continuation of last lecture (split into 2 lessons, but same powerpoint)
...
good news about HIV? what can be prevented?
transmission of HIV can be prevented
initial phase of HIV infection: points of entry
female genital tract, male genital tract, intestinal tract, placenta, blood stream
vagina, ectocervix, endocervix, inner foreskin, penile urethra, other, rectum, upper GI tract, chorionic villi
medium of transmission:
semen, cervicovaginal and rectal secretions and desquamations, maternal blood, genital secretions (intrapartum), breast milk, blood products, sharps
HIV transmission
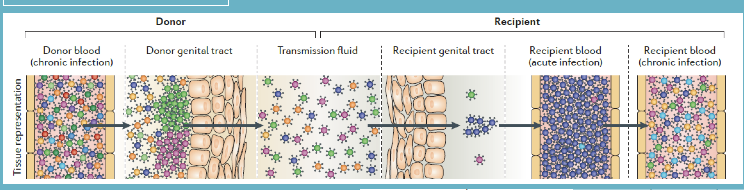
viral burden (or load) determine the chance of transmission
- comes down to levels of HIV virions in blood of donor
- transmission fluid gets in
- = acute infectious and recipient infection
viral burden/load of HIV donor determiens chance of transmission (higher levels of virions donated = greater chance transmission will occur)
is HIV transmission preventable?
yes
start:
- in UM
- test group had AZT
- 1 reason why AZT still used
- gave women AZT before birth (antepartum)
- during birth, gave IV dosage (during labor)
- after birth, gave baby AZT
result
- AZT treated group transmission rate = 7.4
- placebo group transmission rate = 24.4 (almost 25% of babies whose mom is infected got it)
AZT reduced viral load = reduced viral load of transmission fluids (like those the baby is exposed to duing birth) = lowered chance of transmission
ALL HAS TO DO WITH VIRAL LOAD!!!!!!!!!!!
2 benefits of keeping HIV levels "suppressed)
- prevent AIDS in the individual
- lower viral load = keeps individuals from getting AIDS
- reduces
HIV transmission
- lower chance of transmission to others if one's viral # are very low (suppressed bc of medications, etc)
at this point, only knew how to keep babies from getting it (see notecard #5)
...
PrEP
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
- if recipient is taking anti-HIV medication, then any incoming HIV virions will not be able to replicate = individual remains uninfected
individual can start taking HIV drugs if not positive, do this so that if exposed to HIV, drug act agains few virions and attack virus when first enter body = does not go into acute phase (irreversible)
all about stopping it before going into acute phase
PEP
Post exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
- if recipient starts taking anti-HIV medication shortly following exposure, then HIV virions will not be able to replicate and the individual will remain uninfected
therapeutic goal - eliminate HIV PRIOR to acute phase
"exposure to HIV" vs "HIV positive"
- if enter acute phase, individual becomes HIV+ for life
- if exposed to few virions, take short term treatment until theyre gone
DISTINCTION: exposure vs perminanent infection
- condoms not even as necessary anymore bc anti HIV drugs work so well
drugs so good, people good if they jsut remember to take them + be consistent
...
what HIV/AIDS research is being done now?
CDC main page
- miami dade country has high rate
see links
HIV testing

now have tests for drug resistance of HIV
tells if person is infected w/ drug resistant strains and which drugs its resistant to as to avoid giving person those drugs