challenges of an HIV vaccine
why is FL, esp Miami, number 1 in HIV?
HIV-related laws
...
challenges of an HIV vaccine
- while HHS secretary, heckler repeatedly assured the american
public that thw nation's blood supply was 100% safe
- said we must conquer AIDS before it affects the hetersexual population and the general population. very strong public interest in stopping AIDS before spreads outside of risk groups, before becomes an overwhelming problem
ppl had just become aware of virus causing disease at this time
these are quotes from book - gives idea for things said at the time
hecker - secretary under regan
reluctant to safeguard blood supply
what makes a vaccine?
- immune system given head start against pathogen
- trick immune system w/ vaccine with smth that looks like the infectious agent -> immune sysytem thinks being infected + mount immune response, hopefully durable to provide long-term protection
- smth administered to prevent/modify course of an infection
- usually inactive pathogen or antigen (immunogen)
- specific against a given pathogen
2 types of vaccines
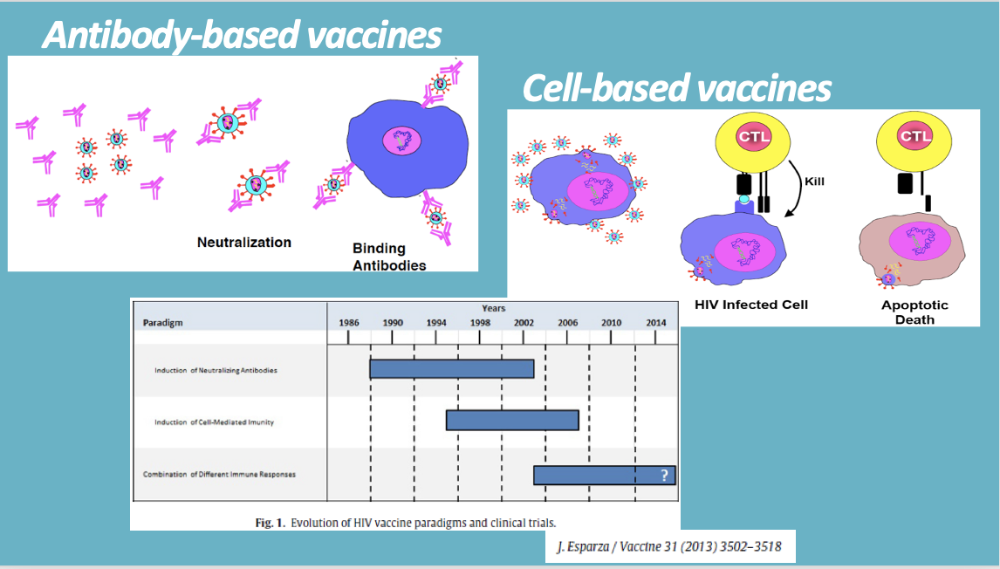
-
antibody based vaccine
- like for covid
- general humoral response = generate antibodies specifically binding to virions (if virus) + neutralize it
-
cell based
- generate response so immune cells (yellow) generate that can recognize the infected cell
- cell is harboring particular virus / infectious agent
- then immune cells are programmed to kill cell (and virus contained in it)
vaccines for HIV all failed so far
currently trying a combination of these 2
several large vaccine trials in the past
- subsahara africa or asia
- RV144 - vaccine trial in thailand, started in 2003 lasted 5 years
- only trial where partial success was received
- ppl had 30% less chance of becoming HIV+
HIV vaccine challenges
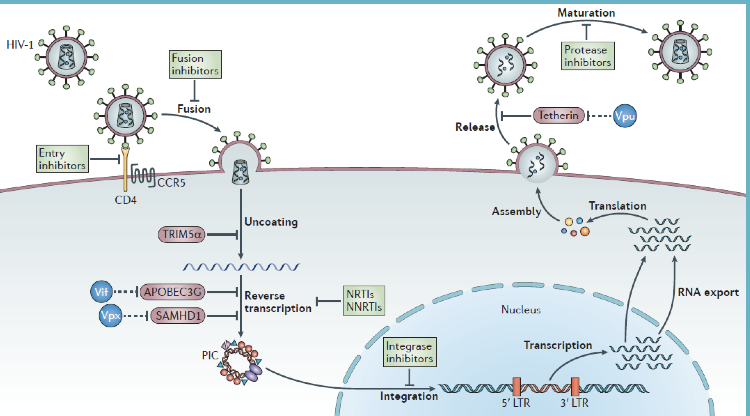
why was it (and still is) hard to dev vaccine?
- HIV good at hiding - provirus immunologically silent
- high intra-host mutation rate
- most important surface protein for infecting cells is very ingenious
1) HIV good at hiding - provirus immunologically silent
infecting CD4+ cells easy for HIV bc have receptor + bind it well
- easy targets for HIV
- HIV does infect other cells too (all types of cells) = other ways HIV infects cells (just not as efficient as CD4+ cells)
- ex: nerve cell, brain cell, etc.
up until provirus integrate into chromosome of cell = phase 2 infection
after = latent stage
- process pauses in many cells at end of phase 1 (integration into chromosome)
- means when cell divides, it also passes on HIV genome to daughter cell
-
cell harboring HIV provirus, its presence is COMPLETELY
undetectable by immune system
- if cell only has provirus, it is silent and immune system cannot know its there = provirus is immunologically silent
2nd reason hard to dev vaccine
2) high intra-host mutation rate
- mutation rate makes it difficult to make vaccine
- even within 1 individual HIV+
- then antibodies cannot effectively target HIV
- = HIV always ahead of immune system
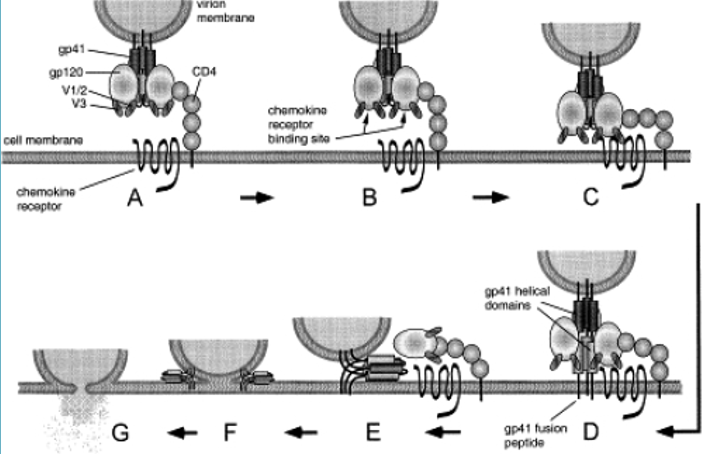
3) most important surface protein for infecting cells is very ingenious
3) most important surface protein for infecting cells is very ingenious
- HIV envelope concealed the places for virus-neutralizing antibodies to bind until they are needed to bind to the chemokine receptor during fusion
-
gp120 protein on surface of HIV virion - interacts
w/ CD4 (does initial tethering)
- interaction w/ chemokine receptor also involves gp120
- best type neutralizing antibodies = those that interfere w/ interaction of gp120/chemokine receptor
- if can get antibody to stop this from happening, HIV cannot infect the cell
-
HIV smart bc it HIDES the part of gp120 ONLY UNTIL ITS
NEEDED
- gp120 part not showed (occluded) normally. only exposed when ready to bind chemokine receptor
- signal within gp120 so that when CD4 binds, it becomes available/exposed so can bind chemokine receptor
- = so is hard to target
- bottom line: still at least several years from having protective HIV vaccine
links
https://apnews.com/article/hiv-vaccine-falls-short-study-b5f556fb004e9e5590b6125d0538ee51
https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/hiv-vaccine-research-history
geography of infection
- miami is worst
- ft lauderdale
- 3 new orleans
- baton rouge
- atlanta
- orlando
- philadelphia division
- jacksn, ms
- jacksonville fl
- memphis, tn
making initiative in miami
programs - some by UM
testmiami
HIV related laws in FL
- to fl statutes
- person msut know their infection status
+ that it is transmittable
- = unlawful to have sex w/ someone unless theyve been informed of the std and consent (for normal stds)
- hiv have longer max sentence, criminally persued whether or not is transmitted, bigger fine, is a FELONY
756 ppl arrested in Florida from 1986-2017 for HIV or other STD incident
614 of those were specifically for HIV
...
READING 1 - sunshine state's darkest cloud
- 2016, highest new infection rate (47/100,000)
- miami is epicenter
- caseload growing -> called for change
- strengthen testing + treatment efforts
- promoted PrEP -> also using in plan to eliminate HIV transmission + AIDS deaths
- why HIV spread so rapidly in FL
- 100 million tourists/year
- population doubled since epidemic start in 1981
- many latins/ppl from caribbeans immigrated, where have more prevalent HIV than the US
- 15% of HIV+ ppl in florida did not know theur status = fuels high transmission rate
- diverse state makes FL hard to handle HIV
- not enough ppl seek out testing
- florida late to have needle / syringe programs
- florida slow to promote PrEP
- then florida surgeon general mandated that all counties offer PrEP at no cost
- UM made mobile clinic
- florida's system falls
short
- not good at keeping ppl in care
- only 1/2 HIV+ ppl suppressing virus w/ ARVs
- = ppl more likely to spread virus
- = greater risk of developing AIDS
READING 2 - the mother of all challenges, Nigeria struggles to slow the spread of HIV to babies
- nigeria - 37k of world's 160k new cases in 2016
- very large HIV+ population in nigeria
- lack of access to ARVS (30% coverage) = a lot of children get HIV+ from mothers
- key is to treat pregnant HIV+ women
- not enough progress in this, though they are trying
- pregnant woman has 15-30% chance of transmitting the virus to her baby in utero or at birth
- standard of care = treat ALL HIV+ ppl with ARV combination therapy
- newborns should receive ARVs for 6 weeks after birth
- formal fees in clinics also deter women from getting care
- corruption is factor - informal fees (scams) are a part of the problem. There has been systematic embezzlement by ministry of health staff + improper auditing
- in a church, had celebration called baby shower + baby reception
- expecting women attend baby showers where get blood drawn to test for things, including HIV
- if newborns, attend baby reception - also get gift bags + check on ppl who were HIV+ at an earlier service (like baby shower) to see if they are following their treatment, etc.
-
these celebrations are part of the healthy beginning
initiative funded by US NIH
- expanded to more churches
- takes advantage of the fact that 90% nigerians regularly attend church/mosque
- also good bc religious leaders dont carry burden of politicians. ppl believe + follow them
- HIV testing in pregnant women in churches inc from 55% to 92%