
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
The total energy of the universe is constant

If the system of a chemical reaction gained 50 kJ of energy per mole what must also be true?
The surroundings lost 50 kJ of energy per mole
Convert 241 Calories to joules.
Hint: The unit Calories is a CAPITAL C.
1 calorie = 4.184 joules
1 Calorie = 1000 calories
Do not type units with your answer.
1008344
Convert 85.0 kJ to calories.
Hint: Notice the little c in calories.
1 calorie = 4.184 joules
1 Calorie = 1000 calories
Do not type units with your answer.
20315.48757
During a certain chemical reaction 1,150 J of heat is released from the system and 285 J of work is done on the surroundings. Calculate the change in internal energy of the system.
Do not type units with your answer.
-1435
During a certain chemical reaction 215 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 440 J of work is done on the surroundings. Calculate the change in internal energy of the system.
Do not type units with your answer.
-225

Which of the following processes are exothermic? Mark all correct answers.
- Water condensing from steam to a liquid
- Water freezing from a liquid to a solid
- Water evaporating from a liquid to a gas
- Water melting from a solid to a liquid
- Water condensing from steam to a liquid
- Water freezing from a liquid to a solid
How many grams of natural gas (CH4) must burn to emit -299 kJ of heat?
CH4 + 2O2 --> CO + 2H2O ΔH = -802 kJ/mol
OR
C H4 + 2 O2 right arrow CO + 2H2 O Delta H = -802 kJ/mol
Do not type units with your answer.
Type your answer to three significant figures.
If this question is on an exam on your scrap paper report your answer to the proper number of significant figures but still type three significant figures online.
5.98
How many grams of oxygen gas must burn to emit -229 kJ of heat?
CH4 + 2O2 --> CO + 2H2O ΔH = -802 kJ/mol
OR
C H4 + 2 O2 right arrow CO + 2H2 O Delta H = -802 kJ/mol
Do not type units with your answer.
Type your answer to three significant figures.
If this question is on an exam on your scrap paper report your answer to the proper number of significant figures but still type three significant figures online.
9.14
WRONG
Answer: 18.3
How much heat (in kJ) is released when 170 grams of CH4 is burned with 2000. grams of O2? If the answer is exothermic be sure your answer has the correct sign!
CH4 + 2O2 --> CO + 2H2O ΔH = -802 kJ/mol
OR
C H4 + 2 O2 right arrow CO + 2H2 O Delta H = -802 kJ/mol
Hint: Determine the limiting reagent.
Do not type units with your answer.
Type your answer to three significant figures.
If this question is on an exam on your scrap paper report your answer to the proper number of significant figures but still type three significant figures online.
-50130
WRONG
Answer: -8,494.7
A silver block, initially at 50.0 °C, is submerged into 100.0 grams of water at 25.2 °C, in an insulated container. The final temperature of the mixture upon reaching thermal equilibrium is 28.0°C. What is the mass of the silver block?
The specific heat capacity of silver is 0.235 J/g°C
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/g°C
Do not type units with your answer.
Type your answer to four significant figures.
If this question is on an exam on your scrap paper report your answer to the proper number of significant figures but still type four significant figures online.
-1166
WRONG
Answer: 226.60
Two pieces of metal (A and B) are in contact with each other and initially at different temperatures. Metal A has a mass of 7.50 grams and an initial temperature of 22ºC and metal B has a mass of 12.25 grams and an initial temperature of 50ºC. When the two metals reach thermal equilibrium they have a final temperature of 35ºC. If metal A has a specific heat capacity of 1.25 J/gºC what is the specific heat capacity of metal B?
Remember:
-q for metal A = q for metal B and q = msΔT
Do not type units with your answer.
Type your answer to three significant figures.
If this question is on an exam on your scrap paper report your answer to the proper number of significant figures but still type three significant figures online.
0.663
Zinc metal reacts with HCl according to the following balanced equation:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) --> ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
When 0.100 grams of Zn(s) is combined with an excess amount of HCl to make 52.0 mL of solution in a coffee-cup calorimeter, all the zinc reacts, raising the temperature of the solution from 22.40ºC to 24.90ºC. Find ΔH for this reaction in kJ/mol.
Assume the density of the solution is 1.00 g/mL and the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.184 J/gºC.
Use an atomic weight of 65.38 g/mol for Zn
Hints:
-q(reaction) = q(solution)
ΔH = q/mol of limiting reagent
Do not type units with your answer.
Type your answer to three significant figures.
If this question is on an exam on your scrap paper report your answer to the proper number of significant figures but still type three significant figures online.
-106
WRONG
Answer: -335.615

Use standard enthalpies of formation to calculate ΔHºrxn for the following chemical reaction:
3NO2 (g) + H2O (l) --> 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g)
OR
3 N" O2 left parenthesis g right parenthesis + H2O left parenthesis l right parenthesis right arrow 2H "N" O3 left parenthesis aq right parenthsis + "N" O left parenthssis g right parenthesis
Given:
Species ΔHf (kJ/mol)
N O2 33.2
H2 O -285.8
H N O3 -207
N O 91.3
Do not type any units with your answer. If the answer is exothermic be sure to include the appropriate sign. Report your answer to 1 decimal place.
-136.5

Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) H2(g) + 1/2 O2 (g) ---> H2O(l) ΔH = -285.8 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) C(s) + O2(g) ---> CO2(g) ΔH = -393.5 kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 C(s) + H2(g) ---> C2H2(g) ΔH = 226.7 kJ/mol
(Equation 4) 2 C2H2(g) + 5 O2(g) ---> 4 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) ΔH = ???????
To find ΔH for equation 4 you must:
Screen Reader Version
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) H2(g) + 1/2 O2 (g) arrow H2O(l) ΔH = minus 285.8 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) C(s) + O2(g) arrow CO2(g) ΔH = minus 393.5 kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 C(s) + H2(g) arrow C2H2(g) ΔH = 226.7 kJ/mol
(Equation 4) 2 C2H2(g) + 5 O2(g) arrow 4 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) ΔH = ???????
To find ΔH for equation 4 you must:
flip equation 3 only

Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 Ca(s) + O2(g) ---> 2 CaO(s) ΔH = -1270.2 kJ
(Equation 2) 4 Zn(s) + 2 O2(g) ---> 4 ZnO(s) ΔH = -696.6 kJ
(Equation 3) 4 Ca(s) + 4 ZnO(s) ---> 4 Zn(s) + 4 CaO(s) ΔH = ???
To find ΔH for equation 3 you must:
Screen Reader Version
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 "C"a(s) + O2(g) arrow 2 "C" a O(s) ΔH = minus 1270.2 kJ
(Equation 2) 4 Zn(s) + 2 O2(g) arrow 4 Z n O(s) ΔH = minus 696.6 kJ
(Equation 3) 4 "C"a(s) + 4 Z n O(s) arrow 4 Zn(s) + 4 "C"a O(s) ΔH = ???
To find ΔH for equation 3 you must:
multiply equation 1 only

Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 HF(g) ---> H2(g) + F2 (g) ΔH = 537 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) C(s) + 2 F2 (g) ---> CF4 (g) ΔH = -680. kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 C(s) + 2 H2 (g) ---> C2H4(g) ΔH = 52.3 kJ/mol
(Equation 4) C2H4(g) + 6 F2(g) ---> 2 CF4(g) + 4 HF(g) ΔH = ???????
To find ΔH for equation 4 you must:
Screen Reader Version
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 HF(g) arrow H2(g) + F2 (g) ΔH = 537 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) C(s) + 2 F2 (g) arrow CF4 (g) ΔH = minus 680. kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 C(s) + 2 H2 (g) arrow C2H4(g) ΔH = 52.3 kJ/mol
(Equation 4) C2H4(g) + 6 F2(g) arrow 2 CF4(g) + 4 HF(g) ΔH = ???????
To find ΔH for equation 4 you must:
flip equation 1 and equation 3 only

Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) H2(g) + F2 (g) ---> 2 HF(g) ΔH = -542.2 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) 2 H2(g) + O2(g)---> 2 H2O(l) ΔH = -571.6 kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 F2 (g) + 2 H2O(l) ---> 4 HF(g) + O2 (g) ΔH = ???????
To find ΔH for equation 3 you must:
Screen Reader Version
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) H2(g) + F2 (g) arrow 2 HF(g) ΔH = minus 542.2 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) arrow 2 H2O(l) ΔH = minus 571.6 kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 F2 (g) + 2 H2O(l) arrow 4 HF(g) + O2 (g) ΔH = ???????
To find ΔH for equation 3 you must:
multiply equation 1 only
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 HF(g) ---> H2(g) + F2 (g) ΔH = 537 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) C(s) + 2 F2 (g) ---> CF4 (g) ΔH = -680. kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 C(s) + 2 H2 (g) ---> C2H4(g) ΔH = 52.3 kJ/mol
(Equation 4) C2H4(g) + 6 F2(g) ---> 2 CF4(g) + 4 HF(g) ΔH = ???????
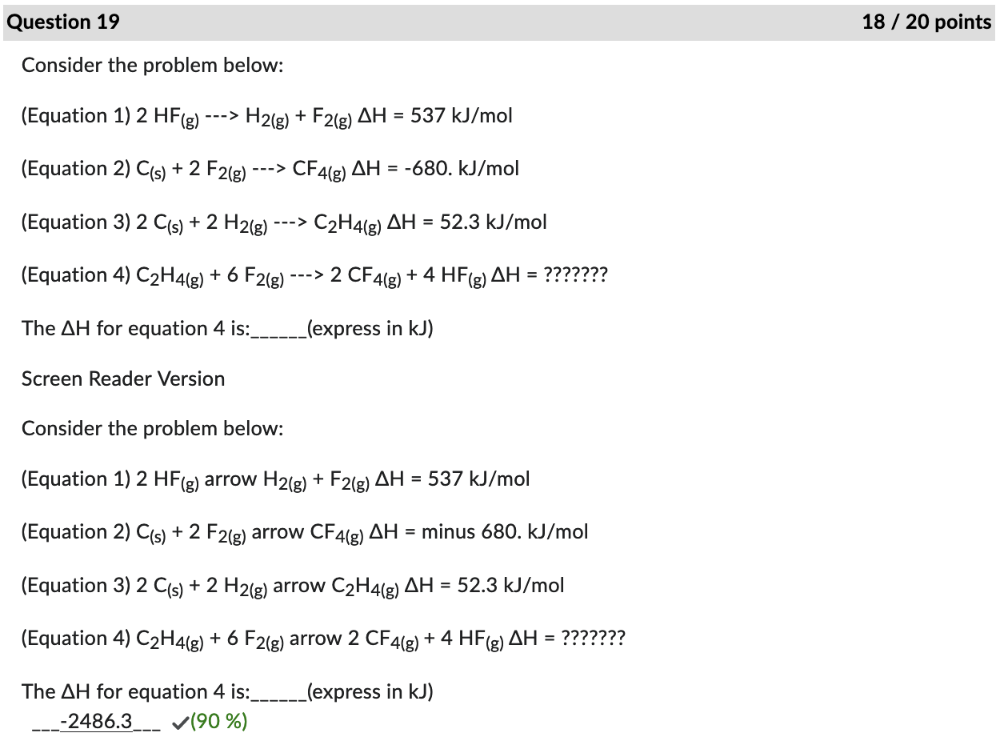
The ΔH for equation 4 is:______(express in kJ)
Screen Reader Version
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 HF(g) arrow H2(g) + F2(g) ΔH = 537 kJ/mol
(Equation 2) C(s) + 2 F2(g) arrow CF4(g) ΔH = minus 680. kJ/mol
(Equation 3) 2 C(s) + 2 H2(g) arrow C2H4(g) ΔH = 52.3 kJ/mol
(Equation 4) C2H4(g) + 6 F2(g) arrow 2 CF4(g) + 4 HF(g) ΔH = ???????
The ΔH for equation 4 is:______(express in kJ)
-2486.3
WRONG
Answer: ?
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 H2O(l) ---> 2 H2(g) + O2 (g) ΔH = 571.6 kJ
(Equation 2) N2O5(g) + H2O(l) ---> 2 HNO3(l) ΔH = -73.7 kJ
(Equation 3) 2 H2(g) + 6 O2 (g) + 2 N2(g) ---> 4 HNO3(l) ΔH = -696.4 kJ
(Equation 4) 2 N2 (g) + 5 O2(g) ---> 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = ???????
The ΔH for equation 4 is:______(express in kJ)
Screen Reader Version
Consider the problem below:
(Equation 1) 2 H2O(l) arrow 2 H2(g) + O2(g) ΔH = 571.6 kJ
(Equation 2) N2O5(g) + H2O(l) arrow 2 HNO3(l) ΔH = minus 73.7 kJ
(Equation 3) 2 H2(g) + 6 O2(g) + 2 N2(g) arrow 4 HNO3(l) ΔH = minus 696.4 kJ
(Equation 4) 2 N2(g) + 5 O2(g) arrow 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = ???????
The ΔH for equation 4 is:______(express in kJ)
22.6