Where does glycosis occur?
In the cytosl
Where does pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle occur?
Mitochondrial matrix
Where does the electron transport chain (oxidation phosphorylation) occur?
Cristae (mitochondria)
Describe the citric acid cycle.
The citric acid cycle, also called the Krebs cycle,
oxidizes
organic fuel derived from pyruvate,
generating 1 ATP, 3 NADH,
and 1 FADH2
per turn. Another 2 CO2 are produced as a waste produce.
Is the citric acid cycle recycled through.
Yes, you start and end with oxaloacetate
Describe the Oxidation phosphorylation
...